2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine diesel
[x] Cancel search: engine dieselPage 3743 of 4284
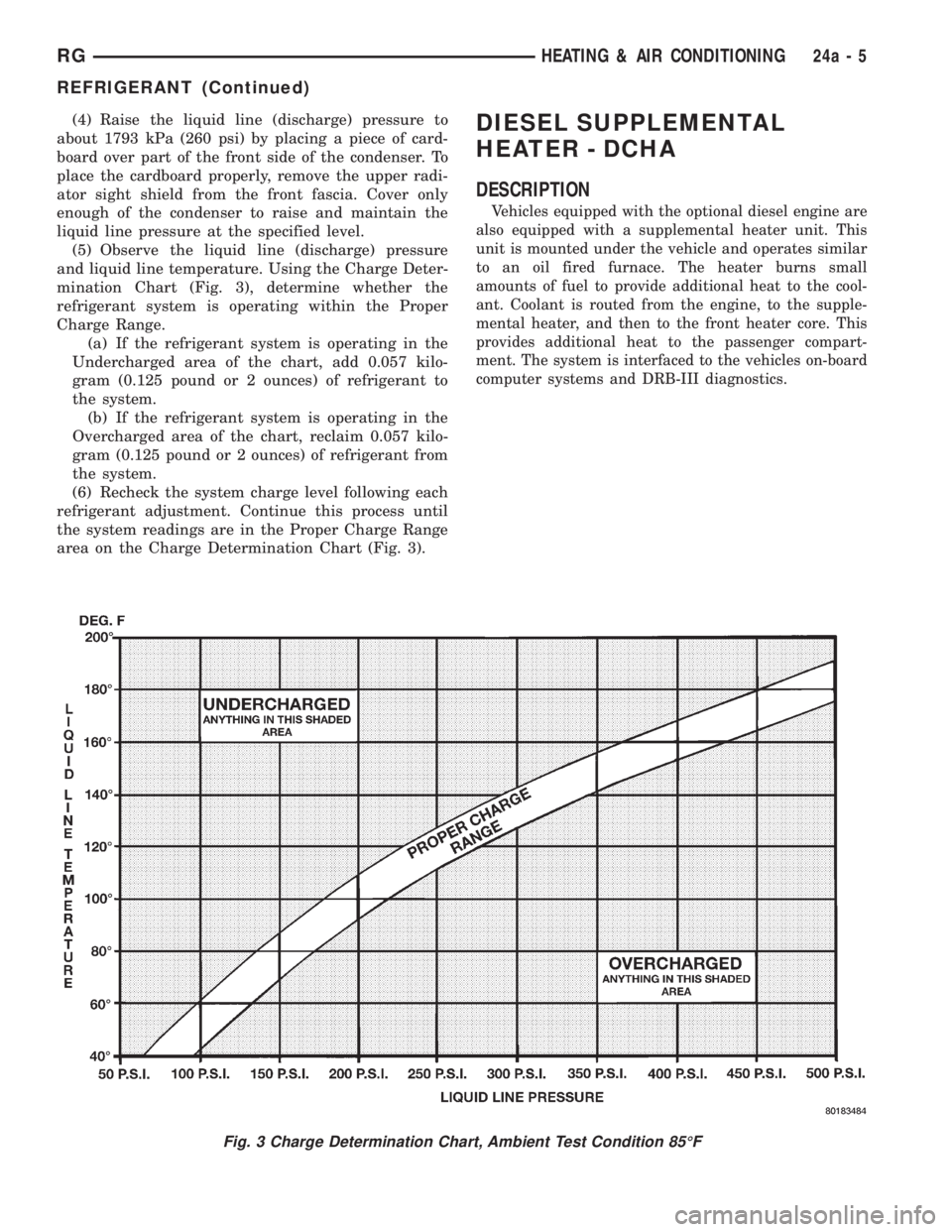
(4) Raise the liquid line (discharge) pressure to
about 1793 kPa (260 psi) by placing a piece of card-
board over part of the front side of the condenser. To
place the cardboard properly, remove the upper radi-
ator sight shield from the front fascia. Cover only
enough of the condenser to raise and maintain the
liquid line pressure at the specified level.
(5) Observe the liquid line (discharge) pressure
and liquid line temperature. Using the Charge Deter-
mination Chart (Fig. 3), determine whether the
refrigerant system is operating within the Proper
Charge Range.
(a) If the refrigerant system is operating in the
Undercharged area of the chart, add 0.057 kilo-
gram (0.125 pound or 2 ounces) of refrigerant to
the system.
(b) If the refrigerant system is operating in the
Overcharged area of the chart, reclaim 0.057 kilo-
gram (0.125 pound or 2 ounces) of refrigerant from
the system.
(6) Recheck the system charge level following each
refrigerant adjustment. Continue this process until
the system readings are in the Proper Charge Range
area on the Charge Determination Chart (Fig. 3).DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL
HEATER - DCHA
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the optional diesel engine are
also equipped with a supplemental heater unit. This
unit is mounted under the vehicle and operates similar
to an oil fired furnace. The heater burns small
amounts of fuel to provide additional heat to the cool-
ant. Coolant is routed from the engine, to the supple-
mental heater, and then to the front heater core. This
provides additional heat to the passenger compart-
ment. The system is interfaced to the vehicles on-board
computer systems and DRB-III diagnostics.
Fig. 3 Charge Determination Chart, Ambient Test Condition 85ÉF
RGHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24a-5
REFRIGERANT (Continued)
Page 3744 of 4284

OPERATION
The supplemental heater unit is activated via the
temperature slide control or knob on the vehicle HVAC
control unit. If the control slide or knob is moved to or
above the upper set point the heater is activated. The
unit can operate in a full or partial load range as well
as an idle mode all dependent on the engine coolanttemperature. The heater unit will also turn off if the
HVAC temperature control is lowered to less than the
lower set point. The heater unit can take up to three
minutes to completely shut down when either the
heater temperature is set below the lower set point or
the vehicle ignition is shut down.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL HEATER - DCHA
The following table lists possible fault symptoms of
diesel fueled heaters.
SYMPTOM POSSIBLE CAUSES
Smell of diesel fuel Check heater system integration in vehicle's fuel system. Check fuel
lines for leakage, kinks or obstructions. If OK, Inspect the inlet muffler,
drain as necessary. Re-test the unit and re-inspect. Inspect the
exhaust tube and heater unit for the presence of external fuel. If a
volume is observed on the unit or in the exhaust tube or after draining
and testing. Remove heater unit from vehicle and repair or replace
components as required.
Heater does not achieve full load
operation.Check heater operation with DRB-III and replace components as
required.
Continuous white smoke from heater
exhaust during combustion operation.Check heater operation with DRB-III and replace components as
required. White smoke is typical in extreme weather conditions.
Heater can not be switched off. Check heater operation with DRB-III and replace components as
required.
Heater does not operate. Diagnosis cabin heater ECU using the DRB-III and the procedures
listed in Vehicle Performance under Cabin Heater Diagnosis in Group
18.
Loss of coolant (Leakage) or heater
develops smoke during combustion
operation and exhaust has an
extremely sweet smell.Inspect coolant hoses for leakage, kinks or loose hose connection.
Inspect the exhaust tube assembly for continuous flow, if OK there is
an internal heater leak and unit should be inspected and components
should be replaced as required.
Loss of fuel (dripping). Check heater system integration in vehicles fuel system. Check fuel
line connection for leakage. If OK there is an internal leak and unit
should be inspected and replaced as required.
EXHAUST TUBE
REMOVAL
WARNING: THERE IS A POTENTIAL DANGER OF
SKIN BURNS AS THE HEATER AND ITS COMPO-
NENTS MAY BE VERY HOT. MAKE SURE THE
HEATER IS ALLOWED TO COOL DOWN BEFORE
ANY SERVICE WORK IS ATTEMPTED.
WARNING: THERE IS A POTENTIAL DANGER OF
SKIN BURNS AS THE EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
VERY HOT. MAKE SURE THE EXHAUST SYSTEM ISALLOWED TO COOL DOWN BEFORE ANY SERVICE
WORK IS ATTEMPTED ON THE CABIN HEATER.
(1) Elevate vehicle on a lift taking note of the
exhaust tube flexible section.
(2) Remove the exhaust clamp at the flexible pipe
and steel pipe connection (Fig. 4).
(3) Remove the clamp at the flexible pipe connec-
tion and the heater unit housing (if required).
(4) Remove the three screws holding the exhaust
pipe to the body.
(5) Remove the steel exhaust pipe from the vehi-
cle.
(6) Remove the flexible exhaust pipe from the
vehicle (if required).
24a - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGRG
DIESEL SUPPLEMENTAL HEATER - DCHA (Continued)
Page 3777 of 4284

EMISSIONS CONTROL 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EMISSIONS CONTROL 2.5L TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION............................1
SPECIFICATIONS.........................2EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION.............3
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS..................6
EMISSIONS CONTROL 2.5L
TURBO DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
The 2.5L diesel Engine Control Module (ECM) con-
trols many different circuits in the fuel injection
pump and engine systems. If the ECM senses a prob-
lem with a monitored circuit that indicates an actual
problem, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will be
stored in the ECM's memory, and eventually may
illuminate the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
constantly while the key is on. If the problem is
repaired, or is intermittent, the ECM will erase the
DTC after 40 warm-up cycles without the the fault
detected. A warm-up cycle consists of starting the
vehicle when the engine is cold, then the engine is
warmed up to a certain temperature, and finally, the
engine temperature falls to a normal operating tem-
perature, then the key is turned off.
Certain criteria must be met for a DTC to be
entered into ECM memory. The criteria may be a
specific range of engine rpm, engine or fuel tempera-
ture and/or input voltage to the ECM. A DTC indi-
cates that the ECM has identified an abnormal
signal in a circuit or the system.
There are several operating conditions that the
ECM does not monitor and set a DTC for. Refer to
the following Monitored Circuits and Non±Monitored
Circuits in this section.
ECM MONITORED SYSTEMS
The ECM can detect certain problems in the elec-
trical system.
Open or Shorted Circuit± The ECM will not
distinguish between an open or a short to ground,
however the ECM can determine if there is excessive
current on a circuit, such as a short to voltage or a
decrease in component resistance.
Output Device Current Flow± The ECM senses
whether the output devices are electrically connected.
If there is a problem with the circuit, the ECM
senses whether the circuit is open, shorted to ground
(±), or shorted to (+) voltage.Fuel Pressure:Fuel pressure is controlled by the
fuel injection pump and fuel pressure solenoid. The
ECM uses a fuel pressure sensor to determine if a
fuel pressure problem exists.
Fuel Injector Malfunctions:The ECM can deter-
mine if a fuel injector has an electrical problem. The
fuel injectors on the diesel engine arecontrolledby
the ECM.
ECM NON±MONITORED SYSTEMS
The ECM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems or conditions that could have malfunctions
that result in driveability problems. A DTC will not
be displayed for these conditions.
Cylinder Compression:The ECM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression.
Exhaust System:The ECM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system.
Vacuum Assist:Leaks or restrictions in the vac-
uum circuits of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sys-
tem (EGR) are not monitored by the ECM.
ECM System Ground:The ECM cannot deter-
mine a poor system ground. However, a DTC may be
generated as a result of this condition.
ECM/PCM Connector Engagement:The ECM
cannot determine spread or damaged connector pins.
However, a DTC may be generated as a result of this
condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The ECM compares input signals from each input
device. It has high and low limits that are pro-
grammed into it for that device. If the inputs are not
within specifications and other DTC criteria are met,
a DTC will be stored in memory. Other DTC criteria
might include engine rpm limits or input voltages
from other sensors or switches. The other inputs
might have to be sensed by the ECM when it senses
a high or low input voltage from the control system
device in question.
RGEMISSIONS CONTROL 2.5L TURBO DIESEL25a-1
Page 3782 of 4284

ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
DESCRIPTION............................6
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
DESCRIPTION - DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
On the following pages, a list of DTC's is provided
for the 2.5L diesel engine. A DTC indicates that the
ECM has recognized an abnormal signal in a circuit
or the system. A DTC may indicate the result of a
failure, but most likely will not identify the failed
component directly. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic manual for more information on diagnosis of trou-
ble codes.
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored DTC can be displayed through the use of
the DRB IIItscan tool. The DRB IIItconnects to the
data link connector. The data link connector is
located under the instrument panel near bottom of
the steering column (Fig. 1).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the DRB
IIItscan tool to erase a DTC.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) - DRBIIITCODES
Generic Scan Tool Code DRB IIITScan Tool Display
P0070 Ambient Air Temperature Circuit Signal Voltage Too High
Ambient Air Temperature Circuit Signal Voltage Too Low
P0100 Mass Air Flow Sensor Plausibility
Mass Air Flow Sensor Plausibility Positive Area
Mass Air Flow Sensor Signal Voltage Too High
Mass Air Flow Sensor Signal Voltage Too Low
Mass Air Flow Sensor Supply Voltage Too High Or Low
P0105 Barometric Pressure Circuit Signal Voltage To High
Barometric Pressure Circuit Signal Voltage To Low
P0110 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Signal Too High
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Signal Too Low
Fig. 1 DATA LINK CONNECTOR
25a - 6 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICSRG