2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER automatic transmission
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmissionPage 1833 of 4284

²Throttle Position Sensor
²Torque Management Input (From TCM)
²Transaxle Control Module (TCM)
²Transaxle Gear Engagement (From TCM)
²Vehicle Speed (from transmission control mod-
ule)
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
²Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
Relays
²Data Link Connector (PCI and SCI Transmit)
²Double Start Override
²EGR Solenoid
²Fuel Injectors
²Generator Field
²High Speed Fan Relay
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Ignition Coils
²Leak Detection Pump
²Low Speed Fan Relay
²MTV Actuator
²Proportional Purge Solenoid
²SRV Valve
²Speed Control Relay
²Speed Control Vent Relay
²Speed Control Vacuum Relay
²8 Volt Output
²5 Volt Output
Based on inputs it receives, the powertrain control
module (PCM) adjusts fuel injector pulse width, idle
speed, ignition timing, and canister purge operation.
The PCM regulates the cooling fans, air conditioning
and speed control systems. The PCM changes gener-
ator charge rate by adjusting the generator field.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel
ratio) based on the following inputs.
²Battery Voltage
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Exhaust Gas Oxygen Content (heated oxygen
sensors)
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Throttle Position
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor based on the following inputs.
²Brake Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Park/Neutral (transmission gear selection)
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
²Vehicle Speed (from Transmission Control Mod-
ule)The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
²Intake Air Temperature
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Knock Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Park/Neutral (transmission gear selection)
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
The automatic shut down (ASD) and fuel pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the powertrain control module through the same
circuit.
The camshaft and crankshaft signals are sent to
the powertrain control module. If the PCM does not
receive both signals within approximately one second
of engine cranking, it deactivates the ASD and fuel
pump relays. When these relays are deactivated,
power is shut off to the fuel injectors, ignition coils,
fuel pump and the heating element in each oxygen
sensor.
The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the engine
coolant temperature sensor, intake air temperature
sensor, manifold absolute pressure sensor and throt-
tle position sensor.
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage in new PCM. Use
the DRB scan tool to change the mileage in the PCM.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Man-
ual and the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
DESCRIPTION
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.
Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-9
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1852 of 4284

STANDARD PROCEDURE - TCC BREAK-IN
VIEW/RESTART PROCEDURE
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) employs
a strategy which modifies torque converter clutch
(TCC) operation. This strategy conditions the torque
converter clutch disc for optimum converter clutch
engagement and feel throughout the life of the trans-
axle. The cycle inhibits FEMCC until six hours of
PEMCC operation have taken place, or the vehicle
has been driven 6,035 km (3750 miles). The cycle
automatically terminates when either the time or
mileage has been achieved, however, the mileage
may vary slightly from vehicle to vehicle.
The TCC break-in cycle must be restarted using
the DRB Scan Tool, and upon:
²Replacement of TCM on vehicle with less than
6,035 km (3750 miles) or less than 6 hours of
PEMCC operation
²Replacement of torque converter assembly at
any vehicle mileage
NOTE: Failure to restart the TCC Break-In Cycle
upon TCM replacement in vehicles with less than
six hours of PEMCC or less than 6,035 km (3750
miles), or upon torque converter replacement at any
mileage, may result in vehicle shudder during cer-
tain operating conditions.
Procedure
The DRB Scan Tool is required to view and/or
restart the TCC Break-In cycle.
(1) Connect the DRB Scan Tool to the vehicle diag-
nostic connector.
(2) Navigate to ªTCC Break-Inº via Transmission/
Transmission Control Module/Miscellaneous.
(3) View or Start TCC Break-In as prompted by
DRB menu.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transmission control module is being
replaced with a new or replacement unit, the Pinion
Factor and Quick Learn procedures must be per-
formed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE) (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE) If vehicle has less than 6,035 km
(3750 miles), the Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
Break-In Strategy reset procedure must also be per-
formed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Remove left front tire/wheel assembly.
(4) Pull back splash shield to gain access to TCM
location.
(5) Disconnect TCM 60-way connector (Fig. 15).
(6) Remove three (3) TCM-to-rail screws and
remove TCM from vehicle (Fig. 16).
Fig. 15 Transmission Control Module 60-way
Connector
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
2 - 60-WAY CONNECTOR
Fig. 16 Transmission Control Module Removal/
Installation
1 - SCREW
2 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
3 - CLIP
4 - LEFT RAIL
8E - 28 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
2001 RS Service Manual
Publication No. 81-370-1005
TSB 26-03-01 March, 2001
Page 1872 of 4284
²If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the
Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a man-
ual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in
the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the
fully depressed position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent the engine from starting, remove the
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) relay. The ASD relay is
located in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), in the
engine compartment. See the fuse and relay layout
label affixed to the underside of the IPM cover for
ASD relay identification and location.
(1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative terminal post. Connect the neg-
ative lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative
cable terminal clamp (Fig. 16). Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct the poor con-
nection between the battery negative cable terminal
clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
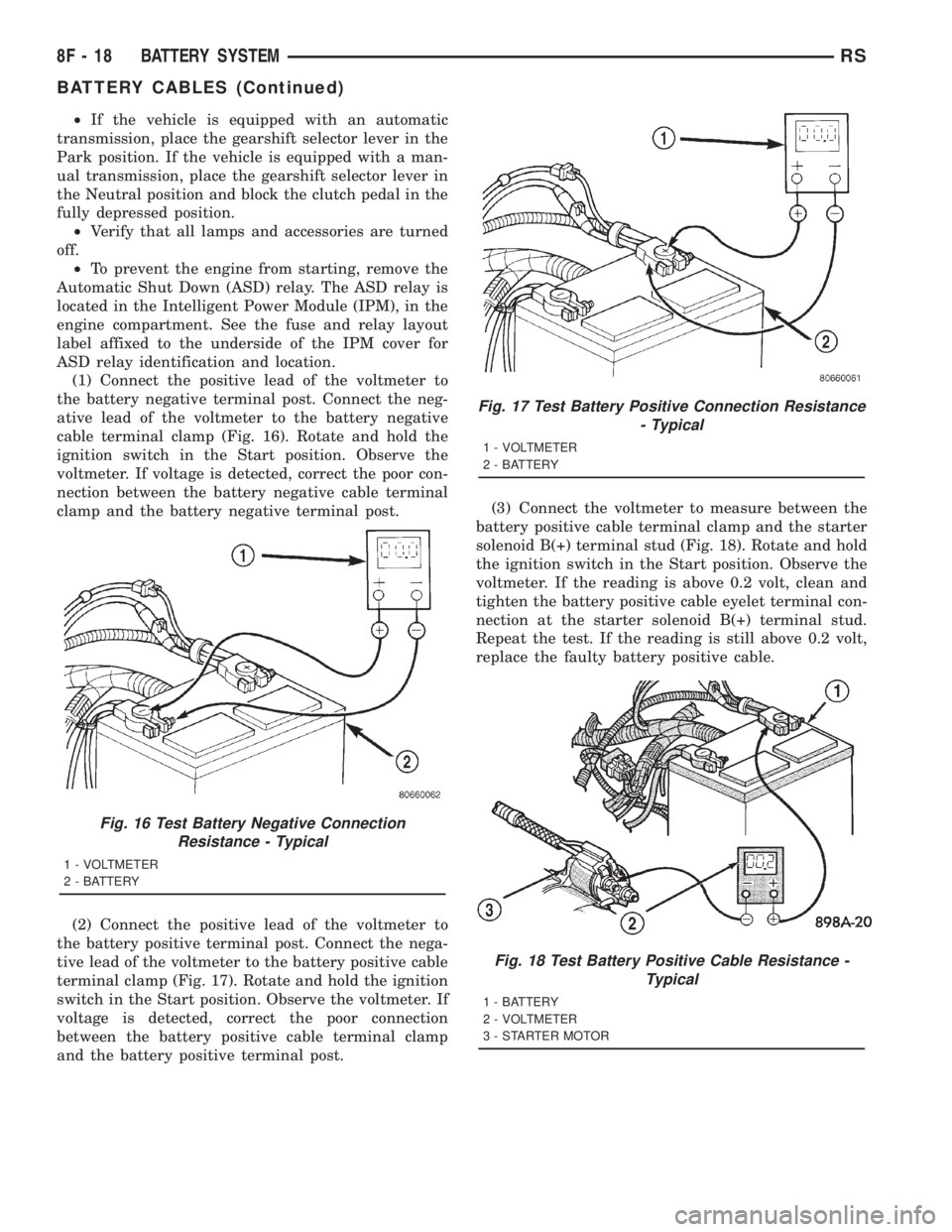
(2) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery positive terminal post. Connect the nega-
tive lead of the voltmeter to the battery positive cable
terminal clamp (Fig. 17). Rotate and hold the ignition
switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If
voltage is detected, correct the poor connection
between the battery positive cable terminal clamp
and the battery positive terminal post.(3) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery positive cable terminal clamp and the starter
solenoid B(+) terminal stud (Fig. 18). Rotate and hold
the ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2 volt, clean and
tighten the battery positive cable eyelet terminal con-
nection at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt,
replace the faulty battery positive cable.
Fig. 16 Test Battery Negative Connection
Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
Fig. 17 Test Battery Positive Connection Resistance
- Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
Fig. 18 Test Battery Positive Cable Resistance -
Typical
1 - BATTERY
2 - VOLTMETER
3 - STARTER MOTOR
8F - 18 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 1883 of 4284

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
3. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.3. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
4. ENGINE SEIZED. 4. REFER TO THE ENGINE SECTION, FOR DIAGNOSTIC AND
SERVICE PROCEDURES.
5. LOOSE
CONNECTION AT
BATTERY, PDC,
STARTER, OR ENGINE
GROUND.5. INSPECT FOR LOOSE CONNECTIONS.
6. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.6. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETHAND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
STARTER
ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT
BEFORE
ENGINE
STARTS.1. BROKEN TEETH ON
STARTER RING GEAR.1. REMOVE STARTER. INSPECT RING GEAR AND REPLACE
IF NECESSARY.
2. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.2. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
STARTER DOES
NOT
DISENGAGE.1. STARTER
IMPROPERLY
INSTALLED.1. INSTALL STARTER. TIGHTEN STARTER MOUNTING
HARDWARE TO CORRECT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.
2. STARTER RELAY
FAULTY.2. REFER TO RELAY TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
RELAY, IF NECESSARY.
3. IGNITION SWITCH
FAULTY.3. REFER TO IGNITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE STEERING
SECTION.. REPLACE SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
4. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.4. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
5. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.5. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
CONTROL CIRCUIT TEST
The starter control circuit has:
²Starter motor with integral solenoid
²Starter relay
²Transmission range sensor, or Park/Neutral
Position switch with automatic transmissions
²Ignition switch
²Battery
²All related wiring and connections
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
²To disable ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover for the proper relay location.
STARTER SOLENOID
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED.
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests.
(2) Perform Starter Solenoid test BEFORE per-
forming the starter relay test.
(3) Perform a visual inspection of the starter/
starter solenoid for corrosion, loose connections or
faulty wiring.
(4) Locate and remove the starter relay from the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the PDC
label for relay identification and location.
RSSTARTING8F-29
STARTING (Continued)
Page 1885 of 4284

(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded
through the transmission range sensor only when the
gearshift selector lever is in the Park or Neutral
positions. Check for continuity to ground at the cav-
ity for relay terminal 85. If not OK with an auto-
matic transmission, check for an open or short circuit
to the transmission range sensor and repair.
SAFETY SWITCHES
For diagnostics of the Transmission Range Sensor,
refer to the Transaxle section for more information.
If equipped with Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing in the Clutch section.
IGNITION SWITCH
After testing starter solenoid and relay, test igni-
tion switch and wiring. Refer to the Ignition Section
or Wiring Diagrams for more information. Check all
wiring for opens or shorts, and all connectors for
being loose or corroded.
BATTERY
For battery diagnosis and testing, refer to the Bat-
tery section for procedures.
ALL RELATED WIRING AND CONNECTORS
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for more information.
FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition and Fuel systems must be dis-
abled to prevent engine start while performing the
following tests.
(1) To disable the Ignition and Fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) Remove the air cleaner assembly for access to
battery terminals. Refer to the Fuel section for ser-
vice procedures.
(3) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
(a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp. Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between cable clamp and post.(b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp. Rotate and hold the igni-
tion switch key in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between the cable clamp and post.
(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point.
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at ground cable attaching point. If
voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(4) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal. Hold the ignition switch key in
the START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor starter to engine ground.
(a) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
battery positive terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid. Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position. If
voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor contact at
battery cable to solenoid connection. If reading is
still above 0.2 volt after correcting poor contacts,
replace battery positive cable.
(b) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, replace the starter motor.FEED CIRCUIT TEST
NOTE: The following results are based upon the
vehicle being at room temperature.
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt-ampere tester (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
Fig. 2 Volt Ampere Tester
RSSTARTING8F-31
STARTING (Continued)
Page 1886 of 4284

(1) Check battery before performing this test. Bat-
tery must be fully charged.
(2) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals. Refer to the operating instructions provided
with the tester being used.
(3) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(4) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARK
and SET parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(5) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
2).
²If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps, check for engine seizing
or faulty starter.
²If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections.
²Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps, the problem is the starter. Replace
the starter refer to starter removal.
(6) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
charge battery if necessary. Disconnect all testingequipment and connect ASD relay. Start the vehicle
several times to assure the problem has been cor-
rected.
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER
MANUFACTURER NIPPONDENSO
Engine Application 2.4L /3.3/3.8L
Power rating 1.2 Kw
Voltage 12 VOLTS
No. of Fields 4
No. of Poles 4
Brushes 4
Drive Conventional Gear Train
Free running Test
Voltage 11
Amperage Draw 73 Amp
Minimum Speed 3401 RPM
SolenoidClosing Voltage 7.5 Volts
Cranking Amperage Draw
test150 - 200 Amps.
Engine should be up to operating temperature.
Extremely heavy oil or tight engine will increase
starter amperage draw.
Torques
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Starter Mounting Bolts 47.4 35
Starter Solenoid Battery
Nut11.3 8.3 100
8F - 32 STARTINGRS
STARTING (Continued)
Page 1930 of 4284

SPEEDOMETER DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO POINTER
MOVEMENT1. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.1.A. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK FOR FAULT CODES.
²IF SPEEDOMETER POINTER MOVES TO
CALIBRATION POINTS DURING TEST LOOK FOR
ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE OF FAILURE.
²IF THE POINTER DOESN'T MOVE DURING TEST,
CHECK FOR POWER AND GROUND TO THE MIC.
IF POWER AND GROUND ARE PRESENT GO TO
STEP 1.B.
1.B. REPLACE CLUSTER. GO TO STEP 1.C.
1.C. CONNECT CLUSTER INTO INSTRUMENT
PANEL WIRING HARNESS. PLACE IT BACK INTO
THE PROPER POSITION IN THE INSTRUMENT
PANEL. PUT IN THE TOP FOUR MOUNTING
SCREWS AND SECURE THE CLUSTER TO THE
INSTRUMENT PANEL.
2. NO SPEED PCI BUS
MESSAGE OR ZERO
MPH PCI SPEED BUS
MESSAGE.2.A. CHECK THE PCM (CODE 10) USING A DRB IIIT
SCAN TOOL. IF OK, GO TO STEP 2.B. IF NOT OK,
REFER TO THE PROPER ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO REPAIR THE PCM.
2.B. CHECK THE SPEED SIGNAL INPUT INTO THE
PCM. THE SPEED SIGNAL ORIGINATES FROM ONE
OF THE FOLLOWING SOURCES:
²A DISTANCE SENSOR FOR VEHICLES WITH 3
SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION. CHECK
CONTINUITY FROM DISTANCE SENSOR TO PCM.
IF OK, REPLACE DISTANCE SENSOR. IF NOT OK,
REPAIR WIRING.
²THE TCM FOR VEHICLES WITH THE 4 SPEED
ELECTRONIC TRANSMISSIONS. CHECK
CONTINUITY FROM TCM TO PCM. IF OK, USE A
DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO CHECK TCM. REFER TO
THE PROPER TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO REPAIR THE TCM. IF
NOT OK, REPAIR WIRING.
8J - 4 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERRS
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 1931 of 4284

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ERRATIC POINTER
MOVEMENT1. ERRATIC MESSAGE
FROM ANOTHER
MODULE.1.A. CHECK THE BCM USING A DRB IIITSCAN
TOOL IF OK, GO TO STEP 1.B. IF NOT OK, REFER
TO THE PROPER BODY DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO REPAIR THE BCM.
1.B. CHECK THE PCM USING A DRB IIITSCAN
TOOL. IF OK, GO TO STEP 1.C. IF NOT OK, REFER
TO THE ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
MANUAL TO REPAIR THE PCM.
1.C. CHECK THE SPEED SIGNAL INPUT INTO THE
PCM. THE SPEED SIGNAL ORIGINATES FROM ONE
OF THE FOLLOWING SOURCES:
²A DISTANCE SENSOR FOR VEHICLES WITH 3
SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION. CHECK
CONTINUITY FROM DISTANCE SENSOR TO PCM.
IF OK, REPLACE DISTANCE SENSOR. IF NOT OK,
REPAIR WIRING.
²THE TCM FOR VEHICLES WITH THE 4 SPEED
ELECTRONIC TRANSMISSIONS. CHECK
CONTINUITY FROM TCM TO ENGINE
CONTROLLER. IF OK, USE A DRB IIITSCAN TOOL
TO CHECK TCM. REFER TO THE PROPER
TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
MANUAL TO REPAIR THE TCM. IF NOT OK, REPAIR
WIRING.
2. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.2.A. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK FOR FAULT CODES.
²IF THE POINTER MOVES DURING TEST BUT
STILL APPEARS ERRATIC, THEN GO TO STEP 2.B.
2.B. REPLACE CLUSTER ASSEMBLY.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-5
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)