2002 CHRYSLER CARAVAN lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 1672 of 2399

ASSEMBLY
(1) Install low/reverse servo assembly (Fig. 208).
(2) Install low/reverse servo snap ring (Fig. 205).
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock system
consists of an electro-magnetic solenoid mounted to
the steering column (Fig. 209). The solenoid's plunger
consists of an integrated hook, which operates the
shift lever pawl (part of shift lever assembly), and a
plunger return spring (Fig. 210). The solenoid also
has an integrated bracket, which facilitates fastening
to the steering column.
OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the OFF, ON/RUN,
or START positions (Fig. 211). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
Fig. 208 Low/Reverse Servo Assembly
1 - SERVO PISTON
2 - SPRINGFig. 209 Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid Location
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
Fig. 210 Solenoid Plunger and Return Spring
1 - PLUNGER
2 - RETURN SPRING
3 - BTSI SOLENOID
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 115
SERVO - LOW/REVERSE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1673 of 2399

When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 212). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 213), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position.A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
Fig. 211 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 212 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 213 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
21 - 116 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1674 of 2399
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
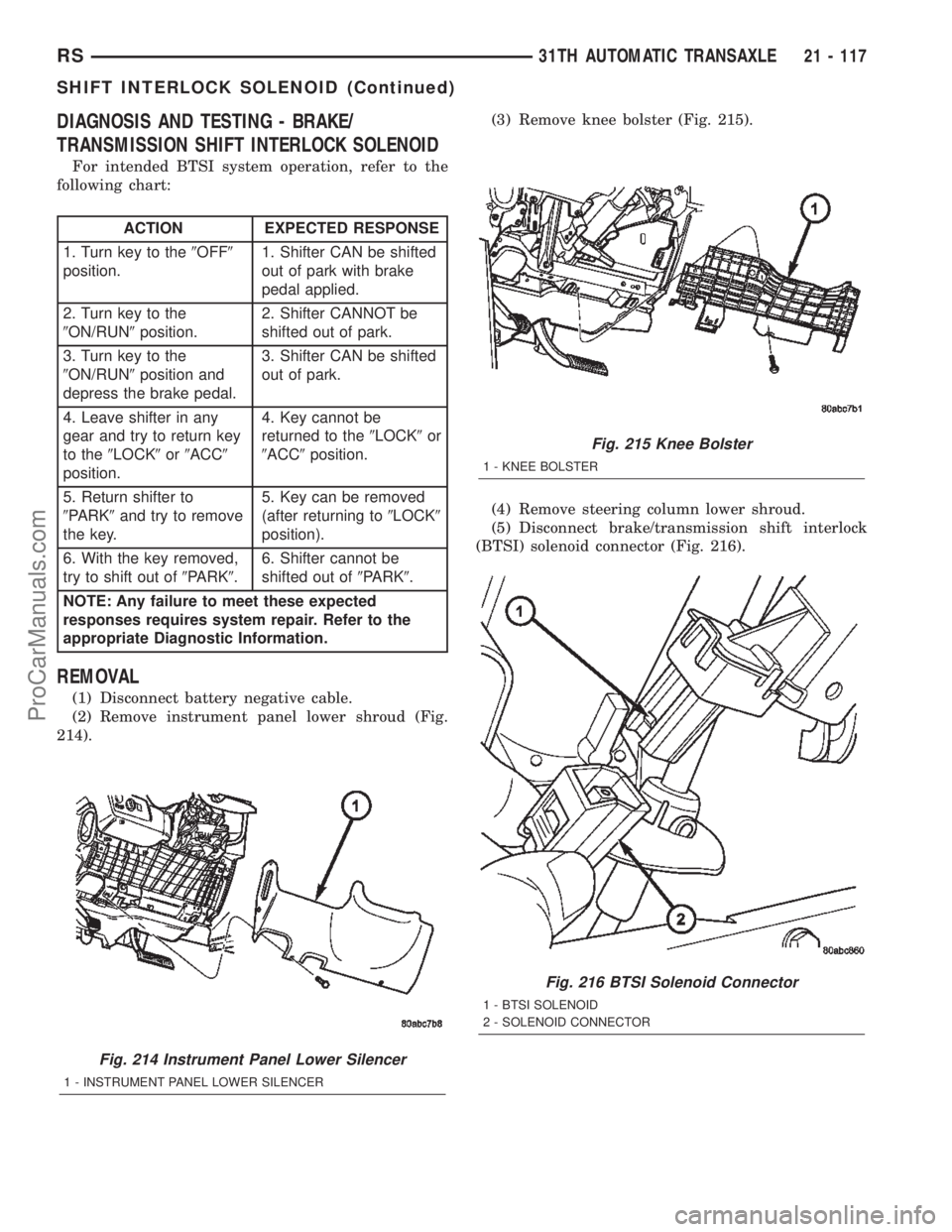
214).(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 215).
(4) Remove steering column lower shroud.
(5) Disconnect brake/transmission shift interlock
(BTSI) solenoid connector (Fig. 216).
Fig. 214 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 215 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 216 BTSI Solenoid Connector
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
2 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 117
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1675 of 2399
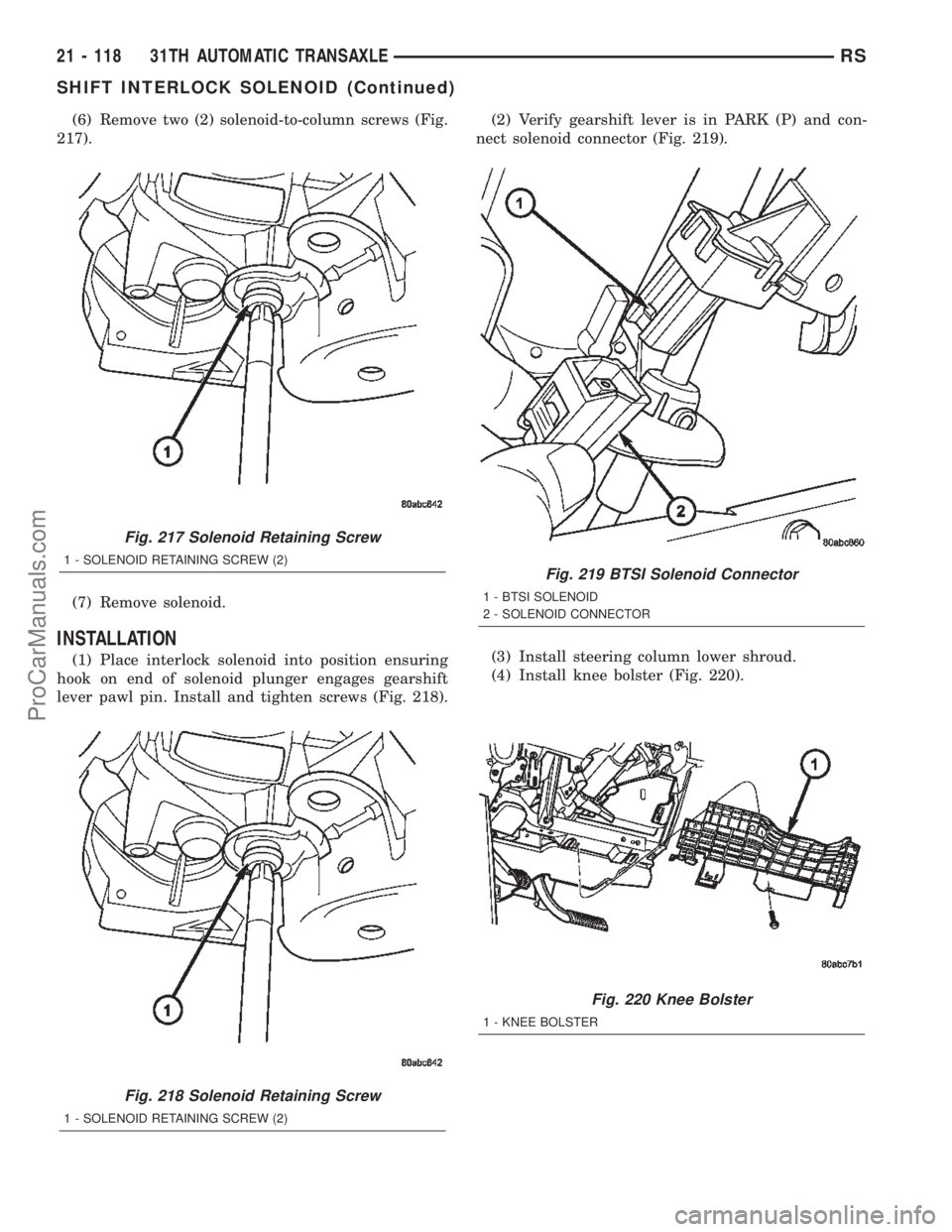
(6) Remove two (2) solenoid-to-column screws (Fig.
217).
(7) Remove solenoid.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place interlock solenoid into position ensuring
hook on end of solenoid plunger engages gearshift
lever pawl pin. Install and tighten screws (Fig. 218).(2) Verify gearshift lever is in PARK (P) and con-
nect solenoid connector (Fig. 219).
(3) Install steering column lower shroud.
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 220).
Fig. 217 Solenoid Retaining Screw
1 - SOLENOID RETAINING SCREW (2)
Fig. 218 Solenoid Retaining Screw
1 - SOLENOID RETAINING SCREW (2)
Fig. 219 BTSI Solenoid Connector
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
2 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
Fig. 220 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
21 - 118 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1676 of 2399

(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
221).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
(7) Verify proper shift interlock system operation.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID -
OPERATION)
SOLENOID - TCC
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid is fas-
tened to the transaxle valve body, and its connector
protrudes through the transaxle case (Fig. 222).
OPERATION
The torque converter clutch solenoid is responsible
for controlling application of the torque converter
clutch. It is controlled by the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM), which determines when conditions
are acceptable for torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body from transaxle. (Refer to 21
- TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
31TH/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove three (3) torque converter clutch sole-
noid-to-valve body screws (Fig. 223).
(3) Remove torque converter clutch solenoid (Fig.
223). Note orientation of plug and spring.
Fig. 221 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 222 Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
1 - TCC SOLENOID WIRING CONNECTOR
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 119
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1679 of 2399

ADJUSTMENTS
THROTTLE VALVE LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
The throttle valve linkage adjustment is very
important to proper transaxle operation. This adjust-
ment positions a valve which controls shift speed,
shift quality, and part throttle downshift sensitivity.
If the setting is too short, early shifts and slippage
between shifts may occur. If the setting is too long,
shifts may be delayed and part throttle downshifts
may be very sensitive.
LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Perform transaxle throttle valve linkage
adjustment while engine is at normal operating tem-
perature.
(2) Using small screwdriver, disengage adjustment
lock at transaxle.
(3) Rotate lever at transaxle all the way to the left
side of vehicle against stop.
(4) Slide cable adjuster until cable core end
touches clip at throttle valve lever.
(5) Press adjuster lock (Fig. 228) to retain setting.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 229) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the fluid cooler and lines.
Fig. 228 Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment Lock
1 - ADJUSTER LOCK
Fig. 229 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 122 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1682 of 2399
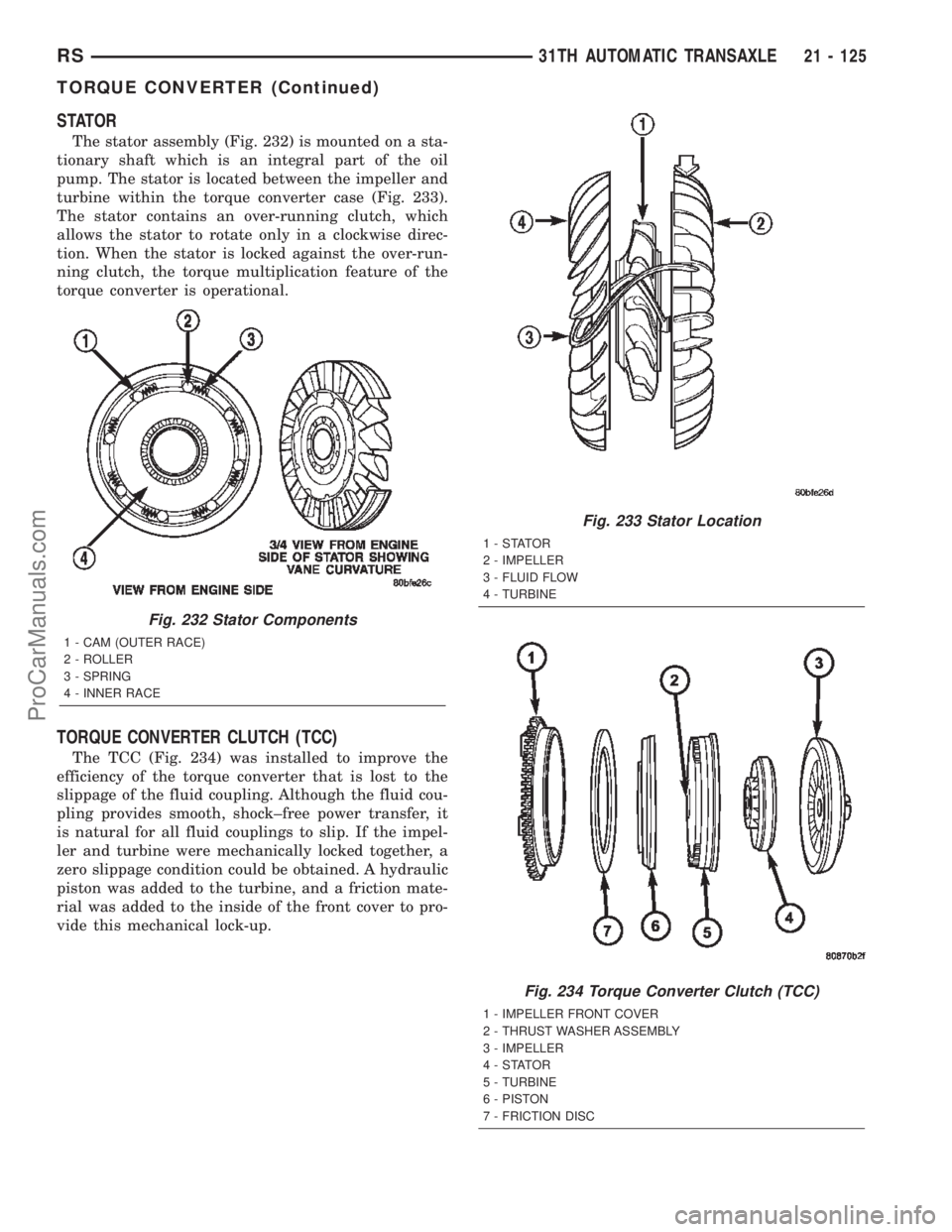
STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 232) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 233).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 234) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock±free power transfer, it
is natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impel-
ler and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
Fig. 232 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 233 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 234 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 125
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1683 of 2399

OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 235) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
Fig. 235 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 126 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com