2001 DODGE RAM warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 1507 of 2889

(6)Open fuel fill door and remove screws mounting
fuel filler tube assembly to body. Do not disconnect
rubber fuel fill or vent hoses from tank at this time.
(7) Place a transmission jack under center of fuel
tank. Apply a slight amount of pressure to fuel tank
with transmission jack.
(8) Remove fuel tank mounting strap nuts from
mounting strap studs (Fig. 35). If equipped, remove
fuel tank shield bolts.
(9) Lower fuel tank only enough to allow access to
top of tank. The 2 tank fittings (where rubber fuel fill
and vent hose connections are made) must be posi-
tioned above tank level. Rotate tank slightly to allow
these fittings to be above tank level.
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(10) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect rubber fuel vent hose at fuel tank (Fig. 35)
(vent hose is the smallest of 2 hoses). Position fuel
siphoning/drain hose into this fitting at tank. Drain
fuel into an approved portable holding tank or a
properly labeled gasoline (or diesel fuel) safety con-
tainer.
(11) Disconnect rubber fuel fill hose at fuel tank
(Fig. 35).
(12)Gas Powered Engines:
(a) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect wiring harness connector from electrical
connector at top of fuel pump module (Fig. 36) or
(Fig. 37).
(b) If equipped with 26 or 34 gallon fuel tank,
two EVAP lines are connected to rollover valves.
Disconnect EVAP line from rollover valve at top of
module (Fig. 36). Disconnect other EVAP line from
rollover valve near rear of tank (Fig. 36).
(c) If equipped with 35 gallon fuel tank, two
EVAP lines are connected to rollover valves. Dis-
connect EVAP lines from rollover valves at top-
front and top-rear of fuel tank (Fig. 38).
(d) Disconnect fuel supply line at fuel filter/fuel
pressure regulator supply fitting (Fig. 36) or (Fig.
37). Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings for proce-
dures.
(13)Diesel Powered Engines:
(a) While working over left rear tire/wheel, dis-
connect wiring harness connector from electrical
connector at top of fuel tank module (Fig. 39).
(b) Disconnect fuel supply and fuel return lines
at the fuel tank module fittings (Fig. 39). Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures.
(14) Gasoline Engines: If fuel pump module
removal is necessary, refer to Fuel Pump Module
Removal/Installation in this group. Diesel Engines: If
fuel tank module removal is necessary, refer to Fuel
Tank Module Removal/Installation in this group.
INSTALLATION
(1) Gasoline Engines: If fuel pump module is being
installed, refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Instal-
lation in this group. Diesel Engines: If fuel tank mod-
ule is being installed, refer to Fuel Tank Module
Removal/Installation in this group.
(2) Place fuel tank on top of transmission jack.
(3) Install rubber fill and vent lines to tank.
Tighten hose clamps to 2.3 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Raise tank into position while guiding fill and
vent hoses to body. Raise tank only enough to allow
access to top of tank.
(5)Gas Powered Engines:
(a) Connect electrical connector to fuel pump
module.
(b) Connect EVAP hoses at rollover valves.
(c) Connect fuel supply line at fuel filter/fuel
pressure regulator. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings
for procedures.
(6)Diesel Powered Engines:
(a) Connect electrical connector to fuel tank
module.
Fig. 35 Fuel Tank MountingÐTypical
1 - STRAP MOUNTING STUDS (AT FRAME)
2 - FUEL FILL HOSE
3 - FUEL VENT HOSE
4 - STRAP MOUNTING NUTS (2)
5 - FUEL TANK STRAPS (2)
6 - FUEL TANK
7 - CLAMPS
14 - 20 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1509 of 2889

(7) Connect two mounting straps and mounting
strap nuts.
(8) Tighten strap nuts to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
torque. Do not over tighten retaining strap nuts.
(9) Remove transmission jack.
(10) Connect fuel filler tube assembly to body.
(11) If equipped, connect grounding wire (strap)
and screw.
(12) Refill fuel tank and inspect all hoses and lines
for leaks.
(13)
Connect negative battery cable(s) to battery(s).
INLET FILTER
REMOVAL
The fuel pump inlet filter (strainer) is located on
the bottom of the fuel pump module (Fig. 40). The
fuel pump module is located inside of fuel tank.
(1) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal/
Installation.
(2) Remove fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(3) Remove filter by carefully prying 2 lock tabs at
bottom of module with 2 screwdrivers. Filter is
snapped to module.
(4) Clean bottom of pump module.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pump inlet filter (strainer) is located on
the bottom of the fuel pump module (Fig. 40). The
fuel pump module is located inside of fuel tank.
(1) Snap new filter to bottom of module. Be sure
o-ring is in correct position.(2) Install fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module Removal/Installation.
(3) Install fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal/
Installation.
QUICK CONNECT FITTING
DESCRIPTION
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Some are equipped with
safety latch clips. Some may require the use of a spe-
cial tool for disconnection and removal. Refer to
Quick-Connect Fittings Removal/Installation for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, clips)
of quick-connect fittings are not serviced sepa-
rately, but new plastic spacers are available for
some types. If service parts are not available, do
not attempt to repair the damaged fitting or fuel line
(tube). If repair is necessary, replace the complete
fuel line (tube) assembly.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - QUICK-CONNECT
FITTINGS
Also refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps.
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components, lines and
tubes. These are: a single-tab type, a two-tab type or
a plastic retainer ring type. Safety latch clips are
used on certain components/lines. Certain fittings
may require use of a special tool for disconnection.
DISCONNECTING
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSE,
FITTING OR LINE, FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST
BE RELEASED. REFER TO FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of some types of quick-connect fitting are not
serviced separately. If service parts are not avail-
able, do not attempt to repair a damaged fitting or
fuel line. If repair is necessary, replace complete
fuel line assembly.
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
Fig. 40 Fuel Pump Inlet Filter
1 - FUEL PUMP INLET FILTER
2 - LOCK TABS (2)
3 - FUEL PUMP MODULE (BOTTOM)
14 - 22 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 1513 of 2889
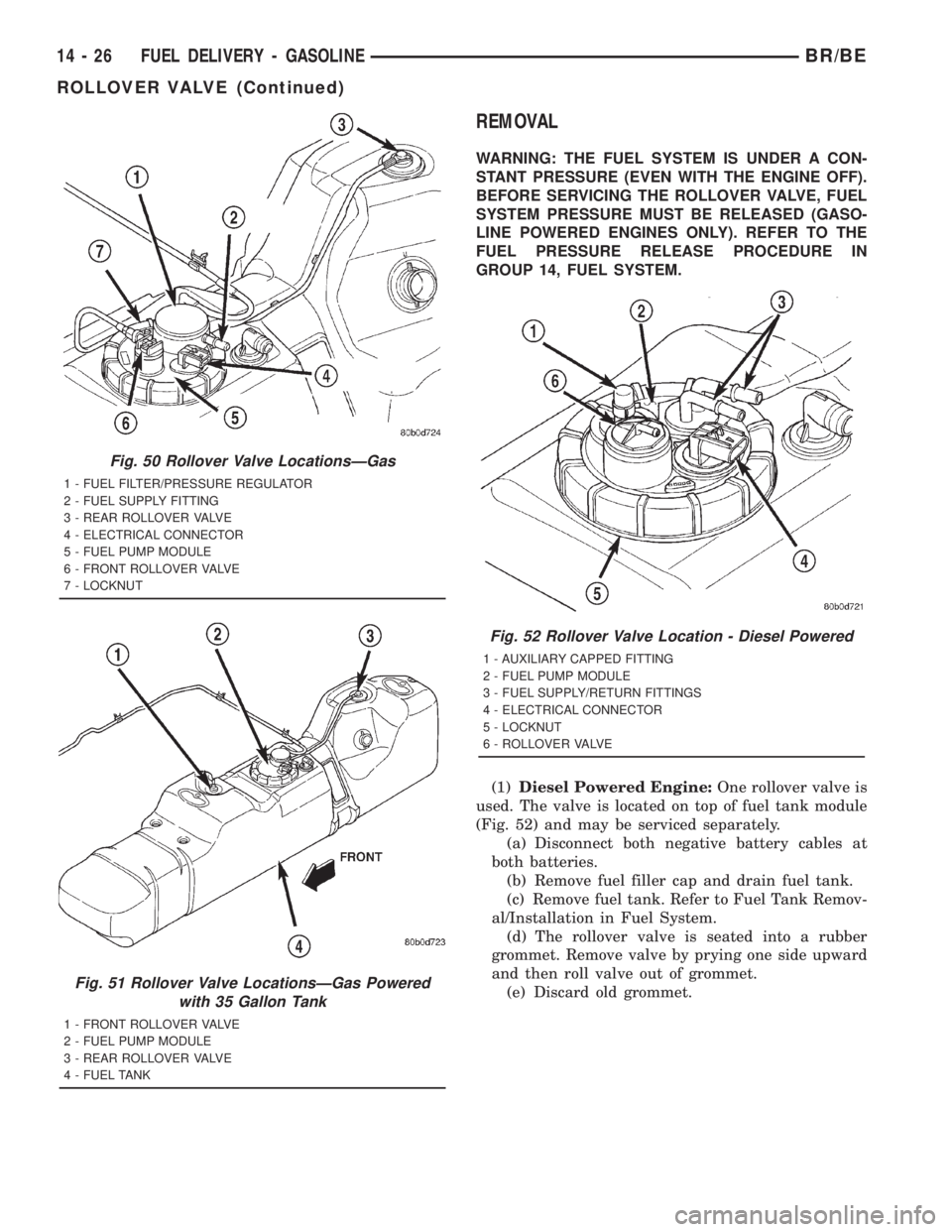
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE ROLLOVER VALVE, FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED (GASO-
LINE POWERED ENGINES ONLY). REFER TO THE
FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
GROUP 14, FUEL SYSTEM.
(1)Diesel Powered Engine:One rollover valve is
used. The valve is located on top of fuel tank module
(Fig. 52) and may be serviced separately.
(a) Disconnect both negative battery cables at
both batteries.
(b) Remove fuel filler cap and drain fuel tank.
(c) Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Remov-
al/Installation in Fuel System.
(d) The rollover valve is seated into a rubber
grommet. Remove valve by prying one side upward
and then roll valve out of grommet.
(e) Discard old grommet.
Fig. 50 Rollover Valve LocationsÐGas
1 - FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 - FUEL SUPPLY FITTING
3 - REAR ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
6 - FRONT ROLLOVER VALVE
7 - LOCKNUT
Fig. 51 Rollover Valve LocationsÐGas Powered
with 35 Gallon Tank
1 - FRONT ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
3 - REAR ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - FUEL TANK
Fig. 52 Rollover Valve Location - Diesel Powered
1 - AUXILIARY CAPPED FITTING
2 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
3 - FUEL SUPPLY/RETURN FITTINGS
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - LOCKNUT
6 - ROLLOVER VALVE
14 - 26 FUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINEBR/BE
ROLLOVER VALVE (Continued)
Page 1535 of 2889

WARNING: THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD, EXHAUST
PIPES AND CATALYTIC CONVERTER BECOME
VERY HOT DURING ENGINE OPERATION. ALLOW
ENGINE TO COOL BEFORE REMOVING OXYGEN
SENSOR.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the wire connector from the O2S
sensor.
CAUTION: When disconnecting the sensor electrical
connector, do not pull directly on wire going into
sensor.
(3) Remove the O2S sensor with an oxygen sensor
removal and installation tool.
INSTALLATION
Threads of new oxygen sensors are factory coated
with anti-seize compound to aid in removal.DO
NOT add any additional anti-seize compound to
the threads of a new oxygen sensor.
(1) Install the O2S sensor. Tighten to 30 N´m (22
ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect the O2S sensor wire connector.
(3) Lower the vehicle.
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
This Powertrain Control Module (PCM) input is
used only on models equipped with aftermarket
Power Take Off (PTO) units.
OPERATION
The input is used only to tell the PCM that the
PTO has been engaged. The PCM will disable (tem-
porarily shut down) certain OBD II diagnostic trou-
ble codes when the PTO is engaged.
When the aftermarket PTO switch has been
engaged, a 12V + signal is sent through circuit G113
to PCM pin A13. The PCM will then sense and deter-
mine that the PTO has been activated.
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The throttle body is located on the intake manifold.
Fuel does not enter the intake manifold through the
throttle body. Fuel is sprayed into the manifold by
the fuel injectors.
OPERATION
Filtered air from the air cleaner enters the intake
manifold through the throttle body. The throttle body
contains an air control passage controlled by an Idle
Air Control (IAC) motor. The air control passage is
used to supply air for idle conditions. A throttle valve
(plate) is used to supply air for above idle conditions.
Certain sensors are attached to the throttle body.
The accelerator pedal cable, speed control cable and
transmission control cable (when equipped) are con-
nected to the throttle body linkage arm.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the PCM.
REMOVAL - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
(1) Remove the air cleaner.
(2) Disconnect throttle body electrical connectors
at MAP sensor, IAC motor and TPS (Fig. 41).
(3) Remove vacuum line at throttle body.
(4) Remove all control cables from throttle body
(lever) arm. Refer to the Accelerator Pedal and Throt-
tle Cable section of this group for additional informa-
tion.
Fig. 41 Sensor Electrical ConnectorsÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
EnginesÐTypical
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
3 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
O2 SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1543 of 2889

²Fuel filter/water separator
²Fuel heater
²Fuel heater relay
²Fuel transfer (lift) pump
²Fuel injection pump
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel heater temperature sensor
²Fuel tank
²Fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²Fuel tank filler tube cap
²Fuel tank module containing the rollover valve,
fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) and a sep-
arate fuel filter located at bottom of tank module
²Fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²High-pressure fuel injector lines
²In-tank fuel filter (at bottom of fuel tank mod-
ule)
²Low-pressure fuel supply lines
²Low-pressure fuel return line
²Overflow valve
²Quick-connect fittings
²Throttle cable
²Water draining
OPERATION
WARNING: HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES DELIVER
DIESEL FUEL UNDER EXTREME PRESSURE FROM
THE INJECTION PUMP TO THE FUEL INJECTORS.
THIS MAY BE AS HIGH AS 120,000 KPA (17,405
PSI). USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING
FOR HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS. INSPECT FOR
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF
CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION PRESSURE
CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF CONTACT IS
MADE WITH THE SKIN.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIR IN FUEL
SYSTEM
Air will enter the fuel system whenever fuel supply
lines, separator filters, injection pump, high-pressure
lines or injectors are removed or disconnected. Air
trapped in the fuel system can result in hard start-
ing, a rough running engine, engine misfire, low
power, excessive smoke and fuel knock. After service
is performed, air must be bled from the system
before starting the engine.Inspect the fuel system from the fuel transfer
pump to the injectors for loose connections. Leaking
fuel is an indicator of loose connections or defective
seals. Air can also enter the fuel system between the
fuel tank and the transfer pump. Inspect the fuel
tank and fuel lines for damage that might allow air
into the system.
For air bleeding, refer to the Air Bleed Procedure.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL SUPPLY
RESTRICTIONS
LOW-PRESSURE LINES
Fuel supply line restrictions or a defective fuel
transfer pump can cause starting problems and pre-
vent engine from accelerating. The starting problems
include; low power and/or white fog like exhaust.
Test all fuel supply lines for restrictions or block-
age. Flush or replace as necessary. Bleed fuel system
of air once a fuel supply line has been replaced. Refer
to Air Bleed Procedure for procedures.
To test for fuel line restrictions, a vacuum restric-
tion test may be performed. Refer to Fuel Transfer
Pump Pressure Test.
HIGH-PRESSURE LINES
Restricted (kinked or bent) high-pressure lines can
cause starting problems, poor engine performance,
engine mis-fire and white smoke from exhaust.
Examine all high-pressure lines for any damage.
Each radius on each high-pressure line must be
smooth and free of any bends or kinks.
Replace damaged, restricted or leaking high-pres-
sure fuel lines with correct replacement line.
CAUTION: All high-pressure fuel lines must be
clamped securely in place in holders. Lines cannot
contact each other or other components. Do not
attempt to weld high-pressure fuel lines or to repair
lines that are damaged. If line is kinked or bent, it
must be replaced. Use only recommended lines
when replacement of high-pressure fuel line is nec-
essary.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - WATER DRAINING
AT FUEL FILTER
Refer to Fuel Filter/Water Separator removal/in-
stallation for procedures.
14 - 56 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1544 of 2889

STANDARD PROCEDURES - CLEANING FUEL
SYSTEM PARTS
CAUTION: Cleanliness cannot be overemphasized
when handling or replacing diesel fuel system com-
ponents. This especially includes the fuel injectors,
high-pressure fuel lines and fuel injection pump.
Very tight tolerances are used with these parts. Dirt
contamination could cause rapid part wear and pos-
sible plugging of fuel injector nozzle tip holes. This
in turn could lead to possible engine misfire.
Always wash/clean any fuel system component
thoroughly before disassembly and then air dry.
Cap or cover any open part after disassembly.
Before assembly, examine each part for dirt, grease
or other contaminants and clean if necessary. When
installing new parts, lubricate them with clean
engine oil or clean diesel fuel only.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - AIR BLEED
A certain amount of air becomes trapped in the
fuel system when fuel system components on the
supply and/or high-pressure side are serviced or
replaced. Primary air bleeding is accomplished using
the electric fuel transfer (lift) pump. If the vehicle
has been allowed to run completely out of fuel, the
fuel injectors must also be bled as the fuel injection
pumpis notself-bleeding (priming).
Servicing or replacing components on the fuel
return side will not require air bleeding.
WARNING: DO NOT BLEED AIR FROM THE FUEL
SYSTEM OF A HOT ENGINE.
(1) Loosen, but do not remove, banjo bolt (test port
fitting) holding low-pressure fuel supply line to side
of fuel injection pump (Fig. 2). Place a shop towel
around banjo fitting to catch excess fuel.
The fuel transfer (lift) pump is self-priming: When
the key is first turned on (without cranking engine),
the pump operates for approximately 2 seconds and
then shuts off. The pump will also operate for up to
25 seconds after the starter is quickly engaged, and
then disengaged without allowing the engine to start.
The pump shuts off immediately if the key is on and
the engine stops running.
(2) Turn key to CRANK position and quickly
release key to ON position before engine starts. This
will operate fuel transfer pump for approximately 25
seconds.
(3) If fuel is not present at fuel supply line after
25 seconds, turn key OFF. Repeat previous step until
fuel is exiting at fuel supply line.(4) Tighten banjo bolt at fuel supply line to 24 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.) torque. Primary air bleeding is now com-
pleted.
(5) Attempt to start engine. If engine will not
start, proceed to following steps.If engine does
start, it may run erratically and be very noisy
for a few minutes. This is a normal condition.
(6)Continue to next step if:
²The vehicle fuel tank has been allowed to run
empty
²The fuel injection pump has been replaced
²High-pressure fuel lines have been replaced
²Vehicle has not been operated after an extended
period
CAUTION: Do not engage the starter motor for more
than 30 seconds at a time. Allow two minutes
between cranking intervals.
(7) Perform previous air bleeding procedure steps
using fuel transfer pump. Be sure fuel is present at
fuel supply line (Fig. 2) before proceeding.
(8) Crank the engine for 30 seconds at a time to
allow air trapped in the injection pump to vent out
the drain manifold.Fig. 2 Fuel Supply Line Banjo Bolt
1 - FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 - FUEL RETURN LINE
3 - BANJO BOLT (TEST PORT FITTING)
4 - OVERFLOW VALVE
5 - BANJO FITTING
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 57
FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1545 of 2889

WARNING: THE FUEL INJECTION PUMP SUPPLIES
EXTREMELY HIGH FUEL PRESSURE TO EACH INDI-
VIDUAL INJECTOR THROUGH THE HIGH-PRES-
SURE LINES. FUEL UNDER THIS AMOUNT OF
PRESSURE CAN PENETRATE THE SKIN AND
CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY. WEAR SAFETY GOG-
GLES AND ADEQUATE PROTECTIVE CLOTHING
AND AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL SPRAY WHEN
BLEEDING HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES.
WARNING: ENGINE MAY START WHILE CRANKING
STARTER MOTOR.
Engine may start, may run erratically and be
very noisy for a few minutes. This is a normal
condition.
(9) Thoroughly clean area around injector fittings
where they join injector connector tubes.
(10) Bleed air by loosening high-pressure fuel line
fittings (Fig. 3) at cylinders number 3, 4 and 5.
(11) Continue bleeding injectors until engine runs
smoothly. It may take a few minutes for engine to
run smooth.
(12) Tighten fuel line(s) at injector(s) to 38 N´m
(28 ft. lbs.) torque.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURESÐDIESEL ENGINES
DESCRIPTION PRESSURE
Fuel Transfer (Lift) Pump Pressure With Engine
RunningMinimum 69 kPa (10 psi)
Fuel Transfer (Lift) Pump Pressure With Engine
CrankingMinimum 48 kPa (7 psi)
Fuel Injector ªPop Offº Pressure 31,026 kPa (310 bars) or (4500 psi6250 psi)
Fuel Injector Leak-Down Pressure Approximately 20 bars (291 psi) lower than pop
pressure
Fuel Pressure Drop Across Fuel Filter Test Ports 34 kPa max. (5 psi. max.) at 2500 rpm (rated rpm)
Overflow Valve Release Pressure 97 kPa max. (14 psi.) at 2500 rpm (rated rpm)
FUEL INJECTOR FIRING ORDERÐDIESEL
1±5±3±6±2±4
Fig. 3 Bleeding High-Pressure Fuel Lines at
Injectors
1 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINE
14 - 58 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL (Continued)
Page 1547 of 2889

REMOVAL
Refer to maintenance schedules in this manual for
recommended fuel filter replacement intervals.
Draining water from fuel filter/water separa-
tor housing:
The housing drain valve (Fig. 5) serves two pur-
poses. One is topartiallydrain filter housing of
excess water. The other is tocompletelydrain hous-
ing for fuel filter, drain valve, heater element or
water-in-fuel sensor replacement.
The filter housing should be drained whenever
water-in-fuel warning lamp remains illuminated.
(Note that lamp will be illuminated for approxi-
mately two seconds when ignition key is initially
placed in ON position for a bulb check).
(1) A drain hose is located at bottom of drain valve
(Fig. 5). Place drain pan under drain hose.
(2)With engine not running,pull drain valve
handle upward to OPEN (DRAIN) position (Fig. 5).
Hold drain valve open until all water and contami-
nants have been removed and clean fuel exits drain
hose.
(3) If drain valve, fuel heater element or Water-In-
Fuel (WIF) sensor is being replaced, drain housing
completely. Dispose of mixture in drain pan according
to applicable regulations.
(4) After draining operation, push valve handle
downward to CLOSE position (Fig. 5).
(5)Fuel Filter Replacement:The fuel filter is
located inside of the fuel filter housing (Fig. 6).
(a) Unscrew and remove fuel filter cap at top of
fuel filter housing (Fig. 5). To unscrew, attach tool
to 6±sided hex center of cap. Do not attempt to
loosen cap at outer edge. The fuel filter cap is
designed to remove filter while pulling up on cap.
(b) Remove o-ring (Fig. 6) from filter cap and
discard.
(c) The filter is retained to the cap with a series
of locking fingers. Carefully pry back a few of the
fingers to unlock filter from cap.
(6)Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor Replacement:
The WIF sensor is located on the side of the fuel fil-
ter housing (Fig. 6).
(a) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor
(Fig. 7).
(b) Unscrew sensor from filter housing.
Fig. 5 Water Drain Valve and Drain Hose
1 - FUEL FILTER CAP
2 - DRAIN VALVE HANDLE
3 - DRAIN HOSE
4 - FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
Fig. 6 Fuel Filter/Water Separator Components
1 - CAP
2 - O-RING
3 - FUEL FILTER
4 - FUEL HEATER ELEMENT
5 - HOUSING
6 - O-RINGS
7 - DRAIN VALVE
8 - FUEL HEATER THERMOSTAT
9 - WATER-IN-FUEL SENSOR
14 - 60 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL FILTER / WATER SEPARATOR (Continued)