2001 DODGE RAM fuel type
[x] Cancel search: fuel typePage 41 of 2889

DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
HOISTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE
Refer to the Owner's Manual for emergency vehicle
lifting procedures.
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN A CHASSIS OR DRIVETRAIN COMPO-
NENT IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE
CENTER OF GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME
HOISTING CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY
SUPPORT (Fig. 9) OR SECURE VEHICLE TO HOIST-
ING DEVICE WHEN THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.
FLOOR JACK
When properly positioned, a floor jack can be used
to lift a vehicle (Fig. 10). Support the vehicle in the
raised position with jack stands at the front and rear
ends of the frame rails (Fig. 9).CAUTION: Do not lift vehicle with a floor jack posi-
tioned under:
²An axle tube.
²A body side sill.
²A steering linkage component.
²A drive shaft.
²The engine or transmission oil pan.
²The fuel tank.
²A front suspension arm.
NOTE: Use the correct frame rail lifting locations
only (Fig. 11).
HOIST
A vehicle can be lifted with:
²A single-post, frame-contact hoist.
²A twin-post, chassis hoist.
²A ramp-type, drive-on hoist.
Fig. 8 Jumper Cable Clamp ConnectionsÐDiesel
Engine
1 - POSITIVE CABLE CONNECTION
2 - BATTERY
3 - NEGATIVE OR GROUND CABLE CONNECTION
Fig. 9 Safety Stands
1 - SAFETY STANDS
0 - 28 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCEBR/BE
JUMP STARTING (Continued)
Page 42 of 2889
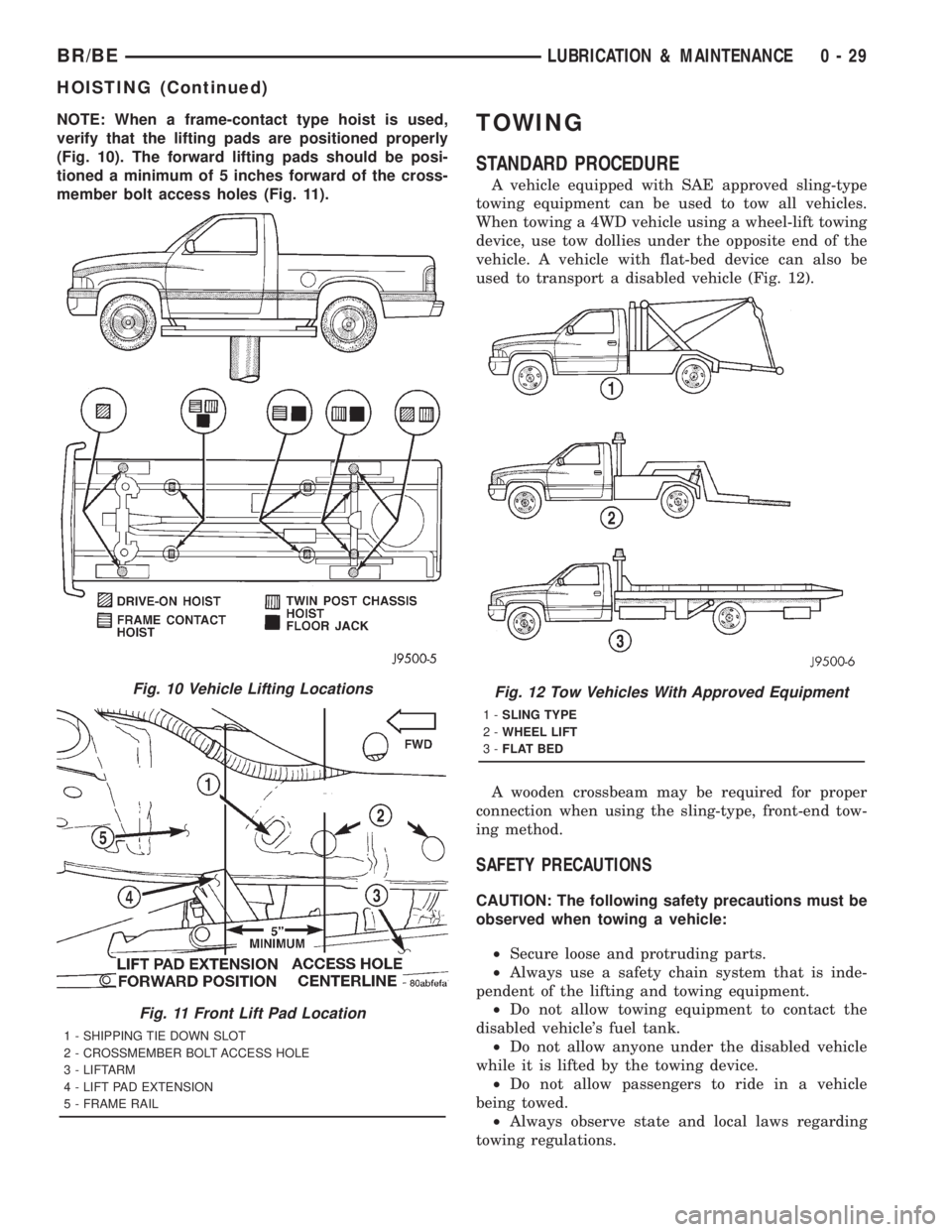
NOTE: When a frame-contact type hoist is used,
verify that the lifting pads are positioned properly
(Fig. 10). The forward lifting pads should be posi-
tioned a minimum of 5 inches forward of the cross-
member bolt access holes (Fig. 11).TOWING
STANDARD PROCEDURE
A vehicle equipped with SAE approved sling-type
towing equipment can be used to tow all vehicles.
When towing a 4WD vehicle using a wheel-lift towing
device, use tow dollies under the opposite end of the
vehicle. A vehicle with flat-bed device can also be
used to transport a disabled vehicle (Fig. 12).
A wooden crossbeam may be required for proper
connection when using the sling-type, front-end tow-
ing method.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
CAUTION: The following safety precautions must be
observed when towing a vehicle:
²Secure loose and protruding parts.
²Always use a safety chain system that is inde-
pendent of the lifting and towing equipment.
²Do not allow towing equipment to contact the
disabled vehicle's fuel tank.
²Do not allow anyone under the disabled vehicle
while it is lifted by the towing device.
²Do not allow passengers to ride in a vehicle
being towed.
²Always observe state and local laws regarding
towing regulations.
Fig. 10 Vehicle Lifting Locations
Fig. 11 Front Lift Pad Location
1 - SHIPPING TIE DOWN SLOT
2 - CROSSMEMBER BOLT ACCESS HOLE
3 - LIFTARM
4 - LIFT PAD EXTENSION
5 - FRAME RAIL
Fig. 12 Tow Vehicles With Approved Equipment
1-SLING TYPE
2-WHEEL LIFT
3-FLAT BED
BR/BELUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE 0 - 29
HOISTING (Continued)
Page 343 of 2889

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
5. Pressure cap not installed tightly. If cap
is loose, boiling point of coolant will be
lowered. Also refer to the following Step
6.5. Tighten cap
6. Poor seals at the radiator cap. 6. (a) Check condition of cap and cap
seals. Refer to Radiator Cap. Replace
cap if necessary.
(b) Check condition of radiator filler neck.
If neck is bent or damaged, replace
radiator.
7. Coolant level low in radiator but not in
coolant reserve/overflow tank. This
means the radiator is not drawing coolant
from the coolant reserve/overflow tank as
the engine cools7. (a) Check condition of radiator cap and
cap seals. Refer to Radiator Cap in this
Group. Replace cap if necessary.
(b) Check condition of radiator filler neck.
If neck is bent or damaged, replace
radiator.
(c) Check condition of the hose from the
radiator to the coolant tank. It should fit
tight at both ends without any kinks or
tears. Replace hose if necessary.
(d) Check coolant reserve/overflow tank
and tanks hoses for blockage. Repair as
necessary.
8. Incorrect coolant concentration 8. Check coolant. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID
TYPES - DESCRIPTION).
9. Coolant not flowing through system 9. Check for coolant flow at radiator filler
neck with some coolant removed, engine
warm and thermostat open. Coolant
should be observed flowing through
radiator. If flow is not observed, determine
area of obstruction and repair as
necessary.
10. Radiator or A/C condenser fins are
dirty or clogged.10. Remove insects and debris. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
11. Radiator core is corroded or plugged. 11. Have radiator re-cored or replaced.
12. Aftermarket A/C installed without
proper radiator.12. Install proper radiator.
13. Fuel or ignition system problems. 13. Refer to 14 - Fuel System or 8 -
Electrical for diagnosis and testing
procedures.
14. Dragging brakes. 14. Check and correct as necessary.
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) for correct procedures.
15. Bug screen or cardboard is being
used, reducing airflow.15. Remove bug screen or cardboard.
7 - 8 COOLINGBR/BE
COOLING (Continued)
Page 383 of 2889

ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
DESCRIPTION
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is
used to sense engine coolant temperature. The sensor
protrudes into an engine water jacket.
The ECT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as engine coolant
temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
At key-on, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
sends out a regulated 5 volt signal to the ECT sensor.
The PCM then monitors the signal as it passes
through the ECT sensor to the sensor ground (sensor
return).
When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
Open Loop cycle. It will demand slightly richer air-
fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds. This is done
until normal operating temperatures are reached.
The PCM uses inputs from the ECT sensor for the
following calculations:
²for engine coolant temperature gauge operation
through CCD or PCI (J1850) communications
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance curves
²ASD relay shut-down times
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor key-on steps
²Pulse-width prime-shot during cranking
²O2 sensor closed loop times
²Purge solenoid on/off times
²EGR solenoid on/off times (if equipped)
²Leak Detection Pump operation (if equipped)²Radiator fan relay on/off times (if equipped)
²Target idle speed
REMOVAL
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM
MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV-
ING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR.
REFER TO GROUP 7, COOLING.
(1) Partially drain cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor
(Fig. 14).
(4)Engines with air conditioning:When
removing the connector from sensor, do not pull
directly on wiring harness. Fabricate an L-shaped
hook tool from a coat hanger (approximately eight
inches long). Place the hook part of tool under the
connector for removal. The connector is snapped onto
the sensor. It is not equipped with a lock type tab.
(5) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Tighten to 6±8 N´m (55±75 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to sensor. The sen-
sor connector is symmetrical (not indexed). It can be
installed to the sensor in either direction.
(4) Install air cleaner assembly.
(5) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 13 Block HeaterÐDiesel Engine
1 - BLOCK HEATER
Fig. 14 Engine Coolant Temperature
1 - GENERATOR
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
7 - 48 ENGINEBR/BE
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 435 of 2889

(5) Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connectors and the antenna coaxial cable connector
from the receptacles on the rear of the radio receiver.
(6) If so equipped, remove the screw that secures
the ground wire to the back of the radio receiver
chassis.
(7) Remove the radio receiver from the instrument
panel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the radio receiver to the instrument
panel.
(2) If so equipped, install and tighten the screw
that secures the ground wire to the back of the radio
receiver chassis. Tighten the screw to 7 N´m (65 in.
lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connectors and the antenna coaxial cable connector
to the receptacles on the rear of the radio receiver.
(4) Position the radio receiver into the mounting
hole in the instrument panel.
(5) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the radio receiver to the instrument panel. Tighten
the screws to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the cluster bezel onto the instrument
panel.
(7) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
RADIO NOISE SUPPRESSION
COMPONENTS
DESCRIPTION
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and Electro-
Magnetic Interference (EMI) noise suppression is
accomplished primarily through circuitry internal to
the radio receivers. These internal suppression
devices are only serviced as part of the radio receiver.
External suppression devices that are used on this
vehicle to control RFI or EMI noise include the fol-
lowing:
²Radio antenna base ground
²Radio receiver chassis ground wire or strap
²Engine-to-body ground straps
²Cab-to-bed ground strap
²Heater core ground strap
²Resistor-type spark plugs
²Radio suppression-type secondary ignition wir-
ing.
For more information on the spark plugs and sec-
ondary ignition components, refer to Electrical, Igni-
tion Control.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RADIO NOISE
SUPPRESSION COMPONENTS
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO ELECTRICAL, RESTRAINTS
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appro-
priate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing
and retention, connector pin-out information and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds. Inspect the ground paths
and connections at the following locations:
²Blower motor
²Cab-to-bed ground strap
²Electric fuel pump
²Engine-to-body ground straps
²Generator
²Ignition module
²Heater core ground strap
²Radio antenna base ground
²Radio receiver chassis ground wire or strap
Fig. 9 Radio Receiver Connections - Typical
1 - ANTENNA CABLE
2 - RADIO
3 - INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRING
4 - GROUND WIRE
8A - 12 AUDIOBR/BE
RADIO (Continued)
Page 491 of 2889

DIESEL ENGINE
Diesel engine models feature a clamping type
female battery terminal made of soft lead die cast
onto one end of the battery cable wire. A square
headed pinch-bolt and hex nut are installed at the
open end of the female battery terminal clamp. The
pinch-bolt on the left side battery positive cable
female terminal clamp also has a stud extending
from the head of the bolt. Large eyelet type terminals
are crimped onto the opposite end of the battery
cable wire and then solder-dipped. The battery posi-
tive cable wires have a red insulating jacket to pro-
vide visual identification and feature a larger female
battery terminal clamp to allow connection to the
larger battery positive terminal post. The battery
negative cable wires have a black insulating jacket
and a smaller female battery terminal clamp.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a return path for electrical current gen-
erated by the charging system for restoring the volt-
age potential of the battery. The female battery
terminal clamps on the ends of the battery cable
wires provide a strong and reliable connection of the
battery cable to the battery terminal posts. The ter-
minal pinch bolts allow the female terminal clamps
to be tightened around the male terminal posts on
the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals secured
to the ends of the battery cable wires opposite the
female battery terminal clamps provide secure and
reliable connection of the battery to the vehicle elec-
trical system.
GASOLINE ENGINE
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is
crimped onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor
solenoid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp
is also crimped onto the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the front of the left engine cylinder head. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the left front fender inner shield,
just ahead of the battery. An additional ground wire
with two eyelet terminals is used to provide ground
to the vehicle frame. One eyelet terminal of this
ground wire is installed under the head of the bat-
tery negative cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt, andthe other eyelet terminal is secured with a ground
screw to the outer surface of the left frame rail,
below the battery.
DIESEL ENGINE
The left battery positive cable terminal clamp is
die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the left battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the left battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter
motor solenoid. The right battery positive cable ter-
minal clamp is die cast onto the end of a single wire.
The eyelet terminal on the other end of the right bat-
tery positive cable is connected to the stud on the
pinch-bolt of the left battery positive cable terminal
clamp. This stud also provides a connection point for
the eyelet terminals from the fuel heater relay and
intake air heater relay jumper harness take outs. All
of these eyelet terminals are secured to the left bat-
tery positive cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt stud
with a single hex nut.
The left battery negative cable terminal clamp is
die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the left battery nega-
tive cable to the vehicle powertrain through a ground
screw on the left side of the engine block, below the
power steering and vacuum pumps. The other wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the left battery
negative cable to the vehicle body through a ground
screw on the left front fender inner shield, just ahead
of the left battery. An additional ground wire with
two eyelet terminals is used to provide ground to the
vehicle frame. One eyelet terminal of this ground
wire is installed under the nut of the left battery
negative cable terminal clamp pinch-bolt, and the
other eyelet terminal is secured with a ground screw
to the outer surface of the left frame rail, below the
left battery. The right battery negative cable terminal
is also die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the right bat-
tery negative cable to the vehicle powertrain through
a ground screw on the right side of the engine block,
just forward of the right engine mount. The other
wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the right
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the right front fender inner shield,
just behind the right battery.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - BATTERY CABLES
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cables. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
8F - 20 BATTERY SYSTEMBR/BE
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 540 of 2889

SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
MINIMUM MAXIMUM
250 Ohms Per Inch 1000 Ohms Per Inch
3000 Ohms Per Foot 12,000 Ohms Per Foot
SPARK PLUGS
ENGINE PLUG TYPE ELECTRODE GAP
3.9L V-6 RC12LC4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
5.2L/5.9L V-8 RC12LC4 1.01 mm (.040 in.)
8.0L V-10 QC9MC4 1.14 mm (.045 in.)
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ3.9L/5.2L/5.9L ENGINES
COIL MANUFACTURERPRIMARY RESISTANCE
21-27ÉC (70-80ÉF)SECONDARY RESISTANCE 21-27ÉC
(70-80ÉF)
Diamond 0.97 - 1.18 Ohms 11,300 - 15,300 Ohms
Toyodenso 0.95 - 1.20 Ohms 11,300 - 13,300 Ohms
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCEÐ8.0L V-10
ENGINE
Primary Resistance: 0.53-0.65 Ohms. Test across the
primary connector. Refer to text for test procedures.
Secondary Resistance: 10.9-14.7K Ohms. Test
across the individual coil towers. Refer to text for test
procedures.
IGNITION TIMING
Ignition timing is not adjustable on any engine.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN
RELAY
DESCRIPTION - PCM OUTPUT
The 5±pin, 12±volt, Automatic Shutdown (ASD)
relay is located in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The ASD relay supplies battery voltage (12+ volts)
to the fuel injectors and ignition coil(s). With certain
emissions packages it also supplies 12±volts to the
oxygen sensor heating elements.
The ground circuit for the coil within the ASD
relay is controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM operates the ASD relay by switch-
ing its ground circuit on and off.The ASD relay will be shut±down, meaning the
12±volt power supply to the ASD relay will be de-ac-
tivated by the PCM if:
²the ignition key is left in the ON position. This
is if the engine has not been running for approxi-
mately 1.8 seconds.
²there is a crankshaft position sensor signal to
the PCM that is lower than pre-determined values.
OPERATION - ASD SENSE - PCM INPUT
A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM
that the ASD has been activated. The relay is used to
connect the oxygen sensor heater element, ignition
coil and fuel injectors to 12 volt + power supply.
This input is used only to sense that the ASD relay
is energized. If the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) does not see 12 volts at this input when the
ASD should be activated, it will set a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ASD AND FUEL
PUMP RELAYS
The following description of operation and
tests apply only to the Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) and fuel pump relays. The terminals on the
bottom of each relay are numbered. Two different
types of relays may be used, (Fig. 1) or (Fig. 2).
²Terminal number 30 is connected to battery volt-
age. For both the ASD and fuel pump relays, termi-
nal 30 is connected to battery voltage at all times.
BR/BEIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 3
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 541 of 2889
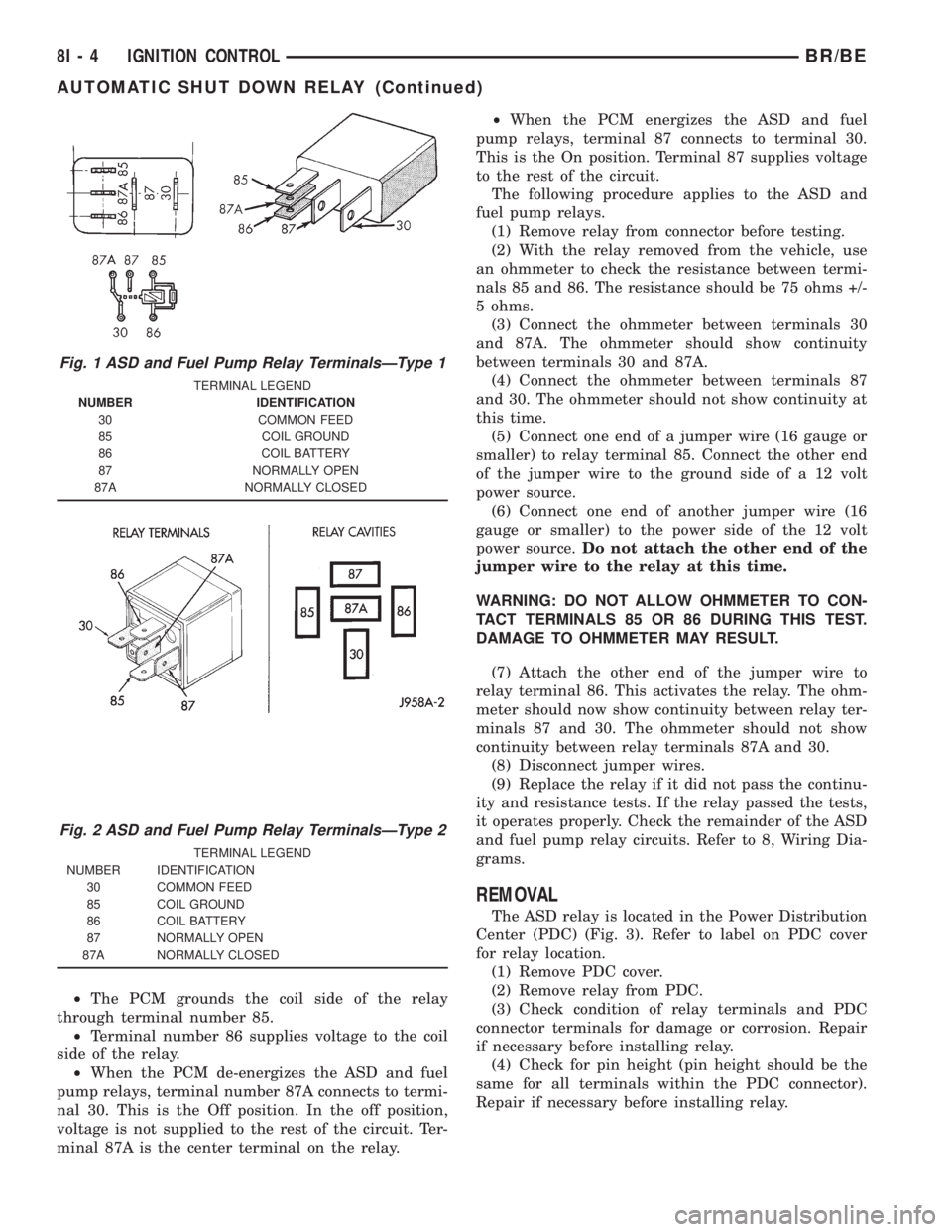
²The PCM grounds the coil side of the relay
through terminal number 85.
²Terminal number 86 supplies voltage to the coil
side of the relay.
²When the PCM de-energizes the ASD and fuel
pump relays, terminal number 87A connects to termi-
nal 30. This is the Off position. In the off position,
voltage is not supplied to the rest of the circuit. Ter-
minal 87A is the center terminal on the relay.²When the PCM energizes the ASD and fuel
pump relays, terminal 87 connects to terminal 30.
This is the On position. Terminal 87 supplies voltage
to the rest of the circuit.
The following procedure applies to the ASD and
fuel pump relays.
(1) Remove relay from connector before testing.
(2) With the relay removed from the vehicle, use
an ohmmeter to check the resistance between termi-
nals 85 and 86. The resistance should be 75 ohms +/-
5 ohms.
(3) Connect the ohmmeter between terminals 30
and 87A. The ohmmeter should show continuity
between terminals 30 and 87A.
(4) Connect the ohmmeter between terminals 87
and 30. The ohmmeter should not show continuity at
this time.
(5) Connect one end of a jumper wire (16 gauge or
smaller) to relay terminal 85. Connect the other end
of the jumper wire to the ground side of a 12 volt
power source.
(6) Connect one end of another jumper wire (16
gauge or smaller) to the power side of the 12 volt
power source.Do not attach the other end of the
jumper wire to the relay at this time.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW OHMMETER TO CON-
TACT TERMINALS 85 OR 86 DURING THIS TEST.
DAMAGE TO OHMMETER MAY RESULT.
(7) Attach the other end of the jumper wire to
relay terminal 86. This activates the relay. The ohm-
meter should now show continuity between relay ter-
minals 87 and 30. The ohmmeter should not show
continuity between relay terminals 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires.
(9) Replace the relay if it did not pass the continu-
ity and resistance tests. If the relay passed the tests,
it operates properly. Check the remainder of the ASD
and fuel pump relay circuits. Refer to 8, Wiring Dia-
grams.
REMOVAL
The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 3). Refer to label on PDC cover
for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
Fig. 1 ASD and Fuel Pump Relay TerminalsÐType 1
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 2 ASD and Fuel Pump Relay TerminalsÐType 2
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
8I - 4 IGNITION CONTROLBR/BE
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN RELAY (Continued)