2002 DODGE RAM lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 588 of 2255

PASSENGER POWER SEAT SWITCH TEST TABLE
PASSENGER SWITCH
POSITIONCONTINUITY BETWEEN
OFF B-N, B-J, B-M,B-E, B-L,
B-K
VERTICAL DOWN A-E, A-M, B-N, B-E
VERTICAL UP A-J, A-N, B-M, B-E
HORIZONTAL
FORWARDA-L, B-K
HORIZONTAL
REARWARDA-K, B-L
FRONT TILT DOWN A-M, B-N
FRONT TILT UP A-N, B-M
REAR TILT DOWN A-E, B-J
REAR TILT UP A-J, B-E
LUMBAR OFF O-P, O-R, P-R
LUMBAR DOWN
(DEFLATE)O-P, Q-R
LUMBAR UP (INFLATE) O-R, P-Q
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Standard cab models, remove the two screws
that secure the power seat switch and bezel unit to
the seat cushion frame.
(3) Quad cab models, remove the seat cushion side
shield from the seat. Refer to Body for the procedure.
(4) Pull the switch bezel or side shield unit out
from the seat far enough to access the switch wire
harness connector. Gently pry the locking tabs of the
switch away from the wire harness connector and
carefully unplug the connector from the power seat
switch module (Fig. 7).
(5) Remove the screws that secure the power seat
switch (Fig. 8).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the power seat switch on the seat
cushion side shield and connect the electrical connec-
tor.
(2) Install the screws that secure the power seat
switch to seat cushion side shield.
(3) Install the seat cushion side shield on the seat.
Refer to Body for the procedure.
(4) If equipped, install the recliner lever on the
recliner mechanism release shaft.
(5) If equipped, install the screw that secures the
recliner lever to the recliner mechanism release shaft
on the outboard side of the front seat.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable.
POWER SEAT TRACK
DESCRIPTION
There are three reversible motors that operate the
power seat adjuster. The motors are connected to
worm-drive gearboxes that move the seat adjuster
through a combination of screw-type drive units.
The front and rear of a seat are operated by differ-
ent motors. They can be raised or lowered indepen-
dently of each other. When the center seat switch is
pushed in the Up or Down direction, both the front
and rear motors operate in unison. On standard cab
models the entire seat is moved up or down, on quad
cab models the seat cushion moves independently of
the seat back in the up or down directions. The for-
ward-rearward motor is operated by pushing the cen-
ter seat switch in the Forward or Rearward direction,
which moves the entire seat in the selected direction
on all models.
Fig. 7 Power Seat Switch Connector Remove -
Standard Cab
1 - RELEASE TABS (3)
Fig. 8 Power Seat Switch Remove/Install - Quad Cab
1 - SEAT SIDE SHIELD
2 - POWER SEAT SWITCH
3 - SCREWS
BR/BEPOWER SEAT SYSTEM 8N - 21
PASSENGER POWER SEAT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 590 of 2255

POWER WINDOWS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER WINDOWS
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
WINDOWS...........................23
POWER WINDOW SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
WINDOW SWITCH.....................24REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................26
WINDOW MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WINDOW
MOTOR .............................26
REMOVAL.............................26
POWER WINDOWS
DESCRIPTION
Power windows are available as factory-installed
optional equipment on this model. The power lock
system is included on vehicles equipped with the
power window option.
OPERATION
The power window system allows each of the front
door windows to be raised and lowered electrically by
actuating a switch on the trim panel of each respec-
tive door. Additionally, the master switch on the
driver side door trim panel allows the driver to raise
or lower the passenger side front door window. The
power window system receives battery feed through a
circuit breaker in the junction block, only when the
ignition switch is in the On position.
The power window system includes the power win-
dow switches on each front door trim panel, the cir-
cuit breaker in the junction block, and the power
window motors inside each front door. This group
covers diagnosis and service of only the electrical
components in the power window system. For service
of mechanical components, such as the regulator, lift
plate, window tracks, or glass refer to Group 23 -
Body.
Refer to the owner's manual in the vehicle glove
box for more information on the features, use and
operation of the power window system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
WINDOWS
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, details of wire harnessrouting and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
ALL WINDOWS INOPERATIVE
(1) Check the circuit breaker in the junction block.
If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty cir-
cuit breaker.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the power window and lock switch and
bezel unit from the driver side front door trim panel.
Unplug the wire harness connector from the switch
and bezel unit.
(3) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity of the switch and bezel unit wire harness
connector and a good ground. If OK, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER WINDOWS/POWER WIN-
DOW SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). If not
OK, repair the circuit to ground as required.
ONE WINDOW INOPERATIVE
The window glass must be free to slide up and
down for the power window motor to function prop-
erly. If the glass is not free to move up and down, the
motor will overload and trip the integral circuit
breaker. To determine if the glass is free, disconnect
the regulator plate from the glass. Then slide the
window up and down by hand.
There is an alternate method to check if the glass
is free. Position the glass between the up and down
stops. Then, shake the glass in the door. Check that
the glass can be moved slightly from side to side,
front to rear, and up and down. Then check that the
glass is not bound tight in the tracks. If the glass is
free, proceed with the diagnosis that follows. If the
glass is not free, (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOOR -
FRONT/DOOR GLASS - REMOVAL).
BR/BEPOWER WINDOWS 8N - 23
Page 591 of 2255

(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the power window and lock switch and
bezel unit from the door trim panel on the side of the
vehicle with the inoperative window. Unplug the wire
harness connector from the switch and bezel unit.
(2) Connect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Check for battery
voltage at the fused ignition switch output (run) cir-
cuit cavity in the body half of the switch and bezel
unit wire harness connector. If OK, and the inopera-
tive power window is on the driver side, go to Step 4.
If OK, and the inoperative power window is on the
passenger side, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the
open circuit to the junction block as required.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Check for continuity between each of the two
master window switch right up/down control circuit
cavities in the body half of the passenger side switch
and bezel unit wire harness connector and a good
ground. In each case, there should be continuity. If
OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit to
the driver side switch and bezel unit as required.
(4) Test the power window switch continuity.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER WINDOWS/
POWER WINDOW SWITCH - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, replace
the faulty power window and lock switch and bezel
unit.
(5) Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
The wiring information includes wiring diagrams,
proper wire and connector repair procedures, details
of wire harness routing and retention, connector pin-
out information and location views for the various
wire harness connectors, splices and grounds. Check
the continuity in each circuit between the inoperative
power window and lock switch and bezel unit wire
harness connector cavities and the corresponding
power window motor wire harness connector cavities.
If OK, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER WIN-
DOWS/WINDOW MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING). If not OK, repair the open circuit(s) as
required.
NOTE: The passenger side power window switch
receives the ground feed for operating the passen-
ger side power window motor through the driver
side power window switch and wire harness con-
nector.
POWER WINDOW SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The power windows are controlled by two-way
switches integral to the power window and lock
switch and bezel unit on the trim panel of each frontdoor. A second power window switch in the driver
side switch and bezel unit allows the driver to control
the passenger side window. A Light-Emitting Diode
(LED) in the paddle of each switch is illuminated
whenever the ignition switch is in the On position.
OPERATION
The power window switch for the driver side front
door has an Auto label on it. This switch has a sec-
ond detent position beyond the normal Down position
that provides an automatic one-touch window down
feature. This feature is controlled by an electronic
circuit and a relay that are integral to the driver side
front door power window and lock switch unit.
The power window switches control the battery
and ground feeds to the power window motors. The
passenger side power window switch receives a
ground feed through the driver side power window
switch for operating the passenger side power win-
dow motor.
The power window and lock switch and bezel unit
cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
entire switch and bezel unit must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER WINDOW
SWITCH
The auto down feature of the driver side power
window switch is controlled by an electronic circuit
within the switch unit. The auto down circuitry is
activated when the driver side power window switch
is moved to the second detent in the Down direction.
The outputs from the auto down circuitry are carried
through the same switch pins that provide the nor-
mal down function. The auto down circuit cannot be
tested. If the driver side power window switch conti-
nuity tests are passed, but the auto down feature is
inoperative, replace the faulty driver side power win-
dow switch unit.
The Light-Emitting Diode (LED) illumination
lamps for all of the power window and lock switch
and bezel unit switch paddles receive battery current
through the power window circuit breaker in the
junction block. If all of the LEDs are inoperative in
either or both power window and lock switch and
bezel units and the power windows are inoperative,
perform the diagnosis for Power Window System in
this group. If the power windows operate, but any or
all of the LEDs are inoperative, the power window
and lock switch and bezel unit with the inoperative
LED(s) is faulty and must be replaced. For circuit
descriptions and diagrams, refer to the appropriate
wiring information. The wiring information includes
wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector repair
procedures, details of wire harness routing and
retention, connector pin-out information and location
8N - 24 POWER WINDOWSBR/BE
POWER WINDOWS (Continued)
Page 592 of 2255
views for the various wire harness connectors, splices
and grounds.
(1) Check the circuit breaker in the junction block.
If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty cir-
cuit breaker.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the circuit breaker in
the junction block. If OK, turn the ignition switch to
the Off position and go to Step 3. If not OK, repair
the circuit to the ignition switch as required.
(3) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the power window and lock switch and
bezel unit from the door trim panel. Unplug the wire
harness connector from the switch and bezel unit.
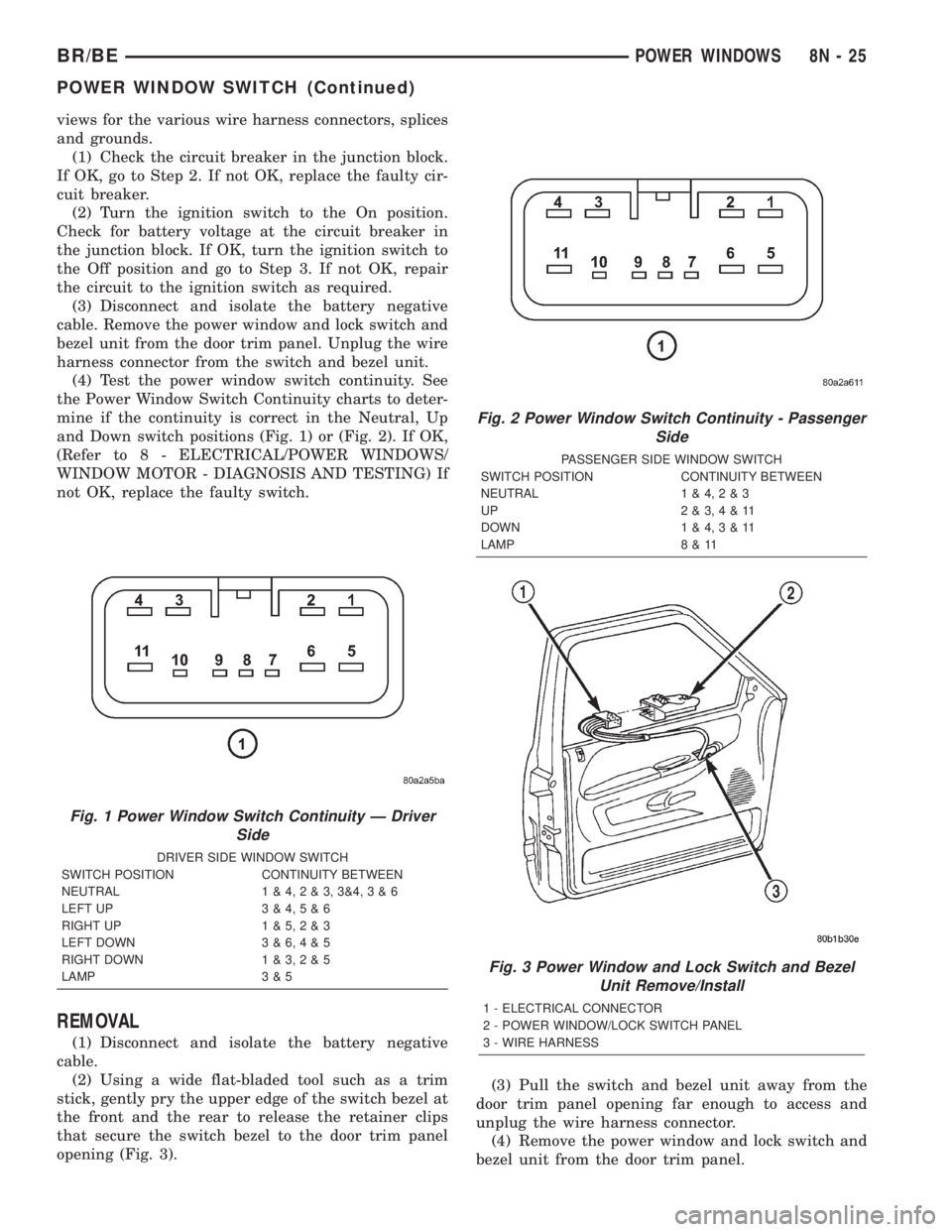
(4) Test the power window switch continuity. See
the Power Window Switch Continuity charts to deter-
mine if the continuity is correct in the Neutral, Up
and Down switch positions (Fig. 1) or (Fig. 2). If OK,
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER WINDOWS/
WINDOW MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) If
not OK, replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Using a wide flat-bladed tool such as a trim
stick, gently pry the upper edge of the switch bezel at
the front and the rear to release the retainer clips
that secure the switch bezel to the door trim panel
opening (Fig. 3).(3) Pull the switch and bezel unit away from the
door trim panel opening far enough to access and
unplug the wire harness connector.
(4) Remove the power window and lock switch and
bezel unit from the door trim panel.
Fig. 1 Power Window Switch Continuity Ð Driver
Side
DRIVER SIDE WINDOW SWITCH
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
NEUTRAL 1 & 4,2&3,3&4,3&6
LEFT UP 3 & 4,5&6
RIGHT UP 1 & 5,2&3
LEFT DOWN 3 & 6,4&5
RIGHT DOWN 1 & 3,2&5
LAMP 3 & 5
Fig. 2 Power Window Switch Continuity - Passenger
Side
PASSENGER SIDE WINDOW SWITCH
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
NEUTRAL 1 & 4,2&3
UP 2&3,4&11
DOWN 1 & 4,3&11
LAMP 8 & 11
Fig. 3 Power Window and Lock Switch and Bezel
Unit Remove/Install
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - POWER WINDOW/LOCK SWITCH PANEL
3 - WIRE HARNESS
BR/BEPOWER WINDOWS 8N - 25
POWER WINDOW SWITCH (Continued)
Page 594 of 2255

RESTRAINTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
RESTRAINTS
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
WARNING.............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM . 4
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HANDLING
NON-DEPLOYED AIRBAGS...............4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SERVICE
AFTER AN AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.........4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VERIFICATION
TEST................................5
SPECIAL TOOLS - AIRBAG SYSTEM.........6
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................8
CHILD TETHER
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
CLOCKSPRING
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING
CENTERING.........................11
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................13
DRIVER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
REMOVAL.............................14
DISASSEMBLY.........................15
ASSEMBLY............................16
INSTALLATION.........................17
FRONT SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - STANDARD CAB............18REMOVAL - CLUB/QUAD CAB............19
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - STANDARD CAB.........19
INSTALLATION - CLUB/QUAD CAB........20
FRONT SEAT BELT BUCKLE
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................20
PASSENGER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................23
PASSENGER AIRBAG ON/OFF SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................24
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................25
REAR SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
REAR SEAT BELT BUCKLE
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................27
SEAT BELT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SEAT BELT
SWITCH............................28
SEAT BELT TURNING LOOP ADJUSTER
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
TURNING LOOP HGT ADJUSTER KNOB
REMOVAL.............................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
RESTRAINTS
DESCRIPTION
A dual front airbag system is standard factory-in-
stalled safety equipment on this model. The airbag
system is a passive, inflatable, Supplemental
Restraint System (SRS) and vehicles with this equip-
ment can be readily identified by the ªSRS - AIR-
BAGº logo molded into the driver airbag trim coverin the center of the steering wheel and also into the
passenger airbag door on the instrument panel above
the glove box (Fig. 1). Vehicles with the airbag sys-
tem can also be identified by the airbag indicator,
which will illuminate in the instrument cluster for
about seven seconds as a bulb test each time the
ignition switch is turned to the On position.
The dual front airbag system consists of the follow-
ing major components, which are described in further
detail elsewhere in this service manual:
BR/BERESTRAINTS 8O - 1
Page 595 of 2255

²Airbag Control Module- The Airbag Control
Module (ACM) is located in a stamped mounting
bracket on the floor panel transmission tunnel, below
the center of the instrument panel.
²Airbag Indicator- The airbag indicator is inte-
gral to the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster
(EMIC), which is located on the instrument panel in
front of the driver.
²Clockspring- The clockspring is located near
the top of the steering column, directly beneath the
steering wheel.
²Driver Airbag- The driver airbag is located in
the center of the steering wheel, beneath the driver
airbag trim cover.
²Driver Knee Blocker- The driver knee blocker
is a molded plastic structural unit secured to the
back side of and integral to the instrument panel
steering column opening cover.
²Passenger Airbag- The passenger airbag is
located on the instrument panel, beneath the passen-
ger airbag door on the instrument panel above the
glove box on the passenger side of the vehicle.
²Passenger Airbag On/Off Switch- The pas-
senger airbag on/off switch is located in a dedicated
opening in the upper right corner of the instrument
panel cluster bezel, to the right of the center panel
outlets of the climate control system.
²Passenger Knee Blocker- The passenger knee
blocker is a structural reinforcement that is integral
to and concealed within the glove box door.
The ACM and the EMIC each contain a central
processing unit and programming that allow them to
communicate with each other using the Chrysler Col-
lision Detection (CCD) data bus network. This
method of communication is used for control of the
airbag indicator on all models. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/
COMMUNICATION - DESCRIPTION).Hard wired circuitry connects the airbag system
components to each other through the electrical sys-
tem of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system, and to the air-
bag system components through the use of a combi-
nation of soldered splices, splice block connectors,
and many different types of wire harness terminal
connectors and insulators. Refer to the appropriate
wiring information. The wiring information includes
wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector repair
procedures, further details on wire harness routing
and retention, as well as pin-out and location views
for the various wire harness connectors, splices and
grounds.OPERATION
The airbag system is referred to as a supplemental
restraint system because it was designed and is
intended to enhance the protection for the front seat
occupants of the vehicleonlywhen used in conjunc-
tion with the seat belts. It is referred to as a passive
system because the vehicle occupants are not
required to do anything to make it work. The pri-
mary passenger restraints in this or any other vehi-
cle are the standard equipment factory-installed seat
belts. Seat belts are referred to as an active restraint
because the vehicle occupants are required to physi-
cally fasten and properly adjust these restraints in
order to benefit from them. The vehicle occupants
must be wearing their seat belts in order to obtain
the maximum safety benefit from the factory-in-
stalled airbag system.
The airbag system electrical circuits are continu-
ously monitored and controlled by a microprocessor
and software contained within the Airbag Control
Module (ACM). An airbag indicator in the ElectroMe-
chanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) lights for about
seven seconds as a bulb test each time the ignition
switch is turned to the On or Start positions. Follow-
ing the bulb test, the airbag indicator is turned on or
off by the ACM to indicate the status of the airbag
system. If the airbag indicator comes on at any time
other than during the bulb test, it indicates that
there is a problem in the airbag system electrical cir-
cuits. Such a problem may cause the airbags not to
deploy when required, or to deploy when not
required.
The clockspring on the top of the steering column
allows a continuous electrical circuit to be main-
tained between the stationary steering column and
the driver airbag inflator, which rotates with the
steering wheel. The passenger airbag on/off switch
allows the passenger side airbag to be disabled when
Fig. 1 SRS Logo
8O - 2 RESTRAINTSBR/BE
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 596 of 2255

circumstances necessitate that a child, or an adult
with certain medical conditions be placed in the front
passenger seating position. Refer to the owner's man-
ual in the vehicle glove box for specific recommenda-
tions concerning the specific circumstances where the
passenger airbag on/off switch should be used to dis-
able the passenger airbag.
Deployment of the airbags depends upon the angle
and severity of the impact. The airbag system is
designed to deploy upon a frontal impact within a
thirty degree angle from either side of the vehicle
center line. Deployment is not based upon vehicle
speed; rather, deployment is based upon the rate of
deceleration as measured by the forces of gravity (G
force) upon the airbag system impact sensor, which is
integral to the ACM. When a frontal impact is severe
enough, the microprocessor in the ACM signals the
inflator units of both airbag modules to deploy the
airbags. During a frontal vehicle impact, the knee
blockers work in concert with properly fastened and
adjusted seat belts to restrain both the driver and
the front seat passenger in the proper position for an
airbag deployment. The knee blockers also absorb
and distribute the crash energy from the driver and
the front seat passenger to the structure of the
instrument panel.
Typically, the driver and front seat passenger recall
more about the events preceding and following a col-
lision than they have of the airbag deployment itself.
This is because the airbag deployment and deflation
occur so rapidly. In a typical 48 kilometer-per-hour
(30 mile-per-hour) barrier impact, from the moment
of impact until both airbags are fully inflated takes
about 40 milliseconds. Within one to two seconds
from the moment of impact, both airbags are almost
entirely deflated. The times cited for these events are
approximations, which apply only to a barrier impact
at the given speed. Actual times will vary somewhat,
depending upon the vehicle speed, impact angle,
severity of the impact, and the type of collision.
When the ACM monitors a problem in any of the
airbag system circuits or components, it stores a
fault code or Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in its
memory circuit and sends an electronic message to
the EMIC to turn on the airbag indicator. Proper
testing of the airbag system components, the
Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD) data bus, the
data bus message inputs to and outputs from the
EMIC or the ACM, as well as the retrieval or erasure
of a DTC from the ACM requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of all of the factory-installed passenger restraints,
including the airbag system.WARNING
WARNING: THE AIRBAG SYSTEM IS A SENSITIVE,
COMPLEX ELECTROMECHANICAL UNIT. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE OR SERVICE ANY AIR-
BAG SYSTEM OR RELATED STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENTS YOU MUST FIRST DISCONNECT
AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND)
CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE FUR-
THER SYSTEM SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE
WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE
TO DO THIS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WARNING: THE DRIVER AIRBAG INFLATOR UNIT
CONTAINS SODIUM AZIDE AND POTASSIUM
NITRATE. THESE MATERIALS ARE POISONOUS
AND EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE. CONTACT WITH
ACID, WATER, OR HEAVY METALS MAY PRODUCE
HARMFUL AND IRRITATING GASES (SODIUM
HYDROXIDE IS FORMED IN THE PRESENCE OF
MOISTURE) OR COMBUSTIBLE COMPOUNDS. THE
PASSENGER AIRBAG UNIT CONTAINS ARGON GAS
PRESSURIZED TO OVER 2500 PSI. DO NOT
ATTEMPT TO DISMANTLE AN AIRBAG UNIT OR
TAMPER WITH ITS INFLATOR. DO NOT PUNCTURE,
INCINERATE, OR BRING INTO CONTACT WITH
ELECTRICITY. DO NOT STORE AT TEMPERATURES
EXCEEDING 93É C (200É F).
WARNING: REPLACE AIRBAG SYSTEM COMPO-
NENTS ONLY WITH PARTS SPECIFIED IN THE
DAIMLERCHRYSLER MOPAR PARTS CATALOG.
SUBSTITUTE PARTS MAY APPEAR INTERCHANGE-
ABLE, BUT INTERNAL DIFFERENCES MAY RESULT
IN INFERIOR OCCUPANT PROTECTION.
WARNING: THE FASTENERS, SCREWS, AND
BOLTS ORIGINALLY USED FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS HAVE SPECIAL COATINGS
AND ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE AIR-
BAG SYSTEM. THEY MUST NEVER BE REPLACED
WITH ANY SUBSTITUTES. ANY TIME A NEW FAS-
TENER IS NEEDED, REPLACE IT WITH THE COR-
RECT FASTENERS PROVIDED IN THE SERVICE
PACKAGE OR SPECIFIED IN THE
DAIMLERCHRYSLER MOPAR PARTS CATALOG.
BR/BERESTRAINTS 8O - 3
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 597 of 2255

WARNING: WHEN A STEERING COLUMN HAS AN
AIRBAG UNIT ATTACHED, NEVER PLACE THE COL-
UMN ON THE FLOOR OR ANY OTHER SURFACE
WITH THE STEERING WHEEL OR AIRBAG UNIT
FACE DOWN.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM
Proper diagnosis and testing of the airbag system
components, the Chrysler Collision Detection (CCD)
data bus, the data bus message inputs to and out-
puts from the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster
(EMIC) or the Airbag Control Module (ACM), as well
as the retrieval or erasure of a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) from the ACM requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HANDLING
NON-DEPLOYED AIRBAGS
At no time should any source of electricity be per-
mitted near the inflator on the back of a non-de-
ployed airbag. When carrying a non-deployed airbag,
the trim cover or airbag cushion side of the unit
should be pointed away from the body to minimize
injury in the event of an accidental deployment. If
the airbag unit is placed on a bench or any other sur-
face, the trim cover or airbag cushion side of the unit
should be face up to minimize movement in the event
of an accidental deployment. In addition, the airbag
system should be disarmed whenever any steering
wheel, steering column, or instrument panel compo-
nents require diagnosis or service. Failure to observe
this warning could result in accidental airbag deploy-
ment and possible personal injury.
All damaged, faulty, or non-deployed airbags which
are replaced on vehicles are to handled and disposed
of properly. If an airbag unit is faulty or damagedand non-deployed, refer to the Hazardous Substance
Control System for proper disposal. Dispose of all
non-deployed and deployed airbags in a manner con-
sistent with state, provincial, local and federal regu-
lations.
AIRBAG STORAGE
An airbag must be stored in its original, special
container until it is used for service. Also, it must be
stored in a clean, dry environment; away from
sources of extreme heat, sparks, and high electrical
energy. Always place or store any airbag on a surface
with its trim cover or airbag cushion side facing up,
to minimize movement in case of an accidental
deployment.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SERVICE AFTER AN
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
Any vehicle which is to be returned to use follow-
ing an airbag deployment, must have both airbags,
the driver airbag trim cover, the clockspring, and the
steering column assembly replaced. These compo-
nents are not intended for reuse and will be damaged
or weakened as a result of an airbag deployment,
which may or may not be obvious during a visual
inspection. Other vehicle components should be
closely inspected, but are to be replaced only as
required by the extent of the visible damage
incurred.
CLEANUP PROCEDURE
Following an airbag deployment, the vehicle inte-
rior will contain a powdery residue. This residue con-
sists primarily of harmless particulate by-products of
the small pyrotechnic charge used to initiate the pro-
pellant used to deploy the airbags. However, this res-
idue may also contain traces of sodium hydroxide
powder, a chemical by-product of the propellant
material that is used to generate the nitrogen gas
that inflates the airbag. Since sodium hydroxide pow-
der can irritate the skin, eyes, nose, or throat, be
sure to wear safety glasses, rubber gloves, and a
long-sleeved shirt during cleanup (Fig. 2).
WARNING: IF YOU EXPERIENCE SKIN IRRITATION
DURING CLEANUP, RUN COOL WATER OVER THE
AFFECTED AREA. ALSO, IF YOU EXPERIENCE
IRRITATION OF THE NOSE OR THROAT, EXIT THE
VEHICLE FOR FRESH AIR UNTIL THE IRRITATION
CEASES. IF IRRITATION CONTINUES, SEE A PHYSI-
CIAN.
Begin the cleanup by removing both airbags from
the vehicle. Refer to the appropriate service removal
procedures.
8O - 4 RESTRAINTSBR/BE
RESTRAINTS (Continued)