2002 DODGE RAM air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 1885 of 2255
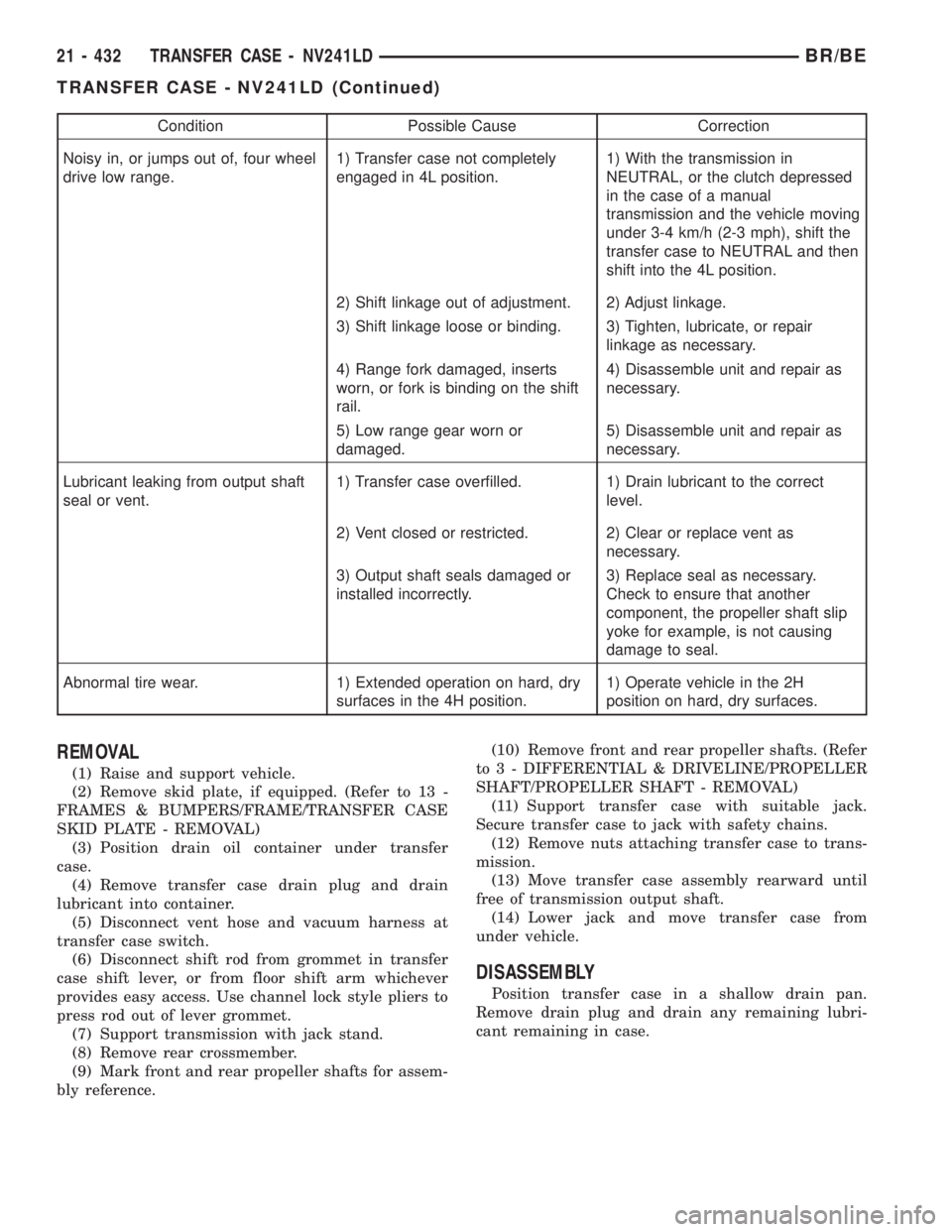
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Noisy in, or jumps out of, four wheel
drive low range.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4L position.1) With the transmission in
NEUTRAL, or the clutch depressed
in the case of a manual
transmission and the vehicle moving
under 3-4 km/h (2-3 mph), shift the
transfer case to NEUTRAL and then
shift into the 4L position.
2) Shift linkage out of adjustment. 2) Adjust linkage.
3) Shift linkage loose or binding. 3) Tighten, lubricate, or repair
linkage as necessary.
4) Range fork damaged, inserts
worn, or fork is binding on the shift
rail.4) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
5) Low range gear worn or
damaged.5) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from output shaft
seal or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Vent closed or restricted. 2) Clear or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Output shaft seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace seal as necessary.
Check to ensure that another
component, the propeller shaft slip
yoke for example, is not causing
damage to seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation on hard, dry
surfaces in the 4H position.1) Operate vehicle in the 2H
position on hard, dry surfaces.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove skid plate, if equipped. (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/FRAME/TRANSFER CASE
SKID PLATE - REMOVAL)
(3) Position drain oil container under transfer
case.
(4) Remove transfer case drain plug and drain
lubricant into container.
(5) Disconnect vent hose and vacuum harness at
transfer case switch.
(6) Disconnect shift rod from grommet in transfer
case shift lever, or from floor shift arm whichever
provides easy access. Use channel lock style pliers to
press rod out of lever grommet.
(7) Support transmission with jack stand.
(8) Remove rear crossmember.
(9) Mark front and rear propeller shafts for assem-
bly reference.(10) Remove front and rear propeller shafts. (Refer
to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(11) Support transfer case with suitable jack.
Secure transfer case to jack with safety chains.
(12) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans-
mission.
(13) Move transfer case assembly rearward until
free of transmission output shaft.
(14) Lower jack and move transfer case from
under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
Position transfer case in a shallow drain pan.
Remove drain plug and drain any remaining lubri-
cant remaining in case.
21 - 432 TRANSFER CASE - NV241LDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241LD (Continued)
Page 1897 of 2255
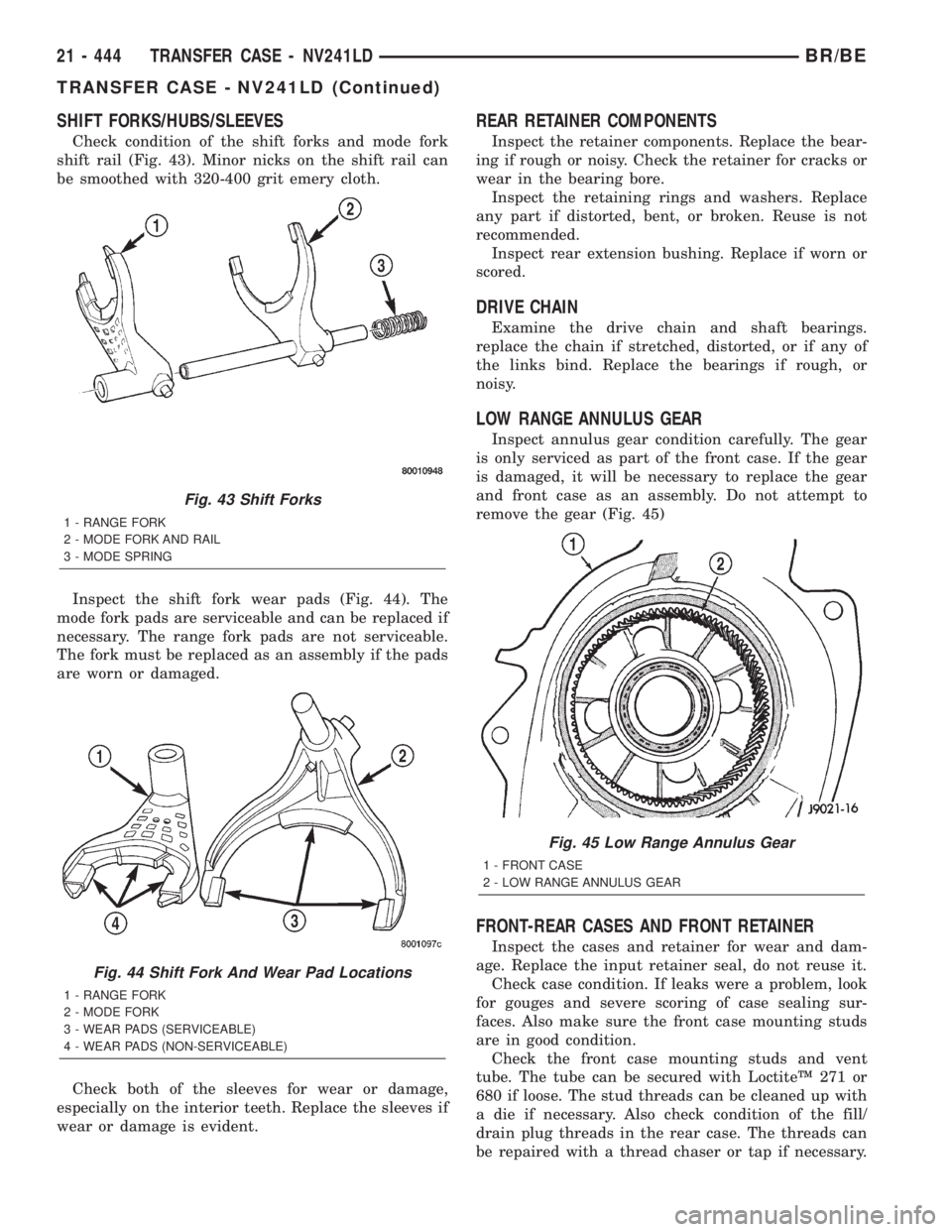
SHIFT FORKS/HUBS/SLEEVES
Check condition of the shift forks and mode fork
shift rail (Fig. 43). Minor nicks on the shift rail can
be smoothed with 320-400 grit emery cloth.
Inspect the shift fork wear pads (Fig. 44). The
mode fork pads are serviceable and can be replaced if
necessary. The range fork pads are not serviceable.
The fork must be replaced as an assembly if the pads
are worn or damaged.
Check both of the sleeves for wear or damage,
especially on the interior teeth. Replace the sleeves if
wear or damage is evident.
REAR RETAINER COMPONENTS
Inspect the retainer components. Replace the bear-
ing if rough or noisy. Check the retainer for cracks or
wear in the bearing bore.
Inspect the retaining rings and washers. Replace
any part if distorted, bent, or broken. Reuse is not
recommended.
Inspect rear extension bushing. Replace if worn or
scored.
DRIVE CHAIN
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
replace the chain if stretched, distorted, or if any of
the links bind. Replace the bearings if rough, or
noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 45)
FRONT-REAR CASES AND FRONT RETAINER
Inspect the cases and retainer for wear and dam-
age. Replace the input retainer seal, do not reuse it.
Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Fig. 43 Shift Forks
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK AND RAIL
3 - MODE SPRING
Fig. 44 Shift Fork And Wear Pad Locations
1 - RANGE FORK
2 - MODE FORK
3 - WEAR PADS (SERVICEABLE)
4 - WEAR PADS (NON-SERVICEABLE)
Fig. 45 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
21 - 444 TRANSFER CASE - NV241LDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241LD (Continued)
Page 1920 of 2255

IDENTIFICATION
An identification tag (Fig. 2) is attached to the rear
case of every transfer case. The tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
OPERATION
OPERATING RANGES
Transfer case operating ranges are:
²2H (2-wheel drive)
²4H (4-wheel drive)
²4LO (4-wheel drive low range)
The 2H range is for use on any road surface at any
time.
The 4H and 4LO ranges are for off road use only.
They are not for use on hard surface roads. The onlyexception being when the road surface is covered by
ice and snow or other loose, slippery material.
The low range reduction gear system is operative
in 4LO range only. This range is for extra pulling
power in off road situations. Low range reduction
ratio is 2.72:1.
A front axle disconnect system is used to achieve
two-wheel drive mode. The axle disconnect vacuum
motor is actuated by a vacuum switch on the transfer
case. The switch is operated by the transfer case
range rod.
SHIFT MECHANISM
The transfer case is operated by an adjustable floor
mounted shift linkage. The transfer case shift lever
is directly attached to the shift sector. The sector
operates the range and mode forks within the trans-
fer case.
A straight line shift pattern is used with a NEU-
TRAL detent. Lever range positions are imprinted in
the shift knob.
SHIFTING
The synchronizer components allow the transfer
case to be shifted between the 2H and 4H operating
ranges while the vehicle is in motion. The vehicle
must have the transmission placed in NEUTRAL, or
the clutch depressed in the case of a manual trans-
mission, and be moving less than 2-3 MPH when
shifting into the 4L operating range.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE
Before beginning repair on a suspected transfer
case malfunction, check all other driveline compo-
nents beforehand.
The actual cause of a problem may be related to
such items as: front hubs, axles, propeller shafts,
wheels and tires, transmission, or clutch instead. If
all other driveline components are in good condition
and operating properly, refer to the Diagnosis Chart
for further information.
1 - FRONT CASE 16 - NEEDLE BEARING
2 - PLANETARY ASSEMBLY 17 - FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - SUPPORT SLEEVE 18 - SPROCKET
4 - SYNCHRO HUB 19 - ROLLER BEARING
5 - STOP RING 20 - SEAL
6 - REAR CASE 21 - COMPANION FLANGE
7 - OIL PUMP 22 - SECTOR SHAFT
8 - REAR RETAINER 23 - SLIDING CLUTCH
9 - OUTPUT BEARING 24 - SLIDING HUB
10 - REAR EXTENSION 25 - PTO GEAR
11 - SEAL 26 - ANNULUS GEAR
12 - BUSHING 27 - INPUT BEARING RETAINER
13 - SPEEDOMETER GEAR 28 - SEAL
14 - DRIVE SPROCKET 29 - INPUT GEAR
15 - CHAIN 30 - INPUT BEARING
Fig. 2 Transfer Case Identification Tag - Typical
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241HD 21 - 467
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 1921 of 2255
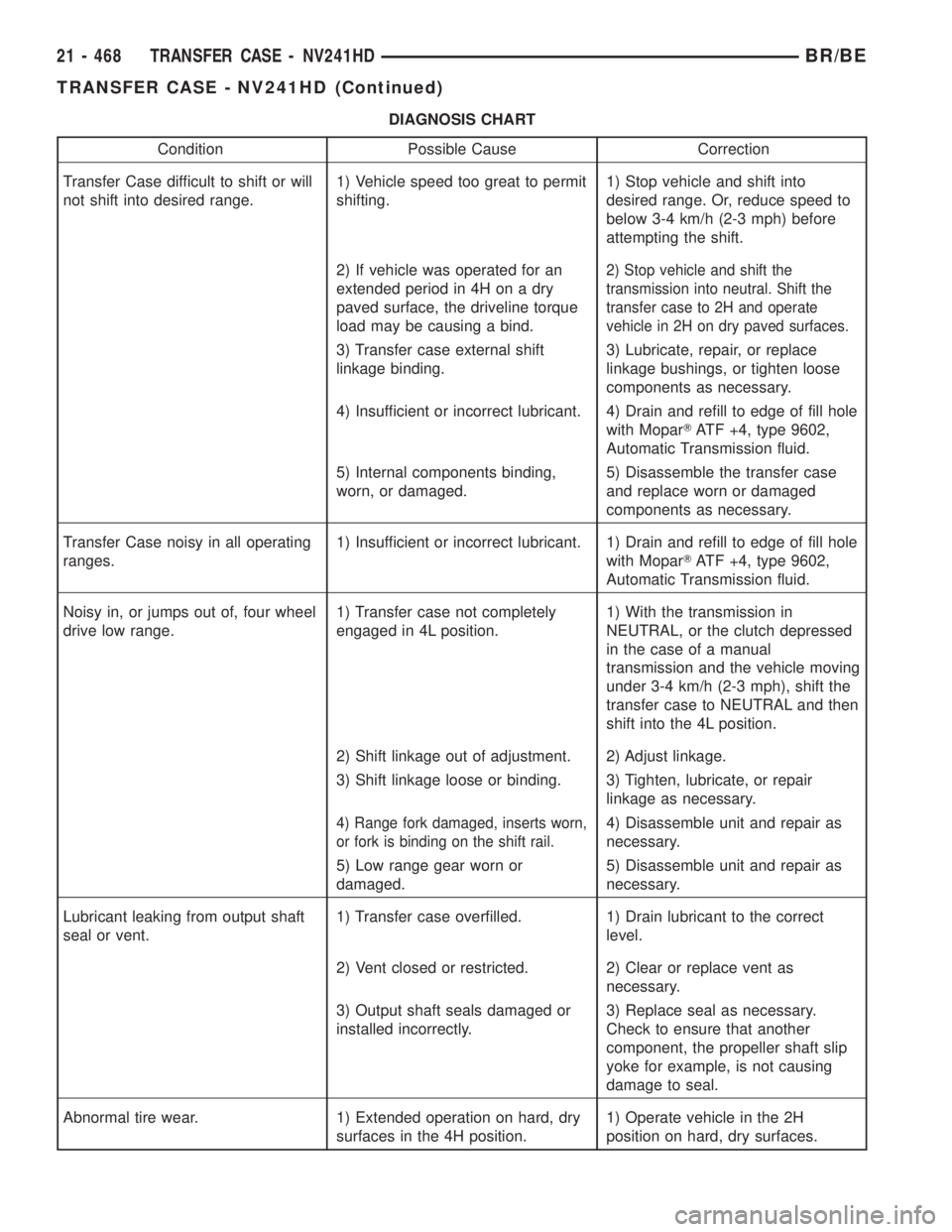
DIAGNOSIS CHART
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Transfer Case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Vehicle speed too great to permit
shifting.1) Stop vehicle and shift into
desired range. Or, reduce speed to
below 3-4 km/h (2-3 mph) before
attempting the shift.
2) If vehicle was operated for an
extended period in 4H on a dry
paved surface, the driveline torque
load may be causing a bind.
2) Stop vehicle and shift the
transmission into neutral. Shift the
transfer case to 2H and operate
vehicle in 2H on dry paved surfaces.
3) Transfer case external shift
linkage binding.3) Lubricate, repair, or replace
linkage bushings, or tighten loose
components as necessary.
4) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 4) Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with MoparTATF +4, type 9602,
Automatic Transmission fluid.
5) Internal components binding,
worn, or damaged.5) Disassemble the transfer case
and replace worn or damaged
components as necessary.
Transfer Case noisy in all operating
ranges.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill to edge of fill hole
with MoparTATF +4, type 9602,
Automatic Transmission fluid.
Noisy in, or jumps out of, four wheel
drive low range.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4L position.1) With the transmission in
NEUTRAL, or the clutch depressed
in the case of a manual
transmission and the vehicle moving
under 3-4 km/h (2-3 mph), shift the
transfer case to NEUTRAL and then
shift into the 4L position.
2) Shift linkage out of adjustment. 2) Adjust linkage.
3) Shift linkage loose or binding. 3) Tighten, lubricate, or repair
linkage as necessary.
4) Range fork damaged, inserts worn,
or fork is binding on the shift rail.4) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
5) Low range gear worn or
damaged.5) Disassemble unit and repair as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from output shaft
seal or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Vent closed or restricted. 2) Clear or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Output shaft seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace seal as necessary.
Check to ensure that another
component, the propeller shaft slip
yoke for example, is not causing
damage to seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation on hard, dry
surfaces in the 4H position.1) Operate vehicle in the 2H
position on hard, dry surfaces.
21 - 468 TRANSFER CASE - NV241HDBR/BE
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 1930 of 2255

Inspect the spline teeth on the synchronizer hub
(Fig. 38). If evidence of chipping or excessive wear is
apparent, replace the hub. The hooked end of each
synchronizer spring should be inserted in one of the
struts. In addition, the springs should not interfere
with the polished gear cone or inside diameters of
the hub.
Inspect the stop ring for cracks and wear. Replace
the ring if necessary or if doubt exists over condition.
Check a replacement synchronizer ring for proper fit
on the cone with a minimum of wobble. Also check
the synchronizer struts for wear or damage.
Inspect all gear teeth and splines for wear or dam-
age. Also check splines for burrs, or nicks. Removeminor nicks and scratches with an oil stone. Replace
any part with damaged splines.
It is recommended that all retaining rings be
replaced during overhaul. Most of the retaining rings
can be distorted during removal and should not be
reused.
Inspect the two case halves, for cracks, porosity,
damaged mating surfaces, stripped bolt threads, or
distortion. Replace either case half if necessary. How-
ever, stripped threads can be repaired with Heli-
CoilŸ stainless steel thread inserts. The case vent
tube can be resecured with LoctiteŸ 680 if necessary.
Inspect the annulus gear. Be sure the gear teeth
are in good condition. Replace the front case and
annulus as an assembly if the gear is damaged.
Fig. 34 Planetary Lock Ring And Front Thrust
Washer Removal
1 - THRUST WASHER
2 - PLANETARY
3 - LOCK RING
Fig. 35 Removing Input Gear From Planetary Carrier
1 - INPUT GEAR
2 - PLANETARY CARRIER
Fig. 36 Support Sleeve Removal
1 - SUPPORT SLEEVE
2 - PLANETARY CARRIER
Fig. 37 Rear Thrust Washer Removal
1 - REAR THRUST WASHER
2 - PLANETARY CARRIER
BR/BETRANSFER CASE - NV241HD 21 - 477
TRANSFER CASE - NV241HD (Continued)
Page 1968 of 2255

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS . . . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS . 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIND NOISE . . . 3
SPECIFICATIONS
WELD LOCATIONS.....................4
STRUCTURAL ADHESIVE LOCATIONS.....44
BODY SEALER LOCATIONS.............47
BODY GAP AND FLUSH MEASUREMENTS . . 56
BODY OPENING DIMENSIONS...........60TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.............61
DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE.......63
DOOR - FRONT.........................68
DOOR - CARGO.........................77
EXTERIOR.............................86
HOOD................................100
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM............105
INTERIOR.............................118
PAINT................................129
SEATS...............................131
STATIONARY GLASS....................145
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................151
BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE AN OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
²AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH
PETROLEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEANING
SOLVENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT STAND UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE
THAT IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched
in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the
outer body panel, electrical wiring, or other compo-
nents. Damage to vehicle can result.
²Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
²Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use
when welding.
²Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from
the battery when servicing electrical components
that are live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to
electrical system can result.
²Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds
on painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
²Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning sol-
vents on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage
to finish or color can result.
²Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel
when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can
break.
BR/BEBODY 23 - 1
Page 1969 of 2255

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.
Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the highest point of the water track or
drop. The highest point usually will show the point of
entry. After leak point has been found, repair the
leak and water test to verify that the leak has
stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
23 - 2 BODYBR/BE
BODY (Continued)
Page 1970 of 2255

BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIND NOISE
Wind noise is the result of most air leaks. Air leaks
can be caused by poor sealing, improper body compo-
nent alignment, body seam porosity, or missing plugs
in the engine compartment or door hinge pillar areas.
All body sealing points should be airtight in normal
driving conditions. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal airtight under all conditions. At times,
side glass or door seals will allow wind noise to be
noticed in the passenger compartment during highcross winds. Over compensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop wind noise that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After a repair pro-
cedure has been performed, test vehicle to verify
noise has stopped before returning vehicle to use.
Wind noise can also be caused by improperly fitted
exterior moldings or body ornamentation. Loose
moldings can flutter, creating a buzzing or chattering
noise. An open cavity or protruding edge can create a
whistling or howling noise. Inspect the exterior of the
vehicle to verify that these conditions do not exist.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place and
body components are aligned and sealed. If compo-
nent alignment or sealing is necessary, refer to the
appropriate section of this group for proper proce-
dures.
ROAD TESTING WIND NOISE
(1) Drive the vehicle to verify the general location
of the wind noise.
(2) Apply 50 mm (2 in.) masking tape in 150 mm
(6 in.) lengths along weatherstrips, weld seams or
moldings. After each length is applied, drive the vehi-
cle. If noise goes away after a piece of tape is applied,
remove tape, locate, and repair defect.
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF WIND NOISE
²Moldings standing away from body surface can
catch wind and whistle.
²Gaps in sealed areas behind overhanging body
flanges can cause wind-rushing sounds.
²Misaligned movable components.
²Missing or improperly installed plugs in pillars.
²Weld burn through holes.
BR/BEBODY 23 - 3
BODY (Continued)