2002 DODGE RAM clutch
[x] Cancel search: clutchPage 1333 of 2255

(20) Raise and support the vehicle.
(21) Verify that all oxygen sensor wire connectors
are firmly connected to the sensors. Inspect sensors
and connectors for damage (Fig. 18), (Fig. 19) or (Fig.
20).
(22) Inspect for pinched or leaking fuel tubes.
Inspect for pinched, cracked or leaking fuel hoses.
(23) Inspect for exhaust system restrictions such
as pinched exhaust pipes, collapsed muffler or
plugged catalytic convertor.
(24) If equipped with automatic transmission, ver-
ify that electrical harness is firmly connected to park/
neutral switch. Refer to 21, Automatic Transmission.
(25) Verify electrical harness is firmly connected to
rear wheel speed sensor. Verify rear wheel speed sen-
sor is firmly attached to rear axle with proper air
gap. Refer to 5, Brakes for information.
(26) If equipped with 4±wheel antilock brake sys-
tem, verify electrical harness is firmly connected to
each front wheel speed sensor. Verify both front
wheel speed sensors are firmly attached. Refer to 5,
Brakes for information.
(27) Verify that fuel pump/gauge sender unit wire
connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
(28) Inspect fuel hoses at fuel pump/gauge sender
unit for cracks or leaks.
(29) Inspect transmission torque convertor housing
(automatic transmission) or clutch housing (manual
transmission) for damage to timing ring on drive
plate/flywheel.
(30) Verify that battery cable and solenoid feed
wire connections to the starter solenoid are tight and
clean. Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing up
against other components.
Fig. 18 Upstream/Downstream Oxygen Sensors
1 - DOWN STREAM OXYGEN SENSOR (1/2)
2 - UP STREAM OXYGEN SENSOR (1/1)
Fig. 19 Left/Right
1 - DUAL OXYGEN SENSORS
2 - TOP OF TRANSMISSION
Fig. 20 Pre-Catalyst/Post Catalyst Oxygen Sensors
1 - POST CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/3)
2 - PRE-CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/2)
14 - 34 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1456 of 2255

GEAR RATIOS
GEAR RATIO
FIRST 5.61:1
SECOND 3.04:1
THIRD 1.67:1
FOURTH 1.00:1
FIFTH 0.75:1
REVERSE 5.04:1
IDENTIFICATION
The transmission identification tag is attached to
the driver side PTO cover (Fig. 3).
The tag provides the transmission model number,
build date and part number. Be sure to reinstall the
I.D. tag if removed during service. The information
on the tag is essential to correct parts ordering.
OPERATION
The manual transmission receives power through
the clutch assembly from the engine. The clutch disc
is splined to the transmission input shaft and is
turned at engine speed at all times that the clutch is
engaged. The input shaft is connected to the trans-
mission countershaft through the mesh of fourth
speed gear on the input shaft and the fourth counter-
shaft gear. At this point all the transmission gears
are spinning.The driver selects a particular gear by moving the
shift lever to the desired gear position. This move-
ment moves the internal transmission shift compo-
nents to begin the shift sequence. As the shift lever
moves the selected shift rail, the shift fork attached
to that rail begins to move. The fork is positioned in
a groove in the outer circumference of the synchro-
nizer sleeve. As the shift fork moves the synchronizer
sleeve, the synchronizer begins to speed-up or slow
down the selected gear (depending on whether we are
up-shifting or down-shifting). The synchronizer does
this by having the synchronizer hub splined to the
mainshaft, or the countershaft in some cases, and
moving the blocker ring into contact with the gear's
friction cone. As the blocker ring and friction cone
come together, the gear speed is brought up or down
to the speed of the synchronizer. As the two speeds
match, the splines on the inside of the synchronizer
sleeve become aligned with the teeth on the blocker
ring and the friction cone and eventually will slide
over the teeth, locking the gear to the mainshaft, or
countershaft, through the synchronizer.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
A low transmission lubricant level is generally the
result of a leak, inadequate lubricant fill or an incor-
rect lubricant level check. A correct lubricant level
check can only be made when the vehicle is level.
Also allow the lubricant to settle for a minute or so
before checking. These recommendations will ensure
an accurate check and avoid an underfill or overfill
condition. Always check the lubricant level after any
addition of fluid to avoid an incorrect lubricant level
condition.
Leaks can occur at the mating surfaces of the gear
case, adaptor or extension housing, or from the front/
rear seals. A suspected leak could also be the result
of an overfill condition. Leaks at the rear of the
extension or adapter housing will be from the hous-
ing oil seals. Leaks at component mating surfaces
will probably be the result of inadequate sealer, gaps
in the sealer, incorrect bolt tightening or use of a
non-recommended sealer. A leak at the front of the
transmission will be from either the front bearing
retainer or retainer seal. Lubricant may be seen drip-
ping from the clutch housing after extended opera-
tion. If the leak is severe, it may also contaminate
the clutch disc causing the disc to slip, grab and or
chatter.
Fig. 3 Identification Tag Location
1 - PTO COVER
2 - I.D. TAG
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 3
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1457 of 2255

HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants. The con-
sequence of using non-recommended lubricants is
noise, excessive wear, internal bind and hard shift-
ing. Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear,
shift rail, synchro, and bearing damage. If a leak
goes undetected for an extended period, the first indi-
cations of component damage are usually hard shift-
ing and noise.
Component damage, incorrect clutch adjustment or
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc are additional
probable causes of increased shift effort. Incorrect
adjustment or a worn/damaged pressure plate or disc
can cause incorrect release. If clutch problem is
advanced, gear clash during shifts can result. Worn
or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash when
shifting into any forward gear. In some new or
rebuilt transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible, but generally only at extreme
speeds. Severe highly audible transmission noise is
generally the initial indicator of a lubricant problem.
Insufficient, improper or contaminated lubricant
will promote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift
rails, forks and bearings. The overheating caused by
a lubricant problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(3) Remove shift boot screws from floorpan and
slide boot upward on the shift lever.
(4) Remove shift lever extension from shift tower
and lever assembly.
(5) Remove shift tower bolts holding tower to iso-
lator plate and transmission shift cover.
(6) Remove shift tower and isolator plate from
transmission shift cover.
(7) Raise and support vehicle.
(8) Remove skid plate, if equipped.
(9) Mark propeller shaft and axle yokes for instal-
lation reference and remove shaft/shafts.
(10) Remove exhaust system Y-pipe.
(11) Disconnect speed sensor and backup light
switch connectors.
(12) Support engine with safety stand and a wood
block.
(13) If transmission is to be disassembled for,
remove drain bolt at bottom of PTO cover and drain
lubricant (Fig. 4).
TWO WHEEL DRIVE
(1) Remove nuts/bolts attaching transmission to
rear mount.
(2) Support and secure transmission with safety
chains to a transmission jack.
(3) Remove rear crossmember.
(4) Remove clutch slave cylinder bolts and move
cylinder aside for clearance.
(5) Remove transmission harness wires from clips
on transmission shift cover.
(6) Remove transmission to clutch housing bolts.
(7) Slide transmission and jack rearward until
input shaft clears clutch housing.
(8) Lower transmission jack and remove transmis-
sion from under vehicle.
FOUR WHEEL DRIVE
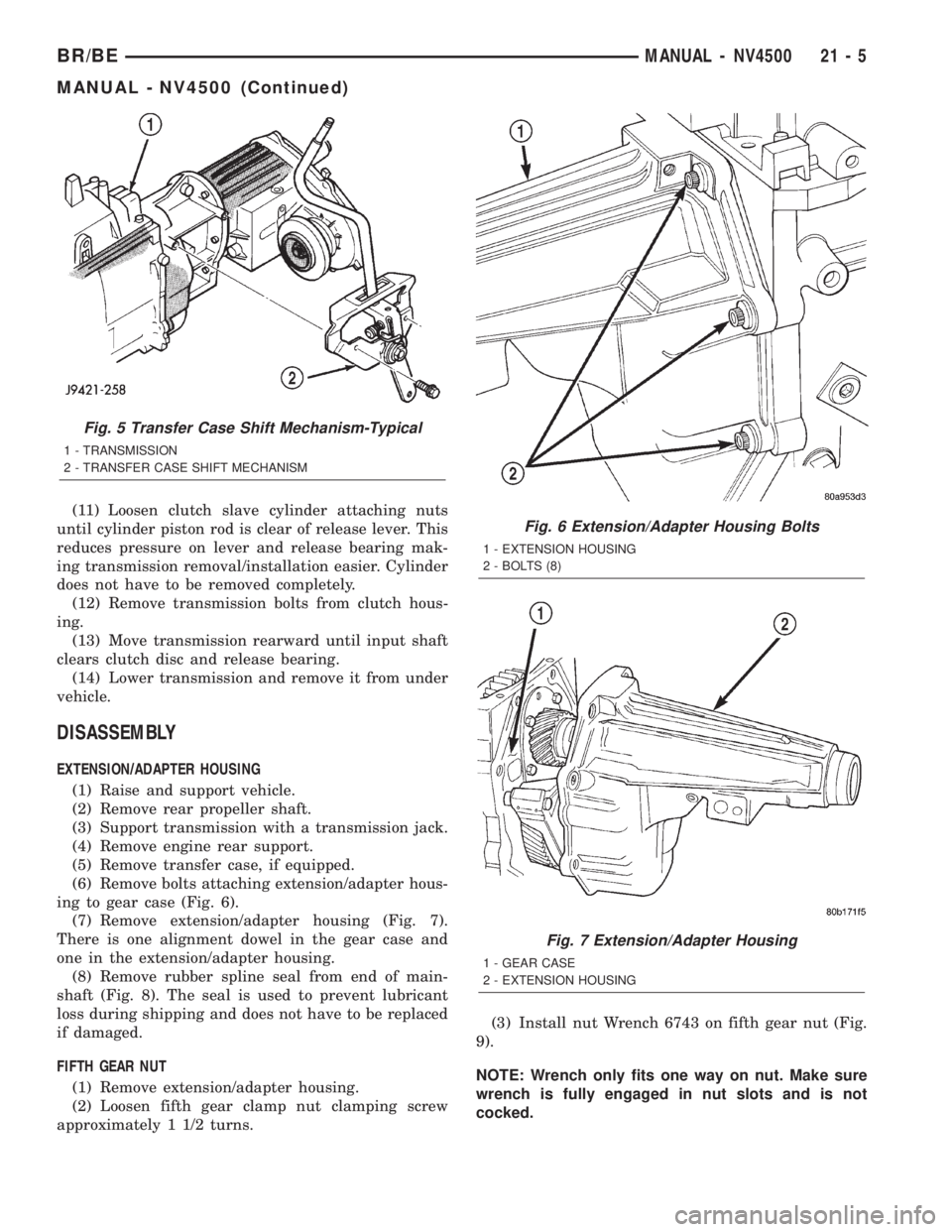
(1) Disconnect transfer case shift linkage at trans-
fer case range lever. Then remove transfer case shift
mechanism from transmission (Fig. 5).
(2) Support and secure transfer case to transmis-
sion jack with safety chains.
(3) Remove transfer case mounting nuts.
(4) Move transfer case rearward until input gear
clears transmission mainshaft.
(5) Lower transfer case assembly and move it from
under vehicle.
(6) Support and secure transmission with safety
chains to a transmission jack.
(7) Remove transmission harness from retaining
clips on transmission shift cover.
(8) Remove bolts/nuts attaching transmission
mount to rear crossmember.
(9) Remove rear crossmember.
(10) Remove clutch slave cylinder splash shield, if
equipped.
Fig. 4 Drain Bolt
1 - PTO COVER
2 - DRAIN BOLT
3 - FILL PLUG
21 - 4 MANUAL - NV4500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1458 of 2255
(11) Loosen clutch slave cylinder attaching nuts
until cylinder piston rod is clear of release lever. This
reduces pressure on lever and release bearing mak-
ing transmission removal/installation easier. Cylinder
does not have to be removed completely.
(12) Remove transmission bolts from clutch hous-
ing.
(13) Move transmission rearward until input shaft
clears clutch disc and release bearing.
(14) Lower transmission and remove it from under
vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
EXTENSION/ADAPTER HOUSING
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove rear propeller shaft.
(3) Support transmission with a transmission jack.
(4) Remove engine rear support.
(5) Remove transfer case, if equipped.
(6) Remove bolts attaching extension/adapter hous-
ing to gear case (Fig. 6).
(7) Remove extension/adapter housing (Fig. 7).
There is one alignment dowel in the gear case and
one in the extension/adapter housing.
(8) Remove rubber spline seal from end of main-
shaft (Fig. 8). The seal is used to prevent lubricant
loss during shipping and does not have to be replaced
if damaged.
FIFTH GEAR NUT
(1) Remove extension/adapter housing.
(2) Loosen fifth gear clamp nut clamping screw
approximately 1 1/2 turns.(3) Install nut Wrench 6743 on fifth gear nut (Fig.
9).
NOTE: Wrench only fits one way on nut. Make sure
wrench is fully engaged in nut slots and is not
cocked.
Fig. 5 Transfer Case Shift Mechanism-Typical
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFT MECHANISM
Fig. 6 Extension/Adapter Housing Bolts
1 - EXTENSION HOUSING
2 - BOLTS (8)
Fig. 7 Extension/Adapter Housing
1 - GEAR CASE
2 - EXTENSION HOUSING
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 5
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1459 of 2255
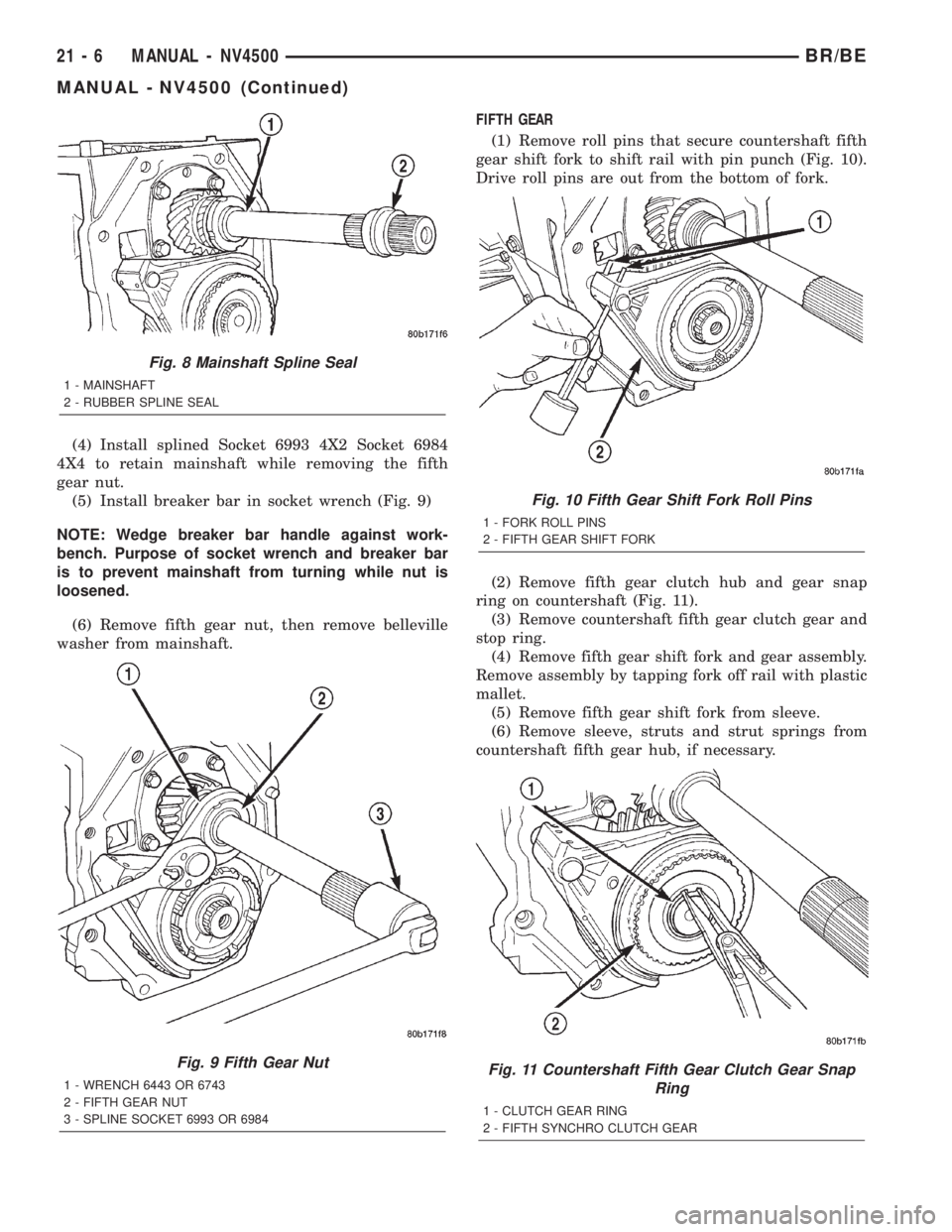
(4) Install splined Socket 6993 4X2 Socket 6984
4X4 to retain mainshaft while removing the fifth
gear nut.
(5) Install breaker bar in socket wrench (Fig. 9)
NOTE: Wedge breaker bar handle against work-
bench. Purpose of socket wrench and breaker bar
is to prevent mainshaft from turning while nut is
loosened.
(6) Remove fifth gear nut, then remove belleville
washer from mainshaft.FIFTH GEAR
(1) Remove roll pins that secure countershaft fifth
gear shift fork to shift rail with pin punch (Fig. 10).
Drive roll pins are out from the bottom of fork.
(2) Remove fifth gear clutch hub and gear snap
ring on countershaft (Fig. 11).
(3) Remove countershaft fifth gear clutch gear and
stop ring.
(4) Remove fifth gear shift fork and gear assembly.
Remove assembly by tapping fork off rail with plastic
mallet.
(5) Remove fifth gear shift fork from sleeve.
(6) Remove sleeve, struts and strut springs from
countershaft fifth gear hub, if necessary.
Fig. 8 Mainshaft Spline Seal
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - RUBBER SPLINE SEAL
Fig. 9 Fifth Gear Nut
1 - WRENCH 6443 OR 6743
2 - FIFTH GEAR NUT
3 - SPLINE SOCKET 6993 OR 6984
Fig. 10 Fifth Gear Shift Fork Roll Pins
1 - FORK ROLL PINS
2 - FIFTH GEAR SHIFT FORK
Fig. 11 Countershaft Fifth Gear Clutch Gear Snap
Ring
1 - CLUTCH GEAR RING
2 - FIFTH SYNCHRO CLUTCH GEAR
21 - 6 MANUAL - NV4500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1464 of 2255

MAINSHAFT AND GEARTRAIN
(1) Move 1-2 and 3-4 synchro sleeves into neutral.
(2) Remove drive gear thrust bearing from forward
end of mainshaft (Fig. 27).
(3) Remove fourth gear clutch gear and synchro
stop ring from mainshaft (Fig. 28).
(4) Roll gear case onto left side (Fig. 29).
(5) To remove mainshaft assembly (Fig. 29) lift
front end of mainshaft slightly.
NOTE: Handling mainshaft carfully because gears
are lose on the mainshaft.(6) Grasp mainshaft rear splines, then turn spline
end of mainshaft counterclockwise to rotate shaft and
geartrain out of case. Tilt mainshaft outward and
removed from case.
REVERSE IDLER AND COUNTERSHAFT
(1) Remove countershaft rear bearing plate (Fig.
30).
Fig. 27 Drive Gear Thrust Bearing
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - DRIVE GEAR THRUST BEARING
Fig. 28 Fourth Gear Clutch Gear Stop Ring
1 - FOURTH GEAR SYNCHRO STOP RING
2 - FOURTH SPEED CLUTCH GEAR
Fig. 29 Mainshaft And Geartrain
1 - MAINSHAFT AND CASE
Fig. 30 Countershaft Rear Bearing Plate
1 - REAR BEARING PLATE
2 - COUNTERSHAFT
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 11
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1469 of 2255

(10) Remove second gear clutch cone snap ring
from mainshaft synchro hub groove (Fig. 49).
(11) Remove second gear clutch cone, synchro
clutch ring and synchro stop ring (Fig. 50).
(12) Remove 1-2 synchro hub snap ring (Fig. 51).
(13) Remove 1-2 synchro sleeve, hub, struts and
springs as an assembly (Fig. 52). Note tapered side of
sleeve also goes toward front. Do not disassemble
synchro components unless worn or damaged.
(14) Remove first gear synchro stop ring and
clutch ring (Fig. 53).
Fig. 46 Thrust Washer Locating Pin
1 - THRUST WASHER LOCATING PIN
Fig. 47 Second Gear
1 - SECOND GEAR
Fig. 48 Second Gear Bearing
1 - SECOND GEAR NEEDLE BEARING
Fig. 49 Second Gear Clutch Cone Snap Ring
1 - 1-2 SLEEVE
2 - SNAP RING
3 - SECOND GEAR CLUTCH CONE
Fig. 50 Second Gear Clutch Cone And Ring
1 - 1-2 SLEEVE AND HUB
2 - SYNCHRO STOP RING
3 - CLUTCH RING
4 - SECOND GEAR CLUTCH CONE
21 - 16 MANUAL - NV4500BR/BE
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)
Page 1470 of 2255
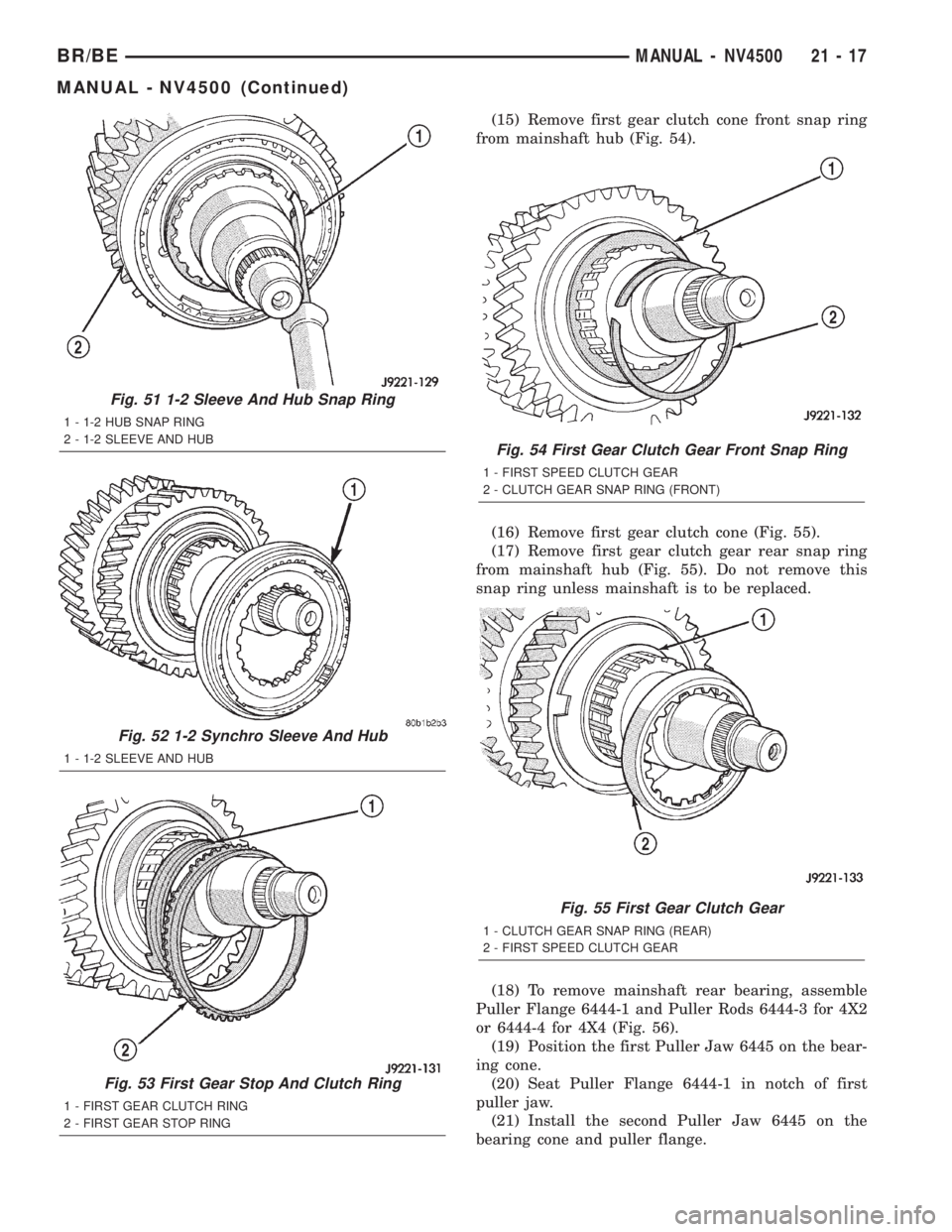
(15) Remove first gear clutch cone front snap ring
from mainshaft hub (Fig. 54).
(16) Remove first gear clutch cone (Fig. 55).
(17) Remove first gear clutch gear rear snap ring
from mainshaft hub (Fig. 55). Do not remove this
snap ring unless mainshaft is to be replaced.
(18) To remove mainshaft rear bearing, assemble
Puller Flange 6444-1 and Puller Rods 6444-3 for 4X2
or 6444-4 for 4X4 (Fig. 56).
(19) Position the first Puller Jaw 6445 on the bear-
ing cone.
(20) Seat Puller Flange 6444-1 in notch of first
puller jaw.
(21) Install the second Puller Jaw 6445 on the
bearing cone and puller flange.
Fig. 51 1-2 Sleeve And Hub Snap Ring
1 - 1-2 HUB SNAP RING
2 - 1-2 SLEEVE AND HUB
Fig. 52 1-2 Synchro Sleeve And Hub
1 - 1-2 SLEEVE AND HUB
Fig. 53 First Gear Stop And Clutch Ring
1 - FIRST GEAR CLUTCH RING
2 - FIRST GEAR STOP RING
Fig. 54 First Gear Clutch Gear Front Snap Ring
1 - FIRST SPEED CLUTCH GEAR
2 - CLUTCH GEAR SNAP RING (FRONT)
Fig. 55 First Gear Clutch Gear
1 - CLUTCH GEAR SNAP RING (REAR)
2 - FIRST SPEED CLUTCH GEAR
BR/BEMANUAL - NV4500 21 - 17
MANUAL - NV4500 (Continued)