Page 344 of 557
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-49
Valve Springs
�Referring to data given below, check to be sure that each spring
is in sound condition, free of any evidence of breakage or weak-
ening. Remember, weakened valve springs can cause chatter,
not to mention possibility of reducing power output due to gas
leakage caused by decreased seating pressure.
Item
StandardLimit
Valve spring
free length36.83 mm
(1.4500 in.)35.67 mm
(1.4043 in.)
Valve spring
preload10.7 – 12.5 kg for
31.5 mm (23.6 –
27.5 lb / 1.24 in.)9.3 kg for 31.5 mm
(20.5 lb / 1.24 in.)
�Spring squareness:
Use a square and surface plate to check each spring for square-
ness in terms of clearance between end of valve spring and
square. Valve springs found to exhibit a larger clearance than limit
given below must be replaced.
Valve spring squareness limit: 1.6 mm (0.063 in.)
Page 345 of 557
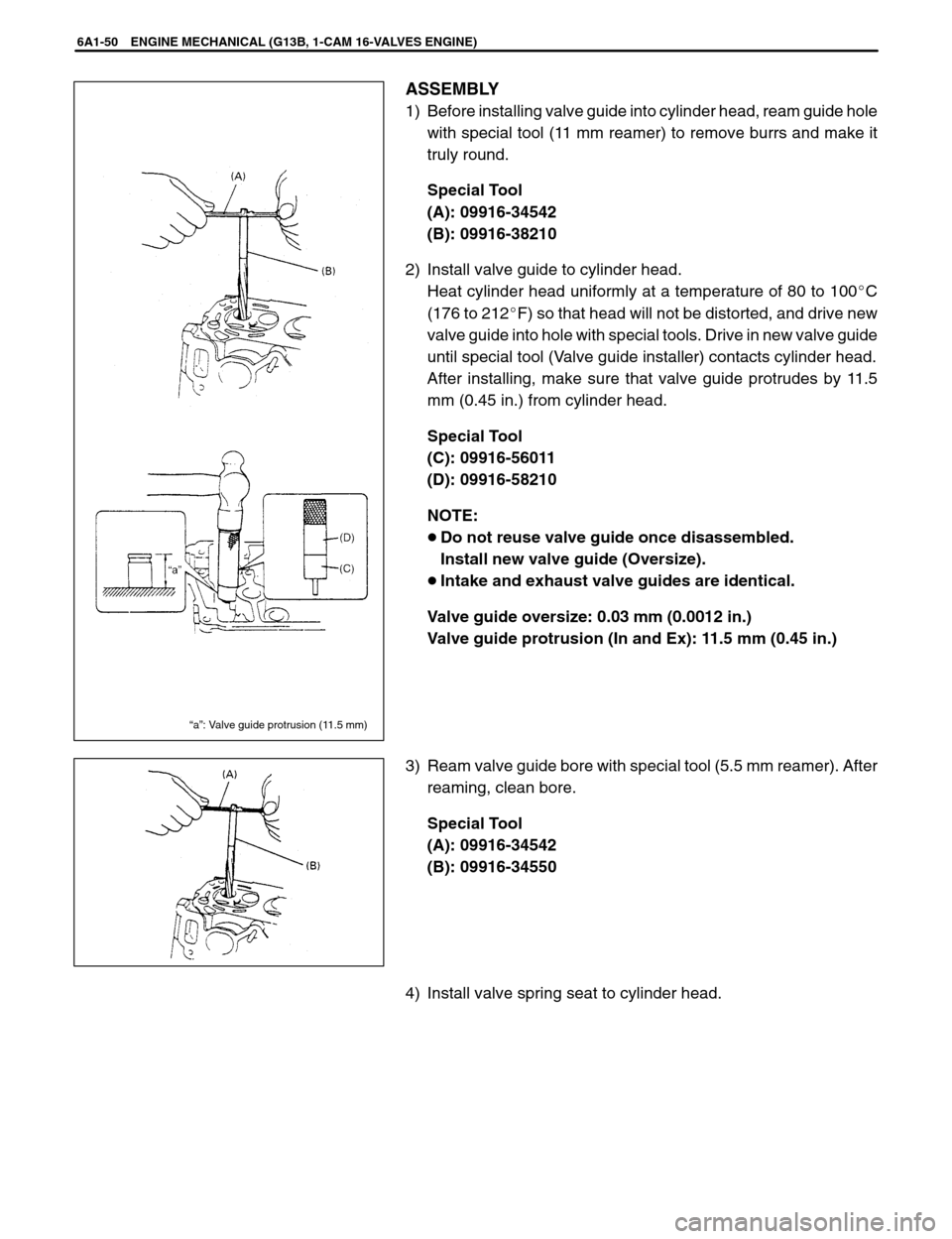
“a”: Valve guide protrusion (11.5 mm)
6A1-50 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
ASSEMBLY
1) Before installing valve guide into cylinder head, ream guide hole
with special tool (11 mm reamer) to remove burrs and make it
truly round.
Special Tool
(A): 09916-34542
(B): 09916-38210
2) Install valve guide to cylinder head.
Heat cylinder head uniformly at a temperature of 80 to 100�C
(176 to 212�F) so that head will not be distorted, and drive new
valve guide into hole with special tools. Drive in new valve guide
until special tool (Valve guide installer) contacts cylinder head.
After installing, make sure that valve guide protrudes by 11.5
mm (0.45 in.) from cylinder head.
Special Tool
(C): 09916-56011
(D): 09916-58210
NOTE:
�Do not reuse valve guide once disassembled.
Install new valve guide (Oversize).
�Intake and exhaust valve guides are identical.
Valve guide oversize: 0.03 mm (0.0012 in.)
Valve guide protrusion (In and Ex): 11.5 mm (0.45 in.)
3) Ream valve guide bore with special tool (5.5 mm reamer). After
reaming, clean bore.
Special Tool
(A): 09916-34542
(B): 09916-34550
4) Install valve spring seat to cylinder head.
Page 346 of 557
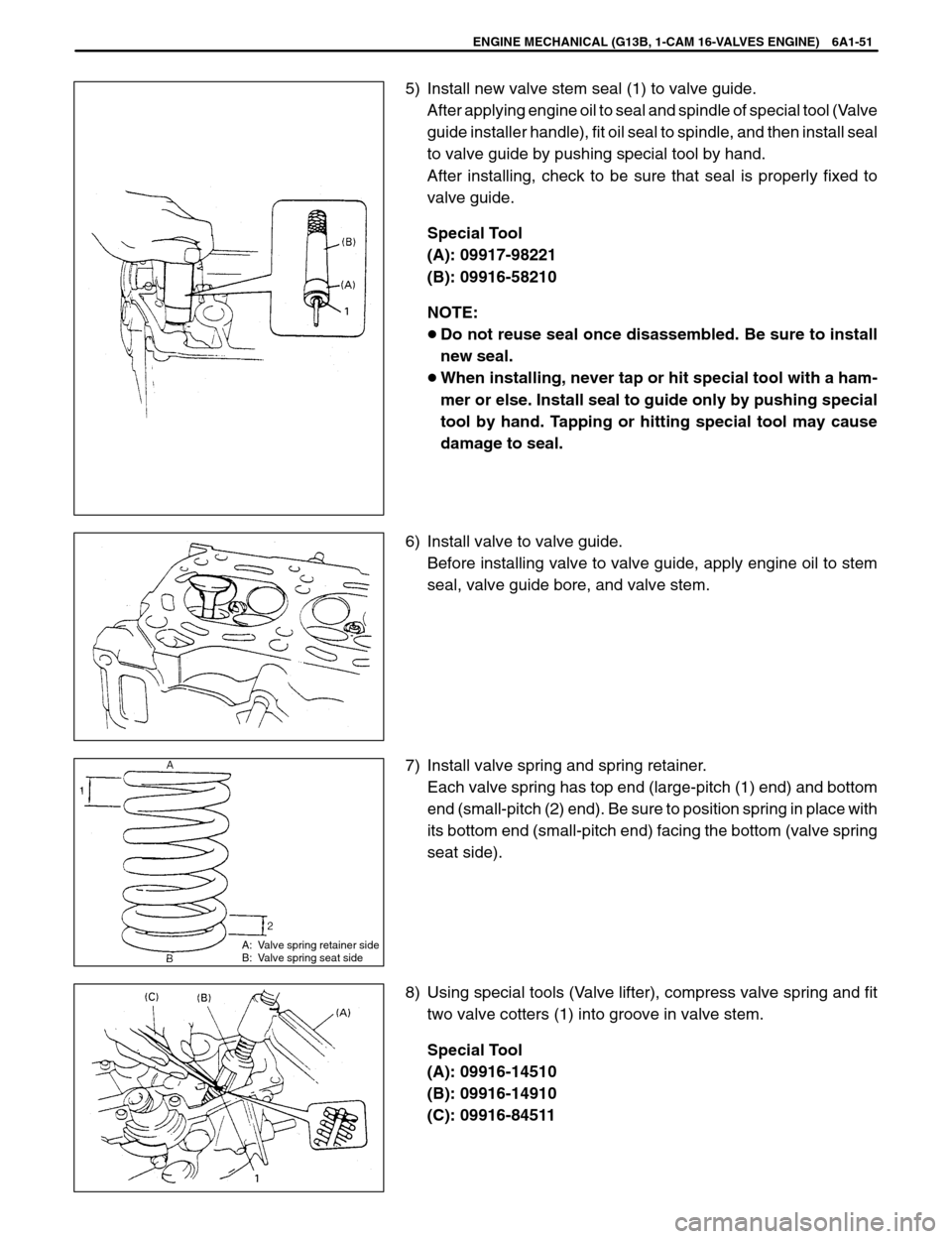
A: Valve spring retainer side
B: Valve spring seat side
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-51
5) Install new valve stem seal (1) to valve guide.
After applying engine oil to seal and spindle of special tool (Valve
guide installer handle), fit oil seal to spindle, and then install seal
to valve guide by pushing special tool by hand.
After installing, check to be sure that seal is properly fixed to
valve guide.
Special Tool
(A): 09917-98221
(B): 09916-58210
NOTE:
�Do not reuse seal once disassembled. Be sure to install
new seal.
�When installing, never tap or hit special tool with a ham-
mer or else. Install seal to guide only by pushing special
tool by hand. Tapping or hitting special tool may cause
damage to seal.
6) Install valve to valve guide.
Before installing valve to valve guide, apply engine oil to stem
seal, valve guide bore, and valve stem.
7) Install valve spring and spring retainer.
Each valve spring has top end (large-pitch (1) end) and bottom
end (small-pitch (2) end). Be sure to position spring in place with
its bottom end (small-pitch end) facing the bottom (valve spring
seat side).
8) Using special tools (Valve lifter), compress valve spring and fit
two valve cotters (1) into groove in valve stem.
Special Tool
(A): 09916-14510
(B): 09916-14910
(C): 09916-84511
Page 385 of 557

2. Thermostat case
2. Thermometer
3. Heater
Upside
6B-8 ENGINE COOLING
4) Remove thermostat (1).
INSPECTION
1) Make sure that air bleed valve (1) of thermostat is clean.
Should this valve be clogged, engine would tend to overheat.
2) Check to make sure that valve seat is free from foreign matters
which would prevent valve from seating tight.
3) Check thermostatic movement of wax pellet as follows:
�Immerse thermostat (1) in water, and heat water gradually.
�Check that valve starts to open at specific temperature.
�If valve starts to open at a temperature substantially below or
above specific temperature, thermostat unit should be re-
placed with a new one. Such a unit, if reused, will bring about
overcooling or overheating tendency.
INSTALLATION
1) When positioning thermostat on thermostat case, be sure to
position it so that air bleed valve comes uppermost and into the
recession of thermostat case.
2) Install thermostat cap to thermostat case. When installing cap,
align arrow marks on cap and case.
3) Fill cooling system.
4) Connect negative cable.
5) After installation, check each part for leakage.
Page 389 of 557
1. Fuel tank
2. Fuel pump and level gauge
3. Fuel filler cap
4. 2-way check valve
5. Breather hose
6. Fuel feed line
7. Fuel return line
8. Fuel vapor line
9. Fuel cut valve
10. Fuel tank pad
11. Fuel tank fixer bolt
: Tightening Torque
6C-2 ENGINE FUEL
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
FUEL LINES
INSPECTION
Visually inspect fuel lines for evidence of fuel leakage, hose crack
and deterioration, or damage.
Make sure all clamps are secure.
Replace parts as needed.
FUEL TANK
REMOVAL
1) Relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line according to procedure de-
scribed in Section 6.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Remove rear seat cushion referring to Section 9.
4) Disconnect connectors (1) of fuel tank wire harness.
5) Hoist vehicle.
6) Disconnect fuel filler hose (3) from fuel tank and breather hose
(2) from filler neck (1).
Page 390 of 557
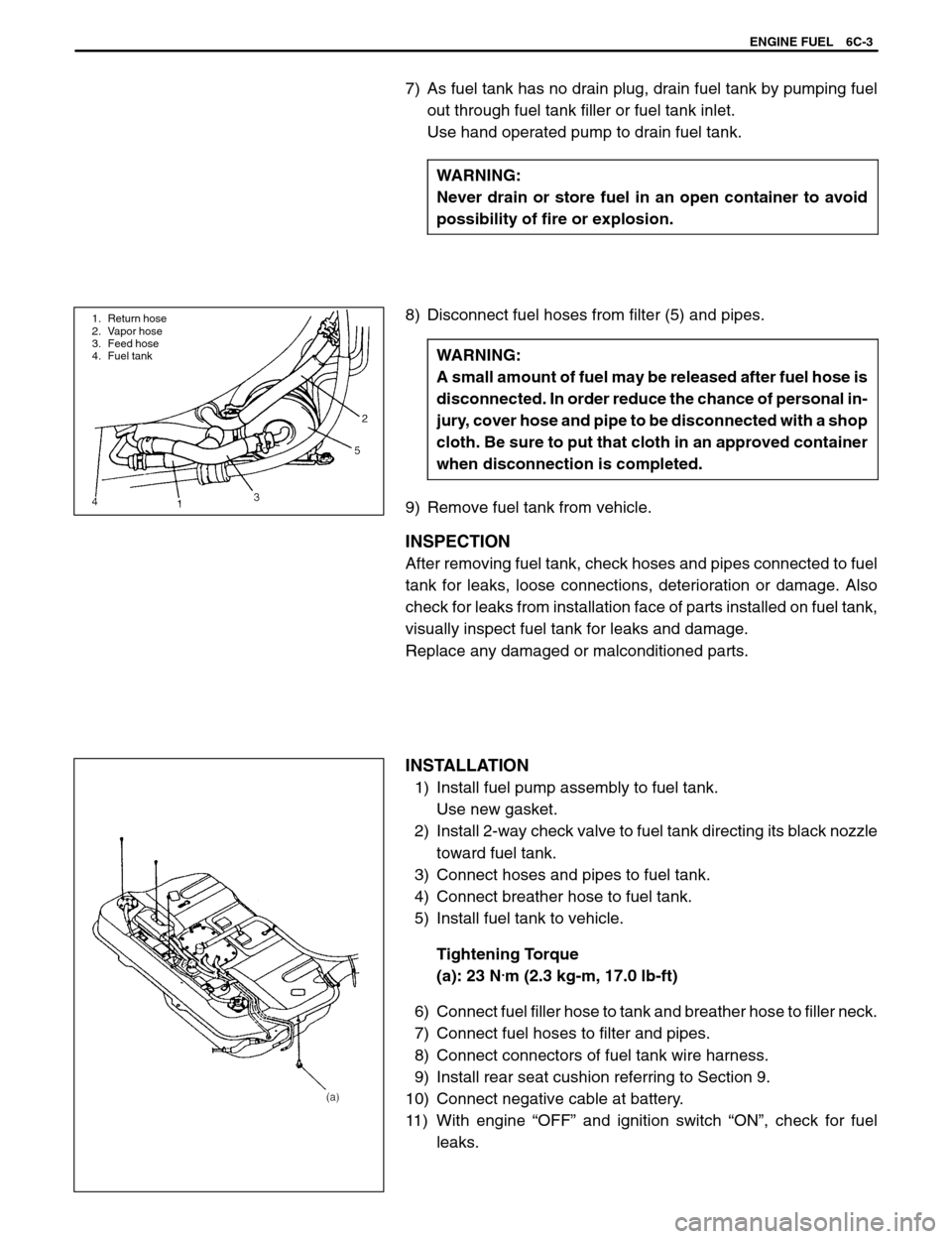
1. Return hose
2. Vapor hose
3. Feed hose
4. Fuel tank
ENGINE FUEL 6C-3
7) As fuel tank has no drain plug, drain fuel tank by pumping fuel
out through fuel tank filler or fuel tank inlet.
Use hand operated pump to drain fuel tank.
WARNING:
Never drain or store fuel in an open container to avoid
possibility of fire or explosion.
8) Disconnect fuel hoses from filter (5) and pipes.
WARNING:
A small amount of fuel may be released after fuel hose is
disconnected. In order reduce the chance of personal in-
jury, cover hose and pipe to be disconnected with a shop
cloth. Be sure to put that cloth in an approved container
when disconnection is completed.
9) Remove fuel tank from vehicle.
INSPECTION
After removing fuel tank, check hoses and pipes connected to fuel
tank for leaks, loose connections, deterioration or damage. Also
check for leaks from installation face of parts installed on fuel tank,
visually inspect fuel tank for leaks and damage.
Replace any damaged or malconditioned parts.
INSTALLATION
1) Install fuel pump assembly to fuel tank.
Use new gasket.
2) Install 2-way check valve to fuel tank directing its black nozzle
toward fuel tank.
3) Connect hoses and pipes to fuel tank.
4) Connect breather hose to fuel tank.
5) Install fuel tank to vehicle.
Tightening Torque
(a): 23 N
.m (2.3 kg-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
6) Connect fuel filler hose to tank and breather hose to filler neck.
7) Connect fuel hoses to filter and pipes.
8) Connect connectors of fuel tank wire harness.
9) Install rear seat cushion referring to Section 9.
10) Connect negative cable at battery.
11) With engine “OFF” and ignition switch “ON”, check for fuel
leaks.
Page 464 of 557
6E2-36 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (SFI FOR G13)
1. EGR valve
2. Connector
1
2
1. EGR valve
2. Valve
3. Valve seat3
Inspection
1) Check resistance between following terminals of EGR valve in
each pair.
Terminal
Standard resistance
A – B
C – B
F – E
D – E
20 – 24 Ω
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assy.
2) Remove carbon from EGR valve gas passage.
NOTE:
Do not use any sharp–edged tool to remove carbon.
Be careful not to damage or bend EGR valve, valve seat and
rod.
3) Inspect valve, valve seat and rod for fault, cracks, bend or other
damage.
If found faulty, replace EGR valve assembly.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting following.
�Clean mating surface of valve and intake manifold.
�Use new gasket.
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
EVAP Canister Purge Inspection
NOTE:
Before inspection, check to make sure that gear shift lever is
in neutral position (with A / T model, selector lever in “P” range)
and that parking brake lever is pulled all the way up.
Page 498 of 557

1. PCM
2. Instrument panel
TP sensor
Transmission range sensor
Output shaft speed sensor
(A / T VSS)
Shift solenoid-B
(2nd brake solenoid valve)
Shift solenoid-A
(Direct clutch solenoid valve)PCM
1. Throttle position sensor
2. Throttle body
A: Ground
3. Ground terminal
4. Reference voltage
terminal
5. Output voltage terminal
6. TP sensor
C: Output voltage
(opening angle signal)
D: Power supply from ECM
(reference voltage)
[G10 engine model]
[G13 engine model]
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (3 A / T) (VEHICLE WITH WU-TWC) 7B-7
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The powertrain control module controls the shift solenoid B (2nd
brake solenoid valve) and the shift solenoid A (direct clutch sole-
noid valve) by sending electric signals to them so as to attain auto-
matic gear shift between the 1st and 2nd gears, and the 2nd and
3rd gears. Equipped as PCM sensed parameters are the throttle
position sensor, transmission range switch and vehicle speed sen-
sor. These switch and sensors sense the throttle valve opening, se-
lector lever’s position and vehicle speed, and send those signals to
the powertrain control module. Then, the powertrain control module
opens and closes valves of the above solenoids according to these
signals. The powertrain control module is installed to the underside
of the instrument panel at the driver’s seat side.
GEAR SHIFT CONTROL SYSTEM
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TP sensor)
The throttle position sensor consisting of a potentiometer is con-
nected to the throttle valve shaft.
Throttle valve opening signal (output voltage) is transmitted from
throttle position sensor to PCM as voltage signal. PCM uses it as
one of the signals to control transmission gear shift.