2001 DODGE RAM check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 1571 of 2889

If a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) has been stored
for ªdecreased engine performance due to high injec-
tion pump fuel temperatureº, the overflow valve may
be stuck in closed position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - OVERFLOW VALVE
Fuel volume from the fuel transfer (lift) pump will
always provide more fuel than the fuel injection
pump requires. The overflow valve (a check valve) is
used to route excess fuel through the fuel return line
and back to the fuel tank. Approximately 70% of sup-
plied fuel is returned to the fuel tank. The valve is
located on the side of the injection pump (Fig. 59). It
is also used to connect the fuel return line (banjo fit-
ting) to the fuel injection pump. The valve opens at
approximately 97 kPa (14 psi). If the check valve
within the assembly is sticking, low engine power or
hard starting may result.
If a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) has been stored
for ªdecreased engine performance due to high injec-
tion pump fuel temperatureº, the overflow valve may
be stuck in closed position.
A rubber tipped blow gun with regulated air line
pressure is needed for this test.
(1) Clean area around overflow valve and fuel
return line at injection pump before removal.(2) Remove valve from pump and banjo fitting.
(3) Discard old sealing gaskets.
(4) Set regulated air pressure to approximately 97
kPa (14±16 psi).
(5) Using blow gun, apply pressure to overflow
valve inlet end (end that goes into injection pump).
(6) Internal check valve should release, and air
should pass through valve at 97 kPa (14±16 psi). If
not, replace valve.
(7) Reduce regulated air pressure to 10 psi and
observe valve. Valve should stay shut. If not, replace
valve.
(8) Install new sealing gaskets to valve.
(9) Install valve through banjo fitting and into
pump.
(10) Tighten to 30 N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
REMOVAL
The overflow valve (pressure relief valve) is located
at the outside of fuel injection pump (Fig. 60). It con-
nects the fuel return line (banjo fitting) to the pump.
The valve has no internal serviceable parts and must
be replaced as an assembly. Two sealing gaskets are
used. One gasket is located between pump and banjo
fitting. The other is located between the banjo fitting
and end of valve.
Fig. 58 Overflow Valve Location
1 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 - FUEL RETURN LINE
3 - BANJO BOLT (TEST PORT FITTING)
4 - OVERFLOW VALVE
5 - BANJO FITTING
Fig. 59 Overflow Valve Location
1 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 - FUEL RETURN LINE
3 - BANJO BOLT (TEST PORT FITTING)
4 - OVERFLOW VALVE
5 - BANJO FITTING
14 - 84 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
OVERFLOW VALVE (Continued)
Page 1573 of 2889

FUEL DRAIN MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The fuel drain manifold is actually a rifled passage
within the cylinder head (Fig. 62).
OPERATION
When the engine is running, and during injection, a
small amount of fuel flows past the injector nozzle and
is not injected into the combustion chamber. This fuel
is used to lubricate the fuel injectors. Excess fuel
drains into the fuel drain manifold (or passage). Fuel is
drained from this passage into a line at the rear of the
cylinder head (Fig. 62). After exiting the cylinder head,
fuel is routed (returned) back to the fuel tank. A ªTº is
installed into the fuel return line (Fig. 62). This ªTº is
used to allow excess fuel from the injection pump to be
returned into the fuel tank. A one-way check valve
within the overflow valve prevents fuel (from the fuel
drain manifold) from entering the fuel injection pump.
Asmallamount of fuel is returned from the fuel
injectors, while alargeamount (about 70% of sup-
plied fuel) is returned from the fuel injection pump.
REMOVAL
The fuel drain manifold (line) connects a fuel
return passage within the cylinder head to a ªTº fit-
ting on the fuel return line. It is located at the rear
of the cylinder head.(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Remove starter motor. Refer to Group 8B for
procedures.
(3) Disconnect fitting at ªTº (Fig. 63).
(4) Remove banjo bolt at rear of cylinder head.
Discard old sealing washers.
(5) Remove fuel line from vehicle.
(6) Clean connection at rear of cylinder head
before line installation.
INSTALLATION
The fuel drain manifold (line) connects a fuel
return passage within the cylinder head to a ªTº fit-
ting on the fuel return line. It is located at the rear
of the cylinder head.
Servicing fuel return components will not require
air bleeding.
(1) Using new sealing washers, assemble banjo
bolt to fuel line.
(2) Position line to engine and loosely tighten fas-
teners.
(3)
Tighten banjo bolt to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Tighten fitting at ªTº to 12 N´m (106 in. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Install starter motor. Refer to 8, Starter for
procedures.
(6) Connect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
Fig. 62 Fuel Drain Manifold Passage
1 - REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
2 - BANJO FITTING/BOLT
3 - FUEL RETURN TO TANK
4 - FUEL RETURN LINES
5 - FUEL RETURN LINE FROM PUMP OVERFLOW VALVE
6 - FUEL DRAIN MANIFOLD PASSAGE
7 - ªTº
Fig. 63 Fuel Return Line at Rear of Cylinder Head
1 - REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
2 - BANJO FITTING/BOLT
3 - FUEL RETURN TO TANK
4 - FUEL RETURN LINES
5 - FUEL RETURN LINE FROM PUMP OVERFLOW VALVE
6 - FUEL DRAIN MANIFOLD PASSAGE
7 - ªTº
14 - 86 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
Page 1576 of 2889

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BOOST PRESSURE
Two pressure gauges attached at two different
points are required for this test.(1) Obtain two 6828 fuel pressure test gauges
(equivalent gauges are OK).Gauge Consistency
Test:Connect the gauges together to a common pres-
sure source and verify pressure consistency of both
gauges. Do this consistency test at approximately 206
kPa (30 psi). If pressures are different, they can still
be used for test. Note and record differences in pres-
sures before testing. Make adjustments as necessary.
(2) Remove 3/4º pipe plug fitting at rear of intake
manifold (Fig. 2). Temporarily replace this fitting
with fitting reducer to adapt to pressure gauge.
Note: This pipe plug is located to front of MAP
sensor. Do not remove plug to rear of MAP sen-
sor. This is a COOLANT passage plug.
(3) Loosen hose clamp and disconnect rubber sig-
nal line (Fig. 3) from 1/8º brass fitting at front of tur-
bocharger.
(4) Remove 1/8º brass fitting (Fig. 3) from turbo-
charger. Temporarily replace this fitting with a 1/8º
ªTº fitting to adapt to pressure gauge.
(5) Reattach signal line to temporary ªTº.
(6) Attach first pressure gauge to intake manifold
fitting.
(7) Attach second pressure gauge to ªTº fitting at
turbocharger.
Engine must be at rated RPM and full load for the
test.
If gauge pressure differential is greater than 3 psi
(6 in. Hg), check intercooler and associated piping for
restrictions, plugging or damage.
Maximum pressure at intake manifold (rated rpm
and load) is 36±37 in/hg63 in/hg (17.7±18.2 psi6
1.5 psi).
Wastegate should open at no higher than 38.7
in/hg (19 psi) at wide open throttle, full load. If
wastegate is out of adjustment, a DTC may have
been set. Refer to Wastegate Adjustment in Engines
for adjustment procedures.
Fig. 2 Boost Pressure Test at Intake Manifold
1 - REAR OF INTAKE MANIFOLD
2 - 3/49PIPE PLUG
Fig. 3 Boost Pressure Test at Turbocharger
1 - TURBOCHARGER
2 - 1/89FITTING
3 - SIGNAL LINE
4 - WASTEGATE ACTUATOR
5 - CONTROL ROD
6 - OIL SUPPLY LINE
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 89
FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1582 of 2889

Always cover or cap any open fuel connections before
a fuel system repair is performed.
Each fuel injector connector tube contains an edge
filter (Fig. 13) that breaks up small contaminants
that enter the injector. The edge filter uses the injec-
tors pulsating high-pressure to break up most parti-
cles so they are small enough to pass through the
injector.The edge filters are not a substitute for
proper cleaning and covering of all fuel system
components during repair.
The bottom of each fuel injector is sealed to the
cylinder head with a1.5mmthick copper shim (gas-
ket) (Fig. 12). The correct thickness shim must
always be re-installed after removing an injector.
Fuel pressure in the injector circuit decreases after
injection. The injector needle valve is immediately
closed by the needle valve spring and fuel flow into
the combustion chamber is stopped. Exhaust gases
are prevented from entering the injector nozzle by
the needle valve.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐFUEL INJECTOR
TEST
The fuel injectors are located in the top of the cylin-
der head between the intake/exhaust valves (Fig. 14).
A leaking fuel injector can cause fuel knock, poor
performance, black smoke, poor fuel economy and
rough engine idle. If fuel injector needle valve does
not operate properly, engine may misfire and produce
low power.
A leak in injection pump-to-injector high-pressure
fuel line can cause many of same symptoms as mal-
functioning injector. Inspect for leaks in high-pressure
lines before checking for malfunctioning fuel injector.
WARNING: THE INJECTION PUMP SUPPLIES HIGH-
PRESSURE FUEL OF UP TO APPROXIMATELY
120,000 kPa (17,400 psi) TO EACH INDIVIDUAL
INJECTOR THROUGH HIGH-PRESSURE LINES. FUEL
UNDER THIS AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENE-
TRATE SKIN AND CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY. WEAR
SAFETY GOGGLES AND ADEQUATE PROTECTIVE
CLOTHING. AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL SPRAY
WHEN BLEEDING HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES.
WARNING: DO NOT BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM OF A HOT ENGINE. DO NOT ALLOW FUEL TO
SPRAY ONTO EXHAUST MANIFOLD WHEN BLEED-
ING AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM.
(1) To determine which fuel injector is malfunc-
tioning, run engine and isolate each cylinder using
DRB scan tool.The DRB scan tool lists the injec-
tor firing order in both cylinder numerical
order (1±2±3±4±5±6), and actual firing order
(1±5±3±6±2±4).
(2) Note RPM drop for each cylinder. As an alter-
native, loosen high-pressure fuel line fitting at fuel
injector connector tube (Fig. 15). Listen for a change
in engine speed. After testing, tighten line fitting to
40 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque. If engine speed drops,
injector was operating normally. If engine speed
remains same, injector may be malfunctioning. Test
all injectors in same manner one at a time.
Fig. 14 Fuel Injector Connections
1 - CONNECTOR
2 - O-RING
3 - FERRULE
4 - FITTING
5 - FUEL LINE
6 - INJECTOR
Fig. 15 Inspecting Injector Operation
1 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINE
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 95
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1583 of 2889
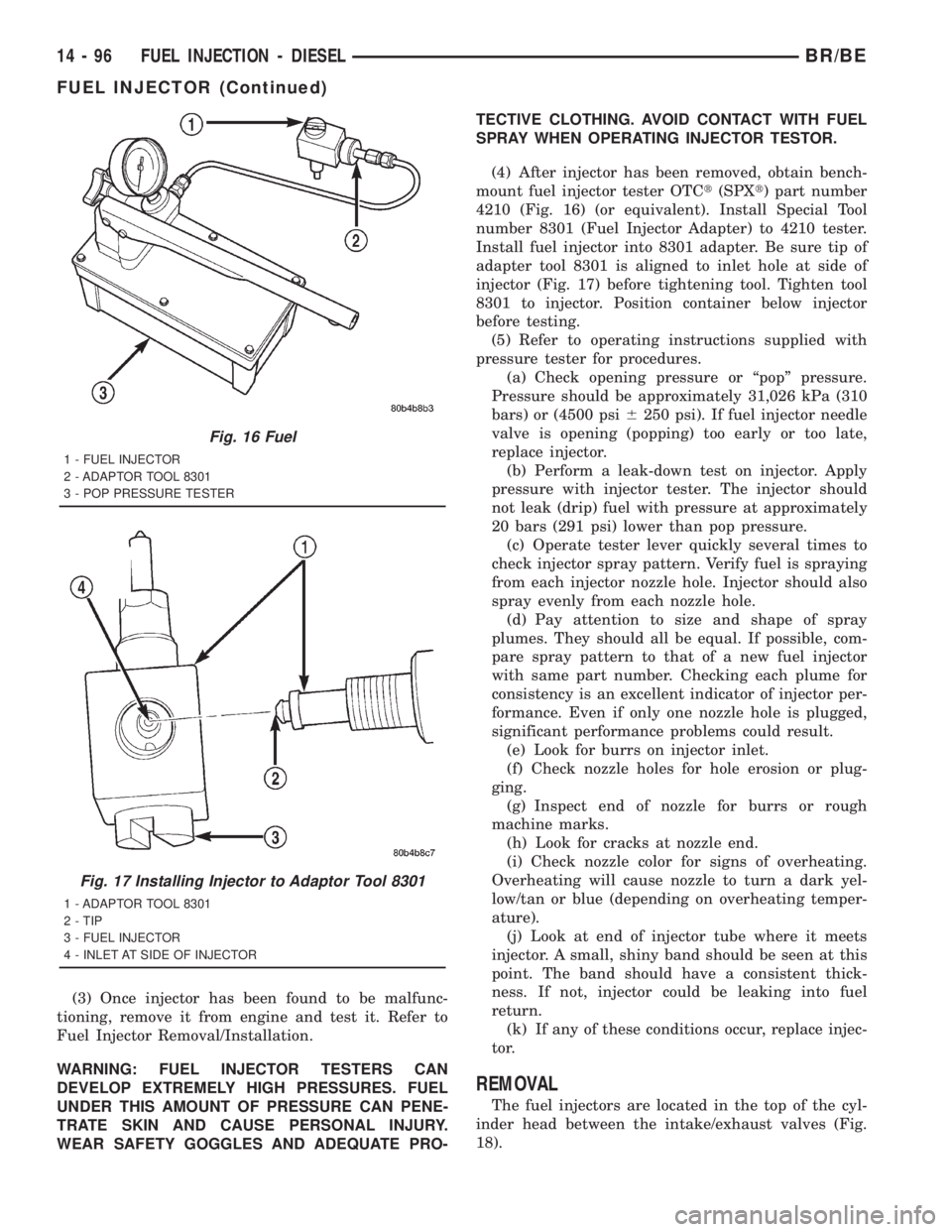
(3) Once injector has been found to be malfunc-
tioning, remove it from engine and test it. Refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
WARNING: FUEL INJECTOR TESTERS CAN
DEVELOP EXTREMELY HIGH PRESSURES. FUEL
UNDER THIS AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENE-
TRATE SKIN AND CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY.
WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES AND ADEQUATE PRO-TECTIVE CLOTHING. AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL
SPRAY WHEN OPERATING INJECTOR TESTOR.
(4) After injector has been removed, obtain bench-
mount fuel injector tester OTCt(SPXt) part number
4210 (Fig. 16) (or equivalent). Install Special Tool
number 8301 (Fuel Injector Adapter) to 4210 tester.
Install fuel injector into 8301 adapter. Be sure tip of
adapter tool 8301 is aligned to inlet hole at side of
injector (Fig. 17) before tightening tool. Tighten tool
8301 to injector. Position container below injector
before testing.
(5) Refer to operating instructions supplied with
pressure tester for procedures.
(a) Check opening pressure or ªpopº pressure.
Pressure should be approximately 31,026 kPa (310
bars) or (4500 psi6250 psi). If fuel injector needle
valve is opening (popping) too early or too late,
replace injector.
(b) Perform a leak-down test on injector. Apply
pressure with injector tester. The injector should
not leak (drip) fuel with pressure at approximately
20 bars (291 psi) lower than pop pressure.
(c) Operate tester lever quickly several times to
check injector spray pattern. Verify fuel is spraying
from each injector nozzle hole. Injector should also
spray evenly from each nozzle hole.
(d) Pay attention to size and shape of spray
plumes. They should all be equal. If possible, com-
pare spray pattern to that of a new fuel injector
with same part number. Checking each plume for
consistency is an excellent indicator of injector per-
formance. Even if only one nozzle hole is plugged,
significant performance problems could result.
(e) Look for burrs on injector inlet.
(f) Check nozzle holes for hole erosion or plug-
ging.
(g) Inspect end of nozzle for burrs or rough
machine marks.
(h) Look for cracks at nozzle end.
(i) Check nozzle color for signs of overheating.
Overheating will cause nozzle to turn a dark yel-
low/tan or blue (depending on overheating temper-
ature).
(j) Look at end of injector tube where it meets
injector. A small, shiny band should be seen at this
point. The band should have a consistent thick-
ness. If not, injector could be leaking into fuel
return.
(k) If any of these conditions occur, replace injec-
tor.
REMOVAL
The fuel injectors are located in the top of the cyl-
inder head between the intake/exhaust valves (Fig.
18).
Fig. 16 Fuel
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - ADAPTOR TOOL 8301
3 - POP PRESSURE TESTER
Fig. 17 Installing Injector to Adaptor Tool 8301
1 - ADAPTOR TOOL 8301
2 - TIP
3 - FUEL INJECTOR
4 - INLET AT SIDE OF INJECTOR
14 - 96 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1587 of 2889

OPERATION
The sensor located in the Bosch VP44 fuel injection
pump is used to check fuel temperature within the
injection pump and to set a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) if a specific high fuel temperature has been
reached. If high temperature has been reached,
engine power will be de-rated by the Engine Control
Module (ECM).
The sensor located in the top of the fuel filter hous-
ing is used to control the fuel heater element. Refer
to Fuel Heater Description and Operation for addi-
tional information.
INTAKE AIR HEATER
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold air heater element assembly
is located in the top of the intake manifold (Fig. 25).
OPERATION
The air heater elements are used to heat incoming
air to the intake manifold. This is done to help
engine starting and improve driveability with cool or
cold outside temperatures.
Electrical supply for the 2 air heater elements is
controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM)
through the 2 air heater relays. Refer to Intake Man-
ifold Air Heater Relays for more information.
Two heavy-duty cables connect the 2 air heater ele-
ments to the 2 air heater relays. Each of these cables will
supply approximately 95 amps at 12 volts to an individ-
ual heating element within the heater block assembly.
Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual for an electrical operation and complete
description of the intake heaters, including pre-heat
and post-heat cycles.
REMOVAL
The 2 intake manifold air heater elements are
attached to a metal block located at the top of the
intake manifold (Fig. 26). If servicing either of the
heater elements, the entire block/element assembly
must be replaced.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Disconnect clamp from rubber hose at air
intake housing.
(3) Disconnect rubber hose at air intake housing.
(4) Remove engine oil dipstick tube mounting bolt
(Fig. 28). Position dipstick tube to the side.
(5) Disconnect heater electrical cables at cable
mounting studs (Fig. 28).
(6) Disconnect ground cable bolt and ground cable
from housing (Fig. 27).
(7) Remove 4 housing bolts (Fig. 28).
(8) Remove air intake housing from top of heater
elements.
(9) Remove heater element assembly from intake
manifold.
(10) Clean old gasket material from air intake
housing and intake manifold.
(11) Clean old gasket material from both ends of
heater block (Fig. 26).
Fig. 25 Air Heater Elements Location
1 - AIR HEATER ELEMENTS
2 - LOWER GASKET
3 - BLOCK
4 - UPPER GASKET
Fig. 26 Intake Manifold Air Heater Element Location
1 - AIR HEATER ELEMENTS
2 - LOWER GASKET
3 - BLOCK
4 - UPPER GASKET
14 - 100 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1592 of 2889

(8) Squeeze 2 pinch tabs on sides of throttle cable
at mounting bracket (Fig. 37) and push cable rear-
ward out of bracket .
INSTALLATION
(1) Install cable through mounting hole on cable
mounting bracket (Fig. 37). Cable snaps into bracket.
Be sure 2 pinch tabs are secure.
(2) Using large pliers, connect cable end socket to
throttle lever ball (snaps on).
(3) Install remaining cable housing end into and
through dash panel opening (snaps into position).
The two plastic pinch tabs (Fig. 21) should lock cable
to dash panel.
(4) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Install throttle cable core wire and plastic cableretainer into and through upper end of pedal arm
(the plastic retainer is snapped into pedal arm).
When installing plastic retainer to accelerator pedal
arm, note index tab on pedal arm (Fig. 21). Align
index slot on plastic cable retainer to this index tab.
(5) Connect negative battery cables to both batter-
ies.
(6) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
(7) Install cable/lever cover.
Fig. 36 Cable/Lever/Throttle Linkage Cover
1 - CABLE/LEVER/LINKAGE COVER
2 - PUSH UP LOWER TAB
3 - SCREWS/CLIPS (2)
4 - TAB PUSH HERE
Fig. 37 Throttle Cable at Throttle Lever
1 - PINCH (2) TABS
2 - CABLE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - PINCH TABS (2)
4 - OFF
5 - THROTTLE CABLE
6 - THROTTLE LEVER
7 - THROTTLE LEVER PIN
8 - OFF
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 105
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE (Continued)
Page 1597 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
VEHICLE PULLS OR LEADS TO
ONE SIDE.1. Tire Pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Radial tire lead. 2. Rotate tires.
3. Brakes dragging. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Wheel alignment. 4. Align front end.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING
FLOW AND PRESSURE
The following procedure is used to test the opera-
tion of the power steering system on the vehicle. This
test will provide the flow rate of the power steering
pump along with the maximum relief pressure. Per-
form test any time a power steering system problem
is present. This test will determine if the power
steering pump or power steering gear is not function-
ing properly. The following pressure and flow test is
performed using Power Steering Analyzer Tool kit
6815 (Fig. 2) and Adapter Kit 6893.
POWER STEERING ANALYZER INSTALLATION
WITHOUT HYDRAULIC BOOSTER
(1) Remove the high pressure hose from the power
steering pump.
(2) Connect Tube 6844 into the pump hose fitting.(3) Connect pressure gauge hose from the Power
Steering Analyzer to Tube 6844.
(4) Connect Adapter 6826 to Power Steering Ana-
lyzer test valve end.
(5) Connect the power steering hose from the
steering gear to Adapter 6826.
WITH HYDRAULIC BOOSTER
(1) Remove high pressure hose which goes to the
steering gear from the tube coming out of the booster.
(2) Connect Adapter 6826 to the Power Steering
Analyzer pressure gauge hose.
(3) Connect pressure gauge hose to the tube com-
ing out of the booster.
(4) Connect Tube 6844 to the steering gear hose
and Power Steering Analyzer test valve end.
FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
(1) Check belt condition and tension.
(2) Open the test valve completely.
(3) Start engine and let idle long enough to circu-
late power steering fluid through flow/pressure test
gauge and to get air out of the fluid. Then shut off
engine.
(4) Check fluid level, add fluid as necessary. Start
engine again and let idle.
(5) Gauge should read below 1034 kPa (150 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure reading should be in
the range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).
(6) Increase the engine speed to 1500 RPM and
read the flow meter. If the flow rate (GPM) is below
specification (Refer to pump specification chart for
GPM) the pump should be replaced.
CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than three seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
Fig. 2 Pressure Test Gauge
1 - GAUGE HOSE
2 - TUBE
3 - ADAPTER FITTINGS
4 - ANALYZER
19 - 4 STEERINGBR/BE
STEERING (Continued)