2000 HONDA CR-V Start
[x] Cancel search: StartPage 788 of 1395
Shift Gable
Adjustment
SRS components are located in this area. Review the SRS
component locations, precautions, and procedures in the
SRS section (241 before performing repairs or service.
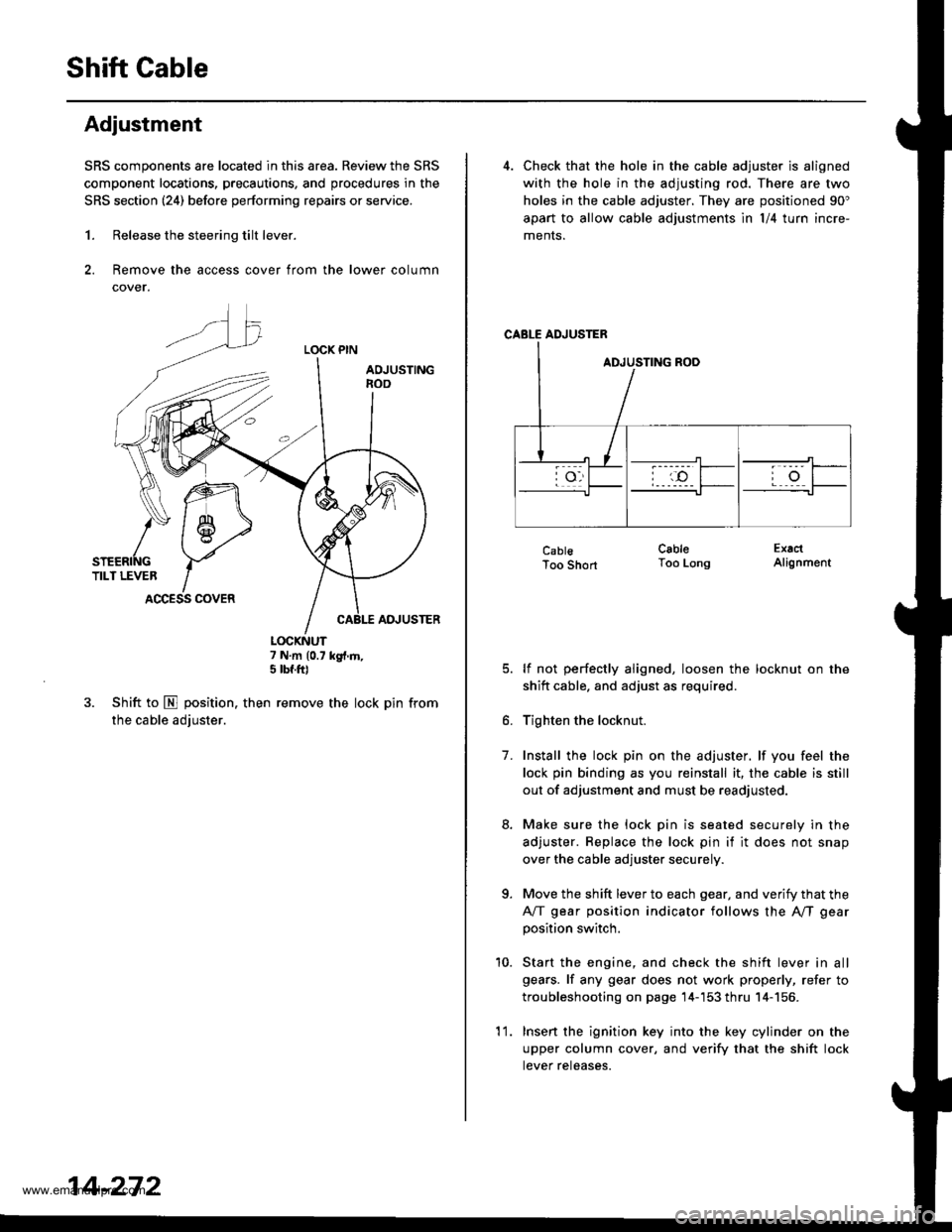
1. Release the steering tilt lever.
2. Remove the access cover from the lower column
cover.
LOCK PIN
AOJUSTINGnoo
ADJUSTER
7 N.m (0.7 kg{.m,5 tbf.ft)
3. Shift to E position. then remove the lock pin from
the cable adjuster.
K\ffi
/* 1 6-,>
snenrftc YTILT LEVER IACCESS COVER
14-272
'l 1.
4. Check that the hole in the cable adjuster is aligned
with the hole in the adjusting rod. There are two
holes in the cable adjuster. They are positioned 90"
apart to allow cable adjustments ln l/4 turn incre-
ments.
CABLE ADJUSTER
CablsToo Short
lf not perfectly aligned, loosen the locknut on the
shitt cable. and adjust as required.
Tighten the locknut.
Install the lock pin on the adjuster. lf you feel the
lock pin binding as you reinstall it, the cable is still
out of adjustment and must be readjusted.
Make sure the lock pin is seated securely in the
adjuster. Replace the lock pin if it does not snap
over the cable adjuster securely.
Move the shift lever to each gear, and verify that the
A/T gear position indicator follows the A"/T gear
position switch.
Start the engine, and check the shift lever in all
gears. lf any gear does not work properly, refer to
troubleshooting on page 14-'153 thru 14-156.
Insert the ignition key into the key cylinder on the
upper column cover, and verify that the shift lock
tever reteases.
CableToo LongExactAlignment
7.
a
10.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 794 of 1395

Description
Rear Differential
Outline
The Real-time 4WD-Dual Pump System model has a hydraulic clutch and a differential mechanism in the rear differential
assembly. Under normal conditions, the vehicle is driven by the front wheels. However, depending on to the driving force
of the front wheels and the road conditions. the system instantly transmits appropriate driving force to the rear wheels
without requiring the driver to switch between 2WD (tront wheel drive) and 4WD (four wheel drive). The switching mecha-
nism between 2WD and 4WD is integrated into the rear differential assembly to make the system light and compact.
ln addition, the dual-pump system switches off the rear-wheel-drive force when braking in a forward gear. This allows the
braking system to work properly on models equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
Construction
The rear differential assembly consists of the torque control differential case assembly and the rear differential carrier
assembly. The torque control differential case assembly consists of the differential clutch assembly, the companion
flange, and the oil pump body assembly. The rear differential carrier assembly consists of the differential mechanism. The
differential drive and driven gears are hypoid gears.
The oil pump body assembly consists of the front oil pump, the rear oil pump, the hydraulic control mechanism, and the
clutch piston. The clutch piston has a disc spring that constantly provides the differential clutch assembly with a preset
torque to Drevent abnormal sound.
The clutch guide in the differential clutch assembly is connected to the propeller shaft via the companion flange, and it
receives the driving force lrom the transfer assembly. The clutch guide rotates the clutch plate and the front oil pump in
the oil pump body.
The clutch hub in the differential clutch assembly has a clutch disc that is splined with the hypoid drive pinion gear. The
hypoid drive gear drives the rear oil pump.
The front and rear oil pumps are trochoidal pumps. The rear oil pump capacity is 2.5 percent larger that the front oil pump
to handle the rotation difference between the front and rear wheels caused by worn front tires and tight corner braking.
The oil pumps are designed so the fluid intake works as a fluid discharge when the oil pumps rotate in reverse. Genuine
Honda CVT fluid is used instead of differential fluid.
Operation
When there is a difference in rotation speed between the front wheels (clutch guide) and rear wheels (hypoid driven gear),
hydraulic pressure from the front and rear oil pumps engages the differential clutch, and drive force from the transler
assembly is applied to the rear wheels.
The hydraulic pressure control mechanism in the oil pump body selects 4WD mode when the vehicle is started abruptly,
or when accelerating in a forward or reverse gear (causing rotation difference between the front and rear wheels). or
when braking in reverse gear {when decelerating). lt switches to 2WD mode when the vehicle is driven at a constant speed
in forwar! or reverse gear (when there is no rotation difference between the front and rear wheels), or when braking in a
fo rwa rd gear (when decelerating).
To protect the system, the differential clutch assembly is lubricated by hydraulic pressure generated by the oil pumps in
both 4WD and 2WD modes. Also, the thermal switch relieves the hydraulic pressure on the clutch piston and cancels 4WD
mode if the temDerature of the differential fluid rises above normal.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 796 of 1395
Description
Hydraulic Flow
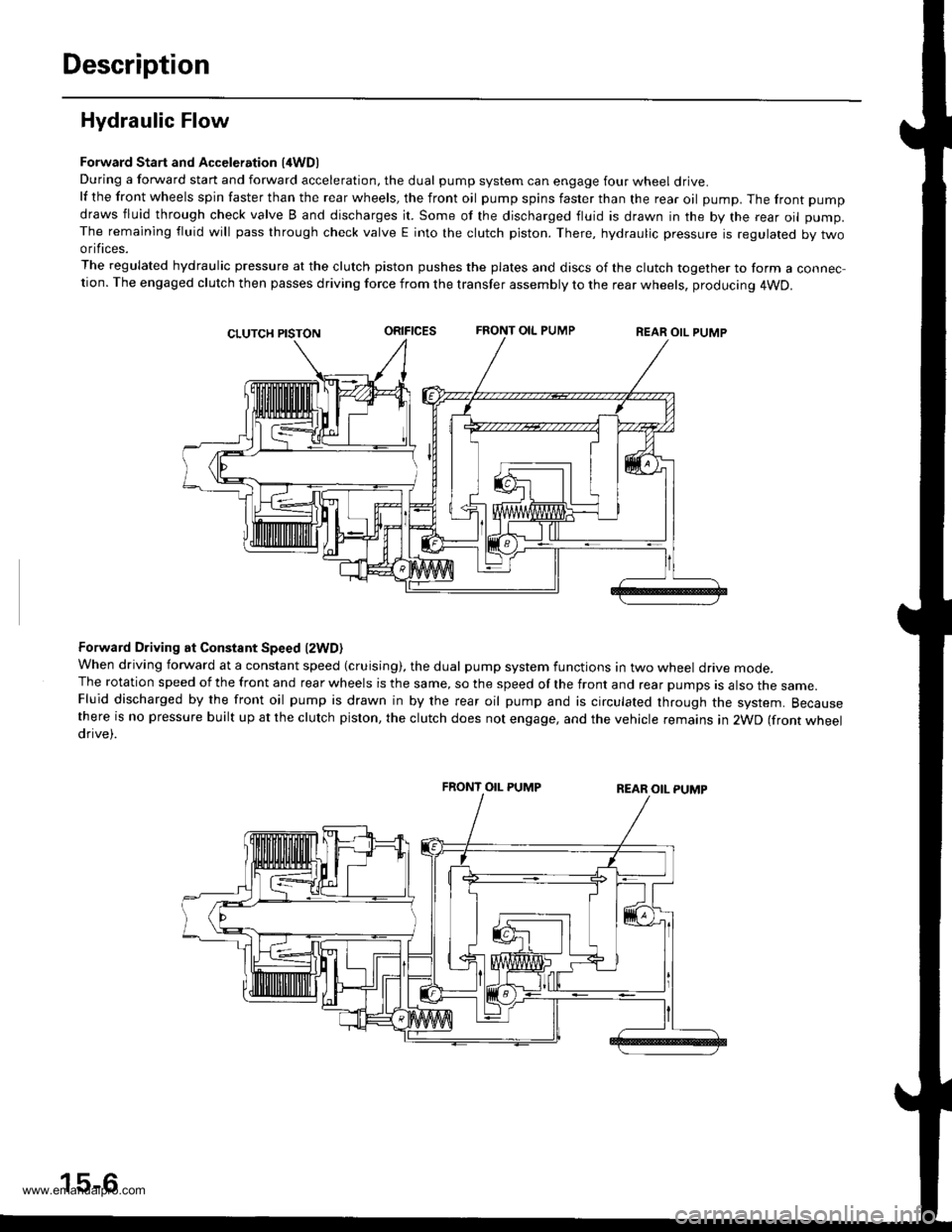
Forward Start and Acceleration l4WD)During a forward start and forward acceleration, the dual pump system can engage four wheel drive.lf the front wheels spin faster than the rear wheels, the front oil pump spins faster than the rear oil pump. The front pump
draws fluid through check valve B and discharges it. Some of the discharged fluid is drawn in the by the rear oil pump.The remaining fluid will pass through check valve E into the clutch piston. There, hydraulic pressure is regulated by twoorifices.
The regulated hydraulic pressure at the clutch piston pushes the plates and discs of the clutch together to form a connec-tion. The engaged clutch then passes driving force from the transfer assembly to the rear wheels, producing 4WD.
oRrFtcEsFRONT OIL PUMPREAR OIL PUMP
Forward Driving at Constant Speed lzWD)When driving forward at a constant speed (cruising), the dual pump system functions in two wheel drive mode.The rotation speed of the front and rear wheels is the same, so the speed of the front and rear pumps is also the same.Fluid discharged by the front oil pump is drawn in by the rear oil pump and is circulated through the system. Becausethere is no pressure built up at the clutch piston, the clutch does not engage, and the vehicle remains in 2WD (front wheeldrive).
FRONT OIL PUMP
15-6
www.emanualpro.com
Page 797 of 1395
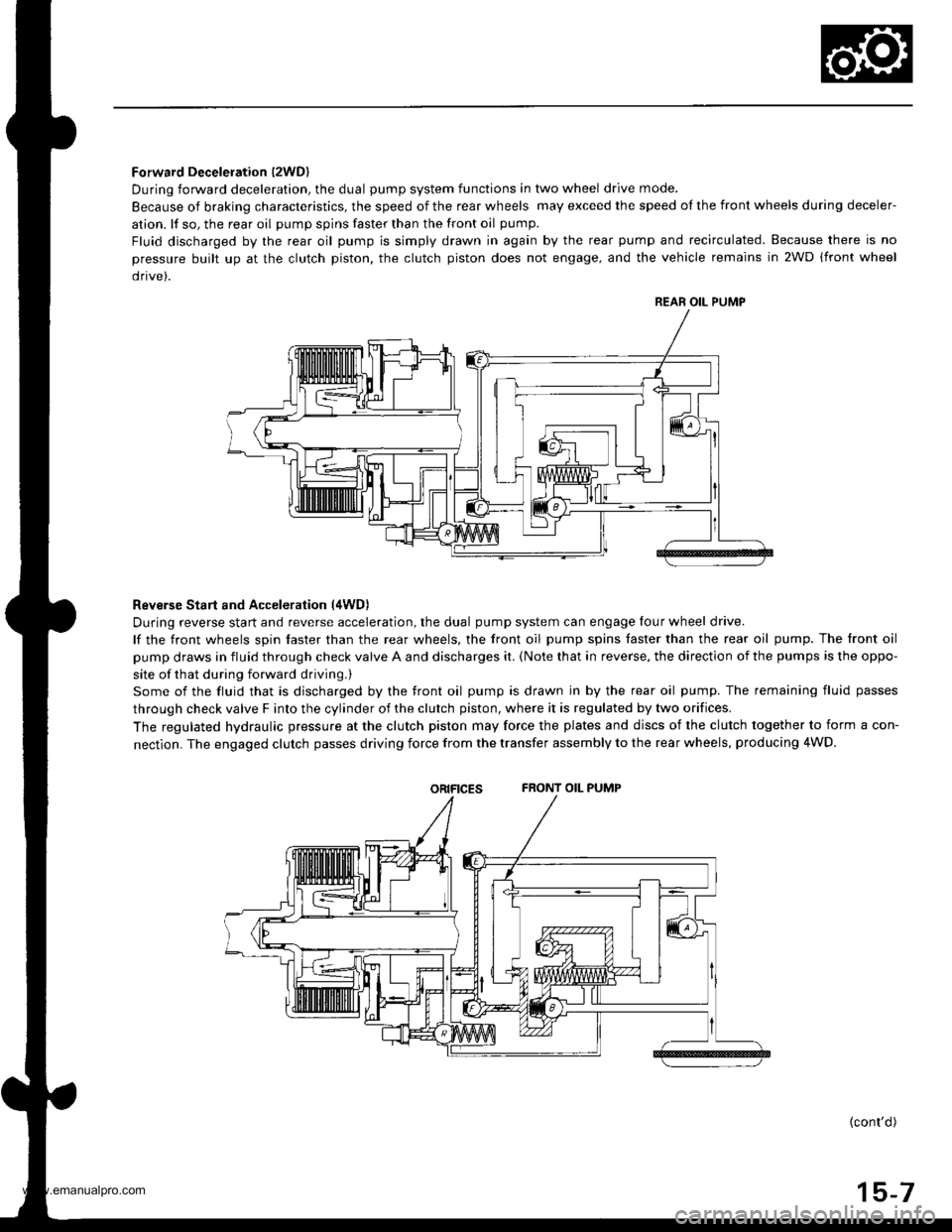
Forward Deceleration l2WDl
During forward deceleration, the dual pump system functions in two wheel drive mode.
Because of braking characteristics, the speed of the rear wheels may exceed the speed ol the front wheels during deceler-
ation. lf so, the rear oil pump spins faster than the front oil pump.
Fluid discharged by the rear oil pump is simply drawn in again by the rear pump and recirculated. Because there is no
pressure built up at the clutch piston. the clutch piston does not engage, and the vehicle remains in 2WD (front wheel
drive).
Reverse Start and Acceleration (4WD)
During reverse start and reverse acceleration, the dual pump system can engage four wheel drive.
lf the front wheels spin faster than the rear wheels, the front oil pump spins faster than the rear oil pump. The front oil
pump draws in fluid through check valve A and discharges it. {Note that in reverse, the direction of the pumps is the oppo-
site of that during forward driving.)
Some of the fluid that is discharged by the front oil pump is drawn in by the rear oil pump. The remaining fluid passes
through check valve F into the cylinder of the clutch piston, where it is regulated by two orifices.
The regulated hydraulic pressure at the clutch piston may force the plates and discs of the clutch together to form a con-
nectlon. The engaged clutch passes driving force from the transfer assembly to the rear wheels, producing 4WD.
oRtFtcEsFRONT OIL PUMP
{cont'd)
15-7
REAR OIL PUMP
www.emanualpro.com
Page 800 of 1395
Real-time 4WD-Dual Pump System
Troubleshooting (Automatic Transmissionl
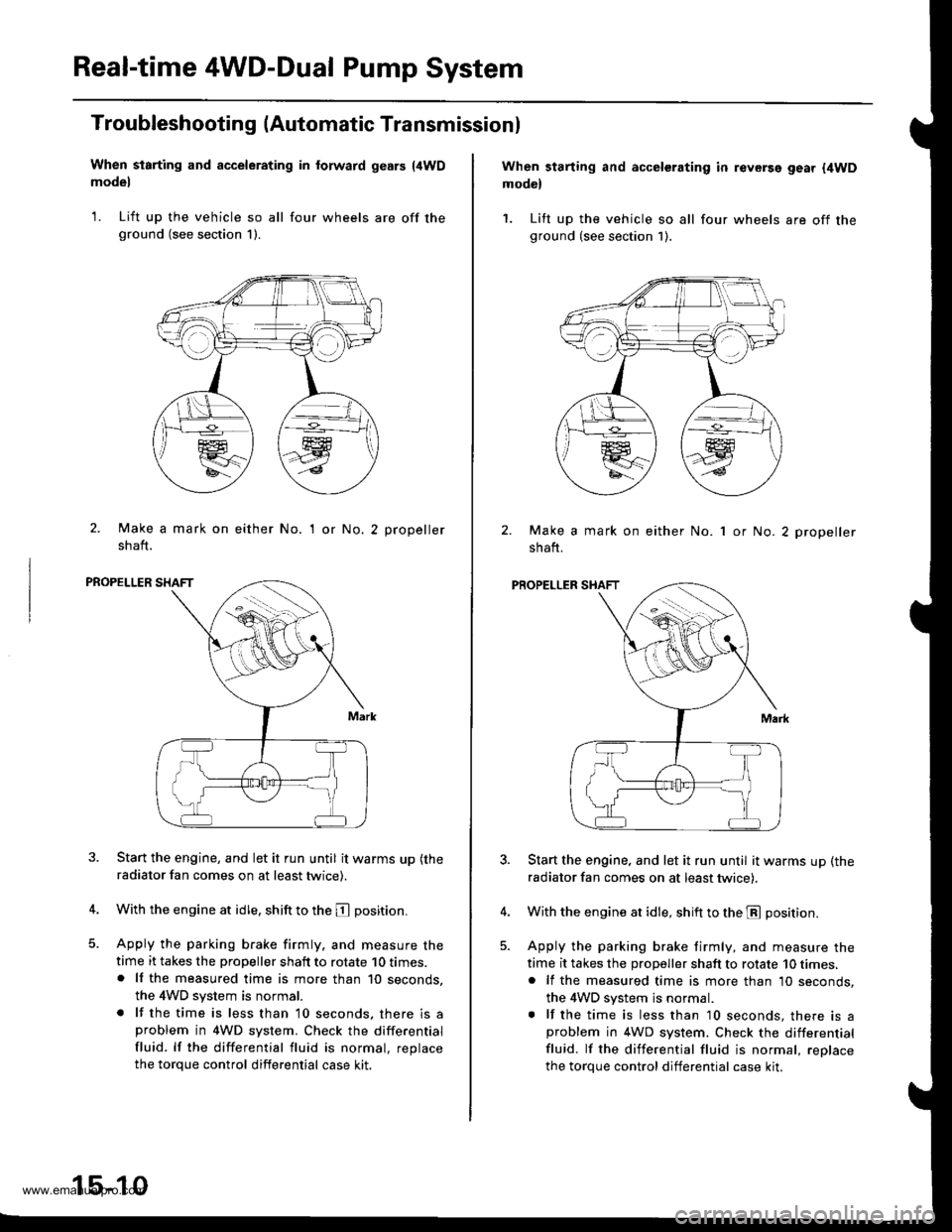
When starting and accelerating in forward gesrs {4WDmodel
1. Lift up the vehicle so all four wheels are off theground (see section 1).
2. Make a mark on either No.
shaft.
'I or No.2 propeller
PROPELLER SHAFT
Start the engine, and let it run until it warms up (the
radiator fan comes on at least twice).
With the engine at idle. shift to the E position.
Apply the parking brake firmly. and measure thetime it takes the propeller shaft to rotate 10 times.. lf the measured time is more than 10 seconds,
the 4WD system is normal.
. lf the time is less than 10 seconds, there is aproblem in 4WD system. Check the differential
fluid. lf the differential fluid is normal, replace
the torque control differential case kit.
15-10
When starting and accelerating in revGrsg gear {4WDmodel
1. Lift up the vehicle so all four wheels are off theground (see section 1).
Make a mark on either No.
shaft.
1 or No. 2 propeller
PROPELLER SHAFT
Start the engine. and let it run until it warms up (the
radiator fan comes on at least twicei.
With the engine at idle, shift to the E position.
Apply the parking brake firmly, and measure the
time it takes the proDeller shaft to rotate 10 times,. lf the measured time is more than 10 seconds,
the 4WD system js normal.. lf the time is less than 10 seconds, there is aproblem in 4WD system. Check the differential
fluid. lf the differential fluid is normal, reolace
the torque control differential case kit.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 801 of 1395
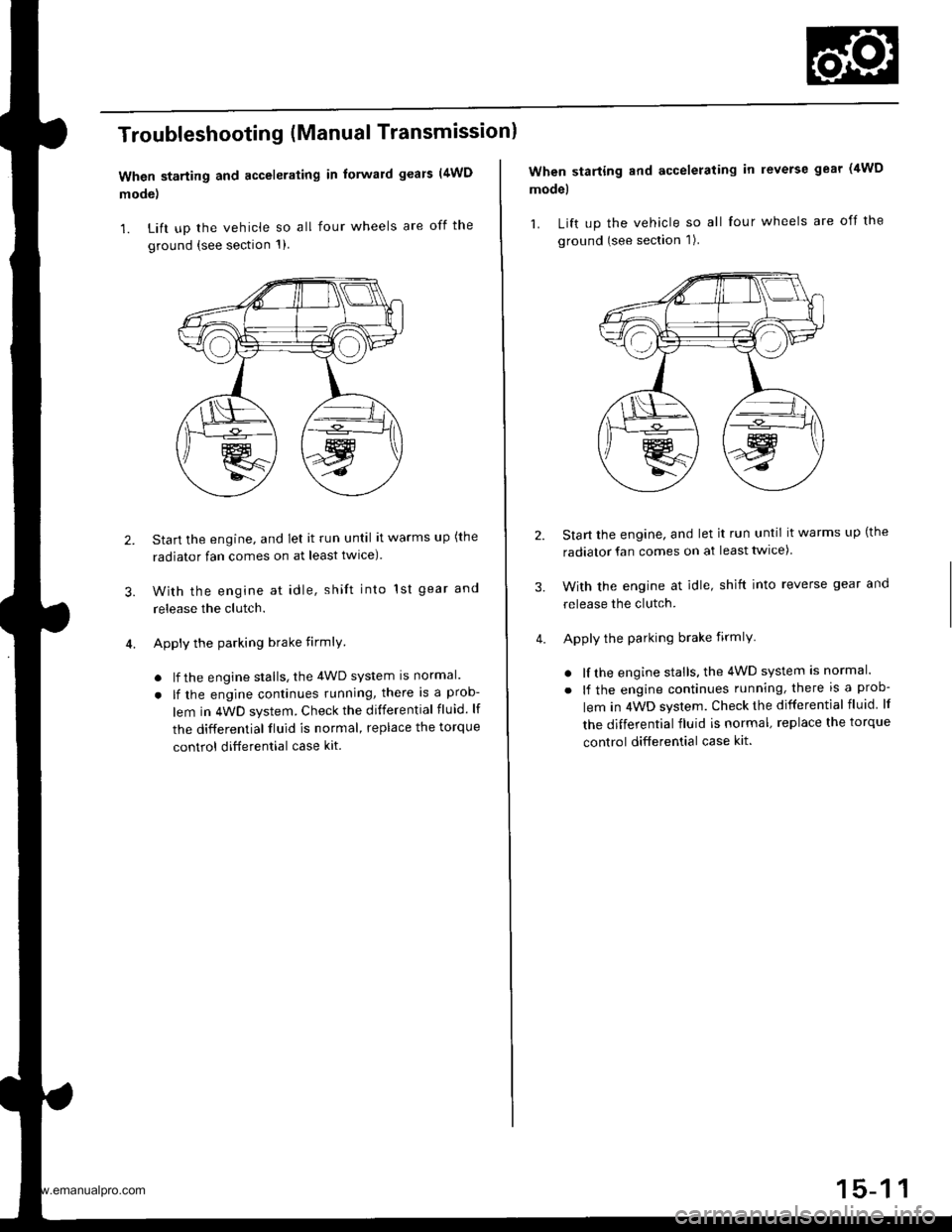
Troubleshooting (Manual Transmissionl
When starting and accelerating in forward gears (4WD
mode)
1. Lift up the vehicle so all four wheels are off the
ground {see section 1)
3.
Start the engine, and let it run until it warms up (the
radiator fan comes on at least twlce).
With the engine at idle, shift into 1st gear and
release the clutch.
Apply the parking brake firmlY
. lf the engine stalls, the 4WD system is normal.
. lf the engine continues running, there is a prob-
lem in 4WD system. Check the differential fluid. lf
the differential fluid is normal, replace the torque
control ditferential case kit.
2.
When starting and accelerating in reverse gear (4WD
model
1. Lift up the vehicle so all four wheels are off the
ground (see section 1).
Start the engine, and let it run until it warms up (the
radiator fan comes on at least twice)
With the engine at idle, shift into reverse gear and
release the clutch.
Apply the parking brake firmlY
. lf the engine stalls, the 4WD system is normal.
. lf the engine continues running, there is a prob-
lem in 4WD system. Check the differential fluid lf
the differential fluid is normal, replace the torque
control differential case kit.
3.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 850 of 1395

Abnormal
Not deformed
Deformed
Faulty cylinder lines
Readjust the rack guide(see page 17-15)
Bent
IFaulty steering gearbox
Compair the steering to anotheralike vehicle.
(cont'd)
17-5
Adjustment OK
Check the force required to turnthe wheel lsee page 17 12).Start the engine and measure theforce required to turn the wheelto the right and left. Difference ofthe force required to turn thewheel to the right and to the leftshould be 2.9 N (0.3 kgf,0.7 lbt)or less,
Normal
www.emanualpro.com
Page 853 of 1395

Troubleshooting
Noise and Vibration
NOTE: Pump noise in first 2 - 3 minutes after starting in cold weather is normal.
Humming
Rattle or chattering
Humming due to pulsation of fluid is normal, particularly when the wheel isturned with the vehicle stooDed.
lf equipped with automatic trans-mission, the hum could be thetorque converter or pump noase.
Confirm by temporarily removingthe pump belt.
Feed hose (high-pressure) touch-ing the frame.Beposition the feed hose.
Loose steering shaft connector,tie-rod, or balljoint.Check and tighten, or replaceparts as necessary,
Column shaft wobbling.Roplace the column assembly.
Check the rack guide for properadjustment (see page 17-15).Adjust, if necessary.
Rattling sound and feeling when turning the steering wheel right and left with th€engine OFF is normal.
Pump noise, though not loud, from the valve body unit can be heard when turn-ing the steering wheel to full lock in either direction. This is normal. Do not holdthe steering wheel at full lock lor more than five seconds when inspecting.
17-8
www.emanualpro.com