2002 JEEP LIBERTY Low power
[x] Cancel search: Low powerPage 1391 of 1803
FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT /
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor track (card).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module has 4 different circuits
(wires). Two of these circuits are used for the fuel
gauge sending unit for fuel gauge operation, and for
certain OBD II emission requirements. The other 2
wires are used for electric fuel pump operation.
For Fuel Gauge Operation:A constant current
source of approximately 32 milliamps is supplied to
the resistor track on the fuel gauge sending unit.
This is fed directly from the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM).NOTE: For diagnostic purposes, this
12V power source can only be verified with the
circuit opened (fuel pump module electrical
connector unplugged). With the connectors
plugged, output voltages will vary from about
0.6 volts at FULL, to about 8.6 volts at EMPTY
(about 8.6 volts at EMPTY for Jeep models, and
about 7.0 volts at EMPTY for Dodge Truck mod-
els).The resistor track is used to vary the voltage
(resistance) depending on fuel tank float level. As
fuel level increases, the float and arm move up,
which decreases voltage. As fuel level decreases, the
float and arm move down, which increases voltage.
The varied voltage signal is returned back to the
PCM through the sensor return circuit.
Both of the electrical circuits between the fuel
gauge sending unit and the PCM are hard-wired (not
multi-plexed). After the voltage signal is sent from
the resistor track, and back to the PCM, the PCM
will interpret the resistance (voltage) data and send
a message across the multi-plex bus circuits to the
instrument panel cluster. Here it is translated into
the appropriate fuel gauge level reading. Refer to
Instrument Panel for additional information.
For OBD II Emission Monitor Requirements:
The PCM will monitor the voltage output sent from
the resistor track on the sending unit to indicate fuel
level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent the
OBD II system from recording/setting false misfire
and fuel system monitor diagnostic trouble codes.
The feature is activated if the fuel level in the tank
is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated
capacity. If equipped with a Leak Detection Pump
(EVAP system monitor), this feature will also be acti-
vated if the fuel level in the tank is more than
approximately 85 percent of its rated capacity.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL LEVEL
SENDING UNIT
The fuel level sending unit contains a variable
resistor (track). As the float moves up or down, elec-
trical resistance will change. Refer to Instrument
Panel and Gauges for Fuel Gauge testing. To test the
gauge sending unit only, it must be removed from
vehicle. The unit is a separate part of the lower fuel
pump module section. Refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation for procedures (remove only the
upper section of the fuel pump module). Measure the
resistance across the sending unit terminals. With
float in up position, resistance should be 20 ohms (+/-
5%). With float in down position, resistance should be
270 ohms (+/- 5%).
REMOVAL
The fuel level sending unit (fuel level sensor) and
float assembly is located on the side of the lower sec-
tion of the fuel pump module. The lower section of
the fuel pump module is located within the fuel tank.
(1) Remove lower section of fuel pump module
from fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/
Installation.
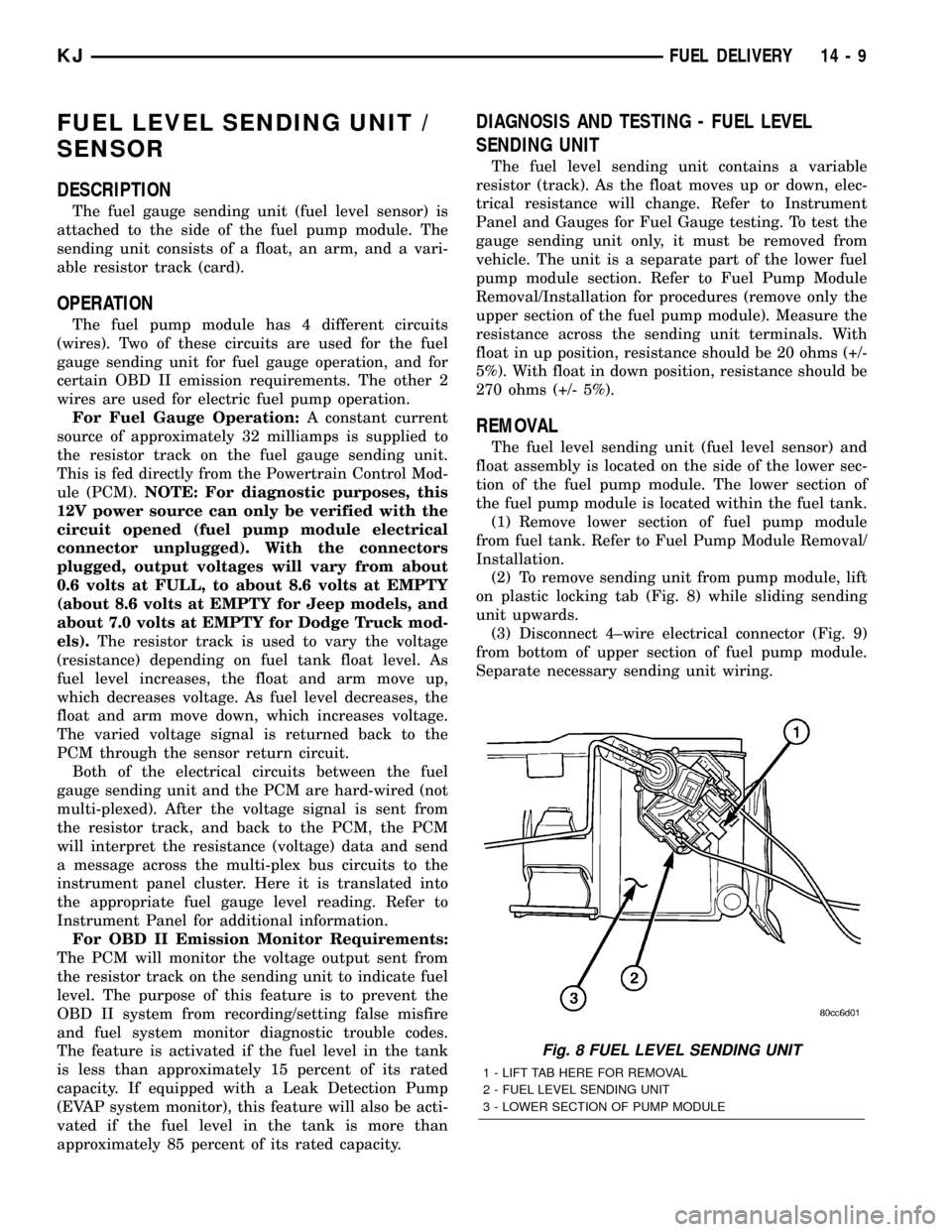
(2) To remove sending unit from pump module, lift
on plastic locking tab (Fig. 8) while sliding sending
unit upwards.
(3) Disconnect 4±wire electrical connector (Fig. 9)
from bottom of upper section of fuel pump module.
Separate necessary sending unit wiring.
Fig. 8 FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT
1 - LIFT TAB HERE FOR REMOVAL
2 - FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT
3 - LOWER SECTION OF PUMP MODULE
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 9
Page 1397 of 1803

FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located inside of the fuel
pump module. A 12 volt, permanent magnet, electric
motor powers the fuel pump. The electric fuel pump
is not a separate, serviceable component.
OPERATION
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay.
Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of
the module and pushed through the electric motor
gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation:The bottom section of
the fuel pump module contains a one-way check
valve to prevent fuel flow back into the tank and to
maintain fuel supply line pressure (engine warm)
when pump is not operational. It is also used to keep
the fuel supply line full of gasoline when pump is not
operational. After the vehicle has cooled down, fuel
pressure may drop to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but
liquid gasoline will remain in fuel supply line
between the check valve and fuel injectors.Fuel
pressure that has dropped to 0 psi on a cooled
down vehicle (engine off) is a normal condition.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test for more
information.
The electric fuel pump is not a separate, service-
able component.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
CAPACITY TEST
Before performing this test, verify fuel pump
pressure. Refer to Fuel Pump Pressure Test.
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down Test.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel rail. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings. Some engines may require
air cleaner housing removal before line disconnection.
(3) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(4) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose into disconnected fuel supply line.
Insert other end of Adaptor Tool Hose into a gradu-
ated container.
(5) Remove fuel fill cap.(6) To activate fuel pump and pressurize system,
obtain DRBtscan tool and actuate ASD Fuel System
Test.
(7) A good fuel pump will deliver at least 1/10 liter
of fuel in 7 seconds. Do not operate fuel pump for
longer than 7 seconds with fuel line disconnected as
fuel pump module reservoir may run empty.
(a) If capacity is lower than specification, but
fuel pump can be heard operating through fuel fill
cap opening, check for a kinked/damaged fuel sup-
ply line somewhere between fuel rail and fuel
pump module.
(b) If line is not kinked/damaged, and fuel pres-
sure is OK, but capacity is low, replace fuel filter.
Refer to Fuel Filter Removal/Installation for addi-
tional information.
(c) If both fuel pressure and capacity are low,
replace bottom section of fuel pump module. Refer
to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Capacity Test, Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and
Fuel Pump Amperage Test found elsewhere in this
group.
Check Valve Operation:The bottom section of
the fuel pump module contains a one-way check
valve to prevent fuel flow back into the tank and to
maintain fuel supply line pressure (engine warm)
when pump is not operational. It is also used to keep
the fuel supply line full of gasoline when pump is not
operational. After the vehicle has cooled down, fuel
pressure may drop to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but
liquid gasoline will remain in fuel supply line
between the check valve and fuel injectors.Fuel
pressure that has dropped to 0 psi on a cooled
down vehicle (engine off) is a normal condition.
When the electric fuel pump is activated, fuel pres-
sure shouldimmediately(1±2 seconds) rise to spec-
ification.
The fuel system is equipped with a separate fuel
pump module mounted, fuel pressure regulator. The
fuel filter is remotely mounted. The fuel pressure
regulator is not controlled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 15
Page 1398 of 1803

(1) Remove protective cap at fuel rail test port.
Connect the 0±414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure gauge
(from gauge set 5069) to test port pressure fitting on
fuel rail (Fig. 20).The DRBtIII Scan Tool along
with the PEP module, the 500 psi pressure
transducer, and the transducer-to-test port
adapter may also be used in place of the fuel
pressure gauge.
(2) Start and warm engine and note pressure
gauge reading. Fuel pressure should be 339 kPa 34
kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi) at idle.
(3) If engine runs, but pressure is below 44.2 psi,
check for a kinked fuel supply line somewhere
between fuel rail and fuel pump module. If line is not
kinked, but specifications for either the Fuel Pump
Capacity, Fuel Pump Amperage or Fuel Pressure
Leak Down Tests were not met, replace lower section
of fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation.
(4) If operating pressure is above 54.2 psi, electric
fuel pump is OK, but fuel pressure regulator is defec-
tive. Replace lower section of fuel pump module.
Refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation.
(5) Install protective cap to fuel rail test port.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PUMP
AMPERAGE TEST
This amperage (current draw) test is to be done in
conjunction with the Fuel Pump Pressure Test, Fuel
Pump Capacity Test and Fuel Pressure Leak Down
Test. Before performing the amperage test, be sure
the temperature of the fuel tank is above 50É F (10É
C).The DRBtScan Tool along with the DRB Low Cur-
rent Shunt (LCS) adapter (Fig. 21) and its test leads
will be used to check fuel pump amperage specifica-
tions.
(1) Be sure fuel tank contains fuel before starting
test. If tank is empty or near empty, amperage read-
ings will be incorrect.
(2) Obtain LCS adapter.
(3) Plug cable from LCS adapter into DRB scan
tool at SET 1 receptacle.
(4) Plug DRB into vehicle 16±way connector (data
link connector).
(5) Connect (-) and (+) test cable leads into LCS
adapter receptacles. Use10 amp (10A +)receptacle
and common (-) receptacles.
(6) Gain access to MAIN MENU on DRB screen.
(7) Press DVOM button on DRB.
(8) Using left/right arrow keys, highlight CHAN-
NEL 1 function on DRB screen.
(9) Press ENTER three times.
(10) Using up/down arrow keys, highlight RANGE
on DRB screen (screen will default to 2 amp scale).
(11) Press ENTER to change 2 amp scale to 10
amp scale.This step must be done to prevent
damage to DRB scan tool or LCS adapter
(blown fuse).
(12) Remove cover from Power Distribution Center
(PDC).
(13) Remove fuel pump relay from PDC. Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
Fig. 20 FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE (TYPICAL
GAUGE INSTALLATION AT TEST PORT)
1 - SERVICE (TEST) PORT
2 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
3 - FUEL RAIL
Fig. 21 LOW CURRENT SHUNT
1 - LOW CURRENT SHUNT ADAPTER
2 - PLUG TO DRB
3 - TEST LEAD RECEPTACLES
14 - 16 FUEL DELIVERYKJ
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1415 of 1803

FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
An individual fuel injector (Fig. 9) is used for each
individual cylinder.
OPERATION
OPERATION - FUEL INJECTOR
The top (fuel entry) end of the injector (Fig. 9) is
attached into an opening on the fuel rail.
The fuel injectors are electrical solenoids. The
injector contains a pintle that closes off an orifice at
the nozzle end. When electric current is supplied to
the injector, the armature and needle move a short
distance against a spring, allowing fuel to flow out
the orifice. Because the fuel is under high pressure, a
fine spray is developed in the shape of a pencil
stream. The spraying action atomizes the fuel, add-
ing it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
The nozzle (outlet) ends of the injectors are posi-
tioned into openings in the intake manifold just
above the intake valve ports of the cylinder head.
The engine wiring harness connector for each fuel
injector is equipped with an attached numerical tag
(INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.). This is used to identify each fuel
injector.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage is supplied to the injectors through
the ASD relay.
The PCM determines injector pulse width based on
various inputs.
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The nozzle ends of the injectors are positioned into
openings in the intake manifold just above the intake
valve ports of the cylinder head. The engine wiring
harness connector for each fuel injector is equipped
with an attached numerical tag (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.).
This is used to identify each fuel injector with its
respective cylinder number.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage (12 volts +) is supplied to the injec-
tors through the ASD relay. The ASD relay will shut-
down the 12 volt power source to the fuel injectors if
the PCM senses the ignition is on, but the engine is
not running. This occurs after the engine has not
been running for approximately 1.8 seconds.
The PCM determines injector on-time (pulse width)
based on various inputs.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL INJECTOR
To perform a complete test of the fuel injectors and
their circuitry, use the DRB scan tool and refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the injector only, refer to the following:
Disconnect the fuel injector wire harness connector
from the injector. The injector is equipped with 2
electrical terminals (pins). Place an ohmmeter across
the terminals. Resistance reading should be approxi-
mately 12 ohms 1.2 ohms at 20ÉC (68ÉF).
Fig. 9 FUEL INJECTOR Ð TYPICAL
KJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 33
Page 1417 of 1803

IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into a
passage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.
The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. Fromthis point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
IAC Stepper Motor Program:The PCM is also
equipped with a memory program that records the
number of steps the IAC stepper motor most recently
advanced to during a certain set of parameters. For
example: The PCM was attempting to maintain a
1000 rpm target during a cold start-up cycle. The last
recorded number of steps for that may have been
125. That value would be recorded in the memory
cell so that the next time the PCM recognizes the
identical conditions, the PCM recalls that 125 steps
were required to maintain the target. This program
allows for greater customer satisfaction due to
greater control of engine idle.
Another function of the memory program, which
occurs when the power steering switch (if equipped),
or the A/C request circuit, requires that the IAC step-
per motor control engine rpm, is the recording of the
last targeted steps into the memory cell. The PCM
can anticipate A/C compressor loads. This is accom-
plished by delaying compressor operation for approx-
imately 0.5 seconds until the PCM moves the IAC
stepper motor to the recorded steps that were loaded
into the memory cell. Using this program helps elim-
inate idle-quality changes as loads change. Finally,
the PCM incorporates a9No-Load9engine speed lim-
iter of approximately 1800 - 2000 rpm, when it rec-
ognizes that the TPS is indicating an idle signal and
IAC motor cannot maintain engine idle.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the IAC motor through the PCM.
KJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 35
Page 1418 of 1803

REMOVAL
2.4L
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
rear side of the throttle body (Fig. 12).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(2) Remove two mounting bolts (screws).
(3) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
3.7L
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
side of the throttle body (Fig. 13).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(2) Remove two mounting bolts (screws).
(3) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
INSTALLATION
2.4L
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
rear side of the throttle body.
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
3.7L
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is located on the
side of the throttle body (Fig. 13).
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The 2±wire Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT)
sensor is installed in the intake manifold with the
sensor element extending into the air stream.
The IAT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as intake mani-
fold temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
The IAT sensor provides an input voltage to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) indicating the
density of the air entering the intake manifold based
upon intake manifold temperature. At key-on, a
5±volt power circuit is supplied to the sensor from
the PCM. The sensor is grounded at the PCM
through a low-noise, sensor-return circuit.
The PCM uses this input to calculate the following:
²Injector pulse-width
²Adjustment of spark timing (to help prevent
spark knock with high intake manifold air-charge
temperatures)
Fig. 12 TPS/IAC MOTOR - 2.4L
1 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
3 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (IAC)
4 - MOUNTING SCREWS
Fig. 13 TPS/IAC MOTOR - 3.7L
1 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
3 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (IAC)
4 - MOUNTING SCREWS
14 - 36 FUEL INJECTIONKJ
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1420 of 1803

INSTALLATION
2.4L
The intake manifold air temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the intake manifold plenum at the
rear end of the intake manifold.
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
(2) Clean sensor mounting hole in intake manifold.
(3) Position sensor into intake manifold and rotate
clockwise until past release tab.
(4) Install electrical connector.
3.7L
The intake manifold air temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the left side of intake manifold ple-
num (Fig. 16).
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
(2) Clean sensor mounting hole in intake manifold.
(3) Position sensor into intake manifold and rotate
clockwise until past release tab (Fig. 16).
(4) Install electrical connector.
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
2.4L
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted into the rear of the intake manifold with 1
screw.
3.7L
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted into the front of the intake manifold with 2
screws.
OPERATION
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to a
very different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
14 - 38 FUEL INJECTIONKJ
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1422 of 1803

INSTALLATION
2.4L
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted into the rear of the intake manifold. An
o-ring is used to seal the sensor to the intake mani-
fold (Fig. 19).
(1) Clean MAP sensor mounting hole at intake
manifold.
(2) Check MAP sensor o-ring seal for cuts or tears.
(3) Position sensor into manifold.
(4) Install MAP sensor mounting screws. Tighten
screw to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect electrical connector.
3.7L
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is
mounted into the front of the intake manifold (Fig.
18). An o-ring is used to seal the sensor to the intake
manifold (Fig. 19).
(1) Clean MAP sensor mounting hole at intake
manifold.
(2) Check MAP sensor o-ring seal for cuts or tears.
(3) Position sensor into manifold.
(4) Install MAP sensor mounting bolts (screws).
Tighten screws to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect electrical connector.
OXYGEN SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Oxygen Sensors (O2S) are attached to, and
protrude into the vehicle exhaust system. Depending
on the engine or emission package, the vehicle may
use a total of either 2 or 4 sensors.
2.4L Engine:Two sensors are used: upstream
(referred to as 1/1) and downstream (referred to as
1/2). With this emission package, the upstream sen-
sor (1/1) is located just before the main catalytic con-
vertor. The downstream sensor (1/2) is located just
after the main catalytic convertor.
3.7L V-6 Engine:On this emissions package, 4
sensors are used: 2 upstream (referred to as 1/1 and
2/1) and 2 downstream (referred to as 1/2 and 2/2).
With this emission package, the right upstream sen-
sor (2/1) is located in the right exhaust downpipe just
before the mini-catalytic convertor. The left upstream
sensor (1/1) is located in the left exhaust downpipe
just before the mini-catalytic convertor. The right
downstream sensor (2/2) is located in the right
exhaust downpipe just after the mini-catalytic con-
vertor, and before the main catalytic convertor. The
left downstream sensor (1/2) is located in the left
exhaust downpipe just after the mini-catalytic con-
vertor, and before the main catalytic convertor.
OPERATION
An O2 sensor is a galvanic battery that provides
the PCM with a voltage signal (0-1 volt) inversely
proportional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
In other words, if the oxygen content is low, the volt-
age output is high; if the oxygen content is high the
output voltage is low. The PCM uses this information
to adjust injector pulse-width to achieve the
14.7±to±1 air/fuel ratio necessary for proper engine
operation and to control emissions.
The O2 sensor must have a source of oxygen from
outside of the exhaust stream for comparison. Cur-
rent O2 sensors receive their fresh oxygen (outside
air) supply through the O2 sensor case housing.
Four wires (circuits) are used on each O2 sensor: a
12±volt feed circuit for the sensor heating element; a
ground circuit for the heater element; a low-noise
sensor return circuit to the PCM, and an input cir-
cuit from the sensor back to the PCM to detect sen-
sor operation.
Oxygen Sensor Heater Relay - 3.7L Engine:On
the 3.7L engine, 4 heated oxygen sensors are used. A
separate oxygen sensor relay is used to supply volt-
age to the sensors heating elements for only the 1/2
and 2/2 downstream sensors. Voltage for the other 2
sensor heating elements is supplied directly from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) through a Pulse
Width Module (PWM) method.
Pulse Width Module (PWM):Voltage to the O2
sensor heating elements is supplied directly from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) through two sepa-
rate Pulse Width Module (PWM) low side drivers.
PWM is used on both the upstream and downstream
O2 sensors on the 2.4L engine, and only on the 2
upstream sensors (1/1 and 2/1) on the 3.7L engine.
The main objective for a PWM driver is to avoid over-
heating of the O2 sensor heater element. With
exhaust temperatures increasing with time and
engine speed, it's not required to have a full-voltage
duty-cycle on the O2 heater elements.
To avoid the large simultaneous current surge
needed to operate all 4 sensors, power is delayed to
the 2 downstream heater elements by the PCM for
approximately 2 seconds.
Oxygen Sensor Heater Elements:
The O2 sensor uses a Positive Thermal Co-efficient
(PTC) heater element. As temperature increases,
resistance increases. At ambient temperatures
around 70ÉF, the resistance of the heating element is
approximately 4.5 ohms. As the sensor's temperature
increases, resistance in the heater element increases.
This allows the heater to maintain the optimum
operating temperature of approximately 930É-1100ÉF
(500É-600É C). Although the sensors operate the
same, there are physical differences, due to the envi-
14 - 40 FUEL INJECTIONKJ
MAP SENSOR (Continued)