Page 377 of 557
6A1-82 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
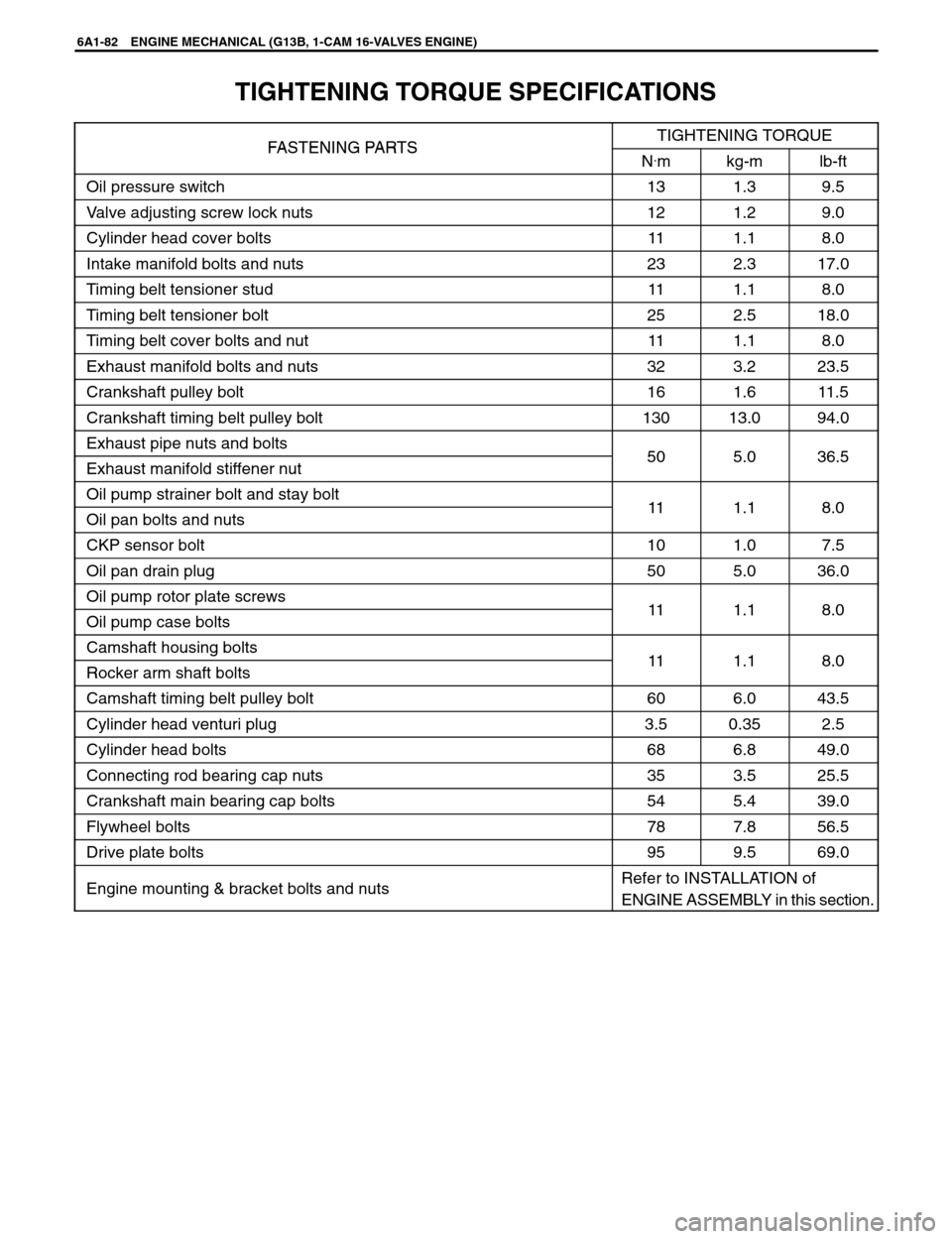
TIGHTENING TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
FASTENING PARTSTIGHTENING TORQUEFASTENING PA R T SN.mkg-mlb-ft
Oil pressure switch131.39.5
Valve adjusting screw lock nuts121.29.0
Cylinder head cover bolts111.18.0
Intake manifold bolts and nuts232.317.0
Timing belt tensioner stud111.18.0
Timing belt tensioner bolt252.518.0
Timing belt cover bolts and nut111.18.0
Exhaust manifold bolts and nuts323.223.5
Crankshaft pulley bolt161.611.5
Crankshaft timing belt pulley bolt13013.094.0
Exhaust pipe nuts and bolts505036 5Exhaust manifold stiffener nut505.036.5
Oil pump strainer bolt and stay bolt111180Oil pan bolts and nuts111.18.0
CKP sensor bolt101.07.5
Oil pan drain plug505.036.0
Oil pump rotor plate screws111180Oil pump case bolts111.18.0
Camshaft housing bolts111180Rocker arm shaft bolts111.18.0
Camshaft timing belt pulley bolt606.043.5
Cylinder head venturi plug3.50.352.5
Cylinder head bolts686.849.0
Connecting rod bearing cap nuts353.525.5
Crankshaft main bearing cap bolts545.439.0
Flywheel bolts787.856.5
Drive plate bolts959.569.0
Engine mounting & bracket bolts and nutsRefer to INSTALLATION of
ENGINE ASSEMBLY in this section.
Page 379 of 557
8. Heater inlet hose
9. Heater outlet hose
10. Radiator
11. Oil cooler (A / T only)
12. Engine
13. ECT sensor1. Radiator inlet hose
2. Radiator outlet hose
3. Water intake pipe
4. Thermostat
5. Water pump
6. IAC valve (throttle body)
7. Breather pipe (air cleaner
outlet hose)
6B-2 ENGINE COOLING
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
COOLING SYSTEM CIRCULATION
During engine warm-up (thermostat closed), the water pump discharges coolant into the water jacket chamber
adjacent to No.1 cylinder. Coolant then flows through the cylinder block and the cylinder heat. Coolant then returns
to the water pump through intake manifold, heater inlet hose, heater unit, heater outlet hose, and water intake pipe.
During normal temperatures (thermostat open), coolant takes the same basic route but is now allowed to flow past
the thermostat, the inlet hose and the radiator, and then back to the water pump through the outlet hose and the
water intake pipe.
Page 380 of 557

1. Cooling fan motor
2. Radiator
ENGINE COOLING 6B-3
THERMOSTAT
A wax pellet type thermostat is used in the coolant outlet passage
to control the flow of engine coolant, to provide fast engine warm
up and to regulate coolant temperatures.
A wax pellet element is hermetically contained in a metal case, and
expands when heated and contracts when cooled.
When the pellet is heated and expands, the metal case pushes
down the valve to open it.
As the pellet is cooled, the contraction allows the spring to close the
valve.
Thus, the valve remains closed while the coolant is cold, preventing
circulation of coolant through the radiator.
At this point, coolant is allowed to circulate only throughout the en-
gine to warm it quickly and evenly.
As the engine warms, the pellet expands and the thermostat valve
opens, permitting coolant to flow through the radiator.
In the top portion of the thermostat, an air bleed valve (1) is pro-
vided; this valve is for venting out the gas or air, if any, that is accu-
mulated in the circuit.
Thermostat functional spec. ± 2.8�C (5.0�F)
Temp. at which valve
begins to open88�C (190�F)
Temp. at which valve
become fully open100�C (212�F)
COOLING FAN
The cooling fan is driven by electric motor, and the motor is acti-
vated by ECM / PCM (engine coolant temp.). For its details, refer to
Section 6E.
WARNING:
Keep hands, tools, and clothing away from engine cooling
fan to help prevent personal injury. This fan is electric and
can come on whether or not the engine is running. The fan
can start automatically in response to the ECM / PCM (en-
gine coolant temp.) with the ignition switch in the “ON”
position.
Page 385 of 557

2. Thermostat case
2. Thermometer
3. Heater
Upside
6B-8 ENGINE COOLING
4) Remove thermostat (1).
INSPECTION
1) Make sure that air bleed valve (1) of thermostat is clean.
Should this valve be clogged, engine would tend to overheat.
2) Check to make sure that valve seat is free from foreign matters
which would prevent valve from seating tight.
3) Check thermostatic movement of wax pellet as follows:
�Immerse thermostat (1) in water, and heat water gradually.
�Check that valve starts to open at specific temperature.
�If valve starts to open at a temperature substantially below or
above specific temperature, thermostat unit should be re-
placed with a new one. Such a unit, if reused, will bring about
overcooling or overheating tendency.
INSTALLATION
1) When positioning thermostat on thermostat case, be sure to
position it so that air bleed valve comes uppermost and into the
recession of thermostat case.
2) Install thermostat cap to thermostat case. When installing cap,
align arrow marks on cap and case.
3) Fill cooling system.
4) Connect negative cable.
5) After installation, check each part for leakage.
Page 389 of 557
1. Fuel tank
2. Fuel pump and level gauge
3. Fuel filler cap
4. 2-way check valve
5. Breather hose
6. Fuel feed line
7. Fuel return line
8. Fuel vapor line
9. Fuel cut valve
10. Fuel tank pad
11. Fuel tank fixer bolt
: Tightening Torque
6C-2 ENGINE FUEL
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
FUEL LINES
INSPECTION
Visually inspect fuel lines for evidence of fuel leakage, hose crack
and deterioration, or damage.
Make sure all clamps are secure.
Replace parts as needed.
FUEL TANK
REMOVAL
1) Relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line according to procedure de-
scribed in Section 6.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Remove rear seat cushion referring to Section 9.
4) Disconnect connectors (1) of fuel tank wire harness.
5) Hoist vehicle.
6) Disconnect fuel filler hose (3) from fuel tank and breather hose
(2) from filler neck (1).
Page 390 of 557
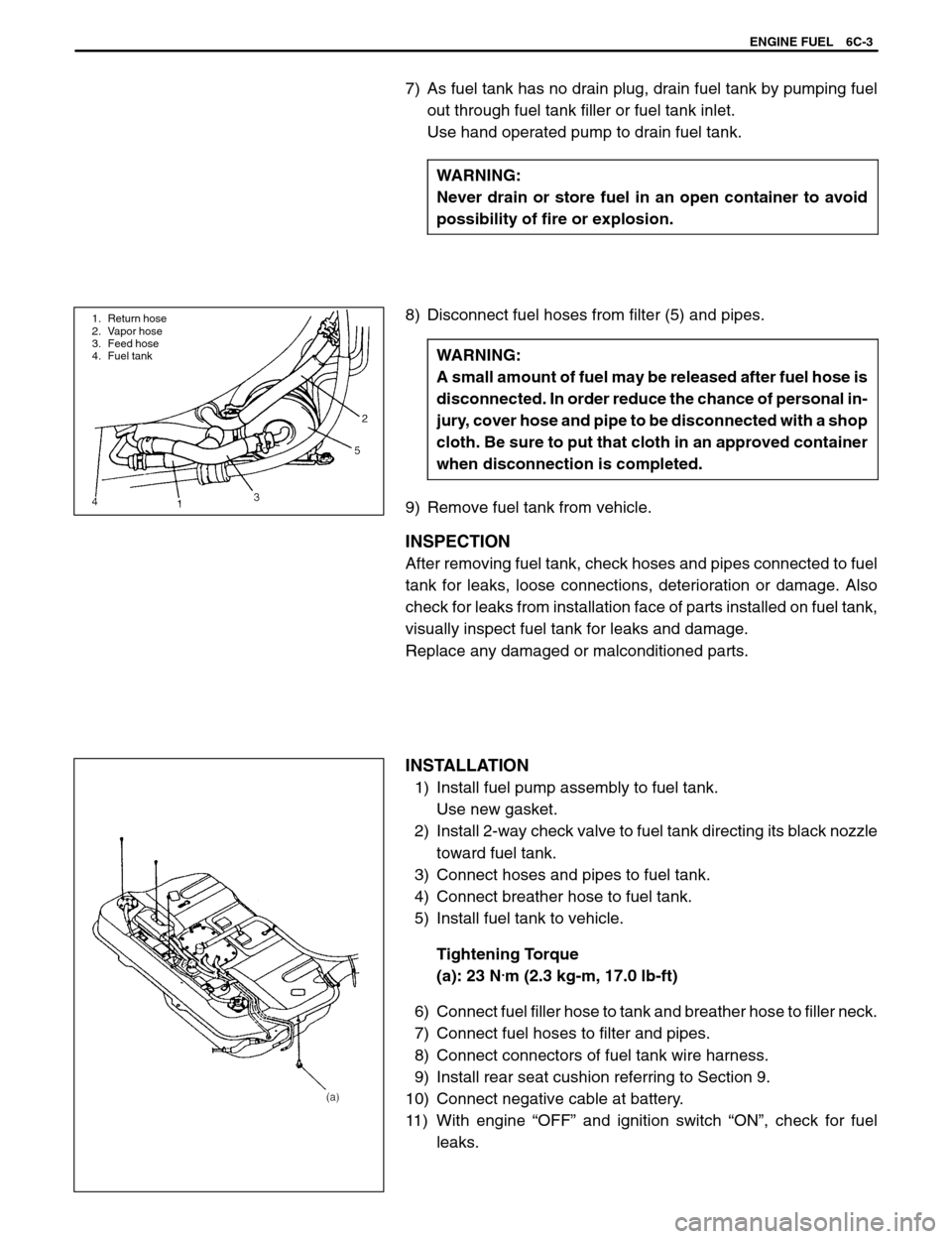
1. Return hose
2. Vapor hose
3. Feed hose
4. Fuel tank
ENGINE FUEL 6C-3
7) As fuel tank has no drain plug, drain fuel tank by pumping fuel
out through fuel tank filler or fuel tank inlet.
Use hand operated pump to drain fuel tank.
WARNING:
Never drain or store fuel in an open container to avoid
possibility of fire or explosion.
8) Disconnect fuel hoses from filter (5) and pipes.
WARNING:
A small amount of fuel may be released after fuel hose is
disconnected. In order reduce the chance of personal in-
jury, cover hose and pipe to be disconnected with a shop
cloth. Be sure to put that cloth in an approved container
when disconnection is completed.
9) Remove fuel tank from vehicle.
INSPECTION
After removing fuel tank, check hoses and pipes connected to fuel
tank for leaks, loose connections, deterioration or damage. Also
check for leaks from installation face of parts installed on fuel tank,
visually inspect fuel tank for leaks and damage.
Replace any damaged or malconditioned parts.
INSTALLATION
1) Install fuel pump assembly to fuel tank.
Use new gasket.
2) Install 2-way check valve to fuel tank directing its black nozzle
toward fuel tank.
3) Connect hoses and pipes to fuel tank.
4) Connect breather hose to fuel tank.
5) Install fuel tank to vehicle.
Tightening Torque
(a): 23 N
.m (2.3 kg-m, 17.0 lb-ft)
6) Connect fuel filler hose to tank and breather hose to filler neck.
7) Connect fuel hoses to filter and pipes.
8) Connect connectors of fuel tank wire harness.
9) Install rear seat cushion referring to Section 9.
10) Connect negative cable at battery.
11) With engine “OFF” and ignition switch “ON”, check for fuel
leaks.
Page 394 of 557
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (TBI FOR G10) 6E1-3
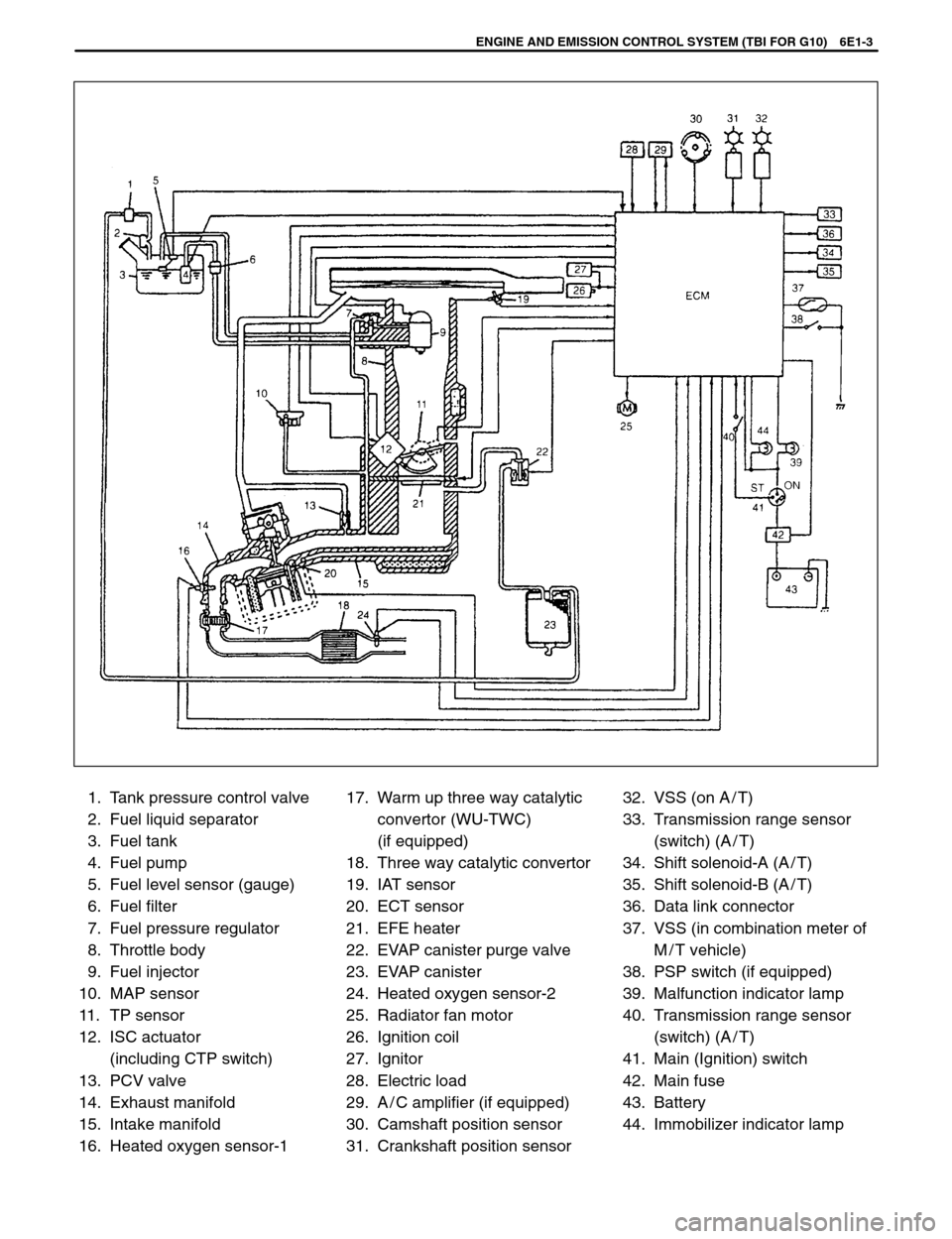
1. Tank pressure control valve
2. Fuel liquid separator
3. Fuel tank
4. Fuel pump
5. Fuel level sensor (gauge)
6. Fuel filter
7. Fuel pressure regulator
8. Throttle body
9. Fuel injector
10. MAP sensor
11. TP sensor
12. ISC actuator
(including CTP switch)
13. PCV valve
14. Exhaust manifold
15. Intake manifold
16. Heated oxygen sensor-117. Warm up three way catalytic
convertor (WU-TWC)
(if equipped)
18. Three way catalytic convertor
19. IAT sensor
20. ECT sensor
21. EFE heater
22. EVAP canister purge valve
23. EVAP canister
24. Heated oxygen sensor-2
25. Radiator fan motor
26. Ignition coil
27. Ignitor
28. Electric load
29. A / C amplifier (if equipped)
30. Camshaft position sensor
31. Crankshaft position sensor32. VSS (on A / T)
33. Transmission range sensor
(switch) (A / T)
34. Shift solenoid-A (A / T)
35. Shift solenoid-B (A / T)
36. Data link connector
37. VSS (in combination meter of
M / T vehicle)
38. PSP switch (if equipped)
39. Malfunction indicator lamp
40. Transmission range sensor
(switch) (A / T)
41. Main (Ignition) switch
42. Main fuse
43. Battery
44. Immobilizer indicator lamp
Page 395 of 557

1. Air cleaner
2. Throttle body
3. Fuel injector
4. Fuel pressure regulator
5. Intake manifold
6. Fuel filter
7. Fuel tank
8. Fuel pump
9. Fuel feed line
10. Fuel return line
11. Air
12. Fuel
13. Air/fuel mixture
6E1-4 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (TBI FOR G10)
The main components of this system are fuel tank,
fuel pump, fuel filter, throttle body (including fuel injec-
tor, fuel pressure regulator and idle speed control ac-
tuator), fuel feed line, fuel return line and air cleaner.
The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel
pump, filtered by the fuel filter and fed under pressure
to injector installed in throttle body. As the fuel pres-
sure applied to the fuel injector (the fuel pressure in
the fuel feed line) is always kept a certain amount
higher than the pressure in the intake manifold by the
fuel pressure regulator, the fuel is injected into the
throttle body in conic dispersion when the injectoropens according to the injection signal from ECM.
The fuel relieved by the fuel pressure regulator re-
turns through the fuel return line to the fuel tank.
The injected fuel is mixed with the air which has been
filtered through the air cleaner in the throttle body. The
air/fuel mixture is drawn through clearance between
throttle valve and bore.
Then the intake manifold distributes the air/fuel mix-
ture to each combustion chamber.
For the structure and operation of the fuel tank and fil-
ter, refer to SECTION 6C “ENGINE FUEL”.
AIR AND FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM