2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 1481 of 2321

PUMP
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PUMP
DESCRIPTION...........................24
OPERATION.............................24
CAUTION...............................25
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................25
POWER STEERING PUMP INITIAL
OPERATION...........................25
REMOVAL..............................25
DISASSEMBLY...........................28
ASSEMBLY.............................28
INSTALLATION...........................29SPECIAL TOOLS.........................30
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................30
POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL
CHECKING............................30
FLUID COOLER
DESCRIPTION...........................30
OPERATION.............................30
REMOVAL..............................31
INSTALLATION...........................31
PUMP
DESCRIPTION
Hydraulic pressure for the operation of the power
steering gear is provided by a belt driven power
steering pump. The power steering pump is mounted
on the back side of the engine on all engine applica-
tions. The pumps are different depending on the
engine option. The pump for the 2.4L engine is made
out of cast iron and steel. The pump used on the
3.3L/3.8L engine is made of aluminum.
The pump for the 3.3L/3.8L engine does not have a
return fitting as the pump for the 2.4L engine does.
The power steering return hose on the 3.3L/3.8L
engine goes to the reservoir instead of the pump.
OPERATION
The power steering pump is a constant flow rate
and displacement vane type pump. The power steer-
ing pump used on all applications is the Vane-Sub-
merged remote reservoir style power steering pump.
The remote reservoir type pump has the pump
housing and internal components combined with the
fluid housing. It has a remote reservoir for the power
steering fluid supply.Fig. 1 POWER STEERING PUMP (2.4L)
1 - PULLEY
2 - BRACKET
3 - PRESSURE FITTING
4 - RETURN FITTING
5 - SUPPLY FITTING
Fig. 2 POWER STEERING PUMP (3.3L/3.8L)
1 - SUPPLY FITTING
2 - PRESSURE FITTING
3 - PULLEY
19 - 24 PUMPRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1482 of 2321

SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
PUMP INITIAL OPERATION
CAUTION: The fluid level should be checked with
engine off to prevent injury from moving compo-
nents. Use only MoparTPower Steering Fluid (MS-
5931) or approved equivalent. Do not overfill.
Read the fluid level through the side of the power
steering fluid reservoir. The fluid level should indi-
cateªFILL RANGEºwhen the fluid is at a temper-
ature of approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to 80ÉF).
(1) Wipe the filler cap and area clean, then remove
the cap.
(2) Fill the fluid reservoir to the proper level and
let the fluid settle for at least two (2) minutes.
(3) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds,
then turn the engine off.
(4) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above steps
until the fluid level remains constant after running
the engine.
(5) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(6) Start the engine.
(7) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops.
(8) Add fluid if necessary.
(9) Lower the vehicle, then turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock-to-lock.
(10) Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and
refill as required.
(11) If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehi-
cle to stabilize a few minutes, then repeat the above
procedure.
REMOVAL - PUMP (2.4L ENGINE)
(1) Remove the (-) negative battery cable from the
battery and isolate cable.
(2) Remove the cap from the power steering fluid
reservoir.
(3) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(4) Raise the vehicle on jack stands or centered on
a frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance.
(5) Disconnect the oxygen sensor wiring harness
from the vehicle wiring harness at the rear engine
mount bracket.
NOTE: The exhaust system needs to be removed
from the engine to allow for an area to remove the
power steering pump from the vehicle.
(6) Remove the four bolts and flag nuts securing
the catalytic converter from the exhaust manifold
(Fig. 3).
(7) Disconnect all the exhaust system isolators/
hangers from the brackets on the exhaust system (2
at the mufflers and 1 at the resonator) (Fig. 4).
(8) Remove the exhaust system by moving it as far
rearward, then lowering the front below the cross-
member and out of the vehicle.
(9) Remove the power steering fluid supply hose
from the fitting on the power steering pump. Drain
off excess power steering fluid from hose.
Fig. 3 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - BOLT
3 - GASKET
4 - FLAG NUT
RSPUMP19-25
PUMP (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1487 of 2321

(4) Install the power steering fluid pressure line
into the pressure output fitting of the power steering
pump (Fig. 11). Tighten the pressure line to pump fit-
ting tube nut to a torque of 31 N´m (275 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the power steering fluid low-pressure
return hose on the power steering pump low pressure
fitting (Fig. 11).Be sure hose clamps are prop-
erly reinstalled.
(6) Raise the vehicle.
(7) Install the routing clip on the engine for the
pressure hose (Fig. 10).
(8) Tighten the pump thru-bolt (Fig. 9). Tighten to
54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the serpentine drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install the drive belt splash shield.
(11) Lower the vehicle.
(12) Install the wiper module (unit)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MOD-
ULE - INSTALLATION).
(13) Connect the negative battery cable on the
negative battery post.
(14) Fill and bleed the power steering system
using the Power Steering Pump Initial Operation
Procedure (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(15) Inspect for leaks.
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING PUMP
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
FLUID LEVEL CHECKING
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING PARTS.
The fluid level can be read on the exterior of the
power steering fluid reservoir. The fluid level should
be within the ªFILL RANGEº when the fluid is at
normal ambient temperature, approximately 21ÉC to
27ÉC (70ÉF to 80ÉF) (Fig. 15).
Before removing the power steering filler cap, wipe
the reservoir filler cap free of dirt and debris. Do not
overfill the power steering system. Use onlyMopart
Power Steering Fluid (MS-5931)or quivalent.
FLUID COOLER
DESCRIPTION
All models of this vehicle are equipped with a
cooler for the power steering system fluid. The power
steering fluid cooler is located on the front suspen-
sion cradle crossmember reinforcement (Fig. 16).
There are two different size coolers offered depending
on options. There is a standard 6-inch and an 8-inch
for vehicles equipped with the heavy duty cooling
package.
OPERATION
The purpose of the power steering fluid cooler is to
keep the temperature of the power steering system
fluid from rising to a level that would affect the per-
formance of the power steering system.
Installer C-4063B
Puller C-4333
Fig. 15 POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
19 - 30 PUMPRS
PUMP (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1521 of 2321

OPERATION
Transmission output is directed to an integral dif-
ferential by a transfer gear system in the following
input-to-output ratios:
FIRST 2.69:1
SECOND 1.55:1
THIRD 1.00:1
REVERSE 2.10:1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
DIAGNOSIS
Automatic transaxle malfunctions are usually
caused by the following general conditions:
²Improper fluid level/condition
²Poor engine performance
²Improper engine or transaxle adjustments
²Transaxle hydraulic malfunctions²Transaxle mechanical malfunctions
Diagnosis of transaxle problems should always
begin with checking the easily accessible variables:
²Fluid level and condition
²Gearshift cable adjustment
²Throttle valve cable adjustment
After verifying or adjusting these variables, road
test the vehicle to determine if the problem has been
corrected or that further diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem still exists, refer to the following diagnosis
charts to aid in determining the source or cause of
failure.
Hydraulic pressure tests should be performed
when a transaxle internal failure is suspected. The
hydraulic flow charts, in the Schematics and Dia-
grams section of this group, outline fluid flow and
hydraulic circuitry. Circuit operation is provided for
all gear ranges. Normal working pressures are also
supplied for each of the gear ranges.
TRANSAXLE DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HARSH ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low 1. Add Fluid
2. Throttle Linkage Misadjusted 2. Adjust linkage - setting may be too
long.
3. Excessive Pinion Backlash 3. Check per Service Manual. Correct as
needed.
4. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect 4. Check pressure. Remove, overhaul or
adjust valve body as needed.
5. Band Misadjusted. 5. Adjust rear band.
6. Valve Body Check Balls Missing. 6. Inspect valve body for proper check
ball installation.
7. Clutch, band or planetary component
Damaged.7. Remove, disassemble and repair
transmission as necessary.
8. Converter Clutch (if equipped) Faulty. 8. Replace converter and flush cooler and
line before installing new converter.
21 - 24 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1525 of 2321

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STUCK IN LOW GEAR
(WILL NOT UPSHIFT)1. Throttle Linkage Misadjusted/Stuck. 1. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if
worn or damaged. Check for binding
cable.
2. Gearshift Linkage Misadjusted. 2. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if
worn or damaged.
3. Governor/Valve Body, Governor Valve
Stuck Closed; Loose Output Shaft
Support or Governor Housing Bolts,
Leaking Seal Rings or Valve Body
Problem (i.e., Stuck 1- 2 Shift Valve/Gov.
Plug).3. Check line and governor pressures to
determine cause. Correct as required.
4. Front Band Out of Adjustment . 4. Adjust Band.
5. Clutch or Servo Malfunction. 5. Air pressure check operation of
clutches and bands. Repair faulty
component.
CREEPS IN NEUTRAL 1. Gearshift Linkage Misadjusted. 1. Adjust linkage.
2. Rear Clutch Dragging/Warped Welded. 2. Disassemble and repair.
3. Valve Body Malfunction. 3. Perform hydraulic pressure test to
determine cause and repair as required.
BUZZING NOISE 1. Fluid Level Low 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Misassembled. 2. Route cable away from engine and bell
housing.
3. Valve Body Misassembled. 3. Remove, disassemble, inspect valve
body. Reassemble correctly if necessary.
Replace assembly if valves or springs are
damaged. Check for loose bolts or
screws.
4. Pump Passages Leaking 4. Check pump for porous casting, scores
on mating surfaces and excess rotor
clearance. Repair as required. Loose
pump bolts.
5. Cooling System Cooler Plugged. 5. Flow check cooler circuit. Repair as
needed.
6.Overrunning Clutch Damaged. 6. Replace clutch.
SLIPS IN REVERSE
ONLY1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Gearshift Linkage Misadjusted. 2. Adjust linkage.
3. Rear Band Misadjusted. 3. Adjust band.
4. Rear Band Worn. 4. Replace as required.
5. Hydraulic Pressure Too Low. 5. Perform hydraulic pressure tests to
determine cause.
6. Rear Servo Leaking. 6. Air pressure check clutch-servo
operation and repair as required.
7. Band Linkage Binding. 7. Inspect and repair as required.
21 - 28 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1527 of 2321

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
WHINE/NOISE
RELATED TO ENGINE
SPEED1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Shift Cable Incorrect Routing. 2. Check shift cable for correct routing.
Should not touch engine or bell housing.
TORQUE CONVERTER
LOCKS UP IN
SECOND AND/OR
THIRD GEARLockup Solenoid, Relay or Wiring
Shorted/Open.Test solenoid, relay and wiring for
continuity, shorts or grounds. Replace
solenoid and relay if faulty. Repair wiring
and connectors as necessary.
HARSH 1-2 OR 2-3
SHIFTSLockup Solenoid Malfunction. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly.
NO START IN PARK
OR NEUTRAL1. Gearshift Linkage/Cable Misadjusted. 1. Adjust linkage/cable.
2. Neutral Switch Wire Open/Cut. 2. Check continuity with test lamp. Repair
as required.
3. Neutral Switch Faulty. 3. Refer to service section for test and
replacement procedure.
4. Neutral Switch Connect Faulty. 4. Connectors spread open. Repair.
5. Valve Body Manual Lever Assembly
Bent/Worn/Broken.5. Inspect lever assembly and replace if
damaged.
NO REVERSE (OR
SLIPS IN REVERSE)1. Direct Clutch Pack (front clutch) Worn. 1. Disassemble unit and rebuild clutch
pack.
2. Rear Band Misadjusted. 2. Adjust band.
3. Front Clutch Malfunctioned/Burnt. 3. Air pressure test clutch operation.
Remove and rebuild if necessary.
OIL LEAKS (ITEMS
LISTED REPRESENT
POSSIBLE LEAK
POINTS AND SHOULD
ALL BE CHECKED.1. Fluid Lines and Fittings Loose/Leaks/
Damaged.1. Tighten fittings. If leaks persist, replace
fittings and lines if necessary.
2. Filler Tube (where tube enters case)
Leaks/Damaged.2. Replace tube seal. Inspect tube for
cracks in tube.
3. Pressure Port Plug Loose Loose/
Damaged.3. Tighten to correct torque. Replace plug
or reseal if leak persists.
4. Pan Gasket Leaks. 4. Tighten pan screws to 150 inch
pounds. If leaks persist, replace gasket.
Do no over tighten screws.
5. Valve Body Manual Lever Shaft Seal
Leaks/Worn.5. Replace shaft seal.
6. Rear Bearing Access Plate Leaks. 6. Replace gasket. Tighten screws.
7. Gasket Damaged or Bolts are Loose. 7. Replace bolts or gasket or tighten both.
8. Adapter/Extension Gasket Damaged
Leaks/Damaged.8. Replace gasket.
9. Neutral Switch Leaks/Damaged. 9. Replace switch and gasket.
10. Converter Housing Area Leaks. 10. Check for leaks at seal caused by
worn seal or burr on converter hub
(cutting seal), worn bushing, missing oil
return, oil in front pump housing or hole
plugged. Check for leaks past O-ring seal
on pump or past pump-to-case bolts;
pump housing porous, oil coming out vent
due to overfill or leak past front band shaft
access plug.
21 - 30 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1528 of 2321
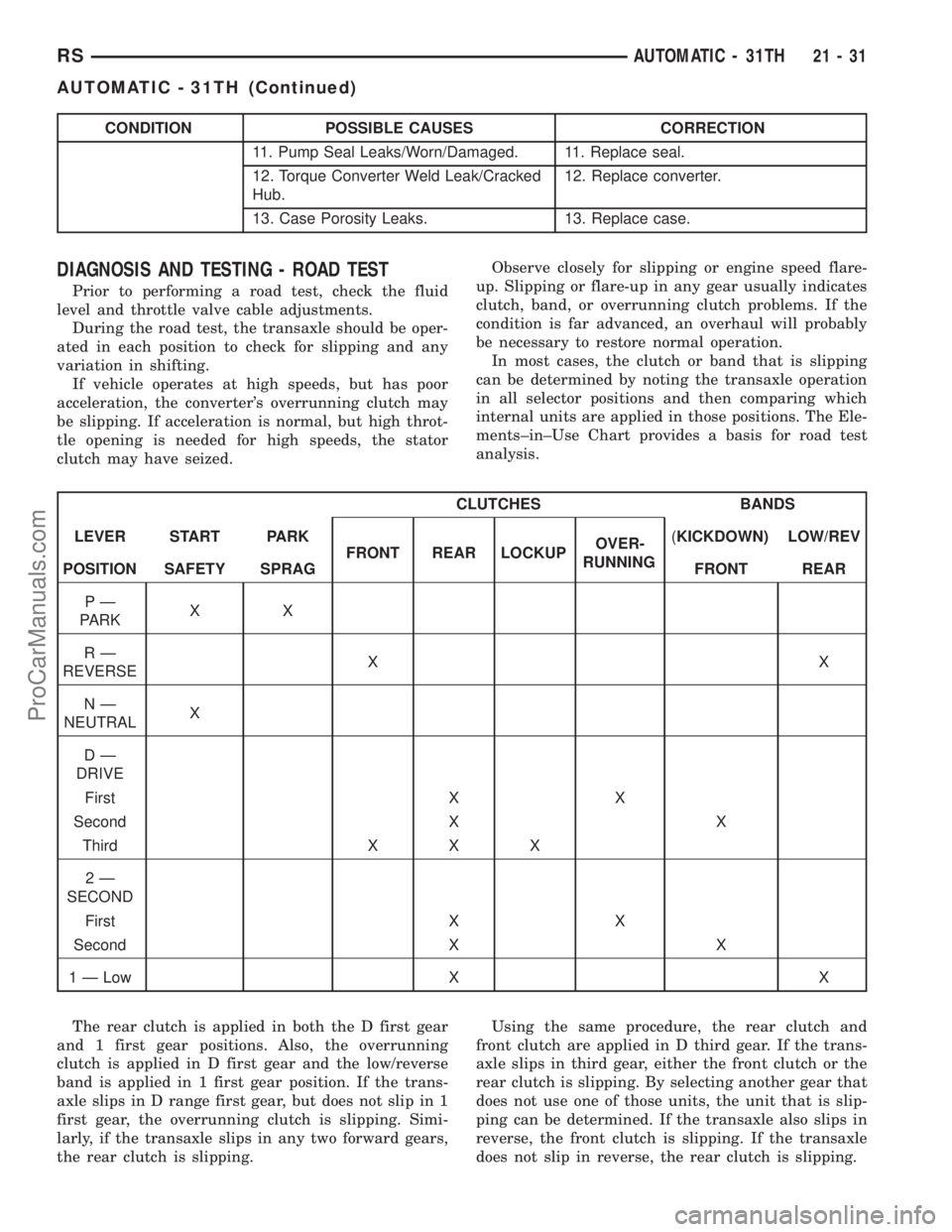
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
11. Pump Seal Leaks/Worn/Damaged. 11. Replace seal.
12. Torque Converter Weld Leak/Cracked
Hub.12. Replace converter.
13. Case Porosity Leaks. 13. Replace case.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, check the fluid
level and throttle valve cable adjustments.
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
If vehicle operates at high speeds, but has poor
acceleration, the converter's overrunning clutch may
be slipping. If acceleration is normal, but high throt-
tle opening is needed for high speeds, the stator
clutch may have seized.Observe closely for slipping or engine speed flare-
up. Slipping or flare-up in any gear usually indicates
clutch, band, or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is far advanced, an overhaul will probably
be necessary to restore normal operation.
In most cases, the clutch or band that is slipping
can be determined by noting the transaxle operation
in all selector positions and then comparing which
internal units are applied in those positions. The Ele-
ments±in±Use Chart provides a basis for road test
analysis.
CLUTCHES BANDS
LEVER START PARK
FRONT REAR LOCKUPOVER-
RUNNING(KICKDOWN) LOW/REV
POSITION SAFETY SPRAG FRONT REAR
PÐ
PARKXX
RÐ
REVERSEXX
NÐ
NEUTRALX
DÐ
DRIVE
First X X
Second X X
Third X X X
2Ð
SECOND
First X X
Second X X
1 Ð Low X X
The rear clutch is applied in both the D first gear
and 1 first gear positions. Also, the overrunning
clutch is applied in D first gear and the low/reverse
band is applied in 1 first gear position. If the trans-
axle slips in D range first gear, but does not slip in 1
first gear, the overrunning clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the transaxle slips in any two forward gears,
the rear clutch is slipping.Using the same procedure, the rear clutch and
front clutch are applied in D third gear. If the trans-
axle slips in third gear, either the front clutch or the
rear clutch is slipping. By selecting another gear that
does not use one of those units, the unit that is slip-
ping can be determined. If the transaxle also slips in
reverse, the front clutch is slipping. If the transaxle
does not slip in reverse, the rear clutch is slipping.
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21-31
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1529 of 2321

The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit that slips and to confirm proper operation of
good units. Road testing can usually diagnose slip-
ping units, although the actual cause of the problem
may not be detected. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
Therefore, unless the condition is obvious, the
transaxle should never be disassembled until hydrau-
lic pressure tests have been performed.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most transaxle problems.
Before performing pressure tests, check fluid level
and condition, as well as control cable adjustments.
Fluid must be at operating temperature (150-200
degrees F.).
Install an engine tachometer. Raise vehicle on a
hoist that allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read.
Disconnect throttle cable and shift cable from
transaxle levers so they can be controlled from out-
side the vehicle.
Attach 100 psi gauges (C-3292) to ports required
for test being conducted. A 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP)
is required for reverse pressure test at rear servo.
Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Test Port Locations
1 - ACCUMULATOR VENT
2 - MANUAL THROTTLE LEVER SHAFT
3 - MANUAL SHIFT LEVER SHAFT
4 - LOW-REVERSE PRESSURE
5 - GOVERNER PRESSURE (BELOW DIFFERENTIAL COVER
ON RIGHT SIDE)
6 - LINE PRESSURE
7 - KICKDOWN APPLY AT ACCUMULATOR8 - TO COOLER
9 - KICKDOWN RELEASE (FRONT CLUTCH)
10 - KICKDOWN APPLY
11 - CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CONNECTOR
12 - FROM COOLER
13 - KICKDOWN BAND ADJUSTING SCREW
21 - 32 AUTOMATIC - 31THRS
AUTOMATIC - 31TH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com