2001 NISSAN X-TRAIL ATC-2
[x] Cancel search: ATC-2Page 3278 of 3833

ATC-2
DEFROSTER (DEF) SWITCH ............................. 30
MODE SWITCH ................................................... 30
FAN SWITCH ...................................................... 30
OFF SWITCH ...................................................... 30
FRESH (FRE) SWITCH ....................................... 30
RECIRCULATION (REC) SWITCH ..................... 30
Discharge Air Flow ................................................. 31
System Description ................................................. 32
SWITCHES AND THEIR CONTROL FUNCTION ... 32
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS ............................................ 33
How to Perform Trouble Diagnoses for Quick and
Accurate Repair ...................................................... 33
WORK FLOW ...................................................... 33
SYMPTOM TABLE .............................................. 33
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location ... 34
ENGINE COMPARTMENT .................................. 34
PASSENGER COMPARTMENT .......................... 35
Circuit Diagram ....................................................... 36
WITH GASOLINE ENGINE ................................. 36
WITH DIESEL ENGINE ....................................... 37
Wiring Diagram ....................................................... 38
WITH GASOLINE ENGINE ................................. 38
WITH DIESEL ENGINE ....................................... 41
Auto Amp. Terminals and Reference Value ............ 44
PIN CONNECTOR TERMINAL LAYOUT ............ 44
AUTO AMP. INSPECTION TABLE ...................... 44
Self-diagnosis Function .......................................... 46
DESCRIPTION .................................................... 46
PROCEDURE ...................................................... 47
AUXILIARY MECHANISM: TEMPERATURE
SETTING TRIMMER ........................................... 52
AUXILIARY MECHANISM: FOOT POSITION
SETTING TRIMMER ........................................... 53
AUXILIARY MECHANISM: INLET PORT MEM-
ORY FUNCTION (FOR LHD MODELS) .............. 54
Operational Check .................................................. 54
CHECKING MEMORY FUNCTION ..................... 54
CHECKING BLOWER ......................................... 55
CHECKING DISCHARGE AIR ............................ 55
CHECKING RECIRCULATION ............................ 55
CHECKING TEMPERATURE DECREASE ......... 56
CHECKING TEMPERATURE INCREASE .......... 56
CHECKING AUTO MODE ................................... 56
Power Supply and Ground Circuit for Auto Amp. ... 57
INSPECTION FLOW ........................................... 57
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ............................ 57
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................. 58
LAN System Circuit ............................................. ... 59
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................. 59
Mode Door Motor Circuit ........................................ 62
INSPECTION FLOW ........................................
... 62
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION .................................... 63
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ............................ 64
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................. 64
Air Mix Door Motor Circuit ...................................... 64
INSPECTION FLOW ........................................... 65
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION .................................... 66
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ............................ 66
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................. 67Intake Door Motor Circuit ........................................ 68
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 68
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ..................................... 69
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ............................ 69
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................... 70
Blower Motor Circuit ................................................ 70
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 71
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ..................................... 72
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ............................ 74
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................... 74
COMPONENT INSPECTION ............................... 77
Magnet Clutch Circuit .............................................. 78
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 78
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION ..................................... 79
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ............................... 79
COMPONENT INSPECTION ............................... 84
Insufficient Cooling .................................................. 86
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 86
PERFORMANCE TEST DIAGNOSES ................ 88
PERFORMANCE CHART .................................... 90
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES FOR UNUSUAL PRES-
SURE ................................................................... 92
Insufficient Heating ................................................. 95
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 95
Noise ....................................................................... 97
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 97
Self-diagnosis ......................................................... 98
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 98
Memory Function .................................................... 99
INSPECTION FLOW ............................................ 99
Ambient Sensor Circuit .........................................100
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ..........................100
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE INPUT PROCESS .100
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................100
COMPONENT INSPECTION .............................102
In-vehicle Sensor Circuit .......................................102
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ..........................102
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................103
COMPONENT INSPECTION .............................104
Sunload Sensor Circuit .........................................105
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ..........................105
SUNLOAD INPUT PROCESS ...........................105
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................105
COMPONENT INSPECTION .............................107
Intake Sensor Circuit .............................................108
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION ..........................108
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE .............................108
CONTROLLER ........................................................ 111
Removal and Installation .......................................111
Disassembly and Assembly ..................................111
AMBIENT SENSOR ................................................112
Removal and Installation .......................................112
IN-VEHICLE SENSOR ............................................113
Removal and Installation .......................................113
SUNLOAD SENSOR ...............................................114
Removal and Installation .......................................114
INTAKE SENSOR CIRCUIT ....................................115
Removal and Installation .......................................115
BLOWER UNIT ........................................................116
Page 3285 of 3833
PRECAUTIONS
ATC-9
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
AT C
CAUTION:
When replacing or cleaning refrigerant cycle components, observe the following.
●When the compressor is removed, store it in the same position as it is when mounted on the car.
Malfunction to do so will cause lubricant to enter the low pressure chamber.
●When connecting tubes, always use a torque wrench and a back-up wrench.
●After disconnecting tubes, immediately plug all openings to prevent entry of dirt and moisture.
●When installing an air conditioner in the vehicle, connect the pipes as the final stage of the opera-
tion. Do not remove the seal caps of pipes and other components until just before required for
connection.
●Allow components stored in cool areas to warm to working area temperature before removing seal
caps. This prevents condensation from forming inside A/C components.
●Thoroughly remove moisture from the refrigeration system before charging the refrigerant.
●Always replace used O-rings.
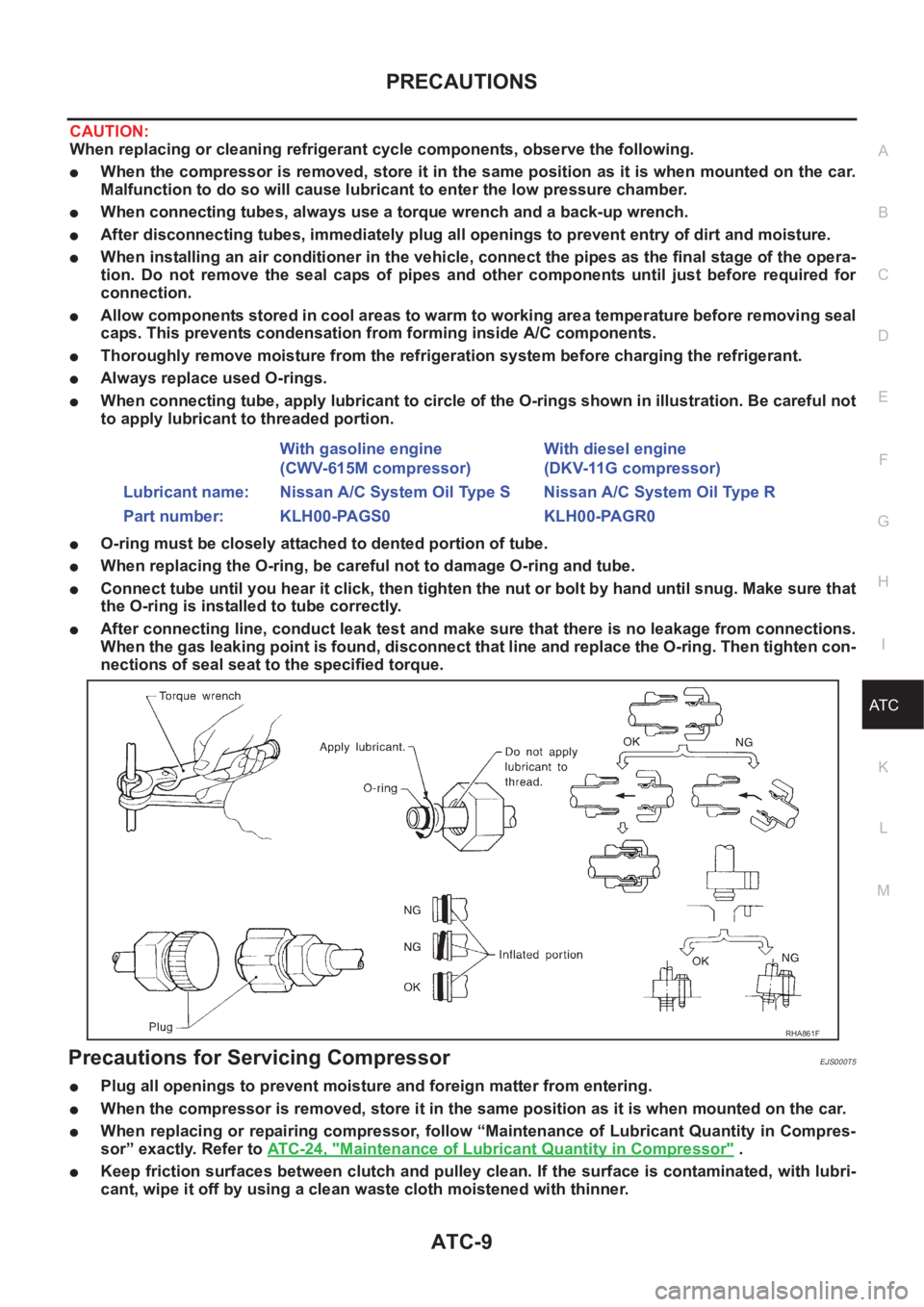
●When connecting tube, apply lubricant to circle of the O-rings shown in illustration. Be careful not
to apply lubricant to threaded portion.
●O-ring must be closely attached to dented portion of tube.
●When replacing the O-ring, be careful not to damage O-ring and tube.
●Connect tube until you hear it click, then tighten the nut or bolt by hand until snug. Make sure that
the O-ring is installed to tube correctly.
●After connecting line, conduct leak test and make sure that there is no leakage from connections.
When the gas leaking point is found, disconnect that line and replace the O-ring. Then tighten con-
nections of seal seat to the specified torque.
Precautions for Servicing CompressorEJS000T5
●Plug all openings to prevent moisture and foreign matter from entering.
●When the compressor is removed, store it in the same position as it is when mounted on the car.
●When replacing or repairing compressor, follow “Maintenance of Lubricant Quantity in Compres-
sor” exactly. Refer to ATC-24, "
Maintenance of Lubricant Quantity in Compressor" .
●Keep friction surfaces between clutch and pulley clean. If the surface is contaminated, with lubri-
cant, wipe it off by using a clean waste cloth moistened with thinner. With gasoline engine
(CWV-615M compressor)With diesel engine
(DKV-11G compressor)
Lubricant name: Nissan A/C System Oil Type S Nissan A/C System Oil Type R
Part number: KLH00-PAGS0 KLH00-PAGR0
RHA861F
Page 3296 of 3833
ATC-20
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
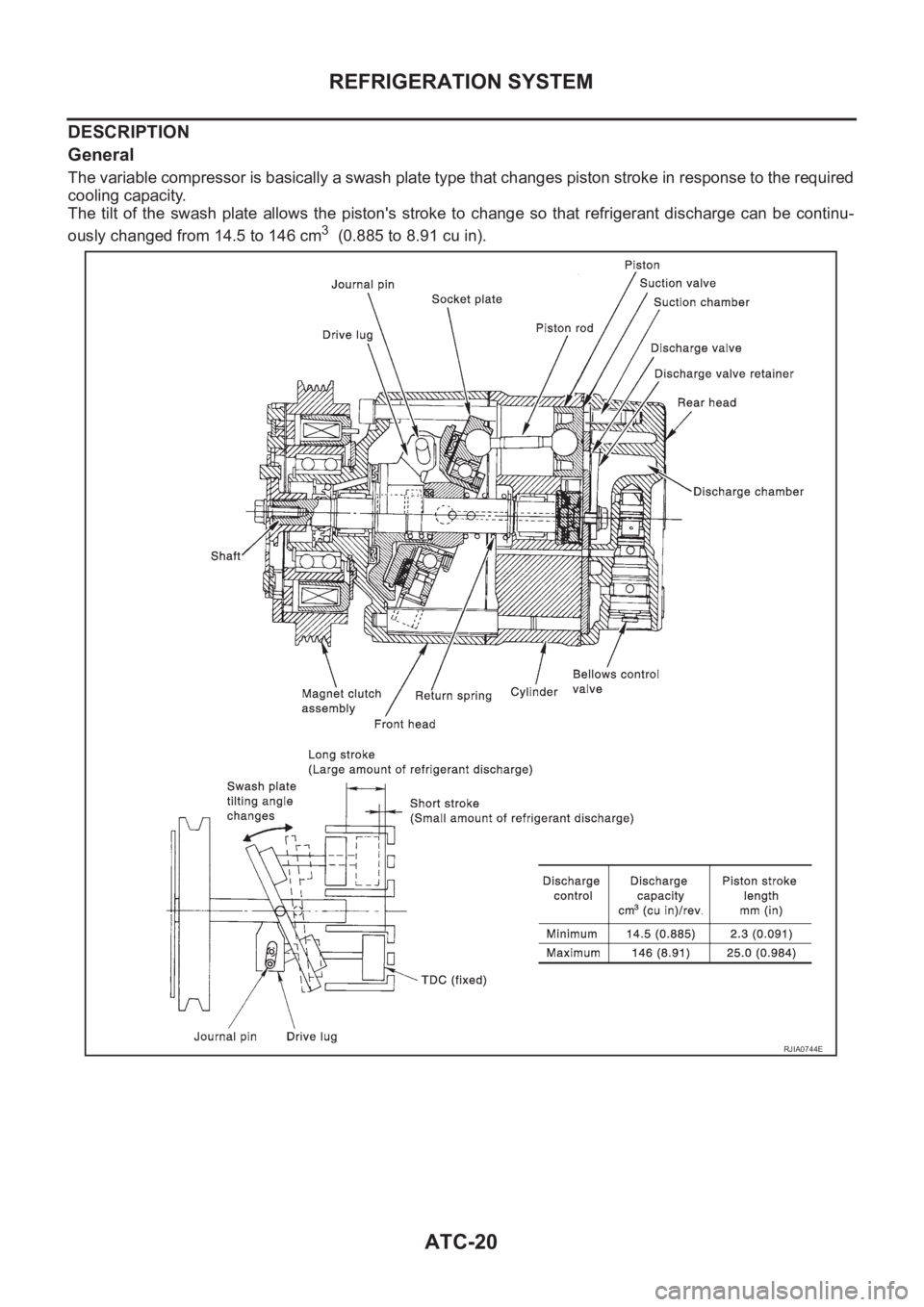
General
The variable compressor is basically a swash plate type that changes piston stroke in response to the required
cooling capacity.
The tilt of the swash plate allows the piston's stroke to change so that refrigerant discharge can be continu-
ously changed from 14.5 to 146 cm
3 (0.885 to 8.91 cu in).
RJIA0744E
Page 3297 of 3833
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
ATC-21
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
AT C
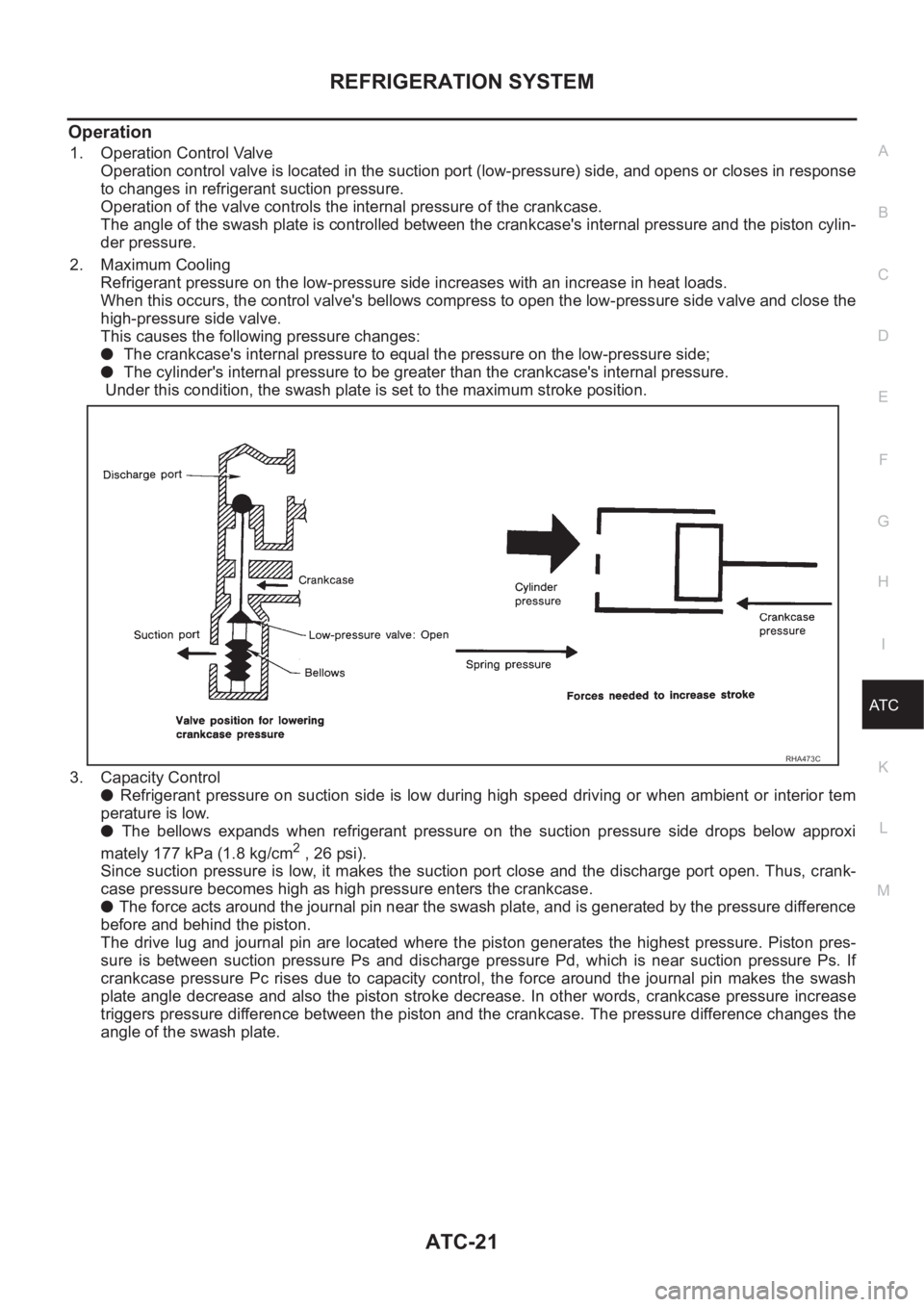
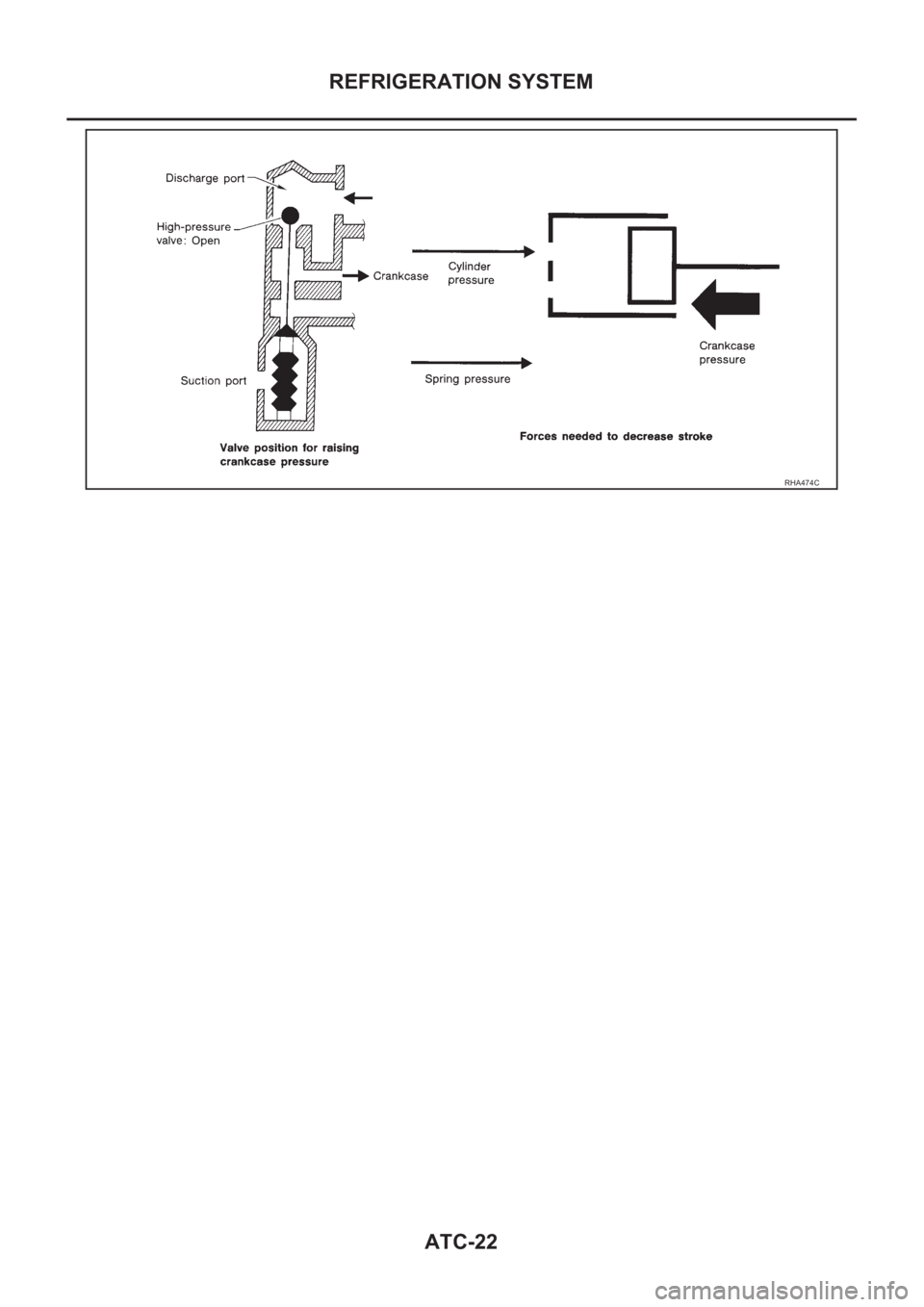
Operation
1. Operation Control Valve
Operation control valve is located in the suction port (low-pressure) side, and opens or closes in response
to changes in refrigerant suction pressure.
Operation of the valve controls the internal pressure of the crankcase.
The angle of the swash plate is controlled between the crankcase's internal pressure and the piston cylin-
der pressure.
2. Maximum Cooling
Refrigerant pressure on the low-pressure side increases with an increase in heat loads.
When this occurs, the control valve's bellows compress to open the low-pressure side valve and close the
high-pressure side valve.
This causes the following pressure changes:
● The crankcase's internal pressure to equal the pressure on the low-pressure side;
● The cylinder's internal pressure to be greater than the crankcase's internal pressure.
Under this condition, the swash plate is set to the maximum stroke position.
3. Capacity Control
● Refrigerant pressure on suction side is low during high speed driving or when ambient or interior tem
perature is low.
● The bellows expands when refrigerant pressure on the suction pressure side drops below approxi
mately 177 kPa (1.8 kg/cm
2 , 26 psi).
Since suction pressure is low, it makes the suction port close and the discharge port open. Thus, crank-
case pressure becomes high as high pressure enters the crankcase.
● The force acts around the journal pin near the swash plate, and is generated by the pressure difference
before and behind the piston.
The drive lug and journal pin are located where the piston generates the highest pressure. Piston pres-
sure is between suction pressure Ps and discharge pressure Pd, which is near suction pressure Ps. If
crankcase pressure Pc rises due to capacity control, the force around the journal pin makes the swash
plate angle decrease and also the piston stroke decrease. In other words, crankcase pressure increase
triggers pressure difference between the piston and the crankcase. The pressure difference changes the
angle of the swash plate.
RHA473C
Page 3298 of 3833
ATC-22
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
RHA474C
Page 3299 of 3833
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
ATC-23
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
AT C
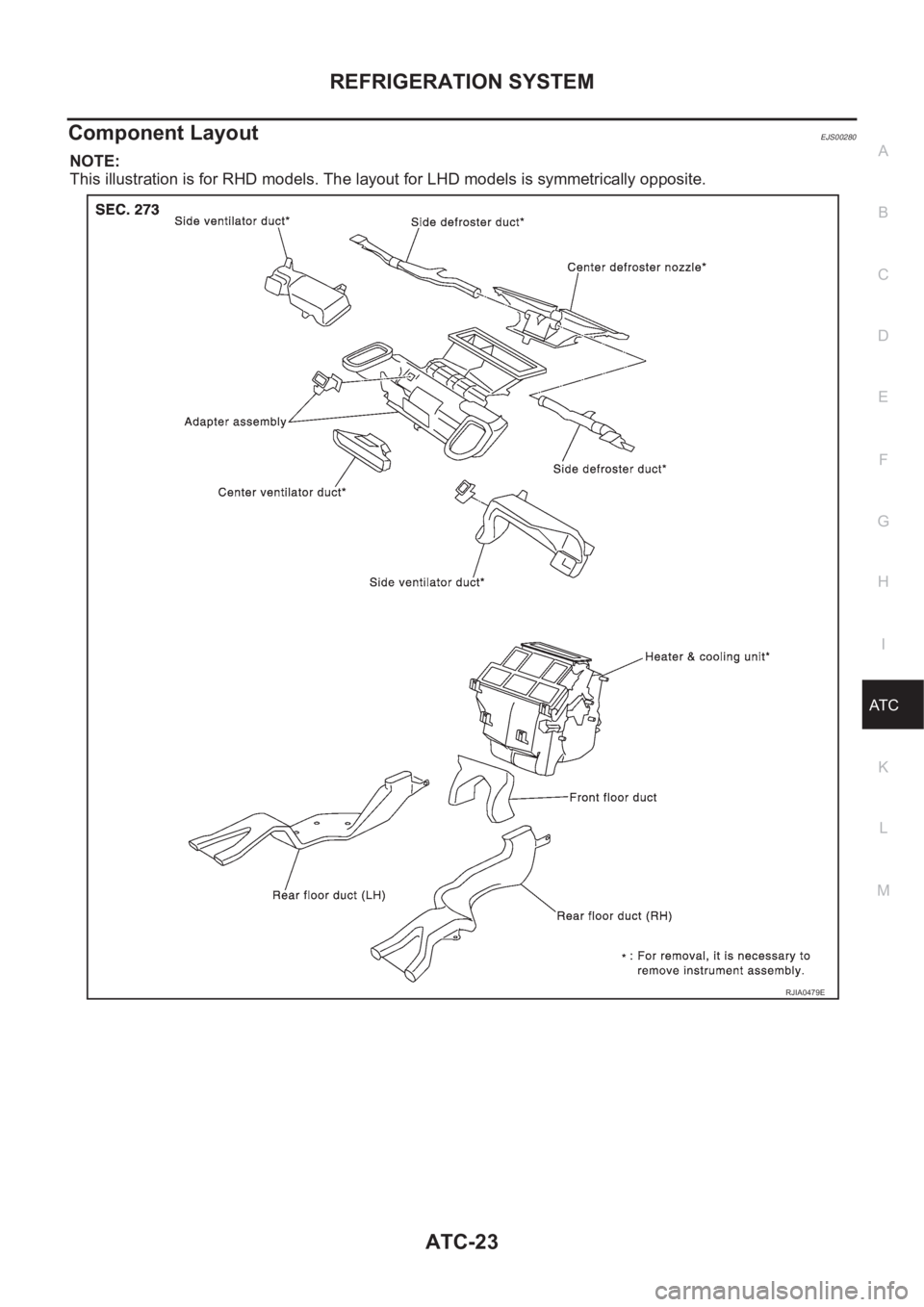
Component LayoutEJS00280
NOTE:
This illustration is for RHD models. The layout for LHD models is symmetrically opposite.
RJIA0479E
Page 3300 of 3833

ATC-24
LUBRICANT
LUBRICANT
PFP:KLG00
Maintenance of Lubricant Quantity in CompressorEJS000TH
The lubricant in the compressor circulates through the system with the refrigerant. Add lubricant to compres-
sor when replacing any component or after a large gas leakage occurred. It is important to maintain the speci-
fied amount.
If lubricant quantity is not maintained properly, the following malfunctions may result:
●Lack of lubricant: May lead to a seized compressor
●Excessive lubricant: Inadequate cooling (thermal exchange interference)
LUBRICANT
LUBRICANT RETURN OPERATION
Adjust the lubricant quantity according to the test group shown below.
1. CHECK LUBRICANT RETURN OPERATION
Can lubricant return operation be performed?
●A/C system works properly.
●There is no evidence of a large amount of lubricant leakage.
YES or NO
YES >> GO TO 2.
NO >> GO TO 3.
2. PERFORM LUBRICANT RETURN OPERATION, PROCEEDING AS FOLLOWS:
1. Start engine, and set the following conditions:
–Test condition
Engine speed: Idling to 1,200 rpm
A/C or AUTO switch: ON
Blower speed: Max. position
Temp. control: Optional [Set so that intake air temperature is 25 to 30°C (77 to 86°F).]
Intake position: Recirculation (REC)
2. Perform lubricant return operation for about 10 minutes.
3. Stop engine.
CAUTION:
If excessive lubricant leakage is noted, do not perform the lubricant return operation.
>> GO TO 3.
3. CHECK COMPRESSOR
Should the compressor be replaced?
YES or NO
YES >> Go to AT C - 2 5 , "LUBRICANT ADJUSTING PROCEDURE FOR COMPRESSOR REPLACE-
MENT" .
NO >> GO TO 4.With gasoline engine
(CWV-615M Compressor)With diesel engine
(DKV-11G Compressor)
Name Nissan A/C System Oil Type S Nissan A/C System Oil Type R
Part number KLH00-PAGS0 KLH00-PAGR0
Page 3301 of 3833
LUBRICANT
ATC-25
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
AT C
4.CHECK ANY PART
Is there any part to be replaced? (Evaporator, condenser, liquid tank or in case there is evidence of a large
amount of lubricant leakage.)
YES or NO
YES >> Go to AT C - 2 5 , "LUBRICANT ADJUSTING PROCEDURE FOR COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT
EXCEPT COMPRESSOR" .
NO >> Carry out the A/C performance test.
LUBRICANT ADJUSTING PROCEDURE FOR COMPONENTS REPLACEMENT EXCEPT COM-
PRESSOR
After replacing any of the following major components, add the correct amount of lubricant to the system.
Amount of lubricant to be added
*1:If refrigerant leak is small, no addition of lubricant is needed.
LUBRICANT ADJUSTING PROCEDURE FOR COMPRESSOR REPLACEMENT
1. Before connecting ACR4 to vehicle, check ACR4 gauges. No refrigerant pressure should be displayed. If
NG, recover refrigerant from equipment lines.
2. Discharge refrigerant into the refrigerant recovery/recycling equipment. Measure lubricant discharged into
the recovery/recycling equipment.
3. Drain the lubricant from the old (removed) compressor into a graduated container and recover the amount
of lubricant drained.
4. Drain the lubricant from the new compressor into a separate, clean container.
5. Measure an amount of new lubricant installed equal to amount drained from old compressor. Add this
lubricant to new compressor through the suction port opening.
6. Measure an amount of new lubricant equal to the amount recovered during discharging. Add this lubricant
to new compressor through the suction port opening.
7. If the liquid tank also needs to be replaced, add an additional 5 m (0.2 Imp fl oz) of lubricant at this time.
Do not add this 5 m (0.2 Imp fl oz) of lubricant if only replacing the compressor.
Part replacedLubricant to be added to system
Remarks
Amount of lubricant
m (Imp fl oz)
Evaporator 75 (2.6) -
Condenser 35 (1.2) -
Liquid tank 10 (0.4) -
In case of refrigerant leak30 (1.1) Large leak
- Small leak *1