2000 DODGE NEON timing
[x] Cancel search: timingPage 5 of 1285

30,000 Miles (48 000 km) or at 24 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Lubricate the front suspension lower ball joint.
²Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
²Replace the engine air cleaner element (fil-
ter).
²Replace the engine spark plugs
²Change the automatic transaxle fluid.
37,500 Miles (60 000 km) or at 30 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
45,000 Miles (72 000 km) or at 36 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace the engine coolant at 36
months, regardless of mileage.
52,500 Miles (84 000 km) or at 42 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Flush and replace the engine coolant if not done
at 36 months.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km) or at 48 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Check the PCV valve and replace, if neces-
sary. Not required if previously changed.*
²Lubricate the front suspension lower ball joints.
²Replace the drive belts.
²Replace the engine air cleaner element (fil-
ter).
²Replace the ignition cables.
²Replace the spark plugs.
²Change the automatic transaxle fluid.
67,500 Miles (108 000 km) or at 54 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km) or at 60 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
82,500 Miles (132 000 km) or at 66 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km) or at 72 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Check the PCV valve and replace, if neces-
sary. Not required if previously changed.*
²Lubricate the front suspension lower ball joints.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
²Replace the engine air cleaner element (fil-
ter).
²Replace the spark plugs.
²Inspect the serpentine drive belt, replace if nec-
essary. This maintenance is not required if the belt
was previously replaced.
²Change the automatic transaxle fluid.
97,500 Miles (156 000 km) or at 78 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km) or at 84 months
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Replace the engine timing belt.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
*This maintenance is recommended by Daimler-
Chrysler Corporation to the owner but is not
required to maintain the emissions warranty.
NOTE: Inspection and service should also be per-
formed anytime a malfunction is observed or sus-
pected. Retain all receipts.
SCHEDULE ± B
3,000 Miles (5 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
6,000 Miles (10 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
9,000 Miles (14 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 7 of 1285

69,000 Miles (110 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
72,000 Miles (115 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
²Inspect theengine air cleaner element (fil-
ter)and replace as necessary.*
²Change the automatic transaxle fluid/filter and
adjust bands.
78,000 Miles (125 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
81,000 Miles (130 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Flush and replace the engine coolant.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
84,000 Miles (134 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
87,000 Miles (139 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
²Inspect front brake pads and rear brake linings
²Check thePCV valveand replace if necessary.
Not required if previously changed.*
²Lubricate the front suspension lower ball joint.
²Replace theengine air cleaner element (fil-
ter).²Replace thespark plugs
²Change the automatic transaxle fluid/filter and
adjust the bands.
93,000 Miles (149 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
96,000 Miles (154 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
99,000 Miles (158 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Inspect the front brake pads and rear brake lin-
ings.
102,000 Miles (163 000 km)
²Change the engine oil.
²Replace the engine oil filter.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Replace theengine timing belt.
²Change the engine oil.
²Adjust the drive belt tension.
²Inspect theengine air cleaner element (fil-
ter)and replace as necessary.*
²Change the automatic transaxle fluid/filter and
adjust the bands.
²Flush and replace the engine coolant.
* This maintenance is recommended by Daimler-
Chrysler Corporation to the owner but is not
required to maintain the emissions warranty.
NOTE: Operating the vehicle more than 50% in
heavy traffic during hot weather, above 90É F (32É
C), using vehicle for police, taxi, limousine type
operation or trailer towing require the more fre-
quent transaxle service noted in Schedule ± B. Per-
form these services if vehicle usually operate under
these conditions.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 184 of 1285
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE WORKING ON VEHI-
CLE. RELIEVE PRESSURE BY PLACING A SHOP
TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITHOUT PUSHING
DOWN ROTATE IT COUNTERCLOCKWISE TO THE
FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS TO ESCAPE
THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND WHEN THE
SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING OUT COOLANT AND
STEAM AND THE PRESSURE DROPS CONTINUE
SERVICE.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN
SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only a original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter (Fig. 6).
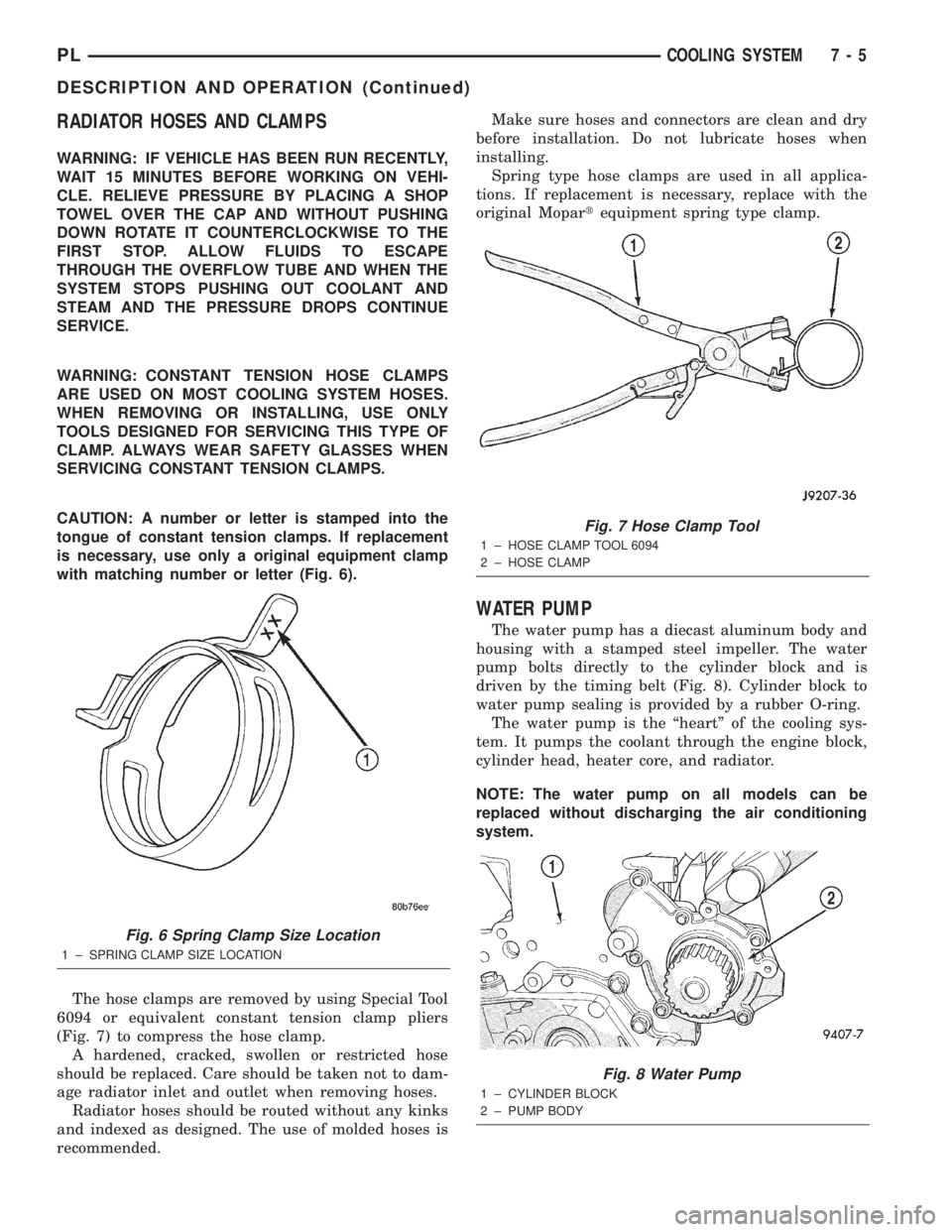
The hose clamps are removed by using Special Tool
6094 or equivalent constant tension clamp pliers
(Fig. 7) to compress the hose clamp.
A hardened, cracked, swollen or restricted hose
should be replaced. Care should be taken not to dam-
age radiator inlet and outlet when removing hoses.
Radiator hoses should be routed without any kinks
and indexed as designed. The use of molded hoses is
recommended.Make sure hoses and connectors are clean and dry
before installation. Do not lubricate hoses when
installing.
Spring type hose clamps are used in all applica-
tions. If replacement is necessary, replace with the
original Mopartequipment spring type clamp.
WATER PUMP
The water pump has a diecast aluminum body and
housing with a stamped steel impeller. The water
pump bolts directly to the cylinder block and is
driven by the timing belt (Fig. 8). Cylinder block to
water pump sealing is provided by a rubber O-ring.
The water pump is the ªheartº of the cooling sys-
tem. It pumps the coolant through the engine block,
cylinder head, heater core, and radiator.
NOTE: The water pump on all models can be
replaced without discharging the air conditioning
system.
Fig. 6 Spring Clamp Size Location
1 ± SPRING CLAMP SIZE LOCATION
Fig. 7 Hose Clamp Tool
1 ± HOSE CLAMP TOOL 6094
2 ± HOSE CLAMP
Fig. 8 Water Pump
1 ± CYLINDER BLOCK
2 ± PUMP BODY
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 198 of 1285

COOLING SYSTEMÐDRAINING
NOTE: Drain, flush, and fill the cooling system at
the mileage or time intervals specified in Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance. If the solution is dirty,
rusty, or contains a considerable amount of sedi-
ment; clean and flush with a reliable cooling system
cleaner. Care should be taken in disposing of the
used engine coolant from your vehicle. Check gov-
ernmental regulations for disposal of used engine
coolant.
Without removing radiator pressure cap and
with system not under pressure:
(1) Shut engine off and turn draincock counter-
clockwise to open (Fig. 18).
(2) The coolant reserve tank should empty first,
then remove the pressure cap. (if not, Refer to Test-
ing Cooling System for leaks).
COOLING SYSTEMÐREFILLING
First clean system to remove old glycol, see Cooling
System Cleaning.
Fill system with 50/50 glycol/water mix. Use anti-
freeze described in Coolant section.
Continue filling system until full, this provides bet-
ter heater performance.Be careful not to spill
coolant on drive belts or the generator.
Fill coolant reserve/recovery system to at least the
FULL HOT mark with 50/50 solution. It may be nec-
essary to add coolant to the reserve/recovery con-
tainer after three or four warm-up/cool down cycles
to maintain coolant level between the FULL HOT
and ADD marks; if any trapped air was removed
from the system.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
WATER PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Remove right inner
splash shield.
(2) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(3) Drain cooling system. Refer to Cooling System
Draining in this section.
(4) Remove power steering pump attaching bolts
and set pump and assembly aside. Power steering
lines do not need to be disconnected.
(5) Remove upper and lower torque isolator struts.
(6) Support engine from the bottom and remove
right engine mount attaching bolt.
(7) Remove right engine mount bracket.
(8) Remove timing belt and timing belt tensioner.
Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedures.
(9) Remove camshaft sprocket and rear timing belt
cover. Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedures.
(10) Remove water pump attaching screws to
engine and remove pump (Fig. 19).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply MopartDielectric Grease to O-ring
before installation.
(2) Install new O-ring gasket in water pump body
O-ring groove (Fig. 20).
CAUTION: Make sure O-ring gasket is properly
seated in water pump groove before tightening
screws. An improperly located O-ring may cause
damage to the O-ring, resulting in a coolant leak.
(3) Assemble pump body to block and tighten
screws to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.). Pressurize cooling
system to 15 psi with pressure tester and check
water pump shaft seal and O-ring for leaks.
Fig. 18 Cooling System Drain Cock Location
1 ± DRAIN COCKFig. 19 Water Pump
1 ± CYLINDER BLOCK
2 ± PUMP BODY
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 19
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 199 of 1285

(4) Rotate pump by hand to check for freedom of
movement.
(5) Install rear timing belt cover and camshaft
sprocket.
(6) Install timing belt tensioner and timing belt.
Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(7) Install right engine mount bracket. Refer to
Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(8) Install upper and lower torque isolator struts.
Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(9) Fill cooling system. Refer to procedures in this
section.
(10) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(11) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
The inlet tube connects the water pump to the
radiator and heater core. This tube is sealed by an
O-ring and held in place by fasteners to the block.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Do not use any sharp tools to remove
hoses from inlet tube. This may cause the tube to
leak.
(1) Drain cooling system. Refer to procedure in
this section.
(2) Remove upper radiator hose to access the hose
connections at the inlet tube.(3) Remove intake manifold. Refer to Group 9,
Engine for procedure.
(4) Remove lower radiator hose and heater hose
from the inlet tube.
(5) Remove lower intake manifold support bracket.
(6) Remove the inlet tube to the block fasteners.
(7) Rotate tube while removing the tube from the
engine block (Fig. 21).
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect the O-ring for damage before installing
the tube into the cylinder block (Fig. 21). Replace
O-ring as necessary.
(2) Lubricate O-ring with MopartDielectric
Grease and install inlet tube into the cylinder block
opening.
(3) Install inlet tube fasteners and tighten fasten-
ers to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Install intake manifold lower support bracket
fasteners and tighten to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(5) Connect lower radiator hose and heater hose to
inlet tube.
(6) Install intake manifold. Refer to Group 9,
Engine for procedure.
(7) Install upper radiator hose.
(8) Fill cooling system. Refer to procedure in this
section.
(9) Pressure system to 104 kPa (15 psi) to check
for leaks.
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system to the thermostat level or
below.
(2) Remove coolant recovery/reserve system hose
and upper radiator hose.
Fig. 20 Water Pump Body
1 ± IMPELLER
2 ± PUMP BODY
3 ± O-RING
Fig. 21 Water Pump Inlet Tube
1 ± O-RING
2 ± WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
FRONT
7 - 20 COOLING SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 236 of 1285

IGNITION SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
IGNITION SYSTEM........................1
SPARK PLUGS...........................1
SPARK PLUG CABLES.....................1
ELECTRONIC IGNITION COILS...............2
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY.............2
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM
INPUT................................3
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM
INPUT................................4
KNOCK SENSOR..........................5
IGNITION SWITCH........................5
LOCK KEY CYLINDER......................5
IGNITION INTERLOCK.....................6
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SPARK PLUG SERVICE....................6SPARK PLUG CABLE SERVICE..............6
IGNITION COIL...........................6
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY.............6
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR..............6
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR............8
KNOCK SENSOR..........................8
IGNITION SWITCH........................8
LOCK KEY CYLINDER......................9
IGNITION INTERLOCK....................10
SPECIFICATIONS
VECI LABEL............................10
FIRING ORDERÐ2.0L....................10
TORQUE SPECIFICATION..................11
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCEÐSOHC....11
SPARK PLUG...........................11
IGNITION COIL..........................11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
IGNITION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The system's three main components are the coil
pack, crankshaft position sensor, and camshaft posi-
tion sensor.
OPERATION
Basic ignition timing is not adjustable.The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) determines spark
advance. The 2.0L engines use a fixed ignition timing
system. The distributorless electronic ignition system
is referred to as the Direct Ignition System (DIS).
SPARK PLUGS
The 2.0L engines uses resistor spark plugs. For
spark plug identification and specifications, Refer to
the Specifications section at the end of this group.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso-
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective. Refer to the
Spark Plug Condition section of this group. Aftercleaning, file the center electrode flat with a small
point file or jewelers file. Adjust the gap between the
electrodes (Fig. 1) to the dimensions specified in the
chart at the end of this section by bending the
ground electrode (just above the attachment weld)
with the appropriate tool.
Never apply any force between the electrode or
damage to the center electrode assembly will result.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion and damage.
Tighten spark plugs to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
SPARK PLUG CABLES
Spark plug cables are sometimes referred to as sec-
ondary ignition wires. The wires transfer electrical
current from the coil pack to individual spark plugs
at each cylinder. The resistor type, nonmetallic spark
plug cables provide suppression of radio frequency
emissions from the ignition system.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil and spark plugs. Terminals should
be fully seated. The nipples and spark plug covers
should be in good condition. Nipples should fit tightly
on the coil. Spark plug boot should completely cover
the spark plug hole in the cylinder head cover. Install
the boot until the terminal snaps over the spark
plug. A snap must be felt to ensure the spark plug
cable terminal engaged the spark plug.
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 1
Page 238 of 1285

OPERATION
The Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to the fuel injectors, electronic ignition
coil and the heating elements in the oxygen sensors.
A buss bar in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
supplies voltage to the solenoid side and contact side
of the relay. The fuse also protects the power circuit
for the fuel pump relay and pump. The fuse is
located in the PDC. Refer to the Wiring Diagrams for
circuit information.
The PCM controls the ASD relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position. When the igni-
tion switch is in On or Start, the PCM monitors the
crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals to
determine engine speed and ignition timing (coil
dwell). If the PCM does not receive crankshaft and
camshaft position sensor signals when the ignition
switch is in the Run position, it will de-energize the
ASD relay.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the generator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 4).
The PCM uses the Crankshaft Position sensor to
calculate the following:
²Engine RPM²TDC number 1 and 4
²Ignition coil synchronization
²Injector synchronization
²Camshaft-to-crankshaft misalignment (Timing
belt skipped 1 tooth or more diagnostic trouble code).
OPERATION
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is a Hall-ef-
fect sensor. The second crankshaft counterweight has
two sets of four timing reference notches including a
60 degree signature notch (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 Timing Reference Notches
1 ± MACHINED NOTCHES
2 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 4 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 ± OIL FILTER
3 ± GENERATOR
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 239 of 1285

The PCM sends approximately 8 volts to the Hall-
effect sensor. This voltage is required to operate the
Hall-effect chip and the electronics inside the sensor.
A ground for the sensor is provided through the sen-
sor return circuit. The input to the PCM occurs on a
5 volt output reference circuit.
The notches generate pulses from high to low in
the crankshaft position sensor output voltage. When
a metal portion of the counterweight aligns with the
crankshaft position sensor, the sensor output voltage
goes low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns
with the sensor, voltage goes high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the output
voltage switches from low (metal) to high (notch)
then back to low.
If available, an oscilloscope can display the square
wave patterns of each voltage pulses. From the width
of the output voltage pulses, the PCM calculates
engine speed. The width of the pulses represent the
amount of time the output voltage stays high before
switching back to low. The period of time the sensor
output voltage stays high before switching back to
low is referred to as pulse width. The faster the
engine is operating, the smaller the pulse width on
the oscilloscope.
By counting the pulses and referencing the pulse
from the 60 degree signature notch, the PCM calcu-
lates crankshaft angle (position). In each group of
timing reference notches, the first notch represents
69 degrees before top dead center (BTDC). The sec-
ond notch represents 49 degrees BTDC. The third
notch represents 29 degrees. The last notch in each
set represents 9 degrees before top dead center
(TDC).
The timing reference notches are machined at 20É
increments. From the voltage pulse width the PCM
tells the difference between the timing reference
notches and the 60 degree signature notch. The 60
degree signature notch produces a longer pulse width
than the smaller timing reference notches. If the
camshaft position sensor input switches from high to
low when the 60 degree signature notch passes under
the crankshaft position sensor, the PCM knows cylin-
der number one is the next cylinder at TDC.CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The camshaft position sensor attaches to the rear
of the cylinder head. The PCM determines fuel injec-
tion synchronization and cylinder identification from
inputs provided by the camshaft position sensor (Fig.
6) and crankshaft position sensor. From the two
inputs, the PCM determines crankshaft position.
OPERATION
The PCM sends approximately 8 volts to the hall
affect sensor. This voltage is required to operate the
hall effect chip and the electronics inside the sensor.
A ground for the sensor is provided through the sen-
sor return circuit. The input to the PCM occurs on a
5 volt output reference circuit.
A target magnet attaches to the rear of the cam-
shaft and indexes to the correct position. The target
magnet has four different poles arranged in an asym-
metrical pattern (Fig. 7). As the target magnet
rotates, the camshaft position sensor senses the
change in polarity (Fig. 8). The sensor output switch
switches from high (5.0 volts) to low (0.5 volts) as the
target magnet rotates. When the north pole of the
target magnet passes under the sensor, the output
switches high. The sensor output switches low when
the south pole of the target magnet passes under-
neath.
The sensor also acts as a thrust plate to control
camshaft endplay.
Fig. 6 Camshaft Position SensorÐSOHC
8D - 4 IGNITION SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)