Page 49 of 118
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine FUEL MIXTURE
Manifolds
12
12-11
Remove the nuts securing the manifolds.
If replacement of the inlet manifold is planned, remove the EGR valve (consult section 14 "Antipollution" for the
method).
REFITTING
Proceed in the reverse order to removal.
Change the manifold gasket and take care to replace it properly.Manifolds
Page 50 of 118
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine FUEL MIXTURE
Priming catalytic converter
12
12-12
Priming catalytic converter
REMOVAL
Put the vehicle on a two post lift.
Disconnect the battery.
Remove the cover and the under body protection.
Disconnect the exhaust downpipe.Remove (for the Scénic) :
– the windscreen wiper arms using tool Elé. 1294-01,
– the scuttle panel,
– the bulkhead panel,
Disconnect the flow meter and remove the air unit.
Remove:
– the priming catalytic converter mounting stay,
– the mounting nuts,
– the pre-catalytic converter. TIGHTENING TORQUES (in daN.m )
Priming catalytic converter mounting nuts
(pre-catalytic converter) 2.4
Lower mounting bolt 2.4
Priming catalytic converter stay bolt 6
16156S
11020R
11036R2
Page 51 of 118
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine FUEL MIXTURE
Priming catalytic converter
12
12-13
REFITTING
Fit the priming catalytic converter (or pre-catalytic
converter) to the turbocharger.
Fit:
– the pre-catalytic converter stay,
– the mounting nuts.
Tighten all the nuts and mounting bolts.
Refit the exhaust downpipe.
Replace the seals.
Page 52 of 118
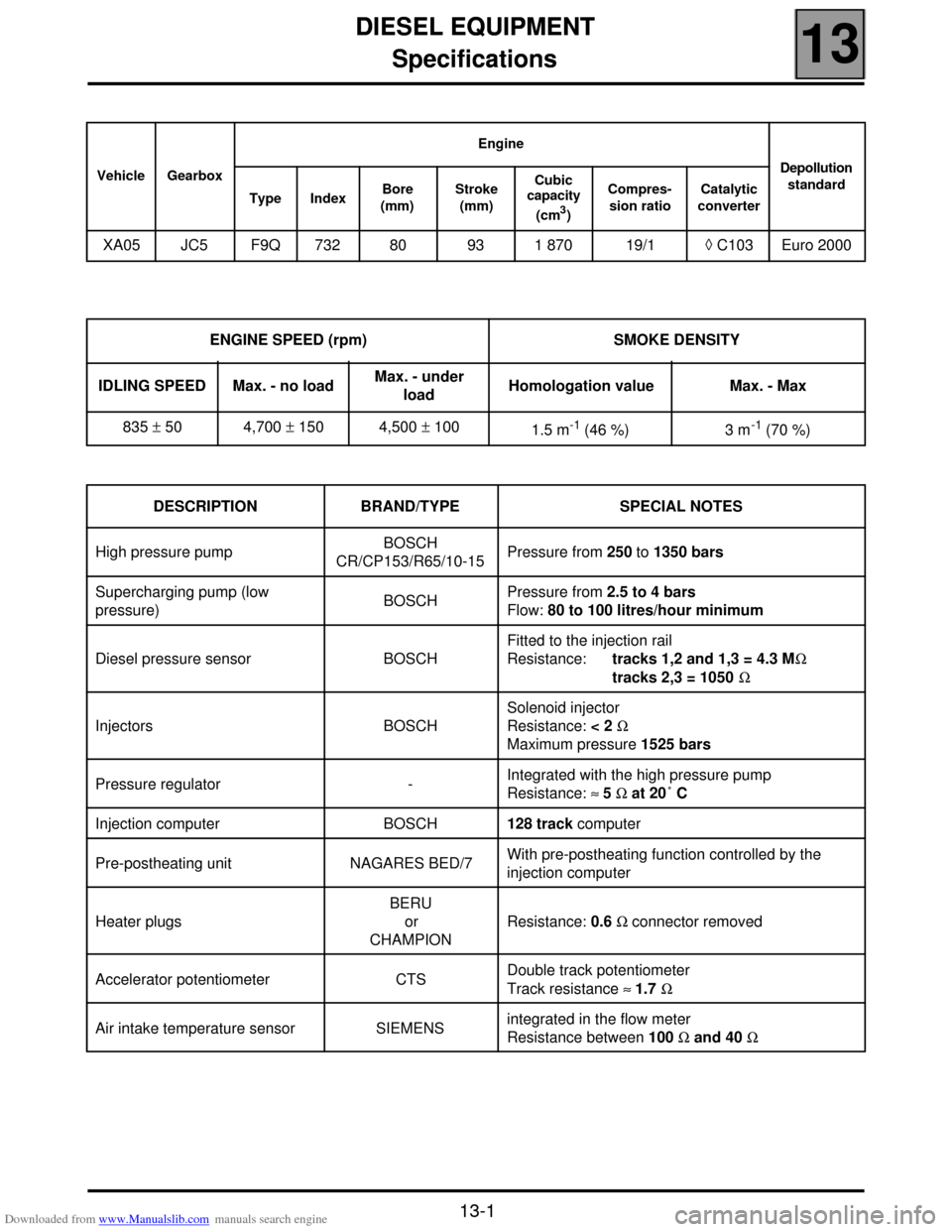
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Specifications
13
113
DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Specifications
Vehicle GearboxEngine
Depollution
standard
Type IndexBore
(mm) Stroke
(mm) Cubic
capacity
(cm
3)Compres-
sion ratioCatalytic
converter
XA05 JC5 F9Q 732 80 93 1 870 19/1◊ C103 Euro 2000
ENGINE SPEED (rpm) SMOKE DENSITY
IDLING SPEED Max. - no loadMax. - under
loadHomologation value Max. - Max
835 ± 50 4,700 ± 150 4,500 ± 100
1.5 m
-1 (46 %) 3 m-1 (70 %)
DESCRIPTION BRAND/TYPE SPECIAL NOTES
High pressure pumpBOSCH
CR/CP153/R65/10-15Pressure from 250 to 1350 bars
Supercharging pump (low
pressure)BOSCHPressure from 2.5 to 4 bars
Flow: 80 to 100 litres/hour minimum
Diesel pressure sensor BOSCHFitted to the injection rail
Resistance: tracks 1,2 and 1,3 = 4.3 MΩ
tracks 2,3 = 1050 Ω
Injectors BOSCHSolenoid injector
Resistance: < 2 Ω
Maximum pressure 1525 bars
Pressure regulator - Integrated with the high pressure pump
Resistance: ≈ 5 Ω at 20˚ C
Injection computer BOSCH128 track computer
Pre-postheating unit NAGARES BED/7With pre-postheating function controlled by the
injection computer
Heater plugsBERU
or
CHAMPIONResistance: 0.6 Ω connector removed
Accelerator potentiometer CTSDouble track potentiometer
Track resistance ≈ 1.7 Ω
Air intake temperature sensor SIEMENSintegrated in the flow meter
Resistance between 100 Ω and 40 Ω
13-1
Page 53 of 118

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Specifications
13
13-2
DESCRIPTION MAKE/MODEL SPECIAL NOTES
Diesel temperature sensorMAGNETTI
MARELIResistance: ≈ 2.050 Ω at 25 ˚C
Engine speed sensor MGI Resistance: 800 ± 80 Ω
Atmospheric pressure sensor - Integrated in the computer
Camshaft sensor ELECTRIFIL Hall effect sensor
Turbocharger pressure sensor DELCOResistance : 4 KΩ across tracks A and C
Resistance : 5 KΩ across tracks A and C
Resistance : 9 KΩ across tracks A and B
Turbocharger operating
solenoidBITRON Resistance 16.5±1 Ω at 25 ˚C
Air flow meter SIEMENSFlow meter with integrated air temperature sensor
track 1 : air temperature
track 2 : earth
track 3 : 5 V reference
track 4 : + battery feed
track 5 : air flow signal
track 6 : earth
EGR solenoid valve PIERBURGTrack resistance: 8±0.5 Ω to 20 ˚C (tracks 1 and 5)
Sensor resistance: 4 KΩ to 20 ˚C (tracks 2 and 4)
Turbocharger KKKCalibration :
120 mbars for rod travel between 1 and 4 mm
400 mbars for a stroke between 10 and 12 mm
Thermal plungers - Resistance: 0.45 ± 0.05 Ω at 20 ˚C
Page 54 of 118
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Special notes
13
13-3
Special notes
The common rail direct high pressure injection system aims to deliver a certain quantity of diesel to the engine at a
specific time.
DESCRIPTION
The system consists of:
– a low pressure pump (1) (located between the induction unit and the fuel filter),
– a fuel filter (2),
– a high pressure pump (3),
– a high pressure regulator (4) attached to the pump,
– an injection rail (5) fitted with a diesel pressure sensor,
– a priming fuel cock (6) (open in normal mode) (depending on version),
– a fuel cooler (7),
– four solenoid injectors,
– various sensors,
– an injection computer.
Removal of the interior of the high pressure pump and the injectors is prohibited.
16311R
Page 55 of 118

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Special notes
13
13-4
OPERATION
The common rail direct high pressure injection system is a sequential diesel injection system (based on the
operation of multipoint injection for petrol engines).
This new injection system reduces operating noise, lowers the quantity of polluting gas and particles and produces
significant engine torque at low engine speeds thanks to a pre-injection procedure.
The low pressure pump (also called the supercharging pump) supplies the HP pump, through the filter with pressure
of between 2.5 and 4 bars.
The HP pump generates the high pressure sent to the injection rail. The pressure regulator located on the pump
modulates the value of the high pressure via the computer. The rail supplies each injector through a steel pipe.
The computer:
– determines the value of injection pressure necessary for the engine to operate well and then controls the pressure
regulator. It checks that the pressure value is correct by analysing the value transmitted by the pressure sensor
located on the rail,
– determines the injection time necessary to deliver the right quantity of diesel and the moment when injection should
be started,
– controls each injector electrically and individually after determining these two values.
The injected flow to the engine is determined depending on:
– the duration of injector control,
– the injector opening and closing speed,
– the needle stroke (determined by the type of injector),
– the nominal injector hydraulic flow (determined by the type of injector),
– the high pressure rail pressure controlled by the computer.
FOR ANY INTERVENTION IN THE HIGH PRESSURE INJECTION SYSTEM YOU MUST RESPECT THE
CLEANING AND SAFETY ADVICE SPECIFIED IN THIS DOCUMENT.
Page 56 of 118

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIESEL EQUIPMENT
Special notes
13
13-5
POST-REPAIR CHECK
A fuel cock is fitted to the fuel filter at the level of the diesel return pipe leading to the tank. It should be in open
position for normal operation.
However, to carry out a circuit reignition after an intervention, a filter change or a fuel fault, you should:
– close the fuel cock,
– start the low pressure pump by switching on the ignition several times,
– start the engine,
– OPEN THE FUEL COCK (the valve is open when the two coloured lines are aligned).
NOTE: certain vehicles are not fitted with a fuel cock. In this case, ignore this operation.
IMPORTANT: the engine must not run with diesel containing more than 10 % diester.
The system can inject the diesel into the engine up to a pressure of 1350 bars. Before any intervention, check
that the injector rail is depressurised.
It is absolutely vital that you observe the tightening torque:
– of the high pressure pipes,
– of the injector on the cylinder head,
– of the pressure regulator,
– of the pressure sensor.
When the high pressure pump, injectors, supply, return and high pressure output unions are repaired or
removed, the bores should be fitted with new and appropriate core seals to avoid impurities.
When replacing a high pressure pipe, the following procedure should be observed:
– remove the high pressure pipe,
– fit the cleanliness plugs,
– loosen the high pressure rail and the pump/rail pipe,
– fit the high pressure pipe,
– tighten the injector side union to torque,
– tighten the connection on the high pressure pump side to torque,
– tighten the high pressure rail fastenings to torque.
– tighten the pump/rail pipe to torque (pump side first).
It is prohibited to remove the interior of the pump.
It is vital that you replace the fuel return pipe placed on the injectors during removal.
The diesel temperature sensor is not removable. It is part of the fuel return rail.
It is forbidden to loosen a high pressure pipe connection when the engine is running.After any operation, check that there are no diesel leaks. Start the engine at idling speed until the fan starts up,
then accelerate several times under no load.