2001 NISSAN ALMERA N16 fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 316 of 2493
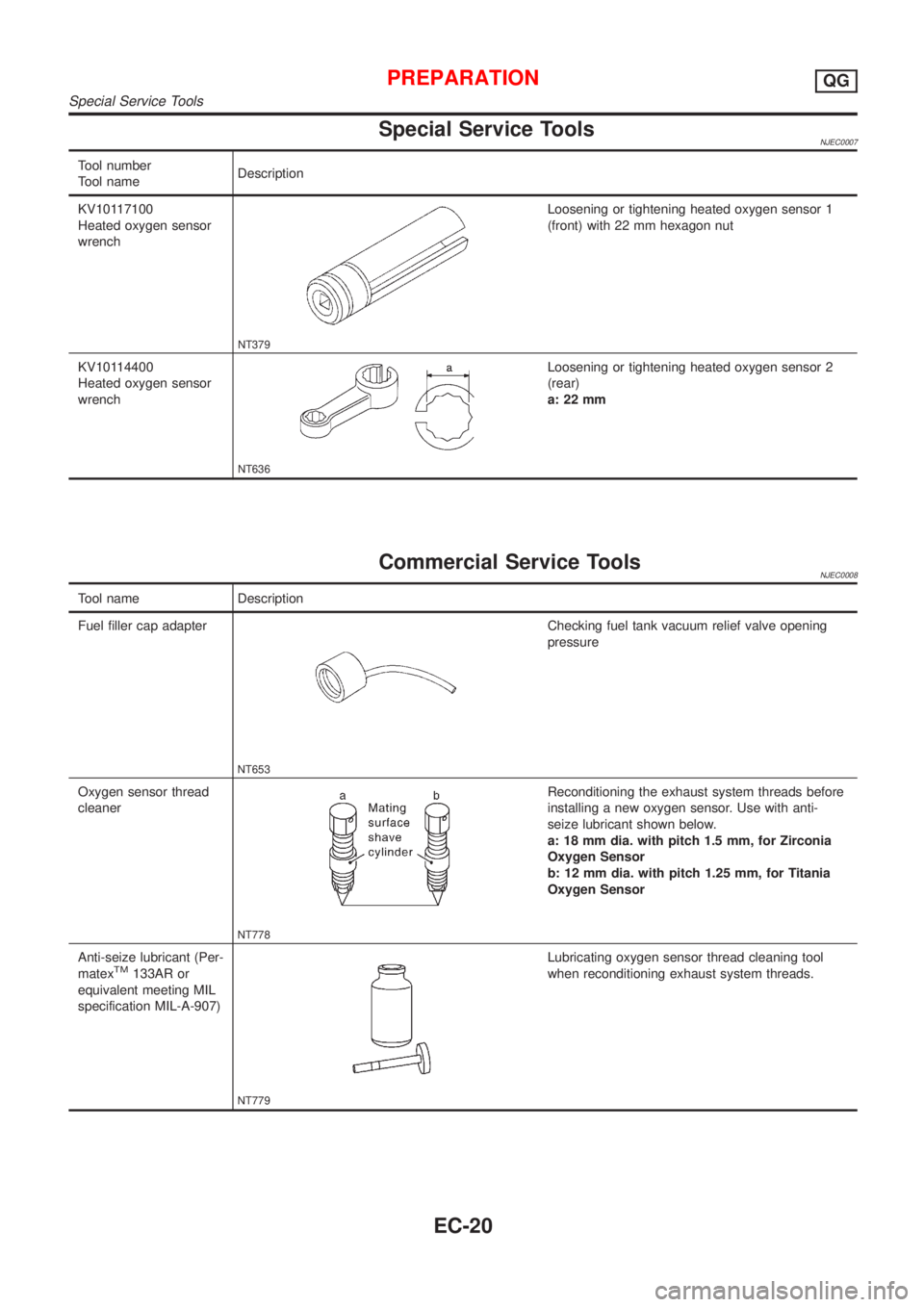
Special Service ToolsNJEC0007
Tool number
Tool nameDescription
KV10117100
Heated oxygen sensor
wrench
NT379
Loosening or tightening heated oxygen sensor 1
(front) with 22 mm hexagon nut
KV10114400
Heated oxygen sensor
wrench
NT636
Loosening or tightening heated oxygen sensor 2
(rear)
a: 22 mm
Commercial Service ToolsNJEC0008
Tool name Description
Fuel filler cap adapter
NT653
Checking fuel tank vacuum relief valve opening
pressure
Oxygen sensor thread
cleaner
NT778
Reconditioning the exhaust system threads before
installing a new oxygen sensor. Use with anti-
seize lubricant shown below.
a: 18 mm dia. with pitch 1.5 mm, for Zirconia
Oxygen Sensor
b: 12 mm dia. with pitch 1.25 mm, for Titania
Oxygen Sensor
Anti-seize lubricant (Per-
matex
TM133AR or
equivalent meeting MIL
specification MIL-A-907)
NT779
Lubricating oxygen sensor thread cleaning tool
when reconditioning exhaust system threads.
PREPARATIONQG
Special Service Tools
EC-20
Page 324 of 2493

System ChartNJEC0013
Input (Sensor) ECM Function Output (Actuator)
+Camshaft position sensor (PHASE)
+Crankshaft position sensor (POS)
+Mass air flow sensor
+Engine coolant temperature sensor
+Heated oxygen sensor 1 (front)
+Ignition switch
+Throttle position sensor
+PNP switch
+Air conditioner switch
+Knock sensor
+EGR temperature sensor*1, *4
+Battery voltage
+Power steering oil pressure switch
+Vehicle speed sensor
+Intake air temperature sensor
+Heated oxygen sensor 2 (rear)*2
+TCM (Transmission Control Module)*3
+Closed throttle position switch
+Electrical load
+Refrigerant pressure sensorFuel injection & mixture ratio control Injectors
Electronic ignition system Power transistor
Idle air control system IACV-AAC valve
Intake valve timing controlIntake valve timing control sole-
noid valve
Fuel pump control Fuel pump relay
On board diagnostic systemMalfunction indicator
(On the instrument panel)
EGR control*4 EGR volume control valve*4
Heated oxygen sensor 1/2 heater (front/
rear) controlHeated oxygen sensor 1/2 heater
(front/rear)
EVAP canister purge flow controlEVAP canister purge volume con-
trol solenoid valve
Cooling fan control Cooling fan relay
Air conditioning cut control Air conditioner relay
*1: These sensors are not used to control the engine system. They are used only for the on board diagnosis.
*2: Under normal conditions, this sensor is not for engine control operation.
*3: The DTC related to A/T will be sent to ECM.
*4: If so equipped
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMQG
System Chart
EC-28
Page 325 of 2493

Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0014Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0014S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
Fuel injec-
tion & mix-
ture ratio
controlInjector Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Heated oxygen sensor 1 (front) Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
Throttle position sensorThrottle position
Throttle valve idle position
PNP switch Gear position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Ignition switch Start signal
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Knock sensor Engine knocking condition
Electrical load Electrical load signal
Battery Battery voltage
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering operation
Heated oxygen sensor 2 (rear)* Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
* Under normal conditions, this sensor is not for engine control operation.
Basic Multiport Fuel Injection SystemNJEC0014S02The amount of fuel injected from the fuel injector is determined by the ECM. The ECM controls the length of
time the valve remains open (injection pulse duration). The amount of fuel injected is a program value in the
ECM memory. The program value is preset by engine operating conditions. These conditions are determined
by input signals (for engine speed and intake air) from both the camshaft position sensor and the mass air
flow sensor.
Various Fuel Injection Increase/Decrease CompensationNJEC0014S03In addition, the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance under various oper-
ating conditions as listed below.
+During warm-up
+When starting the engine
+During acceleration
+Hot-engine operation
+When selector lever is changed from ªNº to ªDº (A/T models)
+High-load, high-speed operation
+During deceleration
+During high engine speed operation
+During high vehicle speed operation (M/T models)
+Extremely high engine coolant temperature
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONQG
Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System
EC-29
Page 328 of 2493
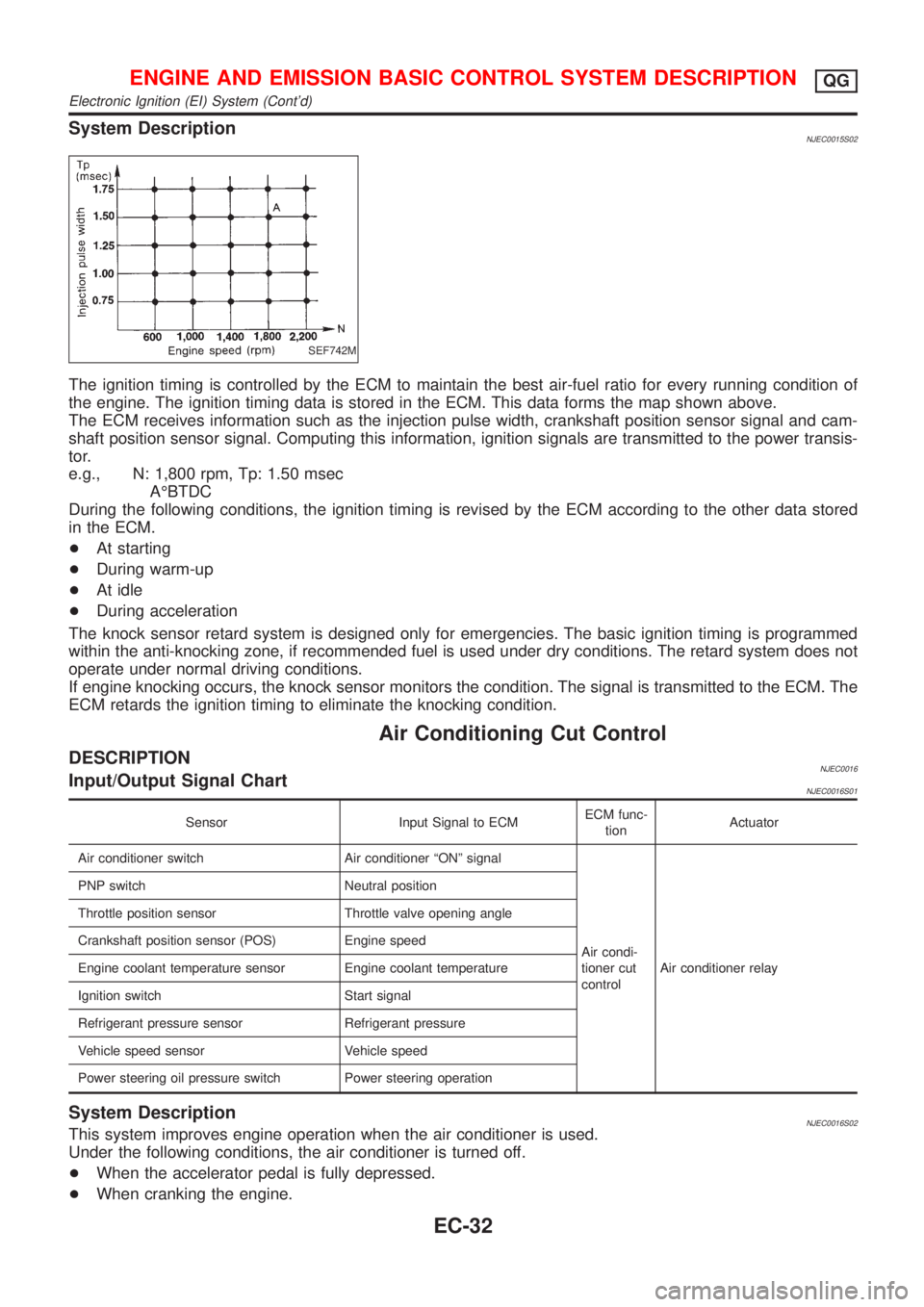
System DescriptionNJEC0015S02
SEF742M
The ignition timing is controlled by the ECM to maintain the best air-fuel ratio for every running condition of
the engine. The ignition timing data is stored in the ECM. This data forms the map shown above.
The ECM receives information such as the injection pulse width, crankshaft position sensor signal and cam-
shaft position sensor signal. Computing this information, ignition signals are transmitted to the power transis-
tor.
e.g., N: 1,800 rpm, Tp: 1.50 msec
AÉBTDC
During the following conditions, the ignition timing is revised by the ECM according to the other data stored
in the ECM.
+At starting
+During warm-up
+At idle
+During acceleration
The knock sensor retard system is designed only for emergencies. The basic ignition timing is programmed
within the anti-knocking zone, if recommended fuel is used under dry conditions. The retard system does not
operate under normal driving conditions.
If engine knocking occurs, the knock sensor monitors the condition. The signal is transmitted to the ECM. The
ECM retards the ignition timing to eliminate the knocking condition.
Air Conditioning Cut Control
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0016Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0016S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner ªONº signal
Air condi-
tioner cut
controlAir conditioner relay PNP switch Neutral position
Throttle position sensor Throttle valve opening angle
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Refrigerant pressure sensor Refrigerant pressure
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering operation
System DescriptionNJEC0016S02This system improves engine operation when the air conditioner is used.
Under the following conditions, the air conditioner is turned off.
+When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed.
+When cranking the engine.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONQG
Electronic Ignition (EI) System (Cont'd)
EC-32
Page 329 of 2493

+At high engine speeds.
+When the engine coolant temperature becomes excessively high.
+When operating power steering during low engine speed or low vehicle speed.
+When engine speed is excessively low.
+When the refrigerant pressure is excessively high or low.
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed)
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0017Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0017S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Fuel cut
controlInjectors PNP switch Neutral position
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
If the engine speed is above 3,950 rpm with no load, (for example, in Neutral and engine speed over 4,000
rpm) fuel will be cut off after some time. The exact time when the fuel is cut off varies based on engine speed.
Fuel cut will operate until the engine speed reaches 1,150 rpm, then fuel cut is cancelled.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control listed under ªMultiport Fuel Injection (MFI) Systemº,
EC-29.
Evaporative Emission System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0018
SEF916WA
The evaporative emission system is used to reduce hydrocarbons emitted into the atmosphere from the fuel
system. This reduction of hydrocarbons is accomplished by activated charcoals in the EVAP canister.
The fuel vapor in the sealed fuel tank is led into the EVAP canister which contains activated carbon and the
vapor is stored there when the engine is not operating or when refueling to the fuel tank.
The vapor in the EVAP canister is purged by the air through the purge line to the intake manifold when the
engine is operating.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONQG
Air Conditioning Cut Control (Cont'd)
EC-33
Page 330 of 2493

EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve is controlled by ECM. When the engine operates, the flow
rate of vapor controlled by EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve is proportionally regulated as
the air flow increases.
EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve also shuts off the vapor purge line during decelerating and
idling.
SEF917W
INSPECTIONNJEC0019EVAP CanisterNJEC0019S01Check EVAP canister as follows:
1. Block port B. Orally blow air through port A. Check that air
flows freely through port C with check valve resistance.
2. Block port A. Orally blow air through port B. Check that air
flows freely through port C.
SEF918W
SEF943S
Fuel Tank Vacuum Relief Valve (Built into fuel filler cap)NJEC0019S031. Wipe clean valve housing.
2. Check valve opening pressure and vacuum.
Pressure:
16.0 - 20.0 kPa (0.16 - 0.20 bar, 0.163 - 0.204 kg/cm
2,
2.32 - 2.90 psi)
Vacuum:
þ6.0 to þ3.5 kPa (þ0.060 to þ0.035 bar, þ0.061 to
þ0.036 kg/cm
2, þ0.87 to þ0.51 psi)
3. If out of specification, replace fuel filler cap as an assembly.
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Volume
Control Solenoid Valve
NJEC0019S07Refer to EC-308.
Checking EVAP Vapour LinesNJEC0019S131. Visually inspect vapor lines for leaks, cracks, damage, loose
connections, chafing and deterioration.
2. Inspect vacuum relief valve of fuel tank filler cap for clogging,
sticking, etc. Refer to next page.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONQG
Evaporative Emission System (Cont'd)
EC-34
Page 334 of 2493

SEF094Y
SEF214Y
Fuel Pressure ReleaseNJEC0024Before disconnecting fuel line, release fuel pressure from fuel
line to eliminate danger.
WITH CONSULT-IINJEC0024S011. Start engine.
2. Perform ªFUEL PRESSURE RELEASEº in ªWORK SUP-
PORTº mode with CONSULT-II.
3. After engine stalls, crank it two or three times to release all fuel
pressure.
4. Turn ignition switch OFF.
JEF086Y
WITHOUT CONSULT-IINJEC0024S021. Remove fuse for fuel pump. Refer to fuse block cover for fuse
location.
2. Start engine.
3. After engine stalls, crank it two or three times to release all fuel
pressure.
4. Turn ignition switch OFF and reconnect fuel pump fuse.
JEF087Y
Fuel Pressure CheckNJEC0025+When reconnecting fuel line, always use new clamps.
+Make sure that clamp screw does not contact adjacent
parts.
+Use a torque driver to tighten clamps.
+Use Pressure Gauge to check fuel pressure.
+Do not perform fuel pressure check with system operat-
ing. Fuel pressure gauge may indicate false readings.
1. Release fuel pressure to zero.
2. Disconnect fuel hose between fuel filter and fuel tube (engine
side).
3. Install pressure gauge between fuel filter and fuel tube.
4. Start engine and check for fuel leakage.
5. Read the indication of fuel pressure gauge.
At idle speed:
With vacuum hose connected
Approximately 235 kPa (2.35 bar, 2.4 kg/cm
2,34
psi)
With vacuum hose disconnected
Approximately 294 kPa (2.94 bar, 3.0 kg/cm
2,43
psi)
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDUREQG
Fuel Pressure Release
EC-38
Page 335 of 2493

If results are unsatisfactory, perform Fuel Pressure Regulator
Check, EC-39.
SEF718B
Fuel Pressure Regulator CheckNJEC00261. Stop engine and disconnect fuel pressure regulator vacuum
hose from intake manifold.
2. Plug intake manifold with a rubber cap.
3. Connect variable vacuum source to fuel pressure regulator.
4. Start engine and read indication of fuel pressure gauge as
vacuum is changed.
Fuel pressure should decrease as vacuum increases. If results
are unsatisfactory, replace fuel pressure regulator.
JEF088Y
SEF927W
Injector
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONNJEC00271. Release fuel pressure to zero.
2. Remove fuel tube assemblies in numerical sequence as
shown in the Figure at left.
3. Expand and remove clips securing fuel injectors.
4. Extract fuel injectors straight from fuel tubes.
+Be careful not to damage injector nozzles during removal.
+Do not bump or drop fuel injectors.
5. Install fuel injectors.
Carefully install O-rings, including the one used with the pres-
sure regulator.
+Lubricate O-rings with a smear of engine oil.
+Be careful not to damage O-rings with service tools or
finger nails or clips. Do not expand or twist O-rings.
+Discard old clips; replace with new ones.
6. Position clips in grooves on fuel injectors.
+Make sure that protrusions of fuel injectors are aligned
with cutouts of clips after installation.
BASIC SERVICE PROCEDUREQG
Fuel Pressure Regulator Check
EC-39