2002 DODGE RAM wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 220 of 2255

(7) Install the drum in hat assembly and verify
that the rotor rotates freely without drag.
(8) Install the wheel/tire assemblies, (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(9) Lower the vehicle enough for access to the park
brake foot pedal. Then fully apply the park brakes.
NOTE: Leave park brakes applied until adjustment
is complete.
(10) Raise the vehicle again.
(11) Mark the tensioner rod 6.35 mm (1/4 in.) from
edge of the tensioner (Fig. 56).
(12) Tighten the adjusting nut on the tensioner rod
until the mark is no longer visible.
CAUTION: Do not loosen, or tighten the tensioner
adjusting nut for any reason after completing
adjustment.
(13) Lower the vehicle until the rear wheels are
15-20 cm (6-8 in.) off the shop floor.
(14) Release the park brake foot pedal and verify
that rear wheels rotate freely without drag. Then
lower the vehicle.
RELEASE HANDLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Reach under the driver side outboard end of
the instrument panel to access and unsnap the plas-tic retainer clip that secures the park brake release
linkage rod to the park brake mechanism on the left
cowl side inner panel.
(3) Disengage the park brake release linkage rod
end from the park brake mechanism.
(4) Lift the park brake release handle to access
and unsnap the plastic retainer clip that secures the
park brake release linkage rod to the lever on the
back of the park brake release handle.
(5) Lower the park brake release handle and reach
under the driver side outboard end of the instrument
panel to disengage the park brake release linkage
rod end from the lever on the back of the park brake
release handle.
(6) Lift the park brake release handle to access the
handle mounting bracket.
(7) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-bladed tool, gently pry each of the park brake
release handle mounting bracket latch tabs away
from the retaining notches in the instrument panel
receptacle (Fig. 57) .
(8) With both of the park brake release handle
mounting bracket latches released, slide the handle
and bracket assembly down and out of the instru-
ment panel receptacle.
Fig. 56 Adjustment Mark
1 - TENSIONER CABLE BRACKET
2 - TENSIONER
3 - CABLE CONNECTOR
4 - 6.35mm
(1/4 IN.)
5 - ADJUSTER NUTFig. 57 Park Brake Release Handle Remove/Install
1 - CLIP
2 - ROD
3 - MOUNTING BRACKET
4 - TRIM STICK
5 - LATCH TABS
6 - PARK BRAKE RELEASE HANDLE
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 31
CABLE TENSIONER (Continued)
Page 221 of 2255

INSTALLATION
(1) Position the park brake release handle to the
instrument panel.
(2) Slide the handle and bracket assembly up into
the instrument panel receptacle until both of the
park brake release handle mounting bracket latches
are engaged with the notches in the instrument
panel receptacle.
(3) Lower the park brake release handle and reach
under the driver side outboard end of the instrument
panel to engage the park brake release linkage rod
end with the lever on the back of the park brake
release handle.
(4) Lift the park brake release handle to access
and snap the plastic retainer clip that secures the
park brake release linkage rod to the lever on the
back of the park brake release handle over the link-
age rod.
(5) Reach under the driver side outboard end of
the instrument panel to access and engage the park
brake release linkage rod end to the park brake
mechanism.
(6) Snap the plastic retainer clip that secures the
park brake release linkage rod to the park brake
mechanism on the left cowl side inner panel over the
linkage rod.
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
SHOES
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the disc brake caliper, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the disc brake rotor, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
REMOVAL)
(5) Lockout the parking brake cable (Fig. 58).
(6) Disengage the park brake cable from behind
the rotor assembly to allow easier disassembly of the
park brake shoes (Fig. 59).
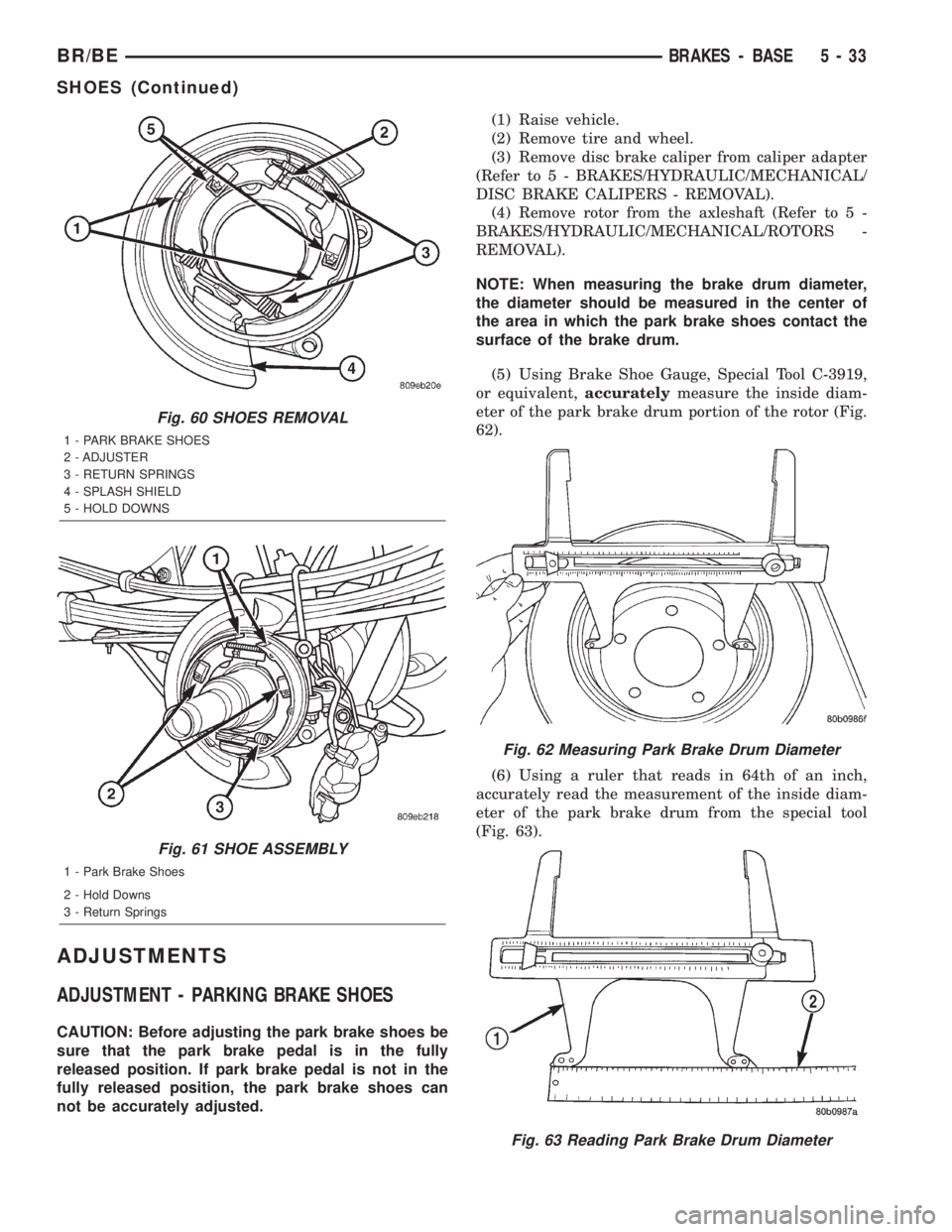
(7) Disassemble the rear park brake shoes (Fig.
60).
INSTALLATION
(1) Reassemble the rear park brake shoes (Fig.
61).
(2) Release the parking brake cable.
(3) Adjust the rear park brake shoes (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/PARKING BRAKE/SHOES - ADJUST-
MENTS).(4) Install the disc brake rotor, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the disc brake caliper, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DISC
BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the tire and wheel assembly, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(7) Lower the vehicle.
Fig. 58 LOCK OUT PARKING CABLE
1 - LOCKING PLIERS
2 - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
Fig. 59 DISENGAGEMENT OF CABLE
1 - LEVER
2 - CABLE END
5 - 32 BRAKES - BASEBR/BE
RELEASE HANDLE (Continued)
Page 222 of 2255
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - PARKING BRAKE SHOES
CAUTION: Before adjusting the park brake shoes be
sure that the park brake pedal is in the fully
released position. If park brake pedal is not in the
fully released position, the park brake shoes can
not be accurately adjusted.(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove tire and wheel.
(3) Remove disc brake caliper from caliper adapter
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove rotor from the axleshaft (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
REMOVAL).
NOTE: When measuring the brake drum diameter,
the diameter should be measured in the center of
the area in which the park brake shoes contact the
surface of the brake drum.
(5) Using Brake Shoe Gauge, Special Tool C-3919,
or equivalent,accuratelymeasure the inside diam-
eter of the park brake drum portion of the rotor (Fig.
62).
(6) Using a ruler that reads in 64th of an inch,
accurately read the measurement of the inside diam-
eter of the park brake drum from the special tool
(Fig. 63).
Fig. 60 SHOES REMOVAL
1 - PARK BRAKE SHOES
2 - ADJUSTER
3 - RETURN SPRINGS
4 - SPLASH SHIELD
5 - HOLD DOWNS
Fig. 61 SHOE ASSEMBLY
1 - Park Brake Shoes
2 - Hold Downs
3 - Return Springs
Fig. 62 Measuring Park Brake Drum Diameter
Fig. 63 Reading Park Brake Drum Diameter
BR/BEBRAKES - BASE 5 - 33
SHOES (Continued)
Page 223 of 2255

(7) Reduce the inside diameter measurement of
the brake drum that was taken using Special Tool
C-3919 by 1/64 of an inch. Reset Gauge, Brake Shoe,
Special Tool C-3919 or the equivalent used, so that
the outside measurement jaws are set to the reduced
measurement (Fig. 64).
(8) Place Gauge, Brake Shoe, Special Tool C-3919,
or equivalent over the park brake shoes. The special
tool must be located diagonally across at the top of
one shoe and bottom of opposite shoe (widest point)
of the park brake shoes.(9) Using the star wheel adjuster, adjust the park
brake shoes until the lining on the park brake shoes
just touches the jaws on the special tool.
(10) Repeat step 8 above and measure shoes in
both directions.
(11) Install brake rotor on the axleshaft (Refer to 5
- BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
INSTALLATION) .
(12) Rotate rotor to verify that the park brake
shoes are not dragging on the brake drum. If park
brake shoes are dragging, remove rotor and back off
star wheel adjuster one notch and recheck for brake
shoe drag against drum. Continue with the previous
step until brake shoes are not dragging on brake
drum.
(13) Install disc brake caliper on caliper adapter
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install wheel and tire.
(15) Tighten the wheel mounting nuts in the
proper sequence until all nuts are torqued to half the
specified torque. Then repeat the tightening sequence
to the full specified torque of 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.).
(16) Lower vehicle.
(17) Apply and release the park brake pedal one
time. This will seat and correctly adjust the park
brake cables.
CAUTION: Before moving vehicle, pump brake
pedal several times to ensure the vehicle has a firm
enough pedal to stop the vehicle.
(18) Road test the vehicle to ensure proper func-
tion of the vehicle's brake system.
Fig. 64 Setting Gauge To Park Brake Shoe
Measurement
5 - 34 BRAKES - BASEBR/BE
SHOES (Continued)
Page 224 of 2255

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................36
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES............................36
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - RWAL SERVICE
PRECAUTIONS.......................36
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM......................36
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................37
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................38
OPERATION...........................38
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4X2......................39REMOVAL - 4X4......................39
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4X2...................39
INSTALLATION - 4X4...................39
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR......................40
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................40
OPERATION...........................40
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................41
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
The antilock brake system (ABS) is an electroni-
cally operated, all wheel brake control system. 2500
and 3500 vehicles have Electronic Brake Distribution
(EBD) designed into the systen which eliminates the
combination/proportioning valve.
The system is designed to prevent wheel lockup
and maintain steering control during periods of high
wheel slip when braking. Preventing lockup is accom-
plished by modulating fluid pressure to the wheel
brake units.
The hydraulic system is a three channel design.
The front wheel brakes are controlled individually
and the rear wheel brakes in tandem (Fig. 1). The
ABS electrical system is separate from other electri-
cal circuits in the vehicle. A specially programmed
controller antilock brake unit operates the system
components.
ABS system major components include:
²Controller Antilock Brakes (CAB)
²Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
²Wheel Speed Sensors (WSS)²ABS Warning Light
Fig. 1 Antilock Brake System
1 - MASTER CYLINDER AND RESERVOIR
2 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
3 - WIRES TO WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
4 - RIGHT REAR WHEEL
5 - LEFT REAR WHEEL
6 - HYDRAULIC BRAKE LINES TO WHEELS
7 - COMBINATION VALVE
8 - HARNESS
9 - RIGHT FRONT WHEEL
10 - LEFT FRONT WHEEL
11 - CAB/HCU
BR/BEBRAKES - ABS 5 - 35
Page 225 of 2255

OPERATION
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB when a
speed of 15 miles per hour is reached. The CAB per-
forms a system initialization procedure at this point.
Initialization consists of a static and dynamic self
check of system electrical components.
The static and dynamic checks occurs at ignition
start up. During the dynamic check, the CAB briefly
cycles the pump and solenoids to verify operation. An
audible noise may be heard during this self check.
This noise should be considered normal.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
The CAB monitors wheel speed sensor inputs con-
tinuously while the vehicle is in motion. However,
the CAB will not activate any ABS components as
long as sensor inputs indicate normal braking.
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of wheel slip. Periods
of wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high
pedal pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
The antilock system prevents lockup during a
wheel slip condition by modulating fluid apply pres-
sure to the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. Sensors at each front wheel convert wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a wheel slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
There are Two solenoid valves (Isolation and Dump
valve) which are used in each antilock control chan-
nel. The valves are all located within the HCU valve
body and work in pairs to either increase, hold, or
decrease apply pressure as needed in the individual
control channels.
During an ABS stop the ISO valve actuates, Stop-
ping anymore pressure build Ðup to the calipers.
Then the Dump valve dumps off pressure until the
wheel unlocks. This will continue until the wheels
quit slipping altogether.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES
The ABS brake system performs several self-tests
every time the ignition switch is turned on and the
vehicle is driven. The CAB monitors the systems
input and output circuits to verify the system is oper-
ating correctly. If the on board diagnostic system
senses that a circuit is malfunctioning the system
will set a trouble code in its memory.
NOTE: An audible noise may be heard during the
self-test. This noise should be considered normal.
NOTE: The MDS or DRB III scan tool is used to
diagnose the ABS system. For additional informa-
tion refer to the Antilock Brake section in Group
8W. For test procedures refer to the Chassis Diag-
nostic Manual.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - RWAL SERVICE
PRECAUTIONS
The RWAL uses an electronic control module, the
CAB. This module is designed to withstand normal
current draws associated with vehicle operation.
Care must be taken to avoid overloading the CAB
circuits.In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the cir-
cuits unless instructed to do so for a diagnostic
procedure.These circuits should only be tested
using a high impedance multi-meter or the DRB
tester as described in this section. Power should
never be removed or applied to any control module
with the ignition in the ON position. Before removing
or connecting battery cables, fuses, or connectors,
always turn the ignition to the OFF position.
CAUTION: Use only factory wiring harnesses. Do
not cut or splice wiring to the brake circuits. The
addition of after-market electrical equipment (car
phone, radar detector, citizen band radio, trailer
lighting, trailer brakes, ect.) on a vehicle equipped
with antilock brakes may affect the function of the
antilock brake system.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-
cedure involves performing a base brake bleeding,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
5 - 36 BRAKES - ABSBR/BE
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 226 of 2255

HCU pump and solenoids. A second base brake bleed-
ing procedure is then required to remove any air
remaining in the system.
(1) Perform the base brake bleeding, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Connect the scan tool to the Data Link Connec-
tor.(3) Select ANTILOCK BRAKES, followed by MIS-
CELLANEOUS, then ABS BRAKES. Follow the
instructions displayed. When scan tool displays TEST
COMPLETE, disconnect scan tool and proceed.
(4) Perform base brake bleeding a second time,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(5) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
ABS Assembly
Bracket Bolts13 10 120
ABS Assembly
Mounting Nuts13 10 102
ABS Assembly
CAB Screws4335
ABS Assembly
Brake Lines21 15 190
Wheel Speed Sensor
Frt. Bolts (4x2)23 17 200
Wheel Speed Sensor
Frt. Bolts (4x4)14 10 120
Wheel Speed Sensor
Rear Bolt24 18 210
BR/BEBRAKES - ABS 5 - 37
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 227 of 2255

FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The ABS brake system uses 3 wheel speed sensors.
A sensor is mounted to each front steering knuckles.
The third sensor is mounted on top of the rear axle
differential housing.
OPERATION
The Wheel Speed Sensor consists of a magnet sur-
rounded by windings from a single strand of wire.
The sensor sends a small AC signal to the CAB. This
signal is generated by magnetic induction. The mag-
netic induction is created when a toothed sensor ring
(exciter ring or tone wheel) passes the stationary
magnetic WSS.
When the ring gear is rotated, the exciter ring
passes the tip of the WSS. As the exciter ring tooth
approaches the tip of the WSS, the magnetic lines of
force expand, causing the magnetic field to cut across
the sensor's windings. This, in turn causes current to
flow through the WSS circuit (Fig. 2) in one direc-
tion. When the exciter ring tooth moves away from
the sensor tip, the magnetic lines of force collapse
cutting the winding in the opposite direction. This
causes the current to flow in the opposite direction.
Every time a tooth of the exciter ring passes the tip
of the WSS, an AC signal is generated. Each AC sig-
nal (positive to negative signal or sinewave) is inter-
preted by the CAB. It then compares the frequency of
the sinewave to a time value to calculate vehicle
speed. The CAB continues to monitor the frequency
to determine a deceleration rate that would indicate
a possible wheel-locking tendency.
The signal strength of any magnetic induction sen-
sor is directly affected by:
²Magnetic field strength; the stronger the mag-
netic field, the stronger the signal
²Number of windings in the sensor; more wind-
ings provide a stronger signal
²Exciter ring speed; the faster the exciter ring/
tone wheel rotates, the stronger the signal will be
²Distance between the exciter ring teeth and
WSS; the closer the WSS is to the exciter ring/tone
wheel, the stronger the signal will be
The rear WSS is not adjustable. A clearance speci-
fication has been established for manufacturing toler-
ances. If the clearance is not within these
specifications, then either the WSS or other compo-
nents may be damaged. The clearance between the
WSS and the exciter ring is 0.005 ± 0.050 in.
The assembly plant performs a ªRolls Testº on
every vehicle that leaves the assembly plant. One of
the test performed is a test of the WSS. To properlytest the sensor, the assembly plant connects test
equipment to the Data Link Connector (DLC). This
connector is located to the right of the steering col-
umn and attached to the lower portion of the instru-
ment panel (Fig. 3). The rolls test terminal is spliced
to the WSS circuit. The vehicle is then driven on a
set of rollers and the WSS output is monitored for
proper operation.
Fig. 2 Operation of the Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - MAGNETIC CORE
2 - CAB
3 - AIR GAP
4 - EXCITER RING
5 - COIL
Fig. 3 Data Link Connector - Typical
1 - 16±WAY DATA LINK CONNECTOR
5 - 38 BRAKES - ABSBR/BE