Page 25 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
25
Notes
Page 26 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
26
The suspension strut mounting is of the bulky
rubber bearing construction.
It consists of two functional components:
– The inner part forms the connection to the
piston rod.
– The larger outer part provides for acoustic
insulation of the shock absorber.
Axles
Four-link front axle
The thorough further development of the
light-weight construction resulted in a weight
reduction of approx. 8.5 kg at the front axle.
In addition to all transverse links, the pivot
bearing is now also made of aluminium.
The wheel bearing is attached to the pivot
bearing via four bolts. The wheel hub can be
pressed in and out.
Running gear
SSP254_087
Aluminium pivot bearing Aluminium mounting bracket
Aluminium
spring plate
Shock absorber valves
SSP254_086
SSP254_085
Page 27 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
27
The front-wheel drive version is fitted with a
wheel bearing unit with integral wheel hub,
which is mounted on a stub axle forged
together with the wheel carrier.
Trapezium link rear axle
The rear axle design with largely identical
components is used in both the front-wheel
drive as well as in the quattro versions.
The wheel bearings of the quattro version
consist of pressed-in, double-row angular ball
bearings with conventional wheel hubs.
SSP254_089
SSP254_091
Toe adjustmentCamber
adjustment
SSP254_082 SSP254_083
Apart from the axle mounting, the two axle
versions differ only in the wheel carrier and
the wheel bearings.
Toe adjustment
Camber
adjustment
Page 28 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
28
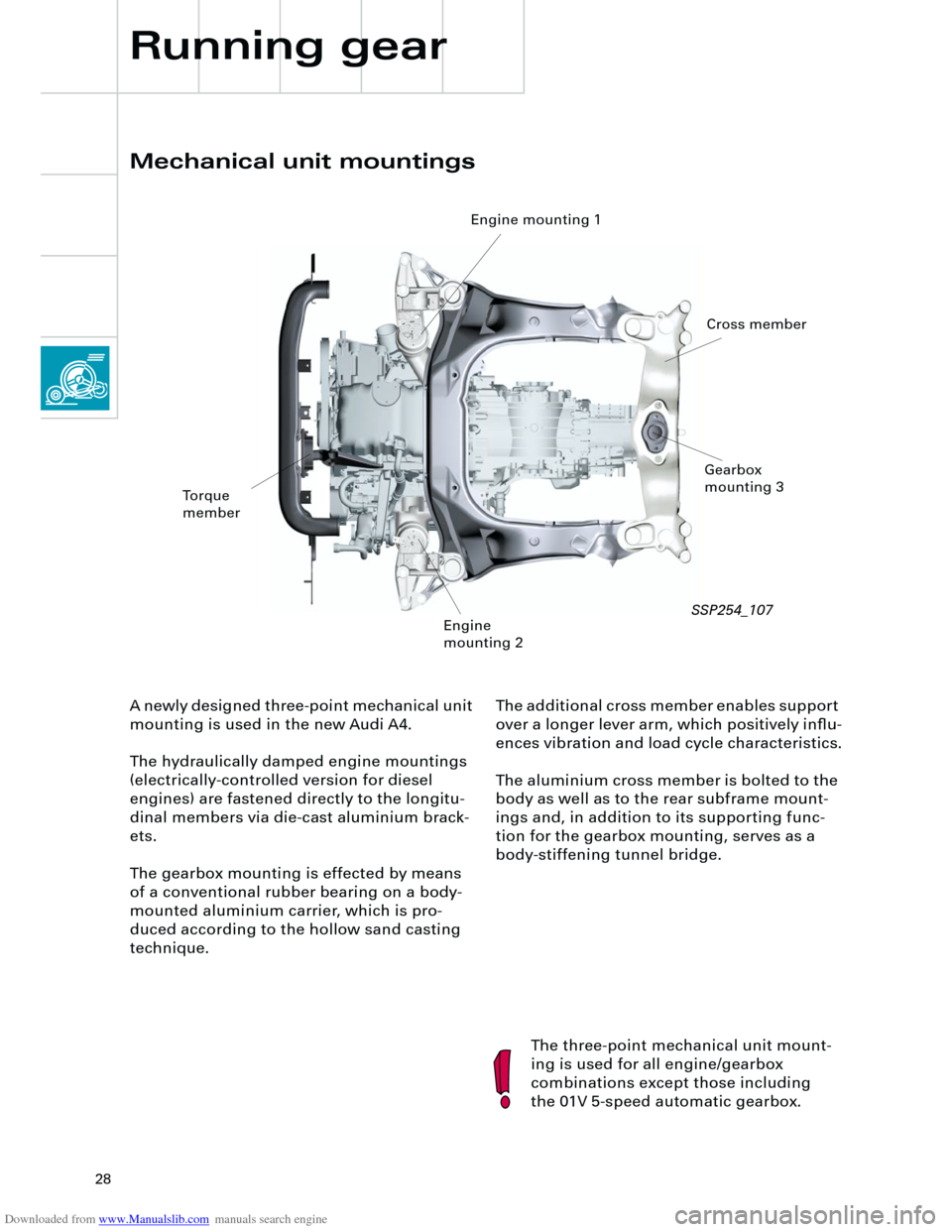
The additional cross member enables support
over a longer lever arm, which positively influ-
ences vibration and load cycle characteristics.
The aluminium cross member is bolted to the
body as well as to the rear subframe mount-
ings and, in addition to its supporting func-
tion for the gearbox mounting, serves as a
body-stiffening tunnel bridge.
Mechanical unit mountings
Running gear
The three-point mechanical unit mount-
ing is used for all engine/gearbox
combinations except those including
the 01V 5-speed automatic gearbox. A newly designed three-point mechanical unit
mounting is used in the new Audi A4.
The hydraulically damped engine mountings
(electrically-controlled version for diesel
engines) are fastened directly to the longitu-
dinal members via die-cast aluminium brack-
ets.
The gearbox mounting is effected by means
of a conventional rubber bearing on a body-
mounted aluminium carrier, which is pro-
duced according to the hollow sand casting
technique.
Torque
member
Engine mounting 1
Engine
mounting 2Gearbox
mounting 3
Cross member
SSP254_107
Page 29 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
29
Brake system
The new Bosch ESP 5.7 is introduced in the
Audi A4. The ESP 5.7 is distinguished by the
following special features:
– The hydraulic unit and control unit form a
single unit.
– The charging pump (actuation of ESP
hydraulic pump V156) is discontinued.
– A brake assistant is included.
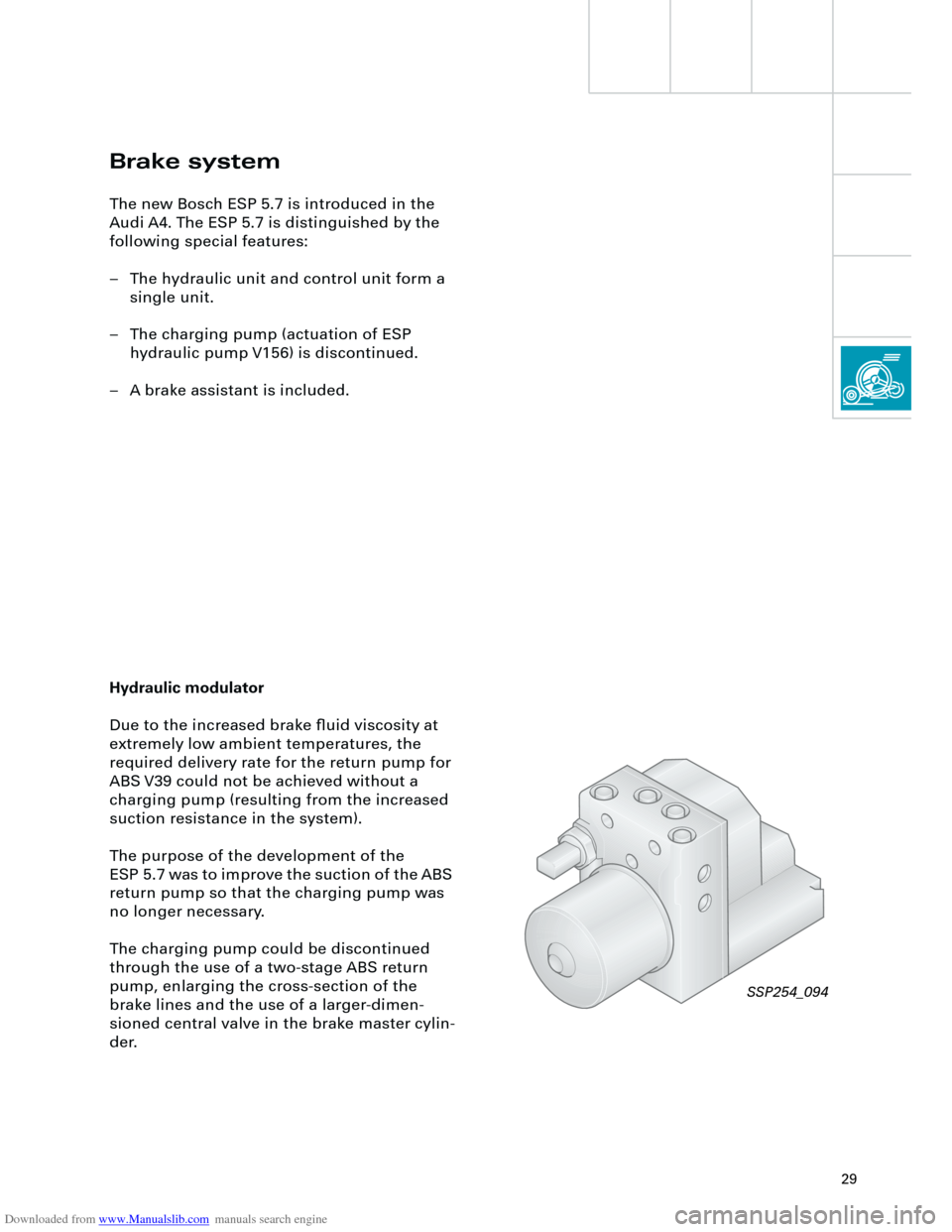
Hydraulic modulator
Due to the increased brake fluid viscosity at
extremely low ambient temperatures, the
required delivery rate for the return pump for
ABS V39 could not be achieved without a
charging pump (resulting from the increased
suction resistance in the system).
The purpose of the development of the
ESP 5.7 was to improve the suction of the ABS
return pump so that the charging pump was
no longer necessary.
The charging pump could be discontinued
through the use of a two-stage ABS return
pump, enlarging the cross-section of the
brake lines and the use of a larger-dimen-
sioned central valve in the brake master cylin-
der.
SSP254_094
Page 30 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
30
UTUTOTOTUT
UTUTOTOTUT
Running gear
The graphic shows a comparison of the
suction volumes of both pump versions.
In the single-stage ABS return pump, the
entire suction volume must be drawn in and
flow through the suction line during one
piston stroke (piston stroke from TDC to BDC). The suction pressure is correspondingly high
and increases with increasing viscosity.
Cavitation and the associated drop in
performance on the pressure side, are the
results.
Single-stage ABS return pump
Suction volumes
SSP254_095
Suction volumes
Page 31 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
31
UTUTOTOT
UTUTOTOT
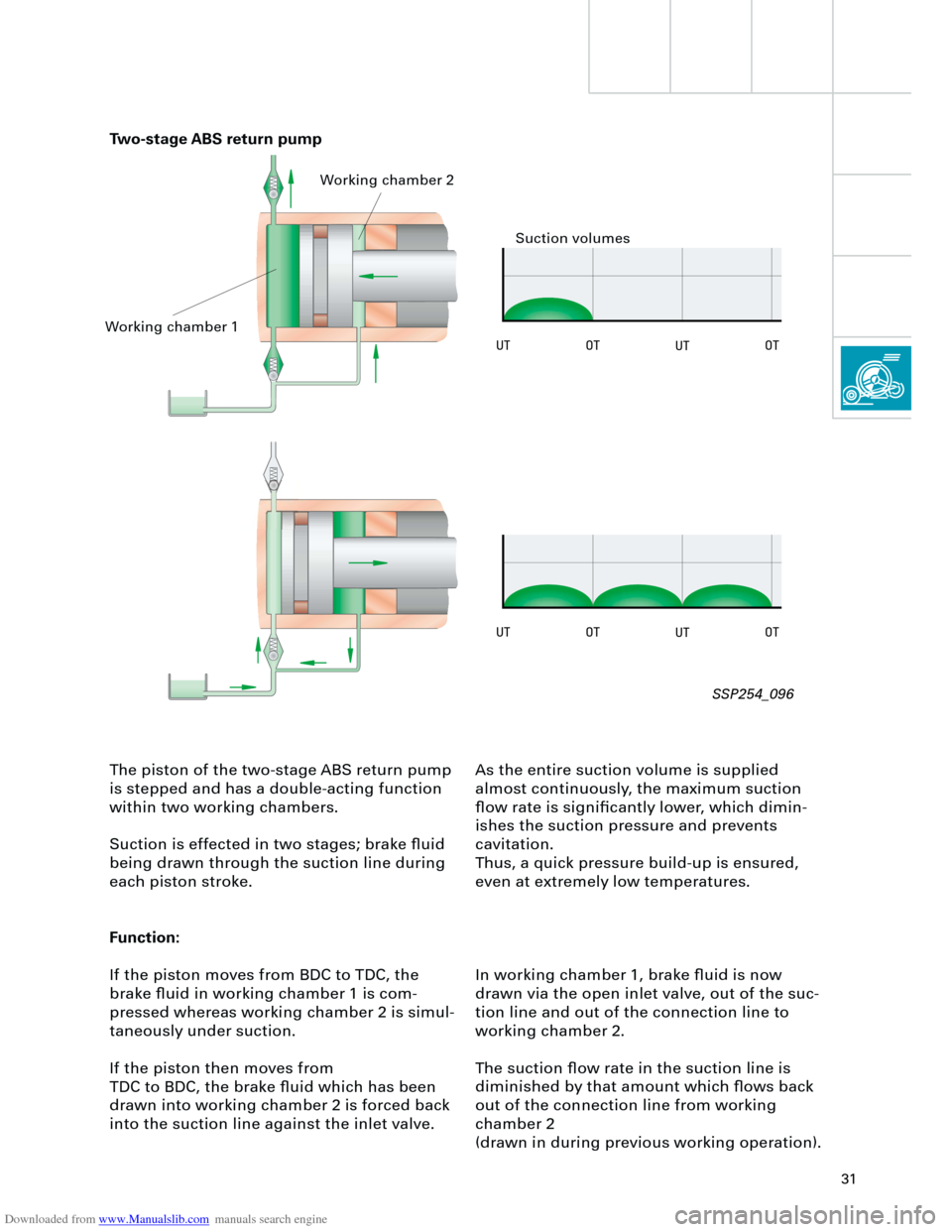
The piston of the two-stage ABS return pump
is stepped and has a double-acting function
within two working chambers.
Suction is effected in two stages; brake fluid
being drawn through the suction line during
each piston stroke.
Function:
If the piston moves from BDC to TDC, the
brake fluid in working chamber 1 is com-
pressed whereas working chamber 2 is simul-
taneously under suction.
If the piston then moves from
TDC to BDC, the brake fluid which has been
drawn into working chamber 2 is forced back
into the suction line against the inlet valve.As the entire suction volume is supplied
almost continuously, the maximum suction
flow rate is significantly lower, which dimin-
ishes the suction pressure and prevents
cavitation.
Thus, a quick pressure build-up is ensured,
even at extremely low temperatures.
In working chamber 1, brake fluid is now
drawn via the open inlet valve, out of the suc-
tion line and out of the connection line to
working chamber 2.
The suction flow rate in the suction line is
diminished by that amount which flows back
out of the connection line from working
chamber 2
(drawn in during previous working operation).
Two-stage ABS return pump
Working chamber 1Working chamber 2
Suction volumes
SSP254_096
Page 32 of 88
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
32
Brake assistant
Investigations in accident research have
shown, that the majority of drivers fail to ade-
quately actuate the brakes in an emergency
situation.
This results in insufficient brake pressure
being generated to achieve maximum vehicle
deceleration.
This lengthens the braking distance.During emergency braking, the brake assist-
ant aids the driver by increasing the brake
pressure automatically, to a level exceeding
the locking limit.
The ABS (
A
nti-lock
b
raking
s
ystem) is thus
quickly brought into the operating range,
which enables a maximum vehicle decelera-
tion to be achieved.
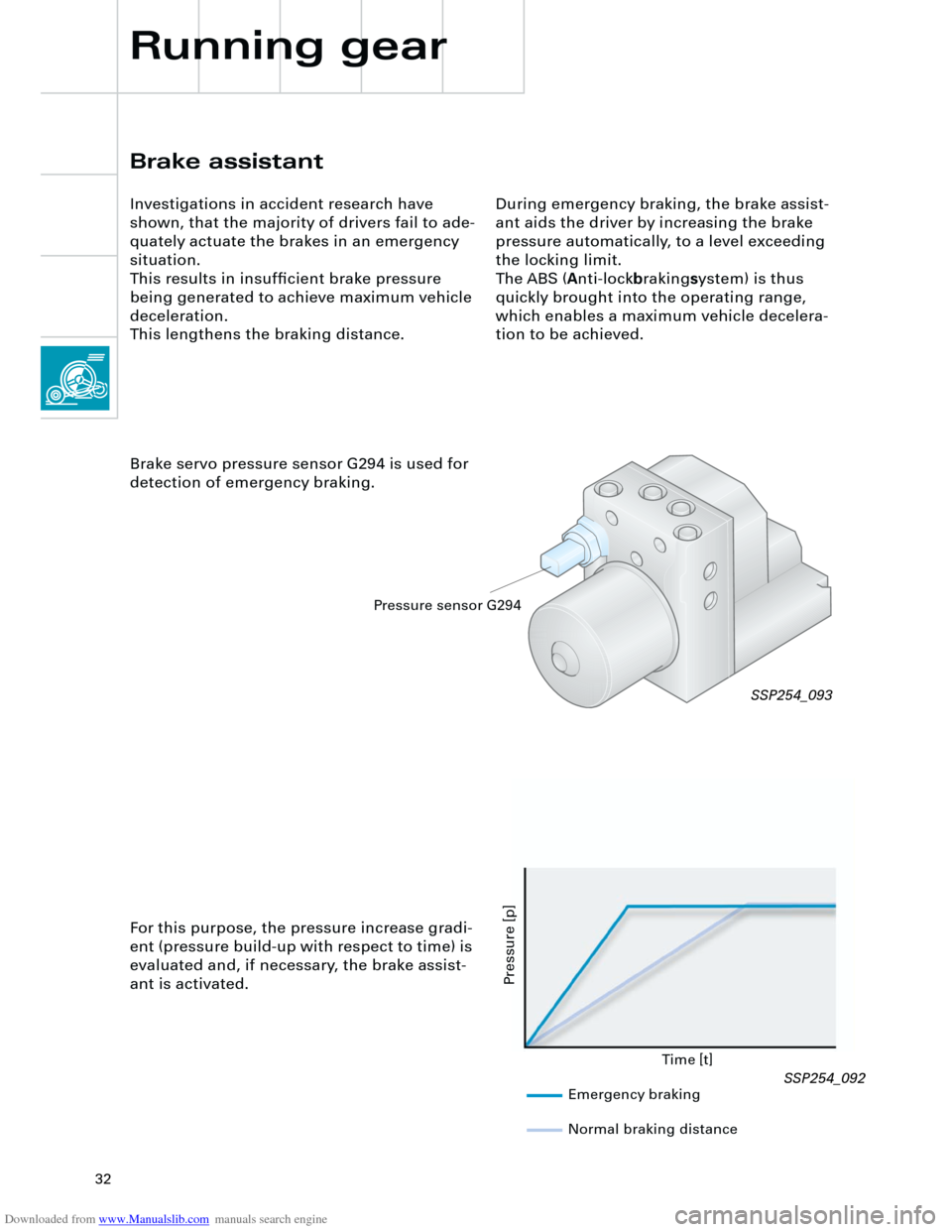
Brake servo pressure sensor G294 is used for
detection of emergency braking.
Time [t]
Pressure [p]
For this purpose, the pressure increase gradi-
ent (pressure build-up with respect to time) is
evaluated and, if necessary, the brake assist-
ant is activated.
SSP254_093
Emergency braking
Normal braking distance
Pressure sensor G294
Running gear
SSP254_092