2000 HONDA ODYSSEY v tech
[x] Cancel search: v techPage 328 of 352
DO
T Tir e Qualit y Gradin g (U.S . Vehicles )
Temperatur e
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing thetire's resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability to dissipate heat
when tested under controlledconditions on a specified indoor
laboratory test wheel. Sustained high
temperature can cause the materialof the tire to degenerate and reduce
tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The
grade C corresponds to a level of
performance which all passenger car
tires must meet under the FederalMotor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent
higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the
minimum required by law. Warning: The temperature grade for
this tire is established for a tire that
is properly inflated and not over-
loaded. Excessive speed, underinfla-
tion, or excessive loading eitherseparately or in combination, can
cause heat build-up and possible tire
failure.
Technical Informatio n
Page 329 of 352
Oxygenated Fuel s
Some conventional gasolines are
being blended with alcohol or an
ether compound. These gasolines
are collectively referred to as
oxygenated fuels. To meet clean air
standards, some areas of the United
States and Canada use oxygenated
fuels to help reduce emissions.
If you use an oxygenated fuel, be
sure it is unleaded and meets the
minimum octane rating requirement.
Before using an oxygenated fuel, try
to confirm the fuel's contents. Some
states/provinces require this
information to be posted on the
pump.
The following are the U.S. EPA and
Canadian CGSB approved
percentages of oxygenates:
ETHANO L (ethyl or grain alcohol)
You may use gasoline containing up to 10 percent ethanol by volume. Gasoline containing ethanol may be
marketed under the name "Gasohol."
MTB E (Methyl Tertiary Butyl
Ether)
You may use gasoline containing up to 15 percent MTBE by volume.
METHANO L (methyl or wood
alcohol)
You vehicle was not designed to use
fuel that contains methanol. Methanol can corrode metal parts in
the fuel system, and also damage
plastic and rubber components. This damage would not be covered by
your warranties. If you notice any undesirable
operating symptoms, try another
service station or switch to another
brand of gasoline.
Fuel system damage or performance
problems resulting from the use of
an oxygenated fuel containing more
than the percentages of oxygenates
given above are not covered under
warranty.
Technica
l Informatio n
Page 330 of 352

Driving in Foreig n Countrie s
Technica l Informatio n
If you are planning to take your
Honda outside the U.S. or Canada,
contact the tourist bureaus in the
areas you will be traveling in to find
out about the availability of unleaded
gasoline with the proper octane
rating.
If unleaded gasoline is not available,
be aware that using leaded gasoline in your Honda will affect perfor-
mance and fuel mileage, and damage
its emissions controls. It will no
longer comply with U.S. andCanadian emissions regulations, and
will be illegal to operate in North
America. To bring your vehicle back into compliance will require the re-
placement of several components,such as the oxygen sensors and the
three way catalytic converter. These
replacements are not covered under
warranty.
Page 331 of 352
Emissions Control s
The burning of gasoline in your
vehicle's engine produces several by-products. Some of these are carbon
monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen (NO
x) and hydrocarbons (HC).
Gasoline evaporating from the tank
also produces hydrocarbons. Con-
trolling the production of NOx, CO, and HC is important to the environ-
ment. Under certain conditions ofsunlight and climate, NOx and HC
react to form photochemical "smog." Carbon monoxide does not contri-
bute to smog creation, but it is a
poisonous gas.
Th e Clea n Ai r Ac t
The United States Clean Air Act*
sets standards for automobile
emissions. It also requires that
automobile manufacturers explain to
owners how their emissions controls
work and what to do to maintain
them. This section summarizes how
the emissions controls work.
Scheduled maintenance is on page
230.
* In Canada, Honda vehicles comply
with the Canadian Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards (CMVSS) for
Emissions valid at the time they are
manufactured.
Crankcas e Emission s Contro l
System
Your vehicle has a Positive
Crankcase Ventilation System. This
keeps gasses that build up in the engine's crankcase from going into
the atmosphere. The Positive Crank- case Ventilation valve routes them
from the crankcase back to the
intake manifold. They are then drawn into the engine and burned.
Evaporativ e Emission s Contro l
Syste m
As gasoline evaporates in the fuel tank, an evaporative emissions
control canister filled with charcoaladsorbs the vapor. It is stored in this
canister while the engine is off. After
the engine is started and warmed up,
the vapor is drawn into the engine and burned during driving.
Technica l Informatio n
Page 332 of 352
Emissions Control s
Exhaus t Emission s Control s
The exhaust emissions controls include four systems: PGM-FI,
Ignition Timing Control, ExhaustGas Recirculation and Three Way
Catalytic Converter. These four
systems work together to control the
engine's combustion and minimize
the amount of HC, CO, and NOx that
comes out the tailpipe. The exhaust emissions control systems are
separate from the crankcase and
evaporative emissions control
systems.
PGM-FI System
The PGM-FI System uses sequential multiport fuel injection.
It has three subsystems: Air Intake,
Engine Control, and Fuel Control.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) uses various sensors to
determine how much air is going
into the engine. It then controls how
much fuel to inject under all operat-
ing conditions.
Ignition Timing Control System
This system constantly adjusts the ignition timing, reducing the amountof HC, CO and NOx produced.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
System
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system takes some of the
exhaust gas and routes it back into
the intake manifold. Adding exhaust
gas to the air/fuel mixture reduces
the amount of NOx produced when
the fuel is burned.
Three Way Catalytic Converter
The three way catalytic converter is in the exhaust system. Through
chemical reactions, it converts HC,CO, and NOx in the engine's exhaust
to carbon dioxide (CO
2), dinitrogen
(N
2), and water vapor. Replacemen
t Part s
The emissions control systems are designed and certified to work to-
gether in reducing emissions to
levels that comply with the Clean Air
Act. To make sure the emissions remain low, you should use only newGenuine Honda replacement parts or
their equivalent for repairs. Using
lower quality parts may increase the emissions from your vehicle.
The emissions control systems are covered by warranties separate from
the rest of your vehicle. Read your
warranty manual for more informa- tion.
Technica l Informatio n
Page 333 of 352
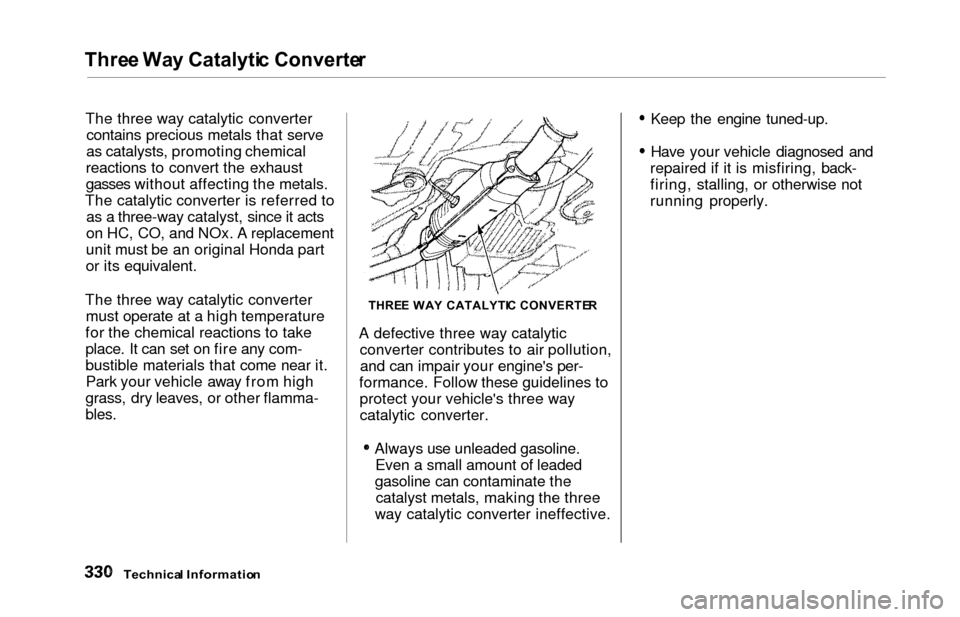
Three Wa y Catalyti c Converte r
The three way catalytic converter
contains precious metals that serve
as catalysts, promoting chemical
reactions to convert the exhaust
gasses without affecting the metals.
The catalytic converter is referred to as a three-way catalyst, since it acts
on HC, CO, and NOx. A replacement
unit must be an original Honda part
or its equivalent.
The three way catalytic converter must operate at a high temperature
for the chemical reactions to take
place. It can set on fire any com-
bustible materials that come near it. Park your vehicle away from high
grass, dry leaves, or other flamma-
bles.
A defective three way catalytic converter contributes to air pollution,and can impair your engine's per-
formance. Follow these guidelines to protect your vehicle's three way
catalytic converter.
Always use unleaded gasoline.Even a small amount of leaded
gasoline can contaminate the catalyst metals, making the three
way catalytic converter ineffective. Keep the engine tuned-up.
Have your vehicle diagnosed and
repaired if it is misfiring, back-
firing, stalling, or otherwise not
running properly.
Technica l Informatio n
THREE WA Y CATALYTI C CONVERTE R
Page 350 of 352

Index
Tachometer...................................... 62
Tailgate............................................. 85
Opening the.................................. 85
Open Monitor Light.................... 60
Taillights, Changing Bulbs in....... 275
Taking Care of the Unexpected .. 291
Tape Player ........................... 160, 181
Technical Descriptions DOT Tire Quality Grading....... 324
Driving in Foreign Countries... 327
Emissions Control Systems...... 328Oxygenated Fuels...................... 326
Three Way Catalytic Converter................................ 330
Temperature Gauge........................ 63 Tensioners, Seat Belts.................... 50Tether Attachment Points.............. 43
Theft Protection............................ .
186
Three Way Catalytic Converter... 330
Time, Setting the........................... 117
Timing Belt..................................... 263
Tire Chains..................................... 269
Tire, How to Change a Flat.......... 293 Tires...............................................
. 263
Air Pressure.............................. . 263
Balancing.................................... 266
Checking Wear.......................... 265
Compact Spare........................... 292
DOT Tire Quality Grading....... 324
Inflation....................................... 263
Inspection................................... 265 Replacing.................................... 267
Rotating....................................... 266
Snow........................................... . 269
Specifications............................ . 323
Tire Chains................................. 269
Towing
A Trailer ................................. 218
Emergency Wrecker................. 317
Traction Control System (TCS)... 213
Transmission
Checking Fluid Level................ 249
Fluid Selection........................... . 249
Identification Number............... 321
Shifting the Automatic.............. 205
Treadwear...................................... 324
Trip Meter......................................... 63
Turn Signals..................................... 68
Tools, Tire Changing ................... 293
Underside, Cleaning...................... 288
Unexpected, Taking Care
of the .......................................... 29 1
Uniform Tire Quality Grading .... 324
Unleaded Gasoline......................... 188
Upholstery Cleaning...................... 286
Used Oil, How to Dispose of........ 242
Vanity Mirror................................. 121
Vehicle Capacity Load.......... 198, 218
Vehicle Dimensions....................... 322
Vehicle Identification Number..... 320
Vehicle Storage.............................. 281
Ventilation............................. 133, 138
VIN ................................................. 320
Vinyl Cleaning ............................... 286
Viscosity, Oil.................................. . 240
CONTINUED