2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 2695 of 4284

ENGINE 3.3/3.8L
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L
DESCRIPTION...........................73
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................74
ENGINE..............................74
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE......74
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL........76
ENGINE OIL LEAK INSPECTION...........77
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
TEST................................78
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE
LEAKAGE TEST........................79
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................79
MEASURING WITH PLASTIGAGE..........79
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS. . . 79
ENGINE GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION . . 80
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE..........81
REPAIR OF DAMAGED OR WORN
THREADS.............................81
ENGINE CORE AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS . . . 81
REMOVAL..............................82
INSTALLATION...........................84
SPECIFICATIONS........................86
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................90
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL..............................93
INSTALLATION...........................93
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL..............................93
INSTALLATION...........................93
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION...........................94
OPERATION.............................94
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................94
CYLINDER HEAD GASKET...............94
REMOVAL..............................95
CLEANING..............................95
INSPECTION............................96
INSTALLATION...........................96
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION...........................97
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - RIGHT
REMOVAL..............................97
INSTALLATION...........................98
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - LEFT
REMOVAL..............................98
INSTALLATION...........................99
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION...........................99
OPERATION.............................99STANDARD PROCEDURE..................99
VALVE SERVICE.......................99
REMOVAL.............................100
CLEANING.............................100
INSPECTION...........................100
INSTALLATION..........................101
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION..........................101
OPERATION............................101
REMOVAL.............................101
INSPECTION...........................103
INSTALLATION..........................103
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION..........................103
OPERATION............................104
REMOVAL.............................104
DISASSEMBLY..........................105
ASSEMBLY............................105
INSTALLATION..........................105
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION..........................106
REMOVAL.............................106
INSTALLATION..........................106
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION..........................106
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................106
CYLINDER BORE HONING...............106
CLEANING.............................107
INSPECTION...........................107
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION..........................107
OPERATION............................107
REMOVAL.............................107
INSPECTION...........................108
INSTALLATION..........................108
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................109
CONNECTING ROD BEARING - FITTING....109
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION..........................109
OPERATION............................110
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................110
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY................110
REMOVAL.............................110
INSPECTION...........................111
INSTALLATION..........................111
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................113
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARING - FITTING . . . 113
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-71
Page 2698 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Engine Mechanical and the Engine
Performance diagnostic charts, for possible causes
and corrections of malfunctions (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MECHANICAL)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- PERFORMANCE).
For fuel system diagnosis, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL
NOT START1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace as
necessary. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
BATTERY SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
2. Corroded or loose battery connections. 2. Clean and tighten battery connections.
Apply a coat of light mineral grease to
terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. Test starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)
4. Faulty coil(s) or control unit. 4. Test and replace as needed. (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. Set gap. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL - SPECIFICATIONS)
6. Contamination in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump. 7. Test fuel pump and replace as needed.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
8. Incorrect engine timing. 8. Check for a skipped timing belt/chain.
Fig. 2 Engine Identification
9 - 74 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 2702 of 4284

²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and fresh air hose (make-up air). Proceed
to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
NOTE: If oil leakage is observed at the dipstick tube
to block location; remove the tube, clean and reseal
using MoparTStud & Bearing Mount (press fit tube
applications only), and for O-ring style tubes,
remove tube and replace the O-ring seal.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible thecrankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.
(4) Disconnect the ignition coil electrical connector.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gage adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer with cable adaptors to the DRBIIIt.
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gage. Record this pressure as #1 cylinder
pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
9 - 78 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 2705 of 4284

CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil
into the cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cyl-
inder walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Install a new oil filter.
(11) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
(13) Start engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
Fig. 4 PROPER TOOL USAGE FOR SURFACE
PREPARATION
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCYBRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-81
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 2710 of 4284

(43) Connect the vacuum hoses to the throttle
body.
(44) Connect the EGR transducer electrical connec-
tor.
(45) Connect the TPS, IAC, and MAP sensor elec-
trical connectors.
(46) Connect throttle cables to throttle body.
(47) Install the radiator fans. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION)
(48) Connect the radiator upper hose.
(49) Connect the heater hoses. Remove pinch-off
pliers from the rear heater hoses, if equipped.
(50) Install the radiator upper support crossmem-
ber. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPEN-
ING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION)
(51) Install the wiper module. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
INSTALLATION)
(52) Connect the fuel line to fuel rail. (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(53) Install the air cleaner and hoses.
(54) Install new oil filter. Fill engine crankcase
with proper oil to correct level.
(55) Connect negative cable to battery.
(56) Fill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(57) Start engine and run until operating temper-
ature is reached.
(58) Adjust transmission linkage, if necessary.
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
General Specification
Type 60É V-6 Engine
Number of Cylinders 6
Displacement
Ð3.3L 3.3 Liters
(201 cu. in.)
Ð3.8L 3.8 Liters
(231 cu. in.)
Bore
Ð3.3L 93.0 mm
(3.66 in.)
Ð3.8L 96.0 mm
(3.779 in.)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Stroke
Ð3.3L 81.0 mm
(3.188 in.)
Ð3.8L 87.0 mm
(3.425 in.)
Compression Ratio
Ð3.3L 9.35:1
Ð3.8L 9.6:1
Firing Order 1-2-3-4-5-6
Cylinder Number (Front
to Rear)
ÐFront Bank 2,4,6
ÐRear Bank 1,3,5
Compression PressureÐ
Minimum689.5 kPa
(100 psi)
Max. Variation Between
Cylinders25%
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter
(Standard)
Ð3.3L 92.993±93.007 mm
(3.661±3.6617 in.)
Ð3.8L 95.993±96.007 mm
(3.7792±3.780 in.)
Out-of-Round (Service
Limits)0.076 mm
(0.003 in.)
Taper (Service Limits) 0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Lifter Bore Diameter 22.980±23.010 mm
(0.905±0.906 in.)
Deck Surface Flatness
(Max.)0.1 mm
(0.004 in.)
Pistons
Piston Diameter
Ð3.3L ÐMeasured 39.8
mm (1.567 in.) from
piston top92.968±92.998 mm
(3.660±3.661 in.)
Ð3.8L ÐMeasured 33.01
mm (1.30 in.) from piston
top95.968±95.998 mm
(3.778±3.779 in.)
Clearance in Bore @
Size Location (New)-0.005±0.039 mm
(-0.0002±0.0015 in.)
9 - 86 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 2711 of 4284
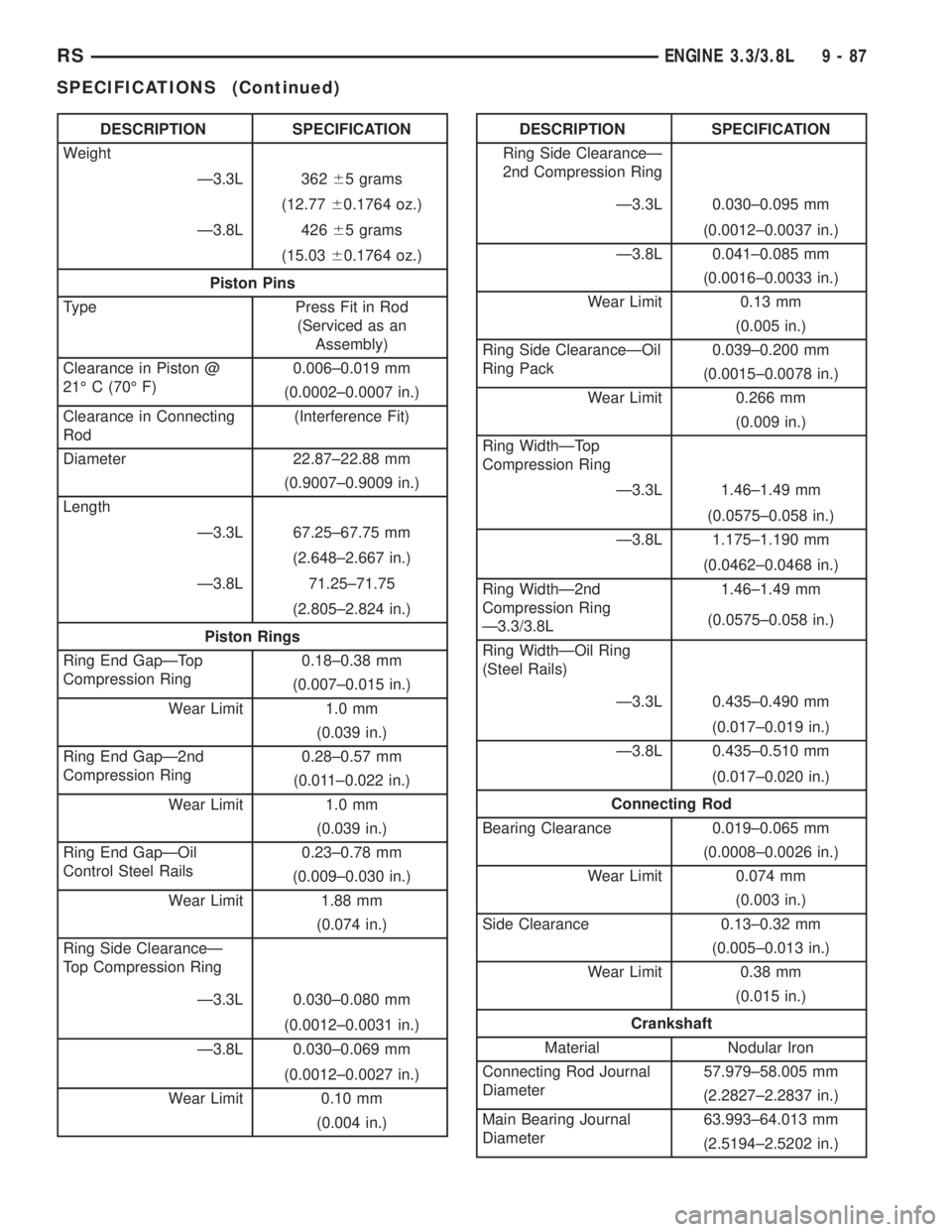
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Weight
Ð3.3L 36265 grams
(12.7760.1764 oz.)
Ð3.8L 42665 grams
(15.0360.1764 oz.)
Piston Pins
Type Press Fit in Rod
(Serviced as an
Assembly)
Clearance in Piston @
21É C (70É F)0.006±0.019 mm
(0.0002±0.0007 in.)
Clearance in Connecting
Rod(Interference Fit)
Diameter 22.87±22.88 mm
(0.9007±0.9009 in.)
Length
Ð3.3L 67.25±67.75 mm
(2.648±2.667 in.)
Ð3.8L 71.25±71.75
(2.805±2.824 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring End GapÐTop
Compression Ring0.18±0.38 mm
(0.007±0.015 in.)
Wear Limit 1.0 mm
(0.039 in.)
Ring End GapÐ2nd
Compression Ring0.28±0.57 mm
(0.011±0.022 in.)
Wear Limit 1.0 mm
(0.039 in.)
Ring End GapÐOil
Control Steel Rails0.23±0.78 mm
(0.009±0.030 in.)
Wear Limit 1.88 mm
(0.074 in.)
Ring Side ClearanceÐ
Top Compression Ring
Ð3.3L 0.030±0.080 mm
(0.0012±0.0031 in.)
Ð3.8L 0.030±0.069 mm
(0.0012±0.0027 in.)
Wear Limit 0.10 mm
(0.004 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Ring Side ClearanceÐ
2nd Compression Ring
Ð3.3L 0.030±0.095 mm
(0.0012±0.0037 in.)
Ð3.8L 0.041±0.085 mm
(0.0016±0.0033 in.)
Wear Limit 0.13 mm
(0.005 in.)
Ring Side ClearanceÐOil
Ring Pack0.039±0.200 mm
(0.0015±0.0078 in.)
Wear Limit 0.266 mm
(0.009 in.)
Ring WidthÐTop
Compression Ring
Ð3.3L 1.46±1.49 mm
(0.0575±0.058 in.)
Ð3.8L 1.175±1.190 mm
(0.0462±0.0468 in.)
Ring WidthÐ2nd
Compression Ring
Ð3.3/3.8L1.46±1.49 mm
(0.0575±0.058 in.)
Ring WidthÐOil Ring
(Steel Rails)
Ð3.3L 0.435±0.490 mm
(0.017±0.019 in.)
Ð3.8L 0.435±0.510 mm
(0.017±0.020 in.)
Connecting Rod
Bearing Clearance 0.019±0.065 mm
(0.0008±0.0026 in.)
Wear Limit 0.074 mm
(0.003 in.)
Side Clearance 0.13±0.32 mm
(0.005±0.013 in.)
Wear Limit 0.38 mm
(0.015 in.)
Crankshaft
Material Nodular Iron
Connecting Rod Journal
Diameter57.979±58.005 mm
(2.2827±2.2837 in.)
Main Bearing Journal
Diameter63.993±64.013 mm
(2.5194±2.5202 in.)
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-87
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 2712 of 4284
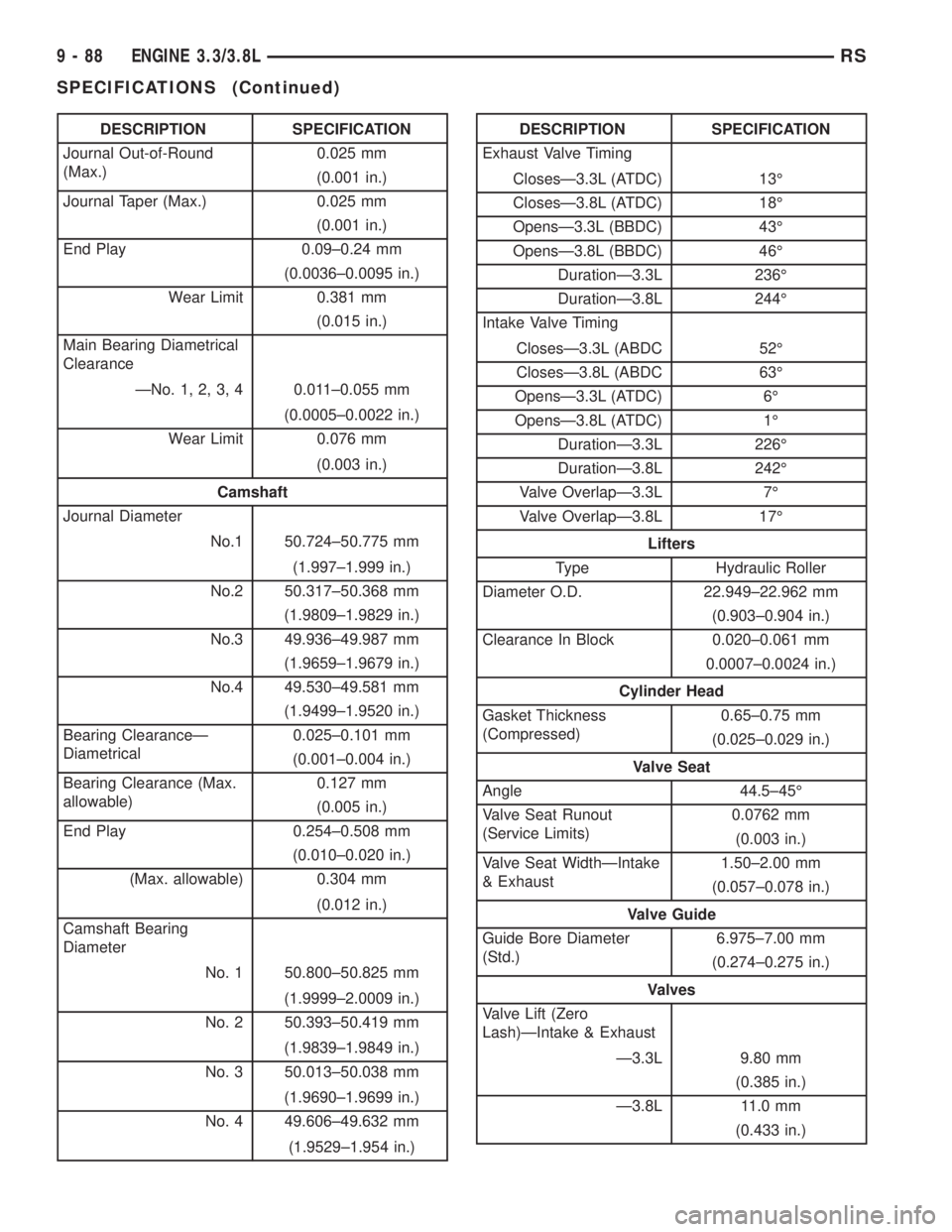
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Journal Out-of-Round
(Max.)0.025 mm
(0.001 in.)
Journal Taper (Max.) 0.025 mm
(0.001 in.)
End Play 0.09±0.24 mm
(0.0036±0.0095 in.)
Wear Limit 0.381 mm
(0.015 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical
Clearance
ÐNo. 1, 2, 3, 4 0.011±0.055 mm
(0.0005±0.0022 in.)
Wear Limit 0.076 mm
(0.003 in.)
Camshaft
Journal Diameter
No.1 50.724±50.775 mm
(1.997±1.999 in.)
No.2 50.317±50.368 mm
(1.9809±1.9829 in.)
No.3 49.936±49.987 mm
(1.9659±1.9679 in.)
No.4 49.530±49.581 mm
(1.9499±1.9520 in.)
Bearing ClearanceÐ
Diametrical0.025±0.101 mm
(0.001±0.004 in.)
Bearing Clearance (Max.
allowable)0.127 mm
(0.005 in.)
End Play 0.254±0.508 mm
(0.010±0.020 in.)
(Max. allowable) 0.304 mm
(0.012 in.)
Camshaft Bearing
Diameter
No. 1 50.800±50.825 mm
(1.9999±2.0009 in.)
No. 2 50.393±50.419 mm
(1.9839±1.9849 in.)
No. 3 50.013±50.038 mm
(1.9690±1.9699 in.)
No. 4 49.606±49.632 mm
(1.9529±1.954 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Exhaust Valve Timing
ClosesÐ3.3L (ATDC) 13É
ClosesÐ3.8L (ATDC) 18É
OpensÐ3.3L (BBDC) 43É
OpensÐ3.8L (BBDC) 46É
DurationÐ3.3L 236É
DurationÐ3.8L 244É
Intake Valve Timing
ClosesÐ3.3L (ABDC 52É
ClosesÐ3.8L (ABDC 63É
OpensÐ3.3L (ATDC) 6É
OpensÐ3.8L (ATDC) 1É
DurationÐ3.3L 226É
DurationÐ3.8L 242É
Valve OverlapÐ3.3L 7É
Valve OverlapÐ3.8L 17É
Lifters
Type Hydraulic Roller
Diameter O.D. 22.949±22.962 mm
(0.903±0.904 in.)
Clearance In Block 0.020±0.061 mm
0.0007±0.0024 in.)
Cylinder Head
Gasket Thickness
(Compressed)0.65±0.75 mm
(0.025±0.029 in.)
Valve Seat
Angle 44.5±45É
Valve Seat Runout
(Service Limits)0.0762 mm
(0.003 in.)
Valve Seat WidthÐIntake
& Exhaust1.50±2.00 mm
(0.057±0.078 in.)
Valve Guide
Guide Bore Diameter
(Std.)6.975±7.00 mm
(0.274±0.275 in.)
Valves
Valve Lift (Zero
Lash)ÐIntake & Exhaust
Ð3.3L 9.80 mm
(0.385 in.)
Ð3.8L 11.0 mm
(0.433 in.)
9 - 88 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 2720 of 4284

DURE) Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
Clean all engine oil passages.
INSPECTION
(1) Before cleaning, check for leaks, damage and
cracks.
(2) Clean cylinder head and oil passages.
(3) Check cylinder head for flatness (Fig. 17).
(4) Cylinder head must be flat within:
²Standard dimension = less than 0.05 mm (0.002
inch.)
²Service Limit = 0.2 mm (0.008 inch.)
²Grinding Limit = Maximum of 0.2 mm (0.008
inch.) is permitted.
CAUTION: 0.20 mm (0.008 in.) MAX is a combined
total dimension of the stock removal limit from cyl-
inder head and block top surface (Deck) together.
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Clean all sealing surfaces of engine block and
cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(2) Position new gasket(s) on engine block (Fig.
18). The left bank gasket is identified with the ªLº
stamped in the exposed area of the gasket located at
front of engine (shown in (Fig. 18)). The right bank
gasket is identified with a ªRº stamped in the
exposed area of the gasket also, but is located at the
rear of the engine.
(3)The cylinder head bolts are torqued using
the torque yield method, they should be exam-
ined BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked
down, the bolts must be replaced(Fig. 19).
(4) Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale the bolt should be replaced.(5) Tighten the cylinder head bolts 1±8 in the
sequence shown in (Fig. 20). Using the 4 step torque
turn method, tighten according to the following val-
ues:
²Step 1: Bolts1±8to61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
²Step 2: Bolts1±8to88N´m(65ft.lbs.)
²Step 3: Bolts1±8(again) to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.)
²Step 4: Bolts1±8turn an additional 1/4 Turn.
(Do not use a torque wrench for this step.)
NOTE: Bolt torque after 1/4 turn should be over 122
N´m (90 ft. lbs.). If not, replace the bolt.
(6) Inspect push rods and replace worn or bent
rods.
(7) Install the push rods.
(8) Install the rocker arm and shaft assemblies.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
ARMS - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 17 Checking Cylinder Head FlatnessÐTypical
Fig. 18 Head Gasket Installation
1 - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
2 - LOCATION IDENTIFICATION (L = LEFT BANK, R = RIGHT
BANK)
Fig. 19 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
9 - 96 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)