2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY tires
[x] Cancel search: tiresPage 1494 of 2321

(14) If equipped, install the power steering cooler
hoses on the cooler inlet and outlet tubes. Install the
clamps.
(15) Install the front tire and wheel assemblies on
vehicle. Install the wheel mounting lug nuts and
tighten to a torque to 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(16) Lower the vehicle to a level were the interior
of vehicle is accessible (keeping tires off the ground).
(17) Using the intermediate coupler, turn the front
wheels of the vehicle to the left until the intermedi-
ate coupler shaft is properly aligned with the steer-
ing column coupler. Assemble the steering columnshaft coupler onto the steering gear intermediate
coupler (Fig. 1). Install steering column coupler to
intermediate shaft retaining pinch bolt. Tighten the
pinch bolt nut to a torque of 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(18) Perform the POWER STEERING PUMP INI-
TIAL OPERATION procedure to properly fill and
bleed the power steering system. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(19) Inspect for leaks.
(20) Adjust front wheel toe (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
RGGEAR19a-5
GEAR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1731 of 2321

in 3rd and 4th gear Autostick mode. Speed control
will be deactivated if the transaxle is shifted to 2nd
gear. Shifting into OD position cancels the Autostick
mode, and the transaxle resumes the OD shift sched-
ule.
DRIVING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION
Three hydraulically applied input clutches are used
to drive planetary components. The underdrive, over-
drive, and reverse clutches are considered input
clutches and are contained within the input clutch
assembly (Fig. 176) . The input clutch assembly also
contains:
²Input shaft
²Input hub
²Clutch retainer
²Underdrive piston
²Overdrive/reverse piston
²Overdrive hub
²Underdrive hub
OPERATION
The three input clutches are responsible for driving
different components of the planetary geartrain.
NOTE: Refer to the ªElements In Useº chart in Diag-
nosis and Testing for a collective view of which
clutch elements are applied at each position of the
selector lever.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
The underdrive clutch is hydraulically applied in
first, second, and third (direct) gears by pressurized
fluid against the underdrive piston. When the under-
drive clutch is applied, the underdrive hub drives the
rear sun gear.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
The overdrive clutch is hydraulically applied in
third (direct) and overdrive gears by pressurized fluid
against the overdrive/reverse piston. When the over-
drive clutch is applied, the overdrive hub drives the
front planet carrier.
REVERSE CLUTCH
The reverse clutch is hydraulically applied in
reverse gear only by pressurized fluid against the
overdrive/reverse piston. When the reverse clutch is
applied, the front sun gear assembly is driven.
FINAL DRIVE
DESCRIPTION
The 41TE differential is a conventional open
design. It consists of a ring gear and a differential
case. The differential case consists of pinion and side
gears, and a pinion shaft. The differential case is
supported in the transaxle by tapered roller bearings
(Fig. 177) .
OPERATION
The differential assembly is driven by the transfer
shaft by way of the differential ring gear. The ring
gear drives the differential case, and the case drives
the driveshafts through the differential gears. The
differential pinion and side gears are supported in
the case by thrust washers and a pinion shaft. Dif-
ferential pinion and side gears make it possible for
front tires to rotate at different speeds while corner-
ing.
Fig. 176 Input Clutch Assembly
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
3 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
4 - REVERSE CLUTCH
5 - OVERDRIVE SHAFT
6 - UNDERDRIVE SHAFT
21 - 234 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
AUTOSTICK SWITCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1810 of 2321

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMMON
PROBLEM CAUSES
The majority of transaxle malfunctions are a result
of:
²Insufficient lubrication
²Incorrect lubricant
²Misassembled or damaged internal components
²Improper operation
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting may be caused by a misadjusted
crossover cable. If hard shifting is accompanied by
gear clash, synchronizer clutch and stop rings or gear
teeth may be worn or damaged.
Hard shifting may also be caused by a binding or
broken shift cover mechanism. Remove shift cover
and verify smooth operation. Replace as necessary.
Misassembled synchronizer components also cause
shifting problems. Incorrectly installed synchronizer
sleeves, keys, balls, or springs can cause shift prob-
lems.
NOISY OPERATION
Transaxle noise is most often a result of worn or
damaged components. Chipped, broken gear or syn-
chronizer teeth, and brinnelled, spalled bearings all
cause noise.
Abnormal wear and damage to the internal compo-
nents is frequently the end result of insufficient
lubricant.
SLIPS OUT OF GEAR
Transaxle disengagement may be caused by mis-
aligned or damaged shift components, or worn teeth
on the drive gears or synchronizer components. Incor-
rect assembly also causes gear disengagement. Check
for missing snap rings.
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
Insufficient transaxle lubricant is usually the
result of leaks, or inaccurate fluid level check or refill
method. Leakage is evident by the presence of oil
around the leak point. If leakage is not evident, the
condition is probably the result of an underfill.
If air±powered lubrication equipment is used to fill
a transaxle, be sure the equipment is properly cali-
brated. Equipment out of calibration can lead to an
underfill condition.
CLUTCH PROBLEMS
Worn, damaged, or misaligned clutch components
can cause difficult shifting, gear clash, and noise.
A worn or damaged clutch disc, pressure plate, or
release bearing can cause hard shifting and gear
clash.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L GAS
(1) Raise hood.
(2) Disconnect gearshift cables from shift levers/
cover assembly (Fig. 10).
(3) Remove gearshift cable retaining clips from
mounting bracket (Fig. 10). Remove cables and
secure out of way.
(4) Remove three (3) right engine mount bracket-
to-transaxle bolts (Fig. 11).
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Remove front wheel/tires and halfshafts.
(7) Drain transaxle fluid into suitable container.
(8) Remove cradle plate.
(9) Remove front harness retainer and secure har-
ness out of way.
(10) Remove clutch release access cover.
(11)RHD Models:Using Tool 6638A, disconnect
clutch hydraulic circuit quick connect (located on
slave cylinder tube). Remove clutch slave cylinder by
depressing towards case and rotating counter-clock-
wise 60É, while lifting anti-rotation tab out of case
slot with screwdriver (Fig. 12).LHD Models:
Remove clutch release cable by pulling outward on
cable housing, then forward to allow cable core to
pass through case slot (Fig. 13). Disengage T-end
from release lever and secure cable out of way.
(12) Remove engine left mount bracket.
(13) Remove starter motor (Fig. 14).
Fig. 10 Gearshift Cables at Transaxle
1 - SELECTOR CABLE
2 - CABLE RETAINER
3 - CABLE RETAINER
4 - CROSSOVER CABLE
5 - MOUNT BRACKET
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-11
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1814 of 2321
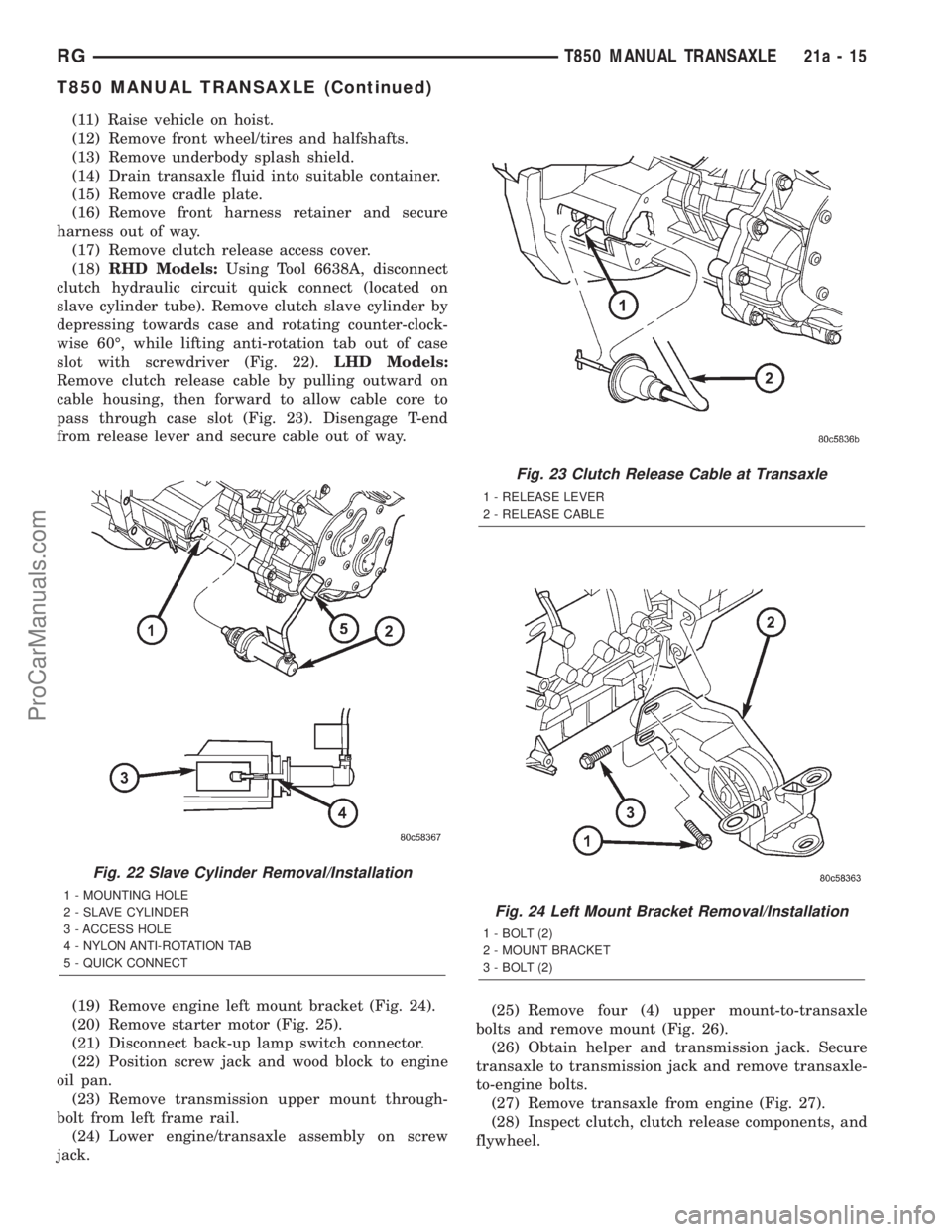
(11) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(12) Remove front wheel/tires and halfshafts.
(13) Remove underbody splash shield.
(14) Drain transaxle fluid into suitable container.
(15) Remove cradle plate.
(16) Remove front harness retainer and secure
harness out of way.
(17) Remove clutch release access cover.
(18)RHD Models:Using Tool 6638A, disconnect
clutch hydraulic circuit quick connect (located on
slave cylinder tube). Remove clutch slave cylinder by
depressing towards case and rotating counter-clock-
wise 60É, while lifting anti-rotation tab out of case
slot with screwdriver (Fig. 22).LHD Models:
Remove clutch release cable by pulling outward on
cable housing, then forward to allow cable core to
pass through case slot (Fig. 23). Disengage T-end
from release lever and secure cable out of way.
(19) Remove engine left mount bracket (Fig. 24).
(20) Remove starter motor (Fig. 25).
(21) Disconnect back-up lamp switch connector.
(22) Position screw jack and wood block to engine
oil pan.
(23) Remove transmission upper mount through-
bolt from left frame rail.
(24) Lower engine/transaxle assembly on screw
jack.(25) Remove four (4) upper mount-to-transaxle
bolts and remove mount (Fig. 26).
(26) Obtain helper and transmission jack. Secure
transaxle to transmission jack and remove transaxle-
to-engine bolts.
(27) Remove transaxle from engine (Fig. 27).
(28) Inspect clutch, clutch release components, and
flywheel.
Fig. 22 Slave Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - MOUNTING HOLE
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
3 - ACCESS HOLE
4 - NYLON ANTI-ROTATION TAB
5 - QUICK CONNECT
Fig. 23 Clutch Release Cable at Transaxle
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE CABLE
Fig. 24 Left Mount Bracket Removal/Installation
1 - BOLT (2)
2 - MOUNT BRACKET
3 - BOLT (2)
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-15
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1896 of 2321

TIRES/WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................1
TIRE AND WHEEL VIBRATION..............1
STANDARD PROCEDURE...................4
TIRE AND WHEEL BALANCE...............4
TIRE AND WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING.......6
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION..............6
REMOVAL...............................7
INSTALLATION............................7
TIRES
DESCRIPTION............................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..................9
TIRE NOISE............................9
TIRE/VEHICLE LEAD.....................9
TIRE WEAR PATTERNS..................11
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS...............11
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................11
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES.............11
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION...........................12TIRE LEAK REPAIRING..................12
CLEANING..............................13
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION...........................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................13
WHEEL INSPECTION....................13
CLEANING..............................14
SPECIFICATIONS........................14
WHEEL COVER
DESCRIPTION...........................14
REMOVAL..............................14
INSTALLATION...........................14
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - FRONT
REMOVAL..............................15
INSTALLATION...........................16
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - REAR
REMOVAL..............................16
INSTALLATION...........................17
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND WHEEL
VIBRATION
Tire and wheel imbalance, runout and force varia-
tion can cause vehicles to exhibit steering wheel
vibration.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Visual inspection of the vehicle is recommended
prior to road testing or performing any other proce-
dure. Raise vehicle on a suitable hoist. Refer to
Hoisting in Lubrication and Maintenance.
Inspect for the following:
²Verify correct (OEM) wheel and tire, as well as
correct wheel weights. Aluminum wheels require
unique wheel weights. They are designed to fit the
contour of the wheel (Fig. 1).
²Inspect tires and wheels for damage, mud pack-
ing and unusual wear; correct as necessary.
²Check and adjust tire air pressure to the pres-
sure listed on the label attached to the rear face of
the driver's door.
ROAD TEST
Road test vehicle on a smooth road for a least five
miles to warm tires (remove any flat spots). Lightlyplace hands on steering wheel at the 10:00 and 2:00
positions while slowly sweeping up and down from 90
to 110 km/h (55 to 70 mph) where legal speed limits
allow.
Observe the steering wheel for:
²Visual Nibble (oscillation: clockwise/counter-
clockwise, usually due to tire imbalance)
Fig. 1 Aluminum Wheel Weight
1 - TIRE
2 - WHEEL
3 - WHEEL WEIGHT
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1897 of 2321

²Visual Buzziness (high frequency, rapid vibra-
tion up and down)
To rule out vibrations due to brakes or powertrain:
²Lightly apply brakes at speed; if vibration occurs
or is enhanced, vibration is likely due to causes other
than tire and wheel assemblies.
²Shift transmission into neutral while vibration
is occurring; if vibration is eliminated, vibration is
likely due to causes other than tire and wheel assem-
blies.
For brake vibrations, (Refer to 5 - BRAKES -
BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ROTORS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
For powertrain vibrations, (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
For tire and wheel assembly vibrations, continue
with this diagnosis an testing procedure.
TIRE AND WHEEL BALANCE
(1) Balance the tire and wheel assemblies as nec-
essary following the wheel balancer manufacturer's
instructions and using the information listed in Stan-
dard Procedure - Tire And Wheel Balance. (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Road test the vehicle for at least 5 miles, fol-
lowing the format described in Road Test.
(3) If the vibration persists, continue with this
diagnosis an testing procedure.
TIRE AND WHEEL RUNOUT/MATCH MOUNTING
(1)System Radial Runout.This on-the-vehicle
system check will measure the radial runout includ-
ing the hub, wheel and tire.
(a) Raise vehicle so tires clear floor. Refer to
Hoisting in Lubrication and Maintenance.
(b) Apply masking tape around the circumfer-
ence of the tire in the locations to be measured
(Fig. 2). Do not overlap the tape.
(c) Check system runout using Dial Indicator
Set, Special Tool C-3339A with 25-W wheel, or
equivalent. Place the end of the indicator against
each taped area (one at a time) (Fig. 2) and rotate
the tire and wheel. System radial runout should
not exceed 0.76 mm (0.030 inch) with no tread
ªdipsº or ªsteps.º Tread ªdipsº and ªstepsº can be
identified by spikes of the dial indicator gauge.
²Tread9dips9; Rapid decrease then increase in
dial indicator reading over 101.6 mm (4.0 inch) of
tread circumference.
²Tread9steps9; Rapid decrease or increase in dial
indicator reading over 101.6 mm (4.0 inch) of tread
circumference.
(d) If system runout is excessive, re-index the
tire and wheel assembly on the hub. Remove
assembly from vehicle and install it back on thehub two studs over from original mounting posi-
tion. If re-indexing the tire and wheel assembly
corrects or reduces system runout, check hub
runout and repair as necessary (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(e) If system runout is still excessive, continue
with this diagnosis an testing procedure.
(2)Tire and Wheel Assembly Radial Runout.
This radial runout check is performed with the tire
and wheel assembly off the vehicle.
(a) Remove tire and wheel assembly from vehicle
and install it on a suitable wheel balancer.
(b) Check system runout using Dial Indicator
Set, Special Tool C-3339A with 25-W wheel, or
equivalent. Place the end of the indicator against
each taped area (one at a time) (Fig. 2) and rotate
the tire and wheel. Radial runout should not
exceed 0.76 mm (0.030 inch) with no tread ªdipsº
or ªsteps.º Tread ªdipsº and ªstepsº can be identi-
fied by spikes of the dial indicator gauge.
(c) If runout exceeds limits, mark the original
location of the tire on the wheel at the valve stem
(Fig. 3). Also, mark the tire and wheel to indicate
the original high spot of the assembly and record
the runout measurement.
(d) If runout exceeds limits, the tire will need to
be dismounted from the wheel to verify wheel vs.
tire contribution. Refer to Wheel Runout below.
(3)Lateral Runout.Lateral runout for the vehi-
cle system as well as the tire and wheel assembly
should be less than 0.76 mm (0.030 inch). The same
Fig. 2 Radial Runout Measurement
1 - MASKING TAPE
2 - DIAL INDICATOR
22 - 2 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1898 of 2321

procedure and theory described for radial runout can
also be applied to identify and reduce lateral runout.
(4)Wheel Runout.This runout check is per-
formed as follows:
(a) Dismount the tire from the wheel.
(b) Mount the wheel back on the wheel balancer.
(c) Measure radial runout of the wheel at the
tire bead seat (Fig. 4). Runout should not exceed
0.254 mm (0.010 inch) for aluminum wheels and
0.508 mm (.020 inch) for steel wheels. Replace the
wheel if it exceeds the limit.
(d) Measure lateral runout of the wheel at the
tire bead seat (Fig. 5). Runout should not exceed
0.762 mm (0.030 inch) for all wheels. Replace the
wheel if it exceeds the limit.
(5)Match Mounting.If the wheel runout is
within specifications, tire and wheel assembly runout
can be improved by re-indexing (match mounting)
the tire to the wheel as described below.
(a) Remount the tire on the rim 180 degrees
from its original location (Fig. 6).
(b) Re-measure the total runout. Mark the tire
at the high spot and record the measurement.
If runout is still excessive, perform the following:
²If the new high spot is within 102 mm (4.0 inch)
of the first high spot on the tire, replace the tire.²If the new high spot is within 102 mm (4.0 inch)
of the first high spot on the wheel, the wheel may be
out of specification. Refer to Wheel Runout above.
²If the new high spot is NOT within 102 mm (4.0
inch) of either high spot, draw an arrow on the tread
Fig. 3 Marking Tire
1 - REFERENCE MARK
2 - EXAMPLE HIGH SPOT ON TIRE
3 - WHEEL
4 - VALVE STEM
Fig. 4 Checking Radial Runout Of Wheel
1 - MOUNTING CONE
2 - SPINDLE SHAFT
3 - WING NUT
4 - PLASTIC CUP
5 - DIAL INDICATOR
6 - WHEEL
7 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 5 Checking Lateral Runout Of Wheel
1 - MOUNTING CONE
2 - SPINDLE SHAFT
3 - WING NUT
4 - PLASTIC CUP
5 - DIAL INDICATOR
6 - WHEEL
7 - DIAL INDICATOR
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-3
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1899 of 2321

from new high spot toward the original (Fig. 7).
Break down the tire and remount it 90 degrees on
rim in that direction, then re-measure runout. This
will normally reduce the runout to an acceptable
amount.(6) Once back together, road test the vehicle for at
least 5 miles, following the format described in Road
Test. If vibration persists, and all components tested
are within specification, the tires may have an exces-
sive radial force condition. Radial forces can only be
checked as indicated below. If this equipment is not
available, consult with the tire manufacturer.
RADIAL FORCES
Radial Forces can be checked using the Hunter
GSP 9700 Vibration Control System (Wheel Bal-
ancer) or equivalent, if available. Use the following
reference values for measuring assembly radial forces
when diagnosing vibration complaints:
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Total Radial Force
Variation (RFV)Less Than 20 Lbs.
Radial First Harmonic
(R1H)Less Than 14 Lbs.
Radial Second Harmonic
(R2H)Less Than 9 Lbs.
Radial forces greater than the reference values do
not automatically mean the tire is out of specifica-
tion. Be sure to examine the wheel runout. Assembly
RFV and R1H can often be reduced by re-indexing
the tire on the wheel.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND WHEEL
BALANCE
NOTE: Balance equipment must be calibrated and
maintained per equipment manufacturer's specifica-
tions.
Wheel balancing can be accomplished with either
on-vehicle or off-vehicle equipment.
NOTE: If using on-vehicle balancing equipment, on
the driving axle, remove the opposite wheel and tire
assembly.
It is recommended that a two-plane dynamic bal-
ancer be used when a wheel and tire assembly
requires balancing. A static balancer should only be
used when a two-plane balancer is not available.
Balance wheel and tire assemblies dynamically and
statically to less than 0.25 ounce.
For static balancing, find location of heavy spot
causing imbalance. Counter balance wheel directly
opposite the heavy spot. Determine weight required
to counterbalance the area of imbalance. Place half of
this weight on theinnerrim flange and the other
half on theouterrim flange (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 Remount Tire 180 Degrees
1 - VALVE STEM
2 - REFERENCE MARK
Fig. 7 Remount Tire 90 Degrees In Direction of
Arrow
1 - 2ND HIGH SPOT ON TIRE
2 - 1ST HIGH SPOT ON TIRE
22 - 4 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com