Page 206 of 557
Throttle
position
sensorTo MAP sensor
To other sensors
6-1-50 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13)
DTC P0120 THROTTLE POSITION CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
�Signal voltage high
�Signal voltage low�“G” circuit open
�“Gr” circuit open or shorted to ground
�“P” circuit open or shorted to power or ground
�TP sensor malfunction
�ECM (PCM) malfunction
NOTE:
�When DTC P0105, P0110, P0115 and / or P0120 are / is indicated together, it is possible that “G” circuit is
open.
�When DTC P0105 and / or P0120 are / is indicated together, it is possible that “P” circuit is open.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min.
2) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
Page 207 of 557

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-51
Fig. 1 for Step 2 Fig. 2 for Step 3 Fig. 3 for Step 4
INSPECTION
STEPACTIONYESNO
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE”
performed?Go to Step 2.Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2Check TP Sensor and Its Circuit.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition
switch OFF and then turn ignition switch
ON.
2) Check throttle valve opening percentage
displayed on scan tool. See Fig. 1.
Is it displayed 2% or less?
3) Check throttle valve opening percentage
displayed on scan tool while opening
throttle valve from idle position to full open
position. See Fig. 1.
Is it displayed 96% or higher?Go to Step 3.Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.
3Check Wire Harness.
1) Disconnect connector from TP sensor
with ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to TP sensor
at “P”, “Gr” and “G” wire terminal.
3) If OK, then with ignition switch ON, check
voltage at each of “P” and “Gr” wire
terminals. See Fig. 2.
Is voltage about 4 – 6 V at each terminal?Go to Step 4.“P” wire open, “P” wire
shorted to ground circuit or
power circuit or “G” wire,
“Gr” wire open or shorted
to ground circuit or poor
C01-22 or C03-5
connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM (PCM) and
recheck.
4Check TP Sensor.
1) Check resistance between terminals of
TP sensor. See Fig. 3.
Between 1 and 2: 2.5 – 6.0 kΩ
Between 1 and 3: 170 Ω – 15.5 kΩ
Are measured values within specifications?“G” wire open or poor
C01-10 connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM (PCM) and
recheck.Replace TP sensor.
Page 208 of 557

6-1-52 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13)
Throttle
position
sensorTo other sensors
To other sensors
DTC P0121 THROTTLE POSITION CIRCUIT RANGE / PERFORMANCE
PROBLEM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
�After engine warmed up.
�While vehicle running at specified engine speed.
�No change in intake manifold pressure (constant throttle opening)
�Difference between actual throttle opening (detected from TP sensor)
and opening calculated by ECM (PCM) (Obtained on the basis of
engine speed and intake manifold pressure) in larger than specified
value.
�2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring�TP sensor malfunction
�High resistance in the circuit
�ECM (PCM) malfunction
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
WARNING:
�When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic accident
and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
�Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF. Clear DTC with ignition switch ON, check vehicle and environmental condition for:
–Indication of fuel level meter in combination meter: 1 / 4 or more
–Altitude (barometric pressure): 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Intake air temp.: between –10�C and 80�C (14�F and 176�F)
–Engine coolant temp.: 70�C, 158�F or higher
2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Increase vehicle speed to 30 – 40 mph, 50 – 60 km / h in 3rd gear or “D” range and hold throttle valve at that
opening position for 1 min.
4) Stop vehicle.
5) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
Page 209 of 557

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-53
Fig. 1 for Step 2 Fig. 2 for Step 2 Fig. 3 for Step 2
Fig. 4 for Step 3
Closed
(condition “A”)Fully open
Throttle Opening When using SUZUKI scan tool:
When not using SUZUKI scan tool:
INSPECTION
STEPACTIONYESNO
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed?Go to Step 2.Go to “ENGINE
DIAG. FLOW
TABLE”.
2Check TP Sensor and Its Circuit.
When using SUZUKI scan tool:
1) Turn ignition switch OFF and connect SUZUKI scan tool to
DLC.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check TP sensor output
voltage when throttle valve is at idle position and fully
opened. See Fig. 1 and 3.
When not using SUZUKI scan tool:
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at terminal C03-5 of ECM (PCM) connector
connected, when throttle valve is at idle position and fully
opened. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Dose voltage vary within specified value linearly as shown in
figure?If voltmeter was
used, check
terminal C03-5 for
poor connection.
If OK, substitute a
known-good ECM
(PCM) and
recheck.Go to Step 3.
3Check TP Sensor.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect TP sensor connector.
3) Check for proper connection to TP sensor at each terminal.
4) If OK, then measure resistance between terminals and
check if each measured value is as specified below.
See Fig. 4.
Between 1 and 2: 2.5 – 6.0 kΩ
Between 1 and 3: 170 Ω – 15.5 kΩ, varying according to
throttle valve opening.
Are measured values as specified?High resistance in
“P”, “Gr” or “G”
circuit.
If wire and
connection are
OK, substitute a
known-good ECM
(PCM) and
recheck.Replace TP
sensor.
Page 224 of 557
6-1-68 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13)
Fig. 1 for Step 3 Fig. 2 for Step 4 Fig. 3 for Step 5
Fig. 4 for Step 5 Fig. 5 for Step 5 Fig. 6 for Step 6
1. Fuel delivery pipe
2. Fuel feed hose
3. Fuel pressure gauge &
3 way joint
STEPACTIONYESNO
8Check engine coolant temp. sensor for performance
(See Section 6E2).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 9.Replace engine
coolant temp. sensor.
9Check intake air temp. sensor for performance
(See Section 6E2).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 10.Replace intake air
temp. sensor.
10Check throttle position sensor for performance (See
Step 3 of DTC P0121 Diag. Flow Table).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 11.Replace throttle
position sensor.
11Check PCV valve for valve clogging
(See Section 6E2).
Is it good condition?Substitute a known-
good ECM (PCM) and
recheck.Replace PCV valve.
Page 225 of 557
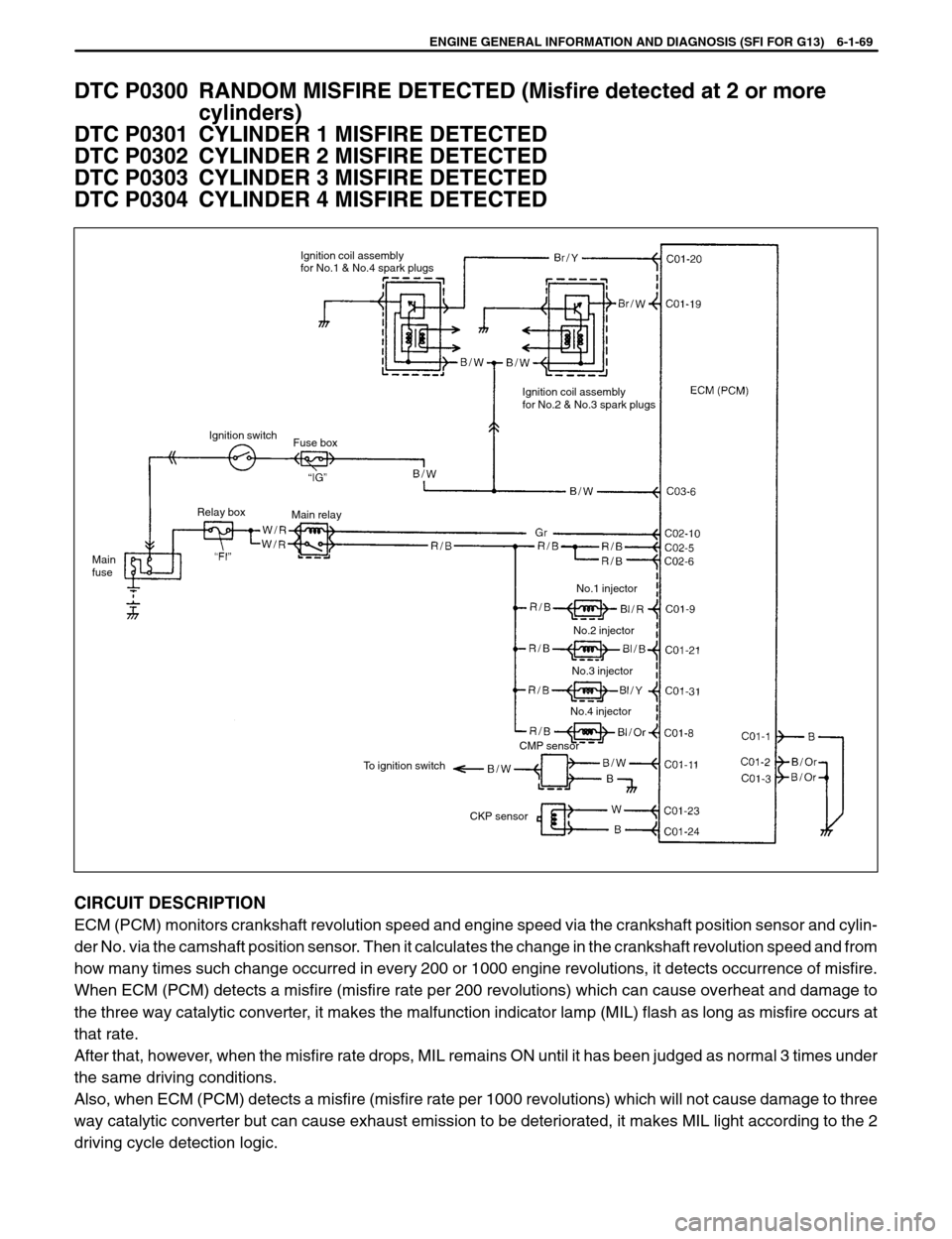
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-69
Ignition coil assembly
for No.1 & No.4 spark plugs
Ignition coil assembly
for No.2 & No.3 spark plugs
Ignition switch
Main relay
Main
fuseRelay box
To ignition switch
CKP sensorCMP sensorNo.1 injector
No.2 injector
No.3 injector
No.4 injector Fuse box
DTC P0300 RANDOM MISFIRE DETECTED (Misfire detected at 2 or more
cylinders)
DTC P0301 CYLINDER 1 MISFIRE DETECTED
DTC P0302 CYLINDER 2 MISFIRE DETECTED
DTC P0303 CYLINDER 3 MISFIRE DETECTED
DTC P0304 CYLINDER 4 MISFIRE DETECTED
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
ECM (PCM) monitors crankshaft revolution speed and engine speed via the crankshaft position sensor and cylin-
der No. via the camshaft position sensor. Then it calculates the change in the crankshaft revolution speed and from
how many times such change occurred in every 200 or 1000 engine revolutions, it detects occurrence of misfire.
When ECM (PCM) detects a misfire (misfire rate per 200 revolutions) which can cause overheat and damage to
the three way catalytic converter, it makes the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) flash as long as misfire occurs at
that rate.
After that, however, when the misfire rate drops, MIL remains ON until it has been judged as normal 3 times under
the same driving conditions.
Also, when ECM (PCM) detects a misfire (misfire rate per 1000 revolutions) which will not cause damage to three
way catalytic converter but can cause exhaust emission to be deteriorated, it makes MIL light according to the 2
driving cycle detection logic.
Page 229 of 557
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-73
Crankshaft
timing belt
pulleyCKP
sensor
Oscilloscope Waveforms
Waveforms at engine cranking (260 r/min) Waveforms at specified idle speed16 waives
for 10� signals13 waives for
10� signals
30� signal 30� signal 0.5 V / Div.
10 ms / Div.0.5 V / Div.
5 ms / Div.
DTC P0335 CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
�NO CKP sensor signal for 2 seconds at engine
cranking.�CKP sensor circuit open or short.
�Crankshaft timing belt pulley teeth damaged.
�CKP sensor malfunction, foreign material being
attached or improper installation.
�ECM (PCM) malfunction.
Reference
Connect oscilloscope between terminals C01-23 (+) and C01-24 (–) of ECM (PCM) connector connected to ECM
(PCM) and check CKP sensor signal.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC and crank engine for 2 sec.
2) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
Page 231 of 557
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS (SFI FOR G13) 6-1-75
To ignition
switch
Signal rotor
on CamshaftCamshaft
position
sensor
Waveforms at specified idle speed
Oscilloscope Waveforms
2 V / Div.
Crank
angle20 ms / Div.
180�
720�
DTC P0340 CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE
�No CMP sensor signal during engine running
(CKP sensor signal is inputted).�CMP sensor circuit open or short.
�Signal rotor teeth damaged.
�CMP sensor malfunction, foreign material being
attached or improper installation.
�ECM (PCM) malfunction.
Reference
Connect oscilloscope between terminals C01-11 of ECM (PCM) connector connected to ECM (PCM) and body
ground and check CKP sensor signal.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC.
2) Start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min.
3) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.