Page 299 of 557
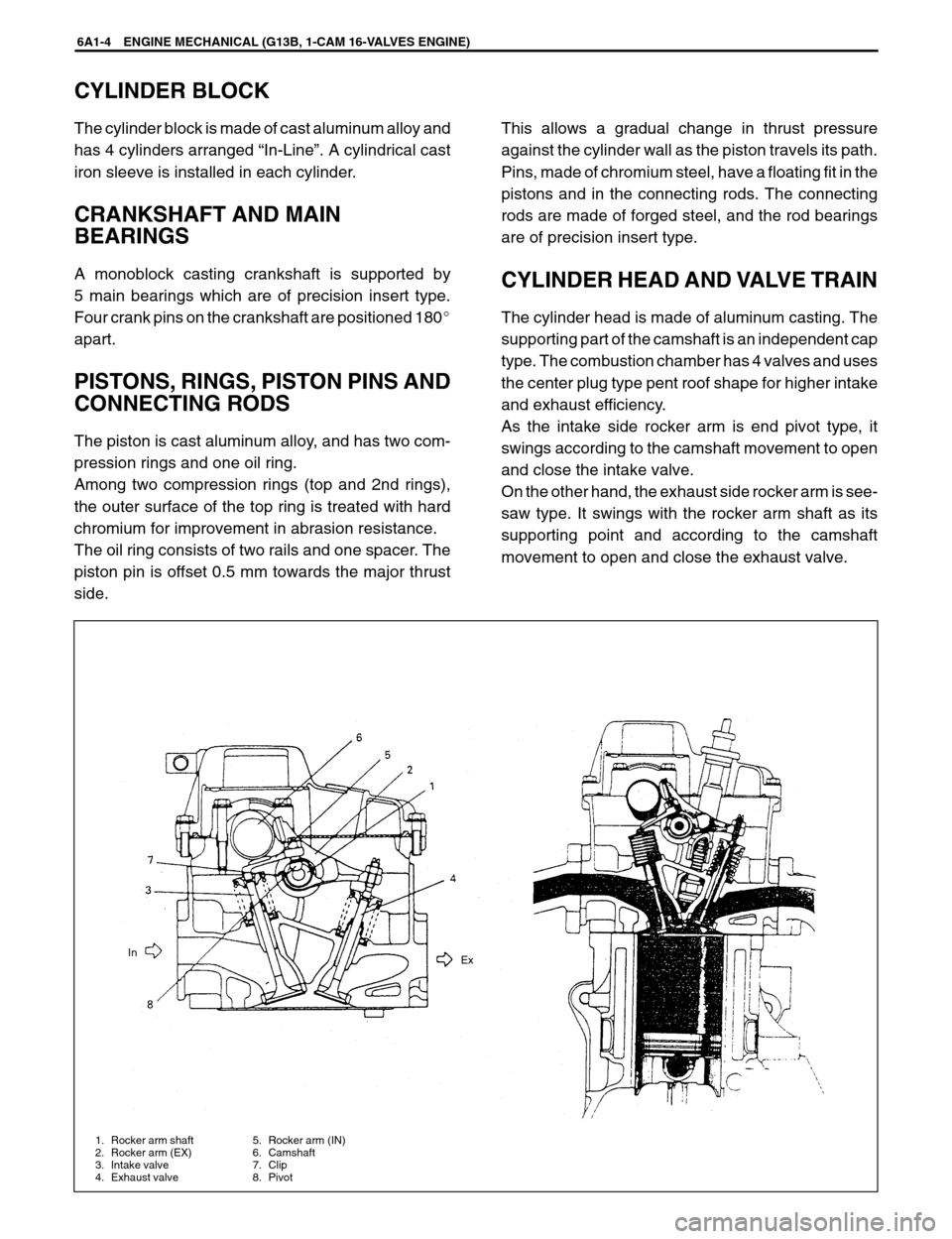
1. Rocker arm shaft
2. Rocker arm (EX)
3. Intake valve
4. Exhaust valve5. Rocker arm (IN)
6. Camshaft
7. Clip
8. PivotEx In
CYLINDER BLOCK
The cylinder block is made of cast aluminum alloy and
has 4 cylinders arranged “In-Line”. A cylindrical cast
iron sleeve is installed in each cylinder.
CRANKSHAFT AND MAIN
BEARINGS
A monoblock casting crankshaft is supported by
5 main bearings which are of precision insert type.
Four crank pins on the crankshaft are positioned 180�
apart.
PISTONS, RINGS, PISTON PINS AND
CONNECTING RODS
The piston is cast aluminum alloy, and has two com-
pression rings and one oil ring.
Among two compression rings (top and 2nd rings),
the outer surface of the top ring is treated with hard
chromium for improvement in abrasion resistance.
The oil ring consists of two rails and one spacer. The
piston pin is offset 0.5 mm towards the major thrust
side.This allows a gradual change in thrust pressure
against the cylinder wall as the piston travels its path.
Pins, made of chromium steel, have a floating fit in the
pistons and in the connecting rods. The connecting
rods are made of forged steel, and the rod bearings
are of precision insert type.
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE TRAIN
The cylinder head is made of aluminum casting. The
supporting part of the camshaft is an independent cap
type. The combustion chamber has 4 valves and uses
the center plug type pent roof shape for higher intake
and exhaust efficiency.
As the intake side rocker arm is end pivot type, it
swings according to the camshaft movement to open
and close the intake valve.
On the other hand, the exhaust side rocker arm is see-
saw type. It swings with the rocker arm shaft as its
supporting point and according to the camshaft
movement to open and close the exhaust valve.
6A1-4 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
Page 300 of 557
1
2
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-5
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
COMPRESSION CHECK
Check compression pressure on all four cylinders as follows:
1) Warm up engine.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE:
After warming up engine, place transmission gear shift le-
ver in “Neutral” (shift selector lever to “P” range for A / T
model), and set parking brake and block drive wheels.
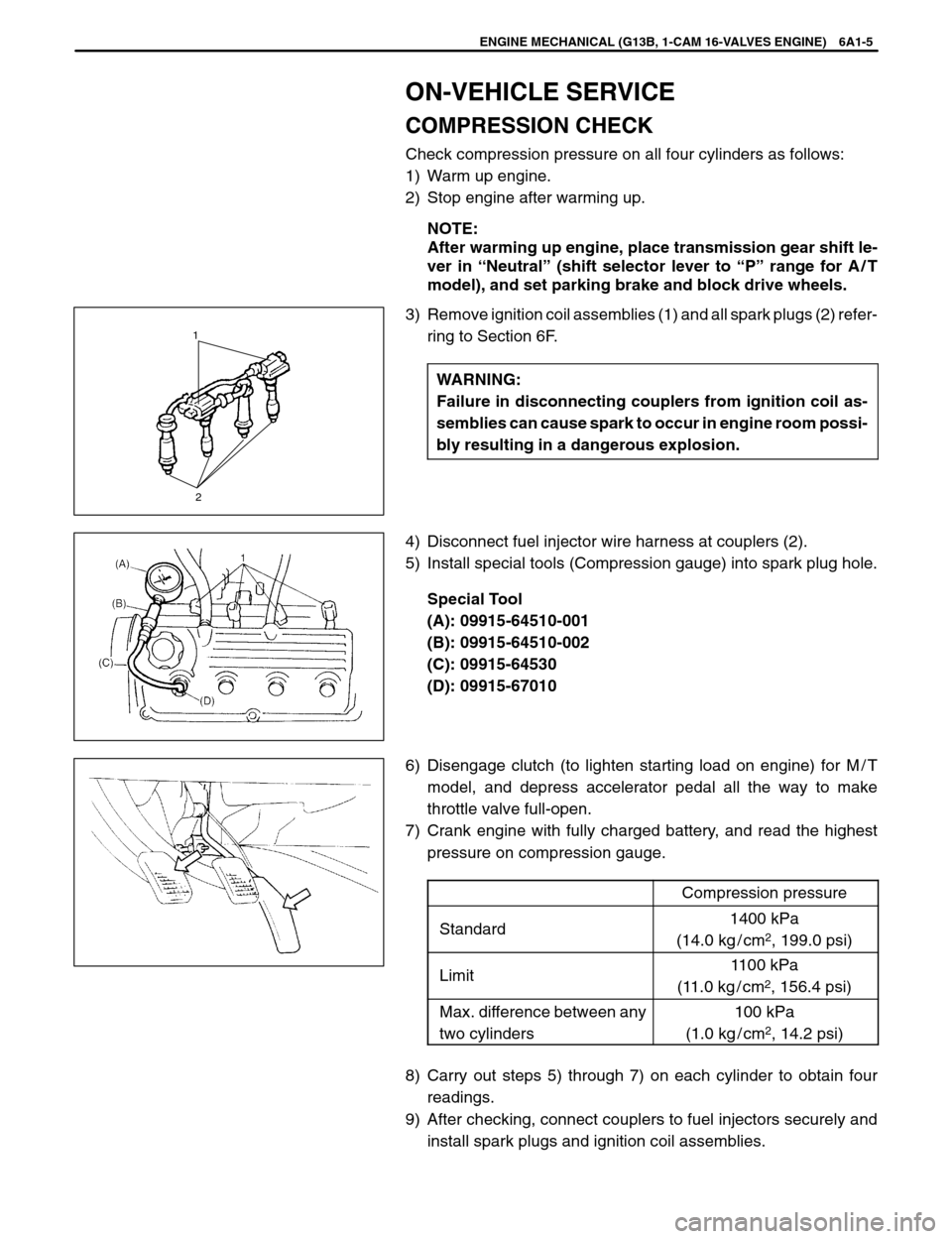
3) Remove ignition coil assemblies (1) and all spark plugs (2) refer-
ring to Section 6F.
WARNING:
Failure in disconnecting couplers from ignition coil as-
semblies can cause spark to occur in engine room possi-
bly resulting in a dangerous explosion.
4) Disconnect fuel injector wire harness at couplers (2).
5) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark plug hole.
Special Tool
(A): 09915-64510-001
(B): 09915-64510-002
(C): 09915-64530
(D): 09915-67010
6) Disengage clutch (to lighten starting load on engine) for M / T
model, and depress accelerator pedal all the way to make
throttle valve full-open.
7) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest
pressure on compression gauge.
Compression pressure
Standard1400 kPa
(14.0 kg / cm
2, 199.0 psi)
Limit1100 kPa
(11.0 kg / cm
2, 156.4 psi)
Max. difference between any
two cylinders100 kPa
(1.0 kg / cm
2, 14.2 psi)
8) Carry out steps 5) through 7) on each cylinder to obtain four
readings.
9) After checking, connect couplers to fuel injectors securely and
install spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies.
Page 302 of 557

ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-7
OIL PRESSURE CHECK
NOTE:
Prior to checking oil pressure, check the following items.
�Oil level in oil pan.
If oil level is low, add oil up to Full level mark on oil level
gauge.
�Oil quality.
If oil is discolored, or deteriorated, change it.
For particular oil to be used, refer to the table in Section 0B.
�Oil leaks.
If leak is found, repair it.
1) Remove oil pressure switch (1) from cylinder block.
2) Install special tool (Oil pressure gauge) to vacated threaded
hole.
Special Tool
(A): 09915-77311
3) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature.
NOTE:
Be sure to place transmission gear shift lever in “Neutral”
(shift selector lever to “P” range for A / T model), and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
4) After warming up, raise engine speed to 4,000 r / min and mea-
sure oil pressure.
Oil pressure specification:
360 – 440 kPa (3.6 – 4.4 kg / cm
2, 51.2 – 62.6 psi) at 4,000 r / min
(rpm)
5) Stop engine and remove oil pressure gauge.
Page 303 of 557
6A1-8 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
6) Before reinstalling oil pressure switch (1), be sure to wrap its
screw threads with sealing tape (2) and tighten switch to speci-
fied torque.
NOTE:
If sealing tape edge is bulged out from screw threads of
switch, cut it off.
Tightening Torque
(a): 13 N
.m (1.3 kg-m, 9.5 lb-ft)
7) Start engine and check oil pressure switch for oil leakage.
Page 308 of 557

3
3
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-13
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Disconnect breather hose (2) and PCV valve (3) from head cov-
er.
3) Disconnect ignition coil couplers (6).
4) Remove ignition coil assemblies (5) with high-tension cord (4).
5) Remove cylinder head cover (1) with cylinder head cover gasket
and O-rings.
INSTALLATION
1) Install O-rings (3) and cylinder head cover gasket (2) to cylinder
head cover (1).
NOTE:
Be sure to check each of these parts for deterioration or any
damage before installation and replace if found defective.
2) Install cylinder head cover to cylinder head and tighten cover
bolts to specified torque.
Tightening Torque
(a): 11 N
.m (1.1 kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
NOTE:
When installing cylinder head cover, use care so that cylin-
der head cover gasket or O-rings will not get out of place or
fall off.
3) Install ignition coil assemblies (5) with high-tension cord (4).
4) Connect ignition coil couplers (6).
5) Connect breather hose (2) and PCV valve (3) to head cover (1).
6) Connect negative cable at battery.
Page 315 of 557
1.“V” mark on cylinder
head cover
2. Timing mark by “E” on
camshaft timing belt pulley
3. Arrow mark on oil
pump case
4. Punch mark on crankshaft
timing belt pulley
4. Tensioner stud
6. Damper
6
6A1-20 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
8) Lock crankshaft inserting flat end rod or the like (2) between fly-
wheel ring gear and transmission case, after removing clutch
housing (torque converter housing for A / T) lower plate.
With crankshaft locked, remove crankshaft timing belt pulley
bolt (3).
9) Remove crankshaft pulley bolts (1).
10) Remove crankshaft pulley (4).
11) Install crankshaft timing belt pulley bolt temporarily to turn
crankshaft.
12) Release harness clamps.
13) Remove timing belt outside cover.
14) For installation of timing belt, align 4 timing marks as shown in
figure by turning crankshaft.
15) Remove timing belt tensioner (3), tensioner plate (2), tensioner
spring (5) and timing belt (1).
Page 316 of 557
1. Camshaft allowable turning range - - - By timing mark,
within 90� from “V” mark on head cover on both right
and left.
2. Crankshaft allowable turning range - - - By punch mark,
within 90� from arrow mark on oil pump case on both
right and left.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE) 6A1-21
CAUTION:
�After timing belt is removed, never turn camshaft and
crankshaft independently more than such an extent as
shown in figure. If turned, interference may occur among
piston and valves, and parts related to piston and valves
may be damaged.
�Never bend timing belt.
INSPECTION
�Inspect timing belt for wear or crack.
Replace it as necessary.
�Inspect tensioner for smooth rotation.
INSTALLATION
1) Install tensioner plate to tensioner.
Insert lug (1) of tensioner plate into hole (2) in tensioner.
Page 317 of 557

4. Damper
6A1-22 ENGINE MECHANICAL (G13B, 1-CAM 16-VALVES ENGINE)
2) Install tensioner (2) and tensioner plate (3):
Do not tighten tensioner bolt (1) with wrench yet. Hand tighten
only at this time.
Check to ensure that plate movement in arrow direction as
shown in figure causes tensioner to move in the same direction.
If no associated movement between plate and tensioner occurs,
remove tensioner and plate again and reinsert plate lug into ten-
sioner hole.
3) Check that timing mark (2) on camshaft timing belt pulley is
aligned with “V” mark (1) on cylinder head cover. If not, align two
marks by turning camshaft but be careful not to turn it more than
its allowable turning range which is described on previous page.
4) Check that timing mark (2) on crankshaft timing belt pulley is
aligned with arrow mark (1) on oil pump case. If not, align two
marks by turning crankshaft but be careful not to turn it more
than its allowable turning range which is described on previous
page.
5) Install timing belt and tensioner spring (2).
With two sets of marks aligned and tensioner plate pushed up,
install timing belt on two pulleys in such a way that drive side (1)
of belt is free from any slack.
And then install tensioner spring as shown in figure, and hand-
tighten tensioner stud (3).
NOTE:
�When installing timing belt, match arrow mark (
) on
timing belt with rotating direction of crankshaft.
�In this state, No. 4 piston is at top dead center of compres-
sion stroke.