2001 LAND ROVER FREELANDER oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 42 of 1007
GENERAL INFORMATION
03-11
Split pins
Always fit new split-pins of the correct size for the
hole in the bolt or stud.
Screw threads
General
Metric threads to ISO standards are used.
Damaged nuts, bolts and screws must always be
discarded. Cleaning damaged threads with a die or
tap impairs the strength and closeness of fit of the
threads and is not recommended.
Always ensure that replacement bolts are at least
equal in strength to those replaced.
Castellated nuts must not be slackened to accept a
split-pin, except in recommended cases when this
forms part of an adjustment.
Do not allow oil or grease to enter blind threaded
holes. The hydraulic action on screwing in the bolt or
stud could split the housing.
Always tighten a nut or bolt to the recommended
torque figure. Damaged or corroded threads can
affect the torque reading.
To check or re-tighten a bolt or screw to a specified
torque figure, first loosen a quarter of a turn, then
retighten to the correct torque figure.
Oil thread lightly before tightening to ensure a free
running thread, except in the case of threads treated
with sealant/lubricant, and self-locking nuts.
Page 43 of 1007
GENERAL INFORMATION
03-12
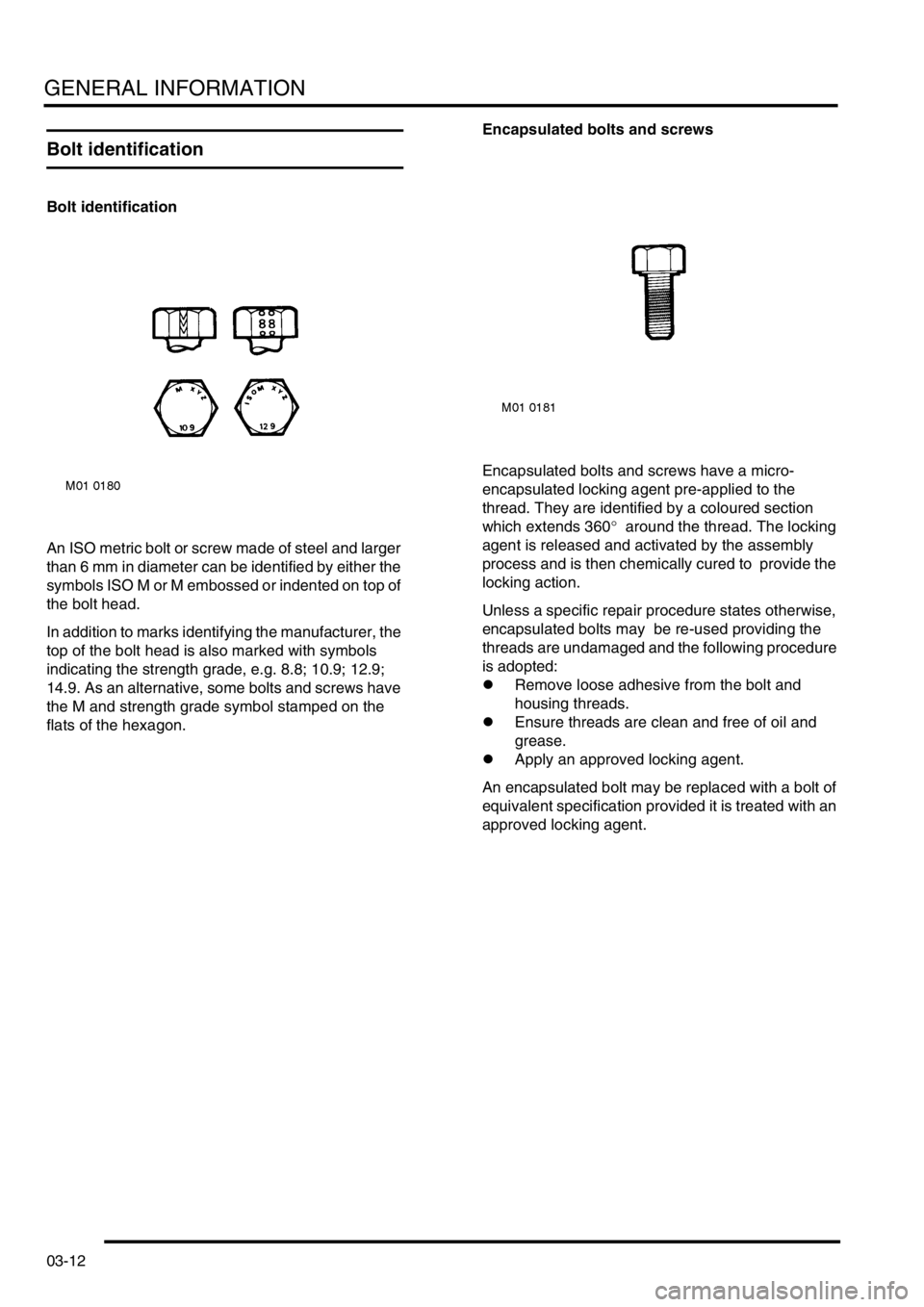
Bolt identification
Bolt identification
An ISO metric bolt or screw made of steel and larger
than 6 mm in diameter can be identified by either the
symbols ISO M or M embossed or indented on top of
the bolt head.
In addition to marks identifying the manufacturer, the
top of the bolt head is also marked with symbols
indicating the strength grade, e.g. 8.8; 10.9; 12.9;
14.9. As an alternative, some bolts and screws have
the M and strength grade symbol stamped on the
flats of the hexagon.Encapsulated bolts and screws
Encapsulated bolts and screws have a micro-
encapsulated locking agent pre-applied to the
thread. They are identified by a coloured section
which extends 360° around the thread. The locking
agent is released and activated by the assembly
process and is then chemically cured to provide the
locking action.
Unless a specific repair procedure states otherwise,
encapsulated bolts may be re-used providing the
threads are undamaged and the following procedure
is adopted:
lRemove loose adhesive from the bolt and
housing threads.
lEnsure threads are clean and free of oil and
grease.
lApply an approved locking agent.
An encapsulated bolt may be replaced with a bolt of
equivalent specification provided it is treated with an
approved locking agent.
Page 50 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-19
Electrical precautions
General
The following guidelines are intended to ensure the
safety of the operator and ensure the prevention of
damage to the electrical and electronic components
fitted to the vehicle. Where necessary, specific
precautions are detailed in the individual procedures
of this manual.
Equipment
Prior to commencing any test procedure on the
vehicle, ensure that the relevant test equipment is
working correctly and any harness or connectors are
in good condition. It is particularly important to check
the condition of the lead and plugs of mains operated
equipment.
Polarity
Never reverse connect the vehicle battery and
always ensure the correct polarity when connecting
test equipment.
High Voltage Circuits
Whenever disconnecting live ht circuits, always use
insulated pliers and never allow the open end of the
ht lead to contact other components, particularly
ECU's.
Exercise caution when measuring the voltage on the
coil terminals while the engine is running, high
voltage spikes can occur on these terminals.
Connectors and harnesses
The engine compartment of a vehicle is a particularly
hostile environment for electrical components and
connectors:
lAlways ensure electrically related items are dry
and oil free before disconnecting and
connecting test equipment.
lEnsure disconnected multiplugs and sensors
are protected from being contaminated with oil,
coolant or other solutions. Contamination could
impair performance or result in catastrophic
failure.
lNever force connectors apart using tools to
prise apart or by pulling on the wiring harness.
lAlways ensure locking tabs are disengaged
before disconnection, and match orientation to
enable correct reconnection.
lEnsure that any protection (covers, insulation
etc.) is replaced if disturbed.Having confirmed a component to be faulty:
lSwitch off the ignition and disconnect the
battery.
lRemove the component and support the
disconnected harness.
lWhen replacing the component, keep oily hands
away from electrical connection areas and push
connectors home until any locking tabs fully
engage.
Battery disconnection
Before disconnecting the battery, disable the alarm
system and switch off all electrical equipment. If the
radio is to be serviced, ensure the security code has
been deactivated.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to electrical
components, always disconnect the battery
when working on the vehicle's electrical system.
The ground lead must be disconnected first and
reconnected last.
CAUTION: Always ensure that battery leads are
routed correctly and are not close to any
potential chafing points.
Battery charging
Only recharge the battery with it removed from the
vehicle. Always ensure any battery charging area is
well ventilated and that every precaution is taken to
avoid naked flames and sparks.
Ignition system safety precautions
The vehicle's ignition system produces high voltages
and the following precautions should be observed
before carrying out any work on the system:
WARNING: Before commencing work on an
ignition system, ensure all high tension
terminals, adapters and diagnostic equipment
are adequately insulated and shielded to prevent
accidental personal contacts and minimise the
risk of shock. Wearers of surgically implanted
pacemaker devices should not be in close
proximity of ignition circuits or diagnostic
equipment.
Page 52 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-21
It should be noted that these precautions are not
restricted to operations performed when servicing
the SRS system, the same care should be exercised
when working on ancillary systems and components
located in the vicinity of SRS components; these
include but are not limited to:
lSteering system – steering wheel airbag,
rotary coupler.
lFront fascia – passenger front airbag (where
fitted); SRS DCU behind centre console, on
transmission tunnel under the HeVAC system.
lFront seats – seat belt pre-tensioners, integral
with seat belt buckle assembly.
lElectrical system – SRS harnesses, link leads
and connectors.
Making the SRS system safe
Before working on or in the vicinity of SRS
components, ensure the system is rendered safe by
performing the following procedures:
lRemove the ignition key from the ignition switch.
lDisconnect both battery leads, earth lead first.
lWait 10 minutes for the SRS DCU back-up
power circuit to discharge.
The SRS system uses energy reserve capacitors
that keep the system active in the event of electrical
supply failure under crash conditions. It is necessary
to allow the capacitor sufficient time to discharge (10
minutes) in order to avoid the risk of accidental
deployment.
WARNING: Always disconnect both battery leads
before beginning work on the SRS system.
Disconnect the negative battery lead first. Never
reverse connect the battery.Installation
In order to assure system integrity, it is essential that
the SRS system is regularly checked and maintained
so that it is ready for effective operation in the event
of a collision. Carefully inspect SRS components
before installation. Do not install a part that shows
signs of being dropped or improperly handled, such
as dents, cracks or deformation.
WARNING: The integrity of SRS system
components is critical for safety reasons. Ensure
the following precautions are always adhered to:
lNever install used SRS components from
another vehicle or attempt to repair an SRS
component.
lWhen repairing an SRS system only use
genuine new parts.
lNever apply electrical power to an SRS
component unless instructed to do so as
part of an approved test procedure.
lSpecial Torx bolts are necessary for
installing the airbag module — do not use
other bolts. Ensure bolts are tightened to the
correct torque.
lAlways use new fixings when replacing an
SRS component.
lEnsure the SRS Diagnostic Control Unit
(DCU) is always installed correctly. There
must not be any gap between the DCU and
the bracket to which it is mounted. An
incorrectly mounted DCU could cause the
system to malfunction.
CAUTION: Ensure SRS components are not
contaminated with oil, grease, detergent or
water.
Ensure that SRS component fixings are correctly
positioned and torqued during service and repair.
CAUTION: Torque wrenches should be regularly
checked for accuracy to ensure that all fixings
are tightened to the correct torque.
If you suspect an airbag assembly could be
defective, install a new unit and dispose of the old
unit. Manually deploy the old unit before disposal.
Page 61 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-30
Remedial actions
If an accident involving R134a should occur, conduct
the following remedial actions:
lIf liquid R134a enters the eye, do not rub it.
Gently run large quantities of eye wash over
affected eye to raise the temperature. If an eye
wash is not available, cool clean water may be
used to flush the eye. After rinsing, cover the
eye with a clean pad and seek immediate
medical attention.
lIf liquid R134a is splashed onto the skin, run
large quantities of water over the affected area
to raise the temperature. Implement the same
action if the skin comes in contact with
discharging cylinders. Wrap the contaminated
body parts in blankets (or similar materials) and
seek immediate medical attention.
lIf the debilitating effects of inhalation of R134a
vapour is suspected, seek fresh air. If the
affected person is unconscious, move them
away from the contaminated area to fresh air
and apply artificial respiration and/or oxygen
and seek immediate medical attention.
Service precautions
Observe the following precautions when handling
components used in the air conditioning system:
lAir conditioning units must not be lifted by their
hoses, pipes or capillary lines.
lHoses and lines must not be subjected to any
twist or stress - the efficiency of the system will
be impaired by kinks or restrictions. Ensure that
hoses are correctly positioned before tightening
couplings, and ensure that all clips and supports
are utilised.
lFlexible hoses should not be positioned close to
the exhaust manifold (less than 100mm) unless
protected by heat shielding.
lCompleted assemblies must be checked for
refrigeration lines touching metal panels. Any
direct contact of components and panels may
transmit noise and so must be eliminated.
lThe appropriate torque wrench must be used
when tightening refrigerant connections to the
stipulated value. An additional spanner must be
used to hold the union to prevent twisting of the
pipe when tightening connections.
lBefore connecting any hose or pipe, ensure that
refrigerant oil is applied to the seat of the new
'O' ring seals, BUT NOT to the threads of the
connection.
lAll protective plugs must remain in place to seal
the component until immediately prior to
connection.
lEnsure components are at room temperature
before uncapping, to prevent condensation of
moisture from the air that enters it.
lComponents must not remain uncapped for
longer than 15 minutes. In the event of a delay,
the caps must be fitted.
lWhen disconnecting, immediately cap all air
conditioning pipes to prevent ingress of dirt and
moisture into the system.
lThe modulator (receiver/drier) contains
desiccant which absorbs moisture. It must be
positively sealed at all times. A modulator that
has been left uncapped must not be used, fit a
new unit.
lThe modulator should be the last component
connected to the system to ensure optimum
dehydration and maximum moisture protection
of the system.
lWhenever the refrigerant system is opened, the
modulator must be renewed immediately before
evacuating and recharging the system.
lUse alcohol and a clean lint-free cloth to clean
dirty connections.
lEnsure that all new parts fitted are marked for
use with R134a.
Page 62 of 1007

GENERAL INFORMATION
03-31
When a major repair has been completed, a leak test
should be conducted; refer to the air conditioning
section of this manual for the correct procedure.
Refrigerant oil
Use an approved refrigerant lubricating oil:
ND Oil 8
CAUTION: Do not use any other type of
refrigerant oil.
CAUTION: Refrigerant oil easily absorbs water
and must not be stored for long periods. Do not
pour unused oil back into the container.
When renewing system components, add the
quantities of refrigerant oil recommended in the Air
Conditioning section of this manual.
Compressor
A new compressor is sealed and pressurised with
Nitrogen gas. When fitting a new compressor, slowly
release the sealing cap; gas pressure should be
heard to vent as the seal is broken.
CAUTION: A new compressor should always be
sealed and could be pressurised with nitrogen
gas. To avoid possible oil loss, release the
sealing cap(s) slowly. Do not remove the cap(s)
until immediately prior to connecting the air
conditioning pipes to the compressor.
Rapid refrigerant discharge
If the air conditioning system is involved in accident
damage and the system is punctured, the refrigerant
will discharge rapidly. The rapid discharge of
refrigerant will also result in the loss of most of the
oil from the system. The compressor must be
removed and all the remaining oil in the compressor
drained and refilled in accordance with the 'Air
Conditioning Compressor Replacement Procedure'.
Air conditioning compressor
replacement
A new compressor is supplied filled with a full charge
of (X cm3) of refrigerant oil.
A new compressor is supplied with an oil fill (X cm) of
120 cm
3.
A calculated quantity of oil must be drained from the
new compressor before fitting. To calculate the
quantity of oil to be drained:
1Remove the drain plug from the old
compressor.
2Invert the compressor and gravity drain the oil
into a calibrated measuring cylinder. Rotate the
compressor clutch to ensure the compressor is
completely drained.
3Note the quantity of oil drained (Y cm
3).
4Calculate the quantity of oil to be drained from
the new compressor using the following
formula:
X cm
3 – (Y cm3 + 20 cm3) = Q cm3
5Remove the drain plug from the new
compressor and drain Q cm3 of oil.
6Fit and tighten the compressor drain plug.
System components
When renewing system components, add the
following quantities of refrigerant oil:
lCondenser = 40 cm
3
lEvaporator = 30 cm 3
lReceiver drier = 15 cm 3
lPipe or hose = 5 cm 3
Page 65 of 1007

GENERAL DATA
04-2
Lubrication
Type Wet aluminium die-cast sump, pressure fed
Oil filter Disposable canister with full flow by-pass
Oil cooler Integral with oil filter assembly, connected to vehicle cooling system
Oil pump:
⇒ Type Crankshaft driven, eccentric rotor
⇒ Oil flow rate 30 litres / min. (6.625 gallons/min.)
⇒ Outer rotor to body clearance 0.080 - 0.158 mm (0.0031 - 0.062 in.)
⇒ Peak pressure up to 20 bar (290 lbf.in
2)
Oil pressure at idle:
⇒ Cold - 1000 rev/min. 1.5 bar (21.8 lbf.in
2)
⇒ Operating temperature (minimum) 0.5 bar (7.3 lbf.in
2)
⇒ Regulated pressure 4.2 ±0.5 bar (60.9 ± 7.3 lbf.in
2)
⇒ Pressure at 3500 rev/min (hot) 3.0 - 4.5 bar (43.5 - 65.3 lbf.in
2)
Relief valve opening pressure 4.2 bar (60.9 lbf.in
2)
Low oil pressure switch opening pressure 0.2 - 0.5 bar (2.9 - 7.3 lbf.in
2)
Cylinder block
Type Grey cast iron with hollow beam structure
Cylinder head warp - maximum 0.03 mm (0.001 in.)
Cylinder head bore:
†
⇒ Standard 84.000 - 84.018 mm (3.3071 - 3.3078 in)
⇒⇒ Wear limit 84.040 mm (3.3087 in)
⇒ Intermediate 84.080 - 84.098 mm (3.3102 - 3.3109 in)
⇒⇒ Wear limit 84.120 mm (3.3118)
⇒ 1st.Oversize (Grinding dimension) 84.250 - 84.268 mm (3.3169 - 3.3176 in)
⇒⇒ Wear limit 84.290 mm (3.3185 in)
Cylinder bore ovality (permitted roundness deviation)
†0.01 mm (0.0004 in)
⇒ Wear limit 0.04 mm (0.0016 in)
Cylinder bore taper (permitted conicity)
†0.01 mm (0.0004 in)
⇒ Wear limit 0.04 mm (0.0016 in)
†Measurements at top centre and bottom of bore
Crankshaft
Main journal diameter 60 mm (2.36 in.)
Crankpin journal diameter 44.975 - 45.009 mm (1.7707 - 1.7720 in)
End float 0.08 - 0.163 mm (0.0031 - 0.0064 in.)
Maximum out of round
†0.15 mm (0.006 in.)
Crankshaft seal PTFE
†At centre main journal; crankshaft supported on outer bearing pins
Page 66 of 1007

GENERAL DATA
04-3
Main bearings
Quantity 5 (4 main, 1 thrust)
Type Grooved shells in crankshaft, plain shells in main bearing caps
Ground sizes of main bearing journals:
Standard:
⇒ Yellow 59.977 - 59.983 mm (2.3613 - 2.3615 in)
⇒ Green 59.970 - 59.976 mm (2.3610 - 2.3613 in)
⇒ White 59.964 - 59.970 mm (2.3608 - 2.3610 in)
1st Undersize (0.25):
⇒ Yellow 59.727 - 59.733 mm (2.3515 - 2.3517 in)
⇒ Green 59.720 - 59.726 mm (2.3512 - 2.3514 in)
⇒ White 59.714 - 59.720 mm (2.3509 - 2.3512 in)
2nd Undersize (0.50):
⇒ Yellow 59.477 - 59.483 mm (2.3416 - 2.3418 in)
⇒ Green 59.470 - 59.476 mm (2.3413 - 2.3416 in)
⇒ White 59.464 - 59.469 mm (2.3411 - 2.3413 in)
Crankshaft radial bearing play 0.027 - 0.063 mm (0.0011 - 0.0025 in)
Connecting Rods
Type Forged H-sections, horizontally split big-end, plain small-end
Distance between centres 135 mm (5.32 in.)
Parallel deviation 0.05 mm (0.002 in)
Parallel distortion 0.5 mm (0.02 in)
Big-end bearings
Quantity 4
Material Sputter bearing on rod end halves
Gudgeon pins
Type Fully floating, retained by circlips
Bush bore diameter 30.008 - 30.015 mm (1.1814 - 1.1817 in.)
Fit in connecting rod Press fit
Length 65 mm (2.56 in.)
Pistons
Type Graphite compound skirt with recessed combustion chamber in crown
and oil cooling channel
Piston running clearance 0.036 - 0.072 mm (0.0014 - 0.0028 in)
Maximum clearance in cylinder bore (engine run in) 0.15 mm (0.006 in)
Piston diameter
†:
⇒ Standard 83.950 ± 0.009 mm (3.3051 ± 0.0004 in)
⇒ Intermediate 84.030 ± 0.009 mm (3.3083 ± 0.0004 in)
⇒ 1st Oversize 84.200 ± 0.009 mm (3.3150 ± 0.0004 in)
†measured 12 mm (0.47 in) from bottom of skirt and 90° to gudgeon pin: