2001 DODGE RAM light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 32 of 2889

²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
²Inspect front wheel bearings. Clean and repack,
if required (4x4).
²Inspect engine air cleaner element, replace
as necessary (8.0L only).
*Requires Service Reminder Indicator Light. If so
equipped, these parts are to be replaced at the indi-
cated mileage or when the service reminder indicator
light remains on continuously with the key in the
ªONº position, whichever occurs first.
HEAVY DUTY SCHEDULE ªBº
Follow this schedule if the vehicle is usually oper-
ated under one or more of the following conditions.
²Frequent short trips driving less than 5 miles
(8km)
²Frequent driving in dusty conditions
²Frequent trailer towing
²Extensive idling
²More than 50% of the driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 90ÉF (32ÉC)
3,000 Miles (5 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
6,000 Miles (10 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x4).
9,000 Miles (14 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x2).
12,000 Miles (19 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect engine air cleaner element and air
pump filter, replace as necessary.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid.
Replace filter and adjust bands.³
²Change rear axle fluid.
²Change front axle fluid (4x4).
²Inspect brake linings.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x4).
15,000 Miles (24 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
18,000 Miles (29 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x4).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x2).
²Drain and refill transfer case fluid every 18,000
miles (4x4).
21,000 Miles (34 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
24,000 Miles (38 000 km)
²Change engine oil
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace engine air cleaner element and air
pump filter.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid.
Replace filter and adjust bands.
²Change rear axle fluid.
²Change front axle fluid (4x4).
²Clean and lubricate crankcase inlet air filter
(5.9L).
²Inspect front wheel bearings. Clean and repack,
if required (4x2).
²Inspect brake linings.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x4).
27,000 Miles (43 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x2).
30,000 Miles (48 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect PCV valve, replace as necessary
(5.9L).
²Replace spark plugs.
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x4).
BR/BELUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 19
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 35 of 2889

99,000 Miles (156 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x2).
102,000 Miles (163 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x4).
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
108,000 Miles (173 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect engine air cleaner element and air
pump filter, replace as necessary.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid.
Replace filter and adjust bands.³
²Drain and refill transfer case fluid (4x4).
²Change rear axle fluid.
²Change front axle fluid (4x4).
²Inspect brake linings.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) since last change.
²Lubricate tie rod ends every 3,000 miles (5 000
km).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x4).
²Inspect front wheel bearings (4x2).
*Requires Service Reminder Indicator Light. If so
equipped, these parts are to be replaced at the indi-
cated mileage or when the service reminder indicator
light remains on continuously with the key in the
ªONº position, whichever occurs first.
³Off-the-highway operation, trailer towing, snow
plowing, prolonged operation with heavy loading,
especially in hot weather require the more frequent
transmission service indicated witha³inSchedule
ªBº. Perform these services if you usually operate
your Ram Truck under these conditions.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
DESCRIPTION - MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
Ð 24±VALVE CUMMINS TURBO DIESEL
There are two maintenance schedules that show
proper service for the vehicle.First is ScheduleªA.ºIt lists all the scheduled
maintenance to be performed under ªnormalº operat-
ing conditions.
Second is ScheduleªB.ºIt is a schedule for vehicles
that are operated under the conditions listed at the
beginning of that schedule.
Use the schedule that best describes the driving
conditions.
Where time and mileage are listed, follow the
interval that occurs first.
At Each Stop For Fuel
²Check engine oil level and add as required.
²Check windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
²Clean windshield and wiper blades as required.
²Drain water from fuel filter.
Once A Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect battery and clean and tighten terminals
as required.
²Check fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering, and transmission.
Add fluid as required.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
²Check Filter Mindery. Replace air cleaner
element if necessary.
²Inspect and clean wiper blades. Replace if
required.
At Each Oil Change
²Inspect exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses.
²Adjust rear brakes.
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown at 7, 5000 miles (12 000 km) on schedule ªAº
or every other interval shown at 7,500 miles (12 000
km) on schedule ªBº.
²Check engine coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²Lubricate steering linkage.
²Drain crankcase breather canister (if equipped).
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
The scheduled emission maintenance listed inbold
typeon the Maintenance Schedules, must be done at
the mileage specified to assure the continued proper
functioning of the emission control system. These,
and all other maintenance services included in this
manual, should be done to provide the best vehicle
performance and reliability. More frequent mainte-
nance may be needed for vehicles in severe operating
conditions such as dusty areas and very short trip
driving.
0 - 22 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEBR/BE
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 46 of 2889

down several times. Always release the bumper in
the down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications while the vehicle is in its NOR-
MALLY LOADED CONDITION.
Camber and caster angle adjustments involve
changing the position of the upper suspension arm
pivot bar (Fig. 3). Refer to the Alignment Specifica-
tion Chart for the correct setting.
CASTER:Move the rear position of the pivot bar
in or out. This will change the caster angle signifi-
cantly and camber angle only slightly. To retain cam-
ber move the forward pivot very slightly in the
opposite direction.
NOTE: For example, to increase a positive caster
angle, move the rear position of the pivot bar
inward (toward the engine). Move the front of pivot
bar outward (away from the engine) slightly until
the original camber angle is obtained.CAMBER:Move the forward position of the pivot
bar in or out. This will change the camber angle sig-
nificantly and caster angle only slightly. The camber
angle should be adjusted as close as possible to the
preferred service specification. After adjustment
is made tighten pivot bar nuts to specifications.
TOE POSITION:The wheel toe position adjust-
ment should be the final adjustment.
(1) Start the engine and turn wheels both ways
before straightening the wheels. Center and secure
the steering wheel and turn off engine.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts/nuts.
NOTE: Each front wheel should be adjusted for
one-half of the total toe position specification. This
will ensure the steering wheel will be centered
when the wheels are positioned straight-ahead.
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by turning the tie
rod adjustment sleeves as necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CASTER
CORRECTION MEASUREMENT
NOTE: To determine the correct caster alignment
angle for Cab-Chassis vehicles the following proce-
dure must be performed.
NOTE: 4x2 11000 GVW has a solid front axle and
uses a 4x4 frame.
(1) Take a height measurement to the center of the
front gauge hole in the frame. Take another measure-
ment to the center of the rear spring hanger bolt
(Fig. 4). Take these measurements on both sides of
the vehicle.
(2) Subtract the front measurement from the rear
measurement and use the average between the right
and left side. Use this number (caster correlation
valve) with the Corrected Caster Chart to obtain the
preferred caster angle.
Fig. 3 Caster Camber Adjustment Location
1 - PIVOT BAR
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - SUSPENSION ARM FRAME MOUNT
4 - ADJUSTMENT SLOTS
BR/BEWHEEL ALIGNMENT 2 - 3
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 55 of 2889

(3) Remove the brake caliper assembly and rotor,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the tie rod.
Remove the tie rod end from the steering knuckle
with Puller C-3894-A.
(5) Remove the stabilizer bar link from the lower
suspension arm.
(6) Support the lower suspension arm outboard
end with a jack. Place a jack under the arm in front
of the shock mount.
(7) Remove the cotter pin and nut from the lower
ball joint. Separate the ball joint with Remover
C-4150A.
(8) Remove the lower shock bolt from the suspen-
sion arm.
(9) Lower the jack and suspension arm until
spring tension is relieved. Remove spring and rubber
isolator (Fig. 5).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the rubber isolator on top of the spring.
Position the spring into the upper spring seat.
(2) Raise the lower suspension arm with a jack
and position the spring into the lower suspension
arm mount.
(3) Install the lower shock bolt and tighten to 142
N´m (105 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install the steering knuckle on the lower ball
joint. Install the lower ball joint nut and tighten to:
²LD: 129 N´m (95 ft. lbs.)
²HD: 136 N´m (110 ft. lbs.)
(4) Install the lower ball joint cotter pin.
(5) Install the stabilizer bar link on the lower sus-
pension arm. Install the grommet, retainer and nut
and tighten to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).(6) Install the tie rod end on the steering knuckle
and tighten nut to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.). Install cotter
pin.
(7) Install the brake rotor and caliper assembly,
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
ROTORS - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the tire and wheel assembly, (Refer to
22 - TIRES/WHEELS/WHEELS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
(9) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION
The bar extends across the front underside of the
chassis and mounts on the frame rails. Links con-
nected the bar to the lower suspension arms. Stabi-
lizer bar mounts are isolated by rubber bushings.
Links are isolated with rubber grommets.
OPERATION
The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle front
sway during turns. The spring steel bar helps to con-
trol the vehicle body in relationship to the suspen-
sion.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the link nuts, retainers and grommets
from lower suspension arm and stabilizer bar (Fig.
6).
(3) Remove the stabilizer bar clamps from the
frame rails. Remove the stabilizer bar.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the stabilizer bar on the frame rail
and install the clamps and bolts. Ensure the bar is
centered with equal spacing on both sides. Tighten
the bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install links on stabilizer bar and lower sus-
pension arm. Install grommets, retainers and nuts.
Tighten nuts to 37 N´m (27 ft. lbs.).
(3) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
UPPER BALL JOINT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - UPPER BALL
JOINT
(1) Position a floor jack under the lower suspen-
sion arm. Raise the wheel and allow the tire to
lightly contact the floor (vehicle weight relieved from
the tire).
(2) Mount a dial indicator solidly on the upper sus-
pension arm.
Fig. 5 Coil Spring
1 - COIL SPRING
2 - RUBBER ISOLATER
2 - 12 FRONT - 2WDBR/BE
SPRING (Continued)
Page 87 of 2889

cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining, or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
3 - 14 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 216FBI (Continued)
Page 101 of 2889
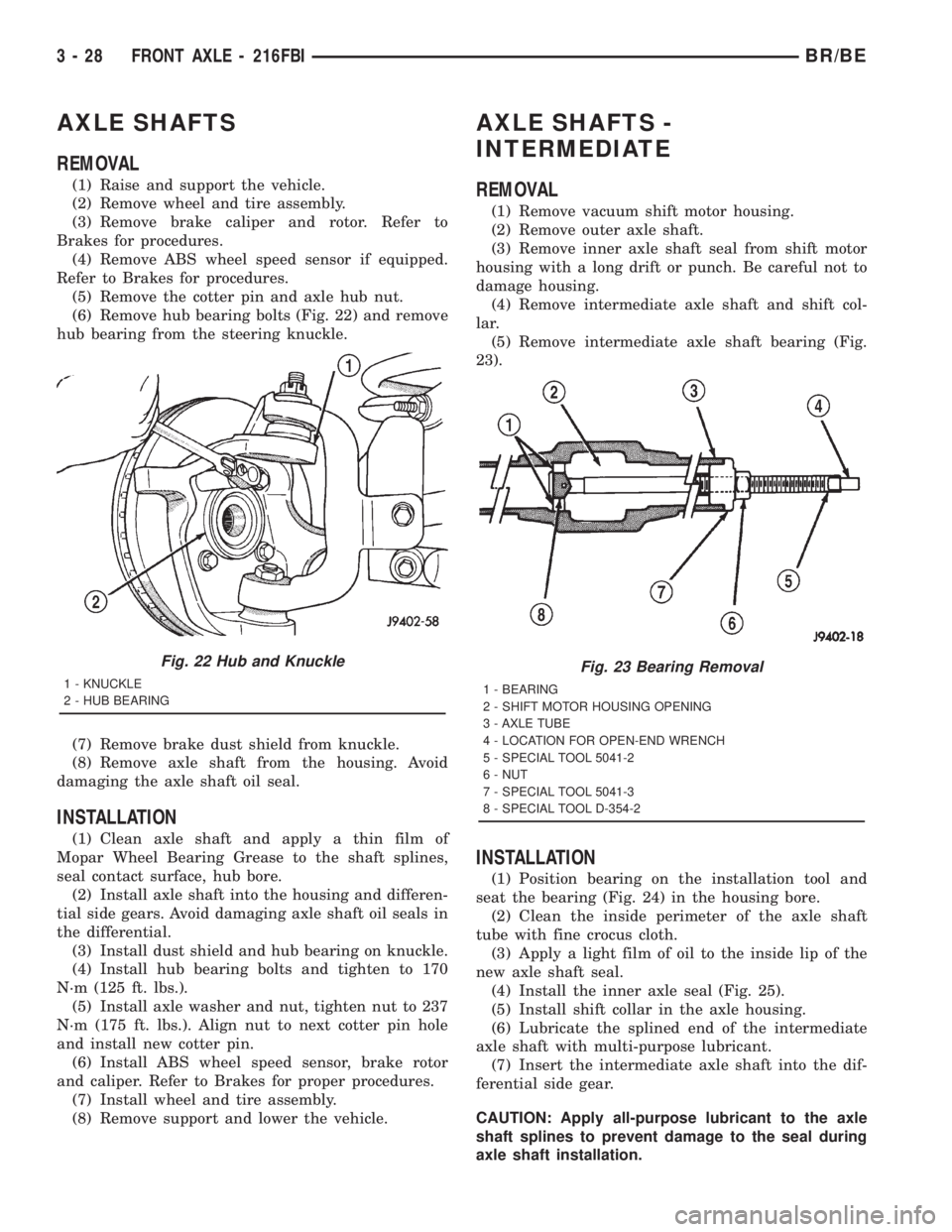
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove brake caliper and rotor. Refer to
Brakes for procedures.
(4) Remove ABS wheel speed sensor if equipped.
Refer to Brakes for procedures.
(5) Remove the cotter pin and axle hub nut.
(6) Remove hub bearing bolts (Fig. 22) and remove
hub bearing from the steering knuckle.
(7) Remove brake dust shield from knuckle.
(8) Remove axle shaft from the housing. Avoid
damaging the axle shaft oil seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean axle shaft and apply a thin film of
Mopar Wheel Bearing Grease to the shaft splines,
seal contact surface, hub bore.
(2) Install axle shaft into the housing and differen-
tial side gears. Avoid damaging axle shaft oil seals in
the differential.
(3) Install dust shield and hub bearing on knuckle.
(4) Install hub bearing bolts and tighten to 170
N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install axle washer and nut, tighten nut to 237
N´m (175 ft. lbs.). Align nut to next cotter pin hole
and install new cotter pin.
(6) Install ABS wheel speed sensor, brake rotor
and caliper. Refer to Brakes for proper procedures.
(7) Install wheel and tire assembly.
(8) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
AXLE SHAFTS -
INTERMEDIATE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove vacuum shift motor housing.
(2) Remove outer axle shaft.
(3) Remove inner axle shaft seal from shift motor
housing with a long drift or punch. Be careful not to
damage housing.
(4) Remove intermediate axle shaft and shift col-
lar.
(5) Remove intermediate axle shaft bearing (Fig.
23).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position bearing on the installation tool and
seat the bearing (Fig. 24) in the housing bore.
(2) Clean the inside perimeter of the axle shaft
tube with fine crocus cloth.
(3) Apply a light film of oil to the inside lip of the
new axle shaft seal.
(4) Install the inner axle seal (Fig. 25).
(5) Install shift collar in the axle housing.
(6) Lubricate the splined end of the intermediate
axle shaft with multi-purpose lubricant.
(7) Insert the intermediate axle shaft into the dif-
ferential side gear.
CAUTION: Apply all-purpose lubricant to the axle
shaft splines to prevent damage to the seal during
axle shaft installation.
Fig. 22 Hub and Knuckle
1 - KNUCKLE
2 - HUB BEARING
Fig. 23 Bearing Removal
1 - BEARING
2 - SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING OPENING
3 - AXLE TUBE
4 - LOCATION FOR OPEN-END WRENCH
5 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-2
6 - NUT
7 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-3
8 - SPECIAL TOOL D-354-2
3 - 28 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
Page 102 of 2889
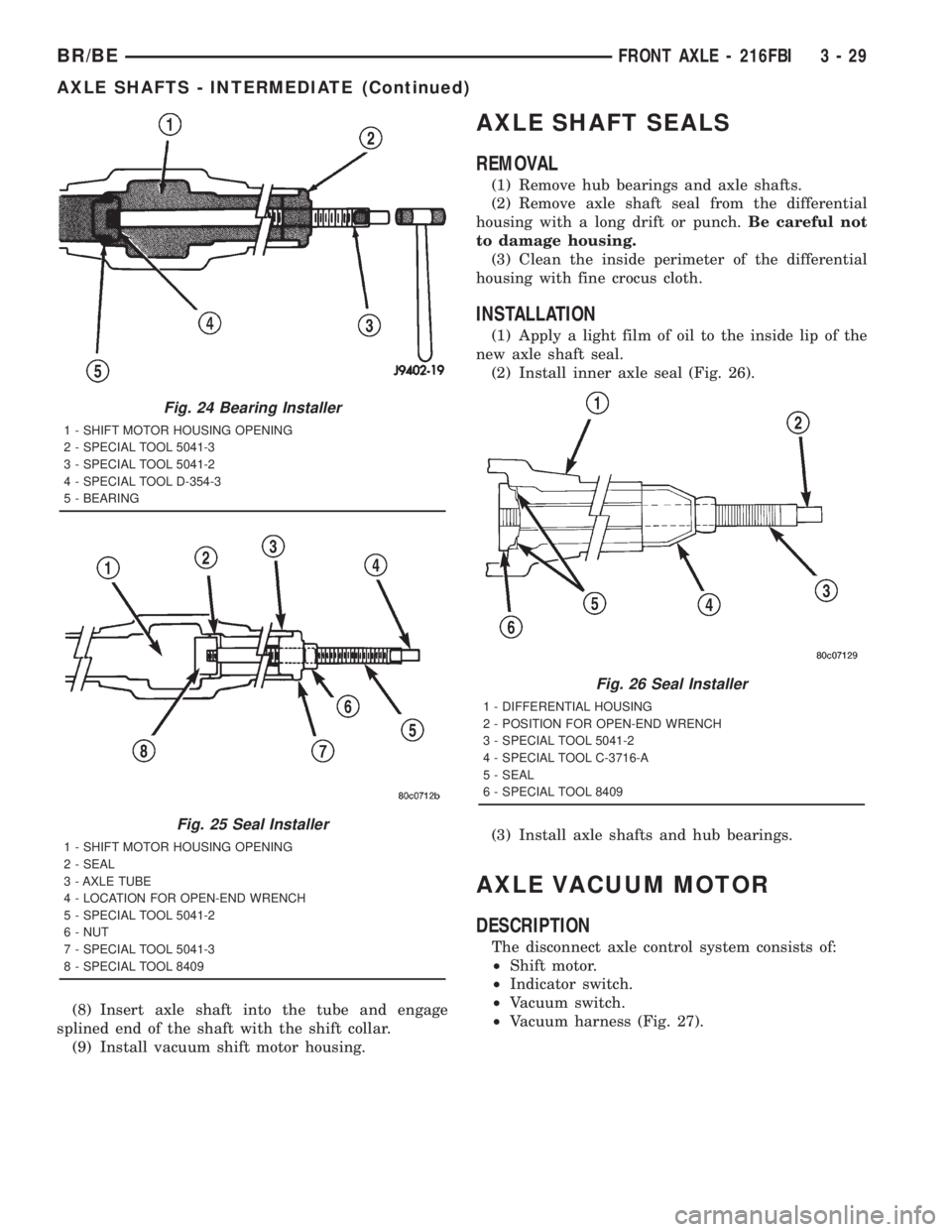
(8) Insert axle shaft into the tube and engage
splined end of the shaft with the shift collar.
(9) Install vacuum shift motor housing.
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearings and axle shafts.
(2) Remove axle shaft seal from the differential
housing with a long drift or punch.Be careful not
to damage housing.
(3) Clean the inside perimeter of the differential
housing with fine crocus cloth.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light film of oil to the inside lip of the
new axle shaft seal.
(2) Install inner axle seal (Fig. 26).
(3) Install axle shafts and hub bearings.
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The disconnect axle control system consists of:
²Shift motor.
²Indicator switch.
²Vacuum switch.
²Vacuum harness (Fig. 27).
Fig. 24 Bearing Installer
1 - SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING OPENING
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-3
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-2
4 - SPECIAL TOOL D-354-3
5 - BEARING
Fig. 25 Seal Installer
1 - SHIFT MOTOR HOUSING OPENING
2 - SEAL
3 - AXLE TUBE
4 - LOCATION FOR OPEN-END WRENCH
5 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-2
6 - NUT
7 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-3
8 - SPECIAL TOOL 8409
Fig. 26 Seal Installer
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - POSITION FOR OPEN-END WRENCH
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-2
4 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3716-A
5 - SEAL
6 - SPECIAL TOOL 8409
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 216FBI 3 - 29
AXLE SHAFTS - INTERMEDIATE (Continued)
Page 107 of 2889

(5) Position yoke with the sockets in a vise (Fig.
31).
(6) Tighten the vise jaws to force the bearing cap
into the larger socket (receiver).
(7) Release the vise jaws. Remove the sockets and
bearing cap that was partially forced out of the yoke.
(8) Repeat the above procedure for the remaining
bearing cap and remove spider from the propeller
shaft yoke.
INSTALLATION
(1) Pack the bearing caps 1/3 full of wheel bearing
lubricant. Apply extreme pressure (EP), lithium-base
lubricant to aid in installation.
(2) Position the spider in the yoke. Insert the seals
and bearings. Tap the bearing caps into the yoke
bores far enough to hold the spider in position.
(3) Place the socket (driver) against one bearing
cap. Position the yoke with the socket in a vise.
(4) Tighten the vise to force the bearing caps into
the yoke. Force the caps enough to install the retain-
ing clips.
(5) Install the bearing cap retaining clips.
(6) Install axle shaft.
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove brake calipers and rotors, Refer to
Brakes for procedure.
(4) Mark the propeller shaft and pinion yoke for
installation reference.
(5) Remove propeller shaft from the yoke.
(6) Rotate pinion gear three or four times and ver-
ify it rotates smoothly.
(7) Record rotating torque of the pinion gear with
an inch pound torque wrench for installation refer-
ence.
(8) Remove pinion yoke nut and washer with
Remover C-452 and Flange Wrench C-3281 (Fig. 32).
(9) Remove pinion shaft seal with a pry tool or
slide hammer mounted screw.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal. Install seal with an appropriate
installer (Fig. 33).
(2) Install yoke on the pinion gear with Installer
W-162-D (Fig. 34).
CAUTION: Do not exceed the minimum tightening
torque when installing the pinion yoke retaining
nut. Damage to collapsible spacer or bearings may
result.
Fig. 30 Axle Shaft U-Joint
1 - SHAFT YOKE
2 - BEARING CAP
3 - SNAP RINGS
4 - BEARING CAP
5 - SPINDLE YOKE
6 - BEARING
7 - BEARING CAP
8 - SNAP RINGS
9 - BEARING CAP
Fig. 31 Yoke Bearing Cap
1 - LARGE-DIAMETER SOCKET WRENCH
2 - VISE
3 - SMALL-DIAMETER SOCKET WRENCH
3 - 34 FRONT AXLE - 216FBIBR/BE
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS (Continued)