Page 64 of 447
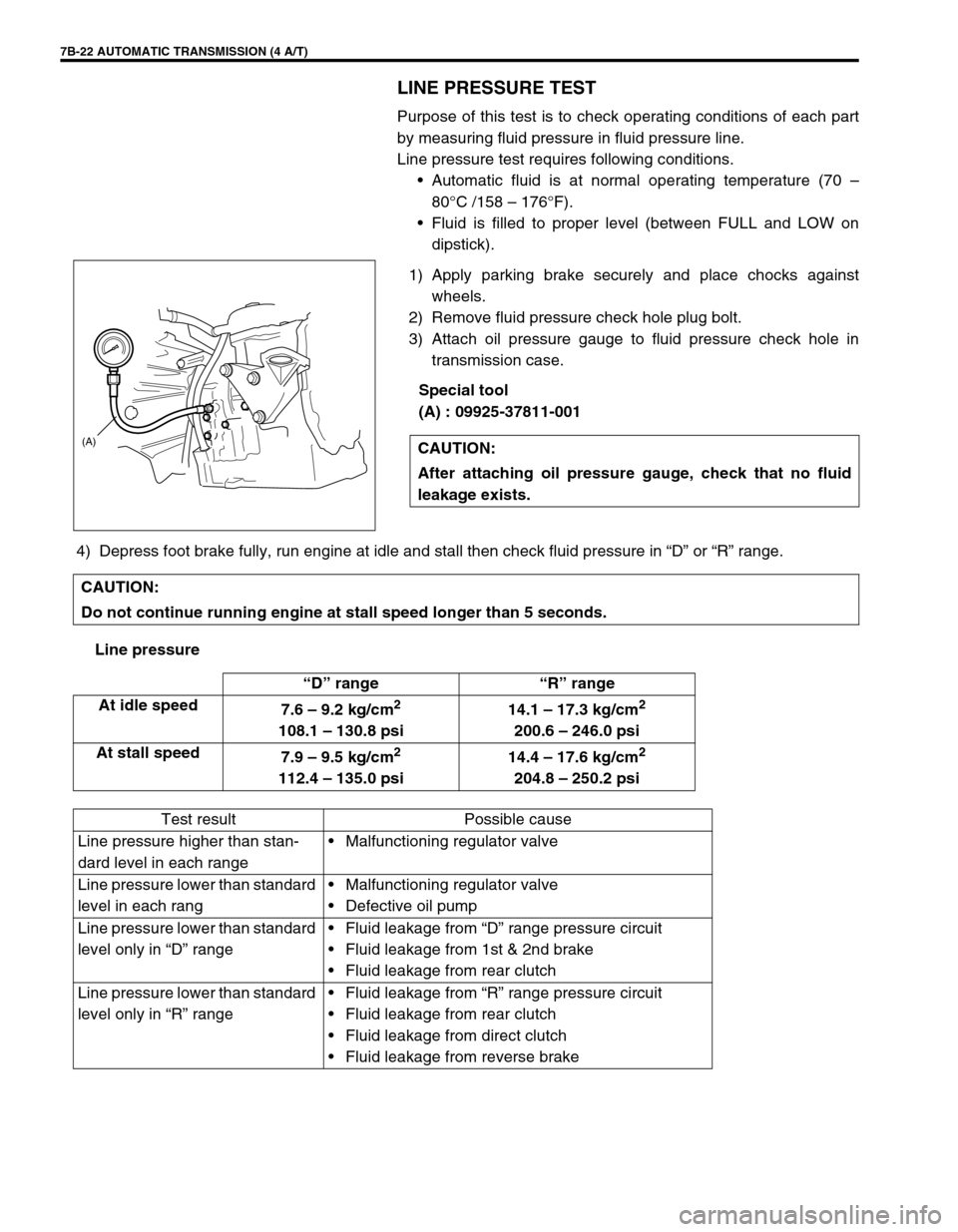
7B-22 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T)
LINE PRESSURE TEST
Purpose of this test is to check operating conditions of each part
by measuring fluid pressure in fluid pressure line.
Line pressure test requires following conditions.
Automatic fluid is at normal operating temperature (70 –
80°C /158 – 176°F).
Fluid is filled to proper level (between FULL and LOW on
dipstick).
1) Apply parking brake securely and place chocks against
wheels.
2) Remove fluid pressure check hole plug bolt.
3) Attach oil pressure gauge to fluid pressure check hole in
transmission case.
Special tool
(A) : 09925-37811-001
4) Depress foot brake fully, run engine at idle and stall then check fluid pressure in “D” or “R” range.
Line pressureCAUTION:
After attaching oil pressure gauge, check that no fluid
leakage exists.
(A)
CAUTION:
Do not continue running engine at stall speed longer than 5 seconds.
“D” range “R” range
At idle speed
7.6 – 9.2 kg/cm
2
108.1 – 130.8 psi14.1 – 17.3 kg/cm
2
200.6 – 246.0 psi
At stall speed
7.9 – 9.5 kg/cm
2
112.4 – 135.0 psi14.4 – 17.6 kg/cm
2
204.8 – 250.2 psi
Test result Possible cause
Line pressure higher than stan-
dard level in each rangeMalfunctioning regulator valve
Line pressure lower than standard
level in each rangMalfunctioning regulator valve
Defective oil pump
Line pressure lower than standard
level only in “D” rangeFluid leakage from “D” range pressure circuit
Fluid leakage from 1st & 2nd brake
Fluid leakage from rear clutch
Line pressure lower than standard
level only in “R” rangeFluid leakage from “R” range pressure circuit
Fluid leakage from rear clutch
Fluid leakage from direct clutch
Fluid leakage from reverse brake
Page 65 of 447

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T) 7B-23
ENGINE BRAKE TEST
1) While driving vehicle in 3rd gear of “D” range, shift select lever down to “2” range and check if engine brake
operates.
2) In the same way as in Step 1), check engine brake for operation when select lever is shifted down to “L”
range.
3) Engine brake should operate in above test.
“P” RANGE TEST
1) Stop vehicle on a slope, shift select lever to “P” range and at the same time apply parking brake.
2) After stopping engine, depress brake pedal and release parking brake.
3) Then, release brake pedal gradually and check that vehicle remains stationary.
4) Depress brake pedal and shift select lever to “N” range.
5) Then, release brake pedal gradually and check that vehicle moves.WARNING:
Before test, make sure that there is no vehicle behind so as to pre-
vent rear-end collision.
Test result Possible cause
Fails to operate when shifted down to “2”
rangeDefective shift switch
1st & 2nd brake defective
Direct clutch defective
Fails to operate when shifted down to “L”
range
WARNING:
Before test, check to make sure no one is around vehicle or
down on a slope and keep watchful for safety during test.
Test result Possible cause
Vehicle moves at “P” range or
remains stationary at “N” rangeDefective parking lock pawl or
spring
Page 66 of 447

7B-24 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T)
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNO-
SIS
TCM has on-board diagnostic system (a system self-diagnosis
function). Investigate where the trouble is by referring to “DIAG-
NOSTIC FLOW TABLE” and “DTC TABLE” in this section.
PRECAUTIONS IN DIAGNOSING TROUBLES
[PRECAUTIONS IN IDENTIFYING DTC]
For vehicle equipped with immobilizer indicator lamp (2)
(which comes on when turning on ignition switch leaving
engine OFF), malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) comes on
when TCM detects malfunction of automatic transmission
system.
For vehicle equipped without immobilizer indicator lamp (2),
malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) (1) does not come on
although TCM detects malfunction of automatic transmission
system.
Don’t disconnect couplers from TCM, battery cable from bat-
tery, TCM ground wire harness from engine or main fuse
before checking DTC stored in TCM memory.
Such disconnection will clear memorized information in TCM
memory.
Using SUZUKI scan tool (Tech-1) (4), diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) stored in TCM memory can be checked and
cleared as well.
Before its use, be sure to read Operator’s (instruction) Man-
ual supplied with it carefully to have good understanding of
its functions and usage.
Not using scan tool, the DTC stored in TCM memory also
can be checked and cleared.
DTC stored in the TCM memory is outputted by flashing of
“O/D OFF” lamp (3) with diagnosis switch terminal of monitor
connector No.2 (5) grounded.
If no DTC is stored in TCM memory, DTC No.12 is outputted
repeatedly.
If one or more DTCs are stored in TCM memory, they are
outputted starting from smallest code number in increasing
order.
After all DTCs are outputted, all DTCs are outputted repeat-
edly.
Be sure to read “PRECAUTIONS FOR ELECTRICAL CIR-
CUIT SERVICE” in Section 0A before inspection and
observe what is written there.
When replacing TCM with used one, all learned contents
which are stored in TCM memory should be erased after the
replacement referring to “LEARNING CONTROL INITIAL-
IZATION” in this section.
Page 79 of 447

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T) 7B-37
DTC P0741 (DTC NO.29) TCC (LOCK-UP) SOLENOID PERFORMANCE OR STUCK OFF
Step Action Yes No
1Was “AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION DIAG-
NOSTIC FLOW TABLE” performed?Go to Step 2. Go to “AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION DIAG-
NOSTIC FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check TCC (lock-up) solenoid referring to
“SHIFT SOLENOID VALVES” in this section.
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 3. Replace TCC (lock-up)
solenoid.
3 Check valve body for fluid passage clog, or
lock-up control valve, secondary regulator valve
or signal valve stuck, referring to “TRANSMIS-
SION UNIT REPAIR OVERHAUL” in this sec-
tion.
Are they in good condition?Go to Step 4. Faulty valve body.
4 Substitute a known-good torque converter and
recheck.
Is it OK?Torque converter mal-
function.Overhaul and repair auto-
matic transmission.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION
Difference between turbine rev. and engine rev. too close even though TCM ordered to turn OFF lock-up.
Difference between turbine rev. and engine rev. too wide even though TCM ordered to turn ON lock-up.
Page 83 of 447

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T) 7B-41
DTC P1700 (DTC NO.32/33) THROTTLE POSITION SIGNAL INPUT MALFUNCTION
1. Throttle position (TP) sensor 4. TCM coupler (viewed from harness side)
2. ECM 5. ECM coupler (viewed from harness side)
3. TCM
DTC DETECTING CONDITION
NO or abnormal throttle opening signal inputted.
Step Action Yes No
1 Check DTC of “ENGINE DIAGNOSIS” referring
to Section 6.
Is there DTC related to throttle position sensor
detected?Inspect and repair refer-
ring to DTC flow table of
“ENGINE DIAGNOSIS” in
Section 6.Go to Step 2.
2 Is DTC No.33? Go to Step 4. Go to Step 3.
3 Is DTC No.32? Go to Step 5. Go to Step 5.
(When DTC is P1700.)
4 1) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect
ECM couplers.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check voltage
between terminal “C41-21” of disconnected
harness side ECM coupler and body
ground.
Is it 10 – 14 V?Poor connection of termi-
nal “C41-21” of ECM cou-
pler.
If connection is OK, sub-
stitute a known-good
ECM and recheck.“PPL” wire open or poor
connection of terminal
“C43-8” of TCM coupler.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good TCM and recheck.
Page 87 of 447
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T) 7B-45
DTC P0725 (DTC NO.35) ENGINE SPEED INPUT CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
1. ECM 3. TCM coupler (viewed from harness side)
2. TCM 4. ECM coupler (viewed from harness side)
DTC DETECTING CONDITION
Inputted engine rev. signal too low or too high.
Step Action Yes No
1 Check DTC of “ENGINE DIAGNOSIS” referring
to Section 6.
Is there DTC related to engine speed sensor?Inspect and repair refer-
ring to DTC flow table of
“ENGINE DIAGNOSIS” in
Section 6.Go to Step 2.
2 1) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect
ECM or TCM couplers.
2) Measure resistance between terminal “G02-
16” and “C43-5” of disconnected harness
side coupler.
Is it about 0 Ω
?Go to Step 3.“BRN” wire open.
3 Measure resistance between terminal “C43-5”
of disconnected harness side coupler and body
ground.
Is it infinity?Go to Step 4.“BRN” wire shorted to
ground
Page 89 of 447

AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T) 7B-47
DTC P0710 (DTC No.36/38) TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT MALFUNC-
TION
1. Transmission temperature sensor 3. TCM
2. Coupler 4. TCM coupler (viewed from harness side)
DTC DETECTING CONDITION
A/T fluid temperature signal input voltage too low.
A/T fluid temperature signal input voltage does not go down although standard value of engine rev. signal
input.
Step Action Yes No
1 1) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect
sensor wire harness coupler.
2) Measure resistance between “BLU/RED”
wire and “GRY/RED” wire terminal of sen-
sor side coupler.
Is it infinity or 0 Ω
?Faulty transmission tem-
perature sensor.
Replace transmission
temperature sensor.Go to Step 2.
2 Is DTC No.36? Go to Step 4. Go to Step 3.
3 Is DTC No.38? Go to Step 5. Go to Step 6.
(When DTC is P0710.)
4 1) Turn ignition switch OFF and connect sen-
sor wire harness coupler.
2) Disconnect TCM couplers.
3) Measure the resistance between terminal
“C44-3” and “C44-16” of disconnected har-
ness side coupler.
Is it about 0 Ω
?“BLU/RED” and “GRY/
RED” wire shorted each
other.Substitute a known-good
TCM and recheck.
Page 90 of 447

7B-48 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4 A/T)
Figure for Step 75 1) Turn ignition switch OFF and connect sen-
sor wire harness coupler.
2) Disconnect TCM couplers.
3) Measure the resistance between terminal
“C44-3” and “C44-16” of disconnected har-
ness side coupler.
Is it infinity?“BLU/RED” or “GRY/
RED” wire open or poor
connection of solenoid
wire harness coupler.Go to Step 7.
6 1) Turn ignition switch OFF and connect sen-
sor wire harness coupler.
2) Disconnect TCM couplers.
3) Measure the resistance between terminal
“C44-3” and “C44-16” of disconnected har-
ness side coupler.
Is it about 0 Ω
or infinity?“BLU/REDl” or “GRY/
RED” wire open, shorted
each other or poor con-
nection of solenoid wire
harness coupler.Go to Step 7.
7 1) Turn ignition switch OFF and connect TCM
couplers.
2) Disconnect solenoid wire harness coupler.
3) Turn ignition switch ON then measure volt-
age between “BLU/RED” wire terminal of
disconnected harness side coupler and
engine ground. (See figure.)
Is it 4 – 6 V?Intermittent trouble or
faulty TCM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “INTERMIT-
TENT AND POOR CON-
NECTION” in Section 0A.
If no trouble found, substi-
tute a known-good TCM
and recheck.“BLU/RED” wire shorted
to power circuit or poor
connection of terminal
“C44-3”.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good TCM. Step Action Yes No
1. BLU/RED wire terminal