2001 CHRYSLER VOYAGER key
[x] Cancel search: keyPage 3079 of 4284
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions. When the ignition key is in the
OFF position, the gearshift lever is unrestricted, and
able to move into any gear position (during towing,
dead battery, etc.).
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
214).
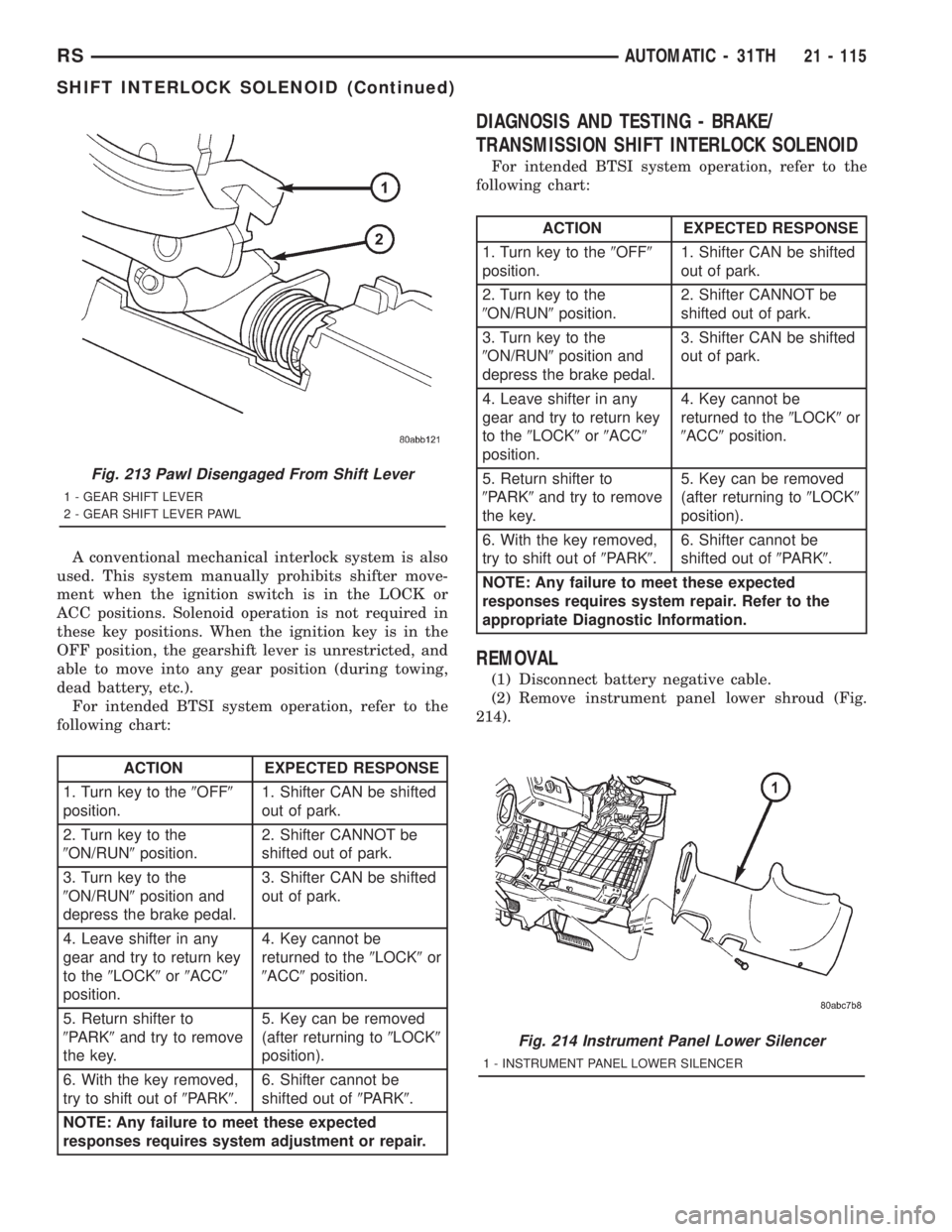
Fig. 213 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 214 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 115
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3215 of 4284
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
VERIFICATION
(1) Place gearshift lever in gated park (P).
(2) Attempt to move vehicle by rocking back and
forth on level ground. If vehicle does not move,
attempt to start engine. If engine starts, the park
position is correct.
(3) Set parking brake.
(4) Turn key to on/run and depress brake pedal.
Place gearshift lever in neutral (N).
(5) Attempt to start engine. If engine starts in
both neutral (N) or park (P), gearshift cable is
adjusted properly. No adjustment is required.
(6) If engine does not start in either park (P) or
neutral (N), perform adjustment procedure.
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Park the vehicle on level ground and set the
parking brake.
(2) Place the gearshift lever in gated park (P) and
remove ignition key.
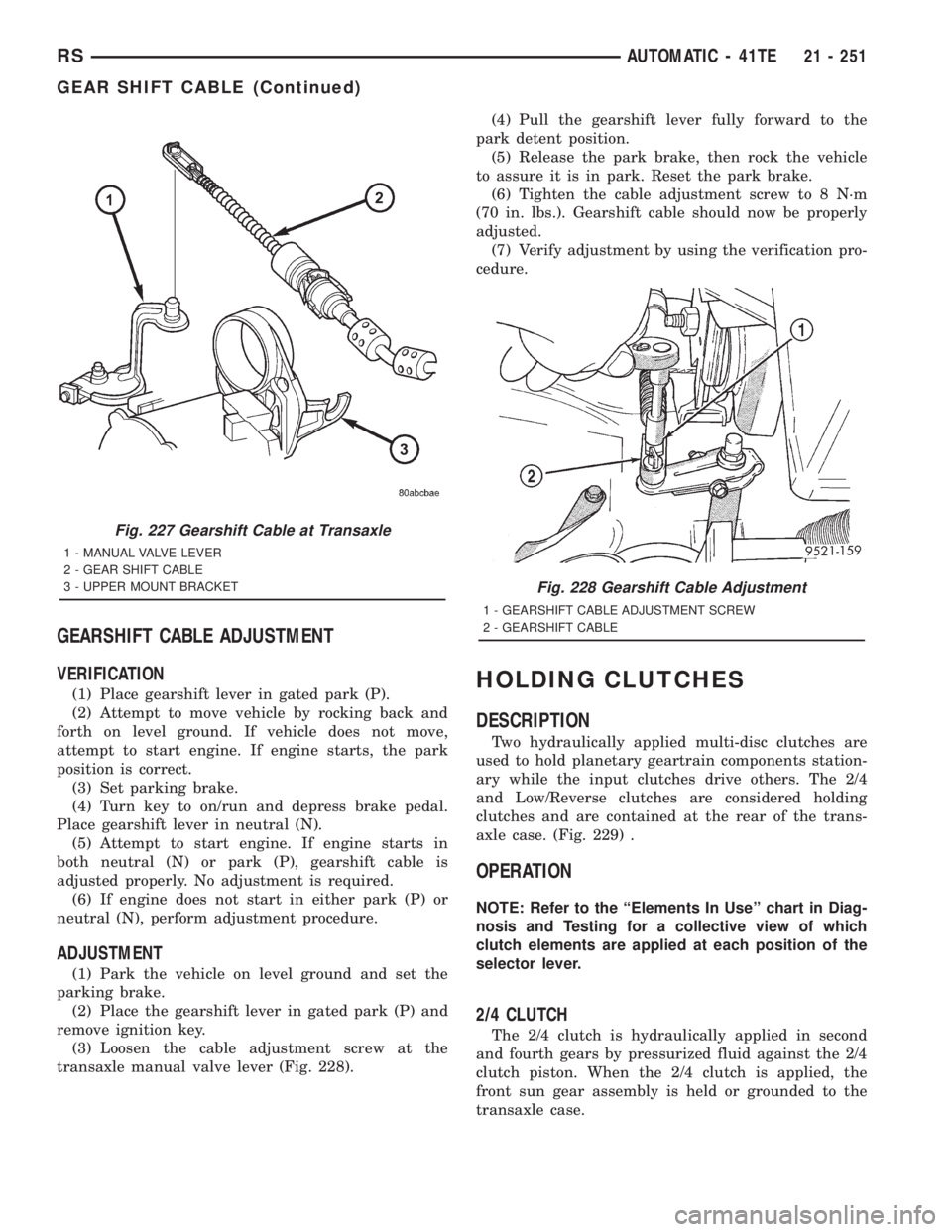
(3) Loosen the cable adjustment screw at the
transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 228).(4) Pull the gearshift lever fully forward to the
park detent position.
(5) Release the park brake, then rock the vehicle
to assure it is in park. Reset the park brake.
(6) Tighten the cable adjustment screw to 8 N´m
(70 in. lbs.). Gearshift cable should now be properly
adjusted.
(7) Verify adjustment by using the verification pro-
cedure.
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION
Two hydraulically applied multi-disc clutches are
used to hold planetary geartrain components station-
ary while the input clutches drive others. The 2/4
and Low/Reverse clutches are considered holding
clutches and are contained at the rear of the trans-
axle case. (Fig. 229) .
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the ªElements In Useº chart in Diag-
nosis and Testing for a collective view of which
clutch elements are applied at each position of the
selector lever.
2/4 CLUTCH
The 2/4 clutch is hydraulically applied in second
and fourth gears by pressurized fluid against the 2/4
clutch piston. When the 2/4 clutch is applied, the
front sun gear assembly is held or grounded to the
transaxle case.
Fig. 227 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
Fig. 228 Gearshift Cable Adjustment
1 - GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT SCREW
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 251
GEAR SHIFT CABLE (Continued)
Page 3237 of 4284

OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the ON/RUN or
START positions (Fig. 306). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the ON/RUN or
START positions, the BTSI solenoid is energized, and
the solenoid plunger hook pulls the shift lever pawl
into position, prohibiting the shift lever from moving
out of PARK (P) (Fig. 307). When the brake pedal is
depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-energizing
the solenoid. This moves the gearshift lever pawl out
of the way (Fig. 308), allowing the shift lever to be
moved into any gear position.
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions. When the ignition key is in the
OFF position, the gearshift lever is unrestricted, and
able to move into any gear position (during towing,
dead battery, etc.).
Fig. 306 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 307 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 308 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 273
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3238 of 4284
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
309).
(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 310).
(4) Remove steering column lower shroud.
(5) Disconnect brake/transmission shift interlock
(BTSI) solenoid connector (Fig. 311).
(6) Remove two (2) solenoid-to-column screws (Fig.
312).
(7) Remove solenoid.
Fig. 309 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 310 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
21 - 274 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3251 of 4284

TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission control relay (Fig. 340) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal oper-
ating mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is
supplied to the solenoid pack and the transmission is
in ªlimp-inº mode. After a controller reset (ignition
key turned to the ªrunº position or after cranking
engine), the TCM energizes the relay. Prior to this,
the TCM verifies that the contacts are open by check-
ing for no voltage at the switched battery terminals.
After this is verified, the voltage at the solenoid pack
pressure switches is checked. After the relay is ener-
gized, the TCM monitors the terminals to verify that
the voltage is greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle and
can only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 341) .
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the TCM.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 342) .
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 341)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the TCM
as a combination of open and closed switches. Each
shift lever position has an assigned combination of
switch states (open/closed) that the TCM receives
from four sense circuits. The TCM interprets this
information and determines the appropriate trans-
axle gear position and shift schedule.
Fig. 340 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERYFig. 341 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 287
Page 3277 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMMON
PROBLEM CAUSES
The majority of transaxle malfunctions are a result
of:
²Insufficient lubrication
²Incorrect lubricant
²Misassembled or damaged internal components
²Improper operation
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting may be caused by a misadjusted
crossover cable. If hard shifting is accompanied by
gear clash, synchronizer clutch and stop rings or gear
teeth may be worn or damaged.
Hard shifting may also be caused by a binding or
broken shift cover mechanism. Remove shift cover
and verify smooth operation. Replace as necessary.
Misassembled synchronizer components also cause
shifting problems. Incorrectly installed synchronizer
sleeves, keys, balls, or springs can cause shift prob-
lems.
NOISY OPERATION
Transaxle noise is most often a result of worn or
damaged components. Chipped, broken gear or syn-
chronizer teeth, and brinnelled, spalled bearings all
cause noise.
Abnormal wear and damage to the internal compo-
nents is frequently the end result of insufficient
lubricant.
SLIPS OUT OF GEAR
Transaxle disengagement may be caused by mis-
aligned or damaged shift components, or worn teeth
on the drive gears or synchronizer components. Incor-
rect assembly also causes gear disengagement. Check
for missing snap rings.
LOW LUBRICANT LEVEL
Insufficient transaxle lubricant is usually the
result of leaks, or inaccurate fluid level check or refill
method. Leakage is evident by the presence of oil
around the leak point. If leakage is not evident, the
condition is probably the result of an underfill.
If air±powered lubrication equipment is used to fill
a transaxle, be sure the equipment is properly cali-
brated. Equipment out of calibration can lead to an
underfill condition.
CLUTCH PROBLEMS
Worn, damaged, or misaligned clutch components
can cause difficult shifting, gear clash, and noise.
A worn or damaged clutch disc, pressure plate, or
release bearing can cause hard shifting and gear
clash.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L GAS
(1) Raise hood.
(2) Disconnect gearshift cables from shift levers/
cover assembly (Fig. 10).
(3) Remove gearshift cable retaining clips from
mounting bracket (Fig. 10). Remove cables and
secure out of way.
(4) Remove three (3) right engine mount bracket-
to-transaxle bolts (Fig. 11).
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Remove front wheel/tires and halfshafts.
(7) Drain transaxle fluid into suitable container.
(8) Remove cradle plate.
(9) Remove front harness retainer and secure har-
ness out of way.
(10) Remove clutch release access cover.
(11)RHD Models:Using Tool 6638A, disconnect
clutch hydraulic circuit quick connect (located on
slave cylinder tube). Remove clutch slave cylinder by
depressing towards case and rotating counter-clock-
wise 60É, while lifting anti-rotation tab out of case
slot with screwdriver (Fig. 12).LHD Models:
Remove clutch release cable by pulling outward on
cable housing, then forward to allow cable core to
pass through case slot (Fig. 13). Disengage T-end
from release lever and secure cable out of way.
(12) Remove engine left mount bracket.
(13) Remove starter motor (Fig. 14).
Fig. 10 Gearshift Cables at Transaxle
1 - SELECTOR CABLE
2 - CABLE RETAINER
3 - CABLE RETAINER
4 - CROSSOVER CABLE
5 - MOUNT BRACKET
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-11
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 3361 of 4284
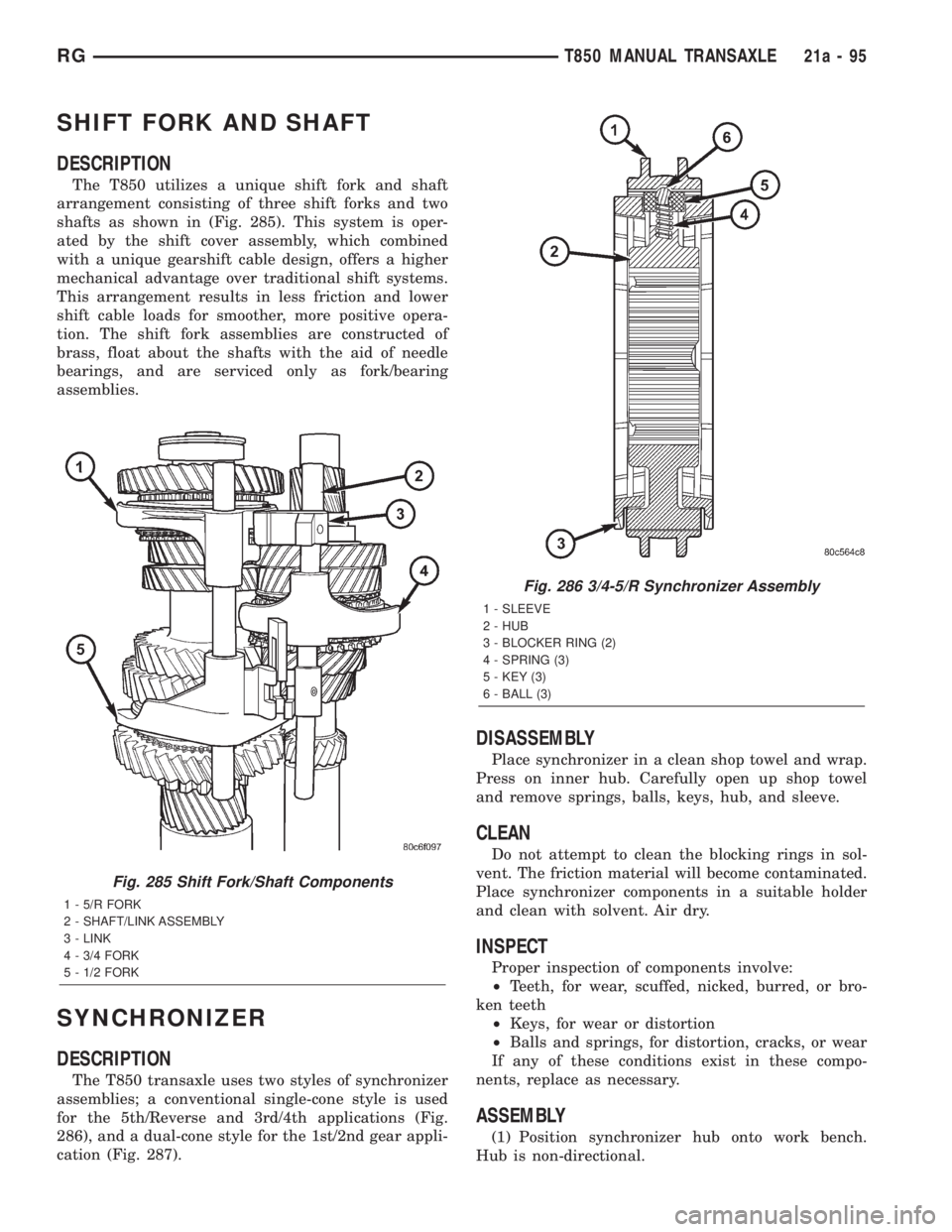
SHIFT FORK AND SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The T850 utilizes a unique shift fork and shaft
arrangement consisting of three shift forks and two
shafts as shown in (Fig. 285). This system is oper-
ated by the shift cover assembly, which combined
with a unique gearshift cable design, offers a higher
mechanical advantage over traditional shift systems.
This arrangement results in less friction and lower
shift cable loads for smoother, more positive opera-
tion. The shift fork assemblies are constructed of
brass, float about the shafts with the aid of needle
bearings, and are serviced only as fork/bearing
assemblies.
SYNCHRONIZER
DESCRIPTION
The T850 transaxle uses two styles of synchronizer
assemblies; a conventional single-cone style is used
for the 5th/Reverse and 3rd/4th applications (Fig.
286), and a dual-cone style for the 1st/2nd gear appli-
cation (Fig. 287).
DISASSEMBLY
Place synchronizer in a clean shop towel and wrap.
Press on inner hub. Carefully open up shop towel
and remove springs, balls, keys, hub, and sleeve.
CLEAN
Do not attempt to clean the blocking rings in sol-
vent. The friction material will become contaminated.
Place synchronizer components in a suitable holder
and clean with solvent. Air dry.
INSPECT
Proper inspection of components involve:
²Teeth, for wear, scuffed, nicked, burred, or bro-
ken teeth
²Keys, for wear or distortion
²Balls and springs, for distortion, cracks, or wear
If any of these conditions exist in these compo-
nents, replace as necessary.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Position synchronizer hub onto work bench.
Hub is non-directional.
Fig. 285 Shift Fork/Shaft Components
1 - 5/R FORK
2 - SHAFT/LINK ASSEMBLY
3 - LINK
4 - 3/4 FORK
5 - 1/2 FORK
Fig. 286 3/4-5/R Synchronizer Assembly
1 - SLEEVE
2 - HUB
3 - BLOCKER RING (2)
4 - SPRING (3)
5 - KEY (3)
6 - BALL (3)
RGT850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21a-95
Page 3362 of 4284
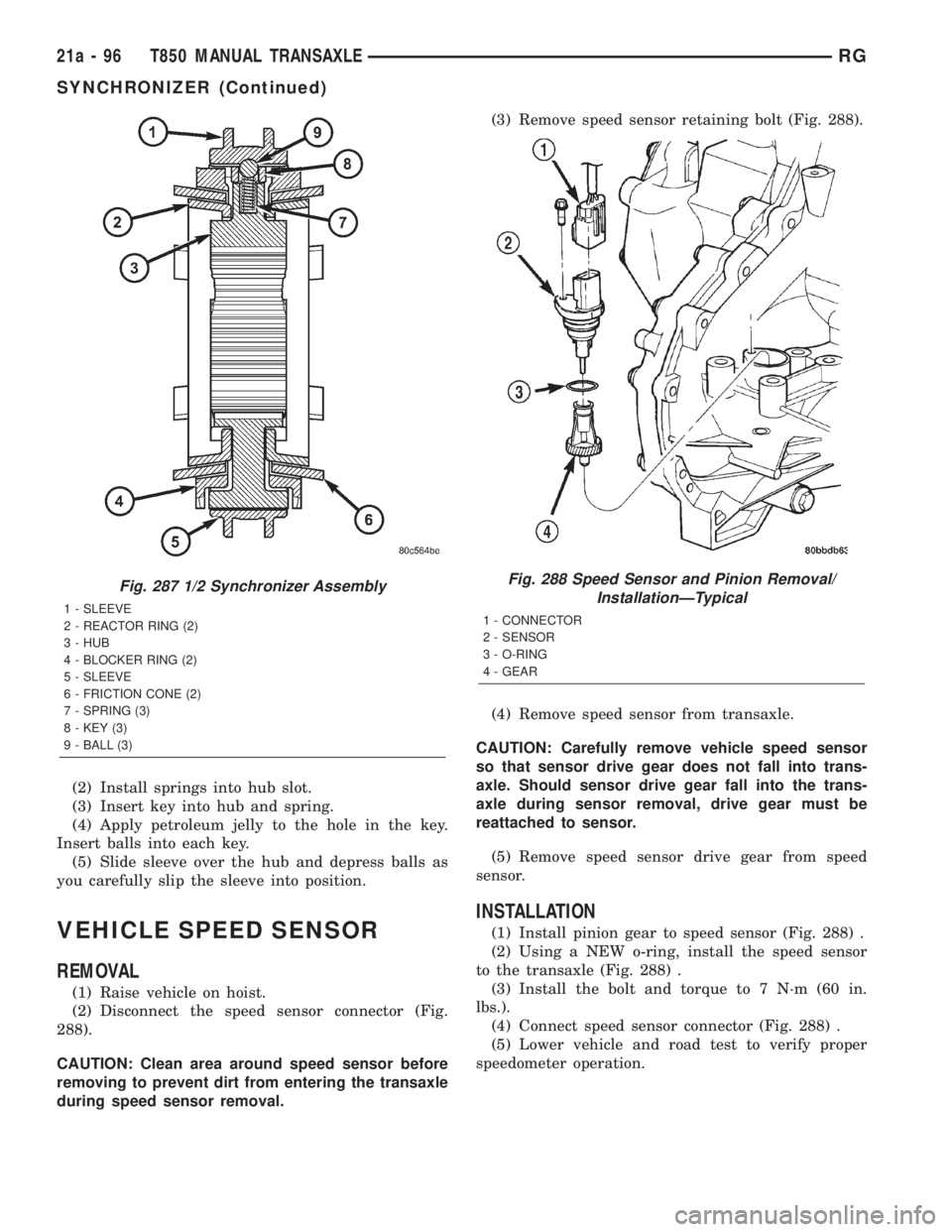
(2) Install springs into hub slot.
(3) Insert key into hub and spring.
(4) Apply petroleum jelly to the hole in the key.
Insert balls into each key.
(5) Slide sleeve over the hub and depress balls as
you carefully slip the sleeve into position.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Disconnect the speed sensor connector (Fig.
288).
CAUTION: Clean area around speed sensor before
removing to prevent dirt from entering the transaxle
during speed sensor removal.(3) Remove speed sensor retaining bolt (Fig. 288).
(4) Remove speed sensor from transaxle.
CAUTION: Carefully remove vehicle speed sensor
so that sensor drive gear does not fall into trans-
axle. Should sensor drive gear fall into the trans-
axle during sensor removal, drive gear must be
reattached to sensor.
(5) Remove speed sensor drive gear from speed
sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install pinion gear to speed sensor (Fig. 288) .
(2) Using a NEW o-ring, install the speed sensor
to the transaxle (Fig. 288) .
(3) Install the bolt and torque to 7 N´m (60 in.
lbs.).
(4) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 288) .
(5) Lower vehicle and road test to verify proper
speedometer operation.
Fig. 287 1/2 Synchronizer Assembly
1 - SLEEVE
2 - REACTOR RING (2)
3 - HUB
4 - BLOCKER RING (2)
5 - SLEEVE
6 - FRICTION CONE (2)
7 - SPRING (3)
8 - KEY (3)
9 - BALL (3)
Fig. 288 Speed Sensor and Pinion Removal/
InstallationÐTypical
1 - CONNECTOR
2 - SENSOR
3 - O-RING
4 - GEAR
21a - 96 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERG
SYNCHRONIZER (Continued)