1999 SUBARU LEGACY checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 117 of 1456
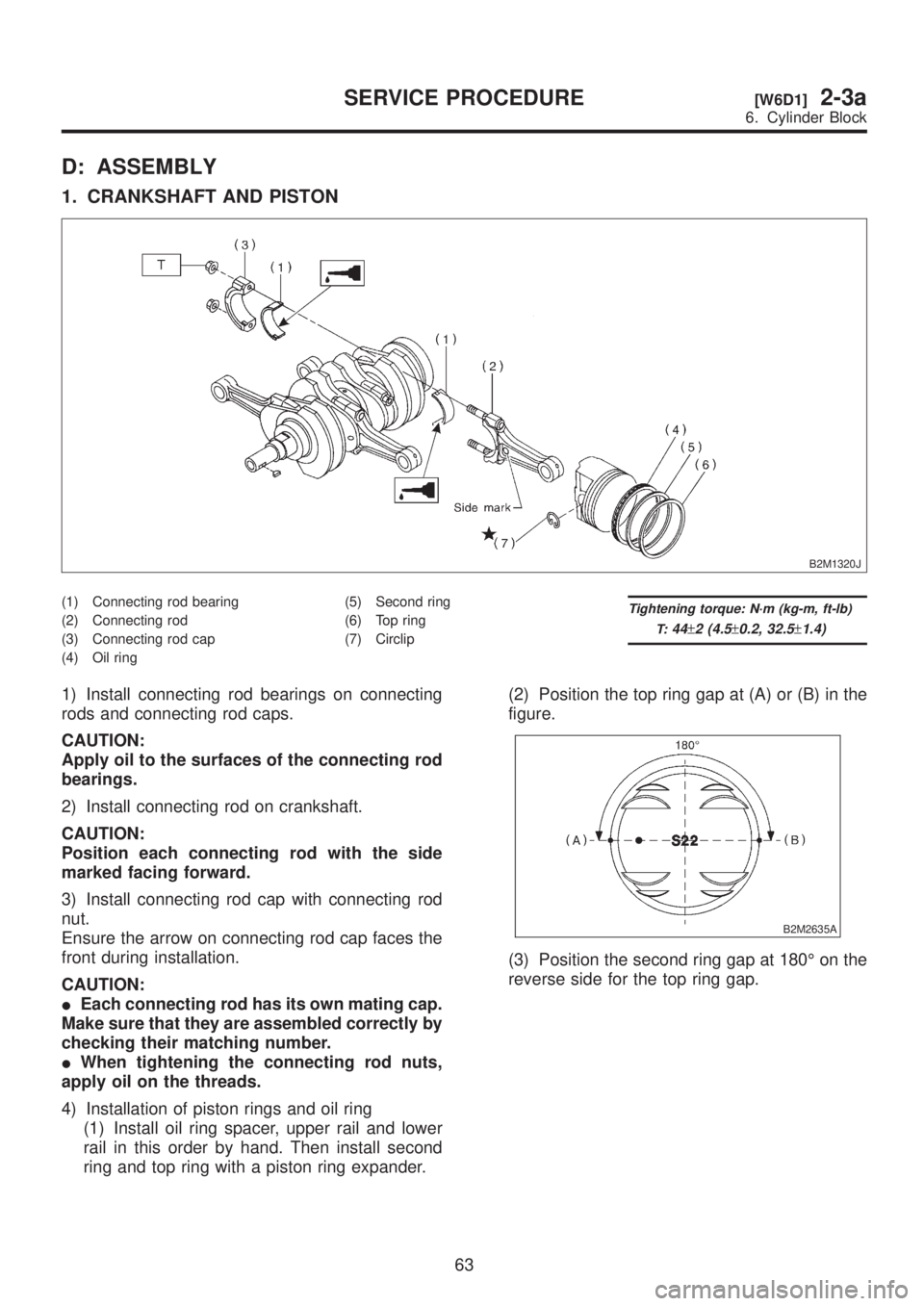
D: ASSEMBLY
1. CRANKSHAFT AND PISTON
B2M1320J
(1) Connecting rod bearing
(2) Connecting rod
(3) Connecting rod cap
(4) Oil ring(5) Second ring
(6) Top ring
(7) CirclipTightening torque: N´m (kg-m, ft-lb)
T:
44±2 (4.5±0.2, 32.5±1.4)
1) Install connecting rod bearings on connecting
rods and connecting rod caps.
CAUTION:
Apply oil to the surfaces of the connecting rod
bearings.
2) Install connecting rod on crankshaft.
CAUTION:
Position each connecting rod with the side
marked facing forward.
3) Install connecting rod cap with connecting rod
nut.
Ensure the arrow on connecting rod cap faces the
front during installation.
CAUTION:
IEach connecting rod has its own mating cap.
Make sure that they are assembled correctly by
checking their matching number.
IWhen tightening the connecting rod nuts,
apply oil on the threads.
4) Installation of piston rings and oil ring
(1) Install oil ring spacer, upper rail and lower
rail in this order by hand. Then install second
ring and top ring with a piston ring expander.(2) Position the top ring gap at (A) or (B) in the
figure.
B2M2635A
(3) Position the second ring gap at 180É on the
reverse side for the top ring gap.
63
[W6D1]2-3aSERVICE PROCEDURE
6. Cylinder Block
Page 193 of 1456

D: ASSEMBLY
1. CRANKSHAFT AND PISTON
B2M1320J
(1) Connecting rod bearing
(2) Connecting rod
(3) Connecting rod cap
(4) Oil ring(5) Second ring
(6) Top ring
(7) CirclipTightening torque: N´m (kg-m, ft-lb)
T:
44±2 (4.5±0.2, 32.5±1.4)
1) Install connecting rod bearings on connecting
rods and connecting rod caps.
CAUTION:
Apply oil to the surfaces of the connecting rod
bearings.
2) Install connecting rod on crankshaft.
CAUTION:
Position each connecting rod with the side
marked facing forward.
3) Install connecting rod cap with connecting rod
nut.
Ensure the arrow on connecting rod cap faces the
front during installation.
CAUTION:
IEach connecting rod has its own mating cap.
Make sure that they are assembled correctly by
checking their matching number.
IWhen tightening the connecting rod nuts,
apply oil on the threads.
4) Installation of piston rings and oil ring
(1) Install oil ring spacer, upper rail and lower
rail in this order by hand. Then install second
ring and top ring with a piston ring expander.(2) Position the top ring gap at (A) or (B) in the
figure.
B2M1223B
(3) Position the second ring gap at 180É on the
reverse side for the top ring gap.
62
2-3b[W5D1]SERVICE PROCEDURE
5. Cylinder Block
Page 489 of 1456

CAUTION:
Replace straight pin with a new one.
NOTE:
ISet other rods to neutral.
IMake sure interlock plunger (5.56´19.6) is on
the 3-4 fork rod side.
9) Install interlock plunger (3´11.9) onto 3-4 fork
rod.
CAUTION:
Apply a coat of grease to plunger to prevent it
from falling.
10) Install 3-4 fork rod into 3-4 shifter fork via the
hole on the rear of transmission case.
11) Align the holes in rod and fork, and drive
straight pin (6´22) into these holes.
ST 398791700 STRAIGHT PIN REMOVER
CAUTION:
Replace straight pin with a new one.
NOTE:
ISet reverse fork rod to neutral.
IMake sure interlock plunger (installed before) is
on the reverse fork rod side.
12) Install 5th shifter fork onto the rear of reverse
fork rod. Align holes in the two parts and drive
straight pin into place.
CAUTION:
Replace straight pin with a new one.
ST 398791700 STRAIGHT PIN REMOVER
B3M0333J
(A) 5th shifter fork
(B) Reverse fork rod
(C) Straight pin
13) Position balls, checking ball springs and gas-
kets into 3-4 and 1-2 rod holes, and install plugs.
CAUTION:
Replace gasket with a new one.
G3M0552
14) Install washer and speedometer shaft, and
press fit oil seal with ST.
CAUTION:
Use new oil seal, if it has been removed.
ST 899824100 or 499827000 PRESS
15) Install vehicle speed sensor 2.
CAUTION:
Use new vehicle speed sensor 2, if it has been
removed.
Tightening torque:
5.9
±1.5 N´m (60±15 kg-cm, 52±13 in-lb)
16) Install speedometer driven gear and snap
ring.
CAUTION:
Use a new snap ring, if it has been removed.
B3M0527C
(A) Speedometer driven gear
(B) Snap ring
21
[W2B1]3-1SERVICE PROCEDURE
2. Transmission Case
Page 524 of 1456

1. Manual Transmission
Symptom Possible cause Remedy
1. Gears are difficult to intermesh.
NOTE:
The cause for difficulty in shifting gears
can be classified into two kinds: one is
malfunction of the gear shift system and
the other is malfunction of the transmis-
sion. However, if the operation is heavy
and engagement of the gears is difficult,
defective clutch disengagement may
also be responsible. Check whether the
clutch is correctly functioning, before
checking the gear shift system and
transmission.(a) Worn, damaged or burred chamfer of
internal spline of sleeve and reverse
driven gearReplace.
(b) Worn, damaged or burred chamfer of
spline of gearsReplace.
(c) Worn or scratched bushings Replace.
(d) Incorrect contact between synchro-
nizer ring and gear cone or wearCorrect or replace.
2. Gear slips out.
IGear slips out when coasting on
rough road.
IGear slips out during acceleration.(a) Defective pitching stopper adjustment Adjust
(b) Loose engine mounting bolts Tighten or replace.
(c) Worn fork shifter, broken shifter fork
rail springReplace.
(d) Worn or damaged ball bearing Replace.
(e) Excessive clearance between splines
of synchronizer hub and synchronizer
sleeveReplace.
(f) Worn tooth step of synchronizer hub
(responsible for slip- out of 3rd gear)Replace.
(g) Worn 1st driven gear, needle bearing
and raceReplace.
(h) Worn 2nd driven gear, needle bear-
ing and raceReplace.
(i) Worn 3rd drive gear and bushing Replace.
(j) Worn 4th drive gear and bushing Replace.
(k) Worn reverse idler gear and bushing Replace.
3. Unusual noise comes from transmis-
sion.
NOTE:
If an unusual noise is heard when the
vehicle is parked with its engine idling
and if the noise ceases when the clutch
is disengaged, it may be considered that
the noise comes from the transmission.(a) Insufficient or improper lubrication Lubricate or replace with specified oil.
(b) Worn or damaged gears and bear-
ings
NOTE:
If the trouble is only wear of the tooth
surfaces, merely a high roaring noise will
occur at high speeds, but if any part is
broken, rhythmical knocking sound will
be heard even at low speeds.Replace.
52
3-1[K100]DIAGNOSTICS
1. Manual Transmission
Page 552 of 1456

1. General
A: PRECAUTION
When disassembling or assembling the automatic
transmission, observe the following instructions.
1) Workshop
Provide a place that is clean and free from dust.
Principally the conventional workshop is suitable
except for a dusty place. In a workshop where
grinding work, etc. which produces fine particles is
done, make independent place divided by the vinyl
curtain or the equivalent.
2) Work table
The size of 1 x 1.5 m (40 x 60 in) is large enough
to work, and it is more desirable that its surface be
covered with flat plate like iron plate which is not
rusted too much.
3) Cleaning of exterior
(1) Clean the exterior surface of transmission
with steam and/or kerosene prior to
disassembly, however it should be noted that
vinyl tape be placed on the air breather or oil
level gauge to prevent infiltration of the steam
into the transmission and also the cleaning job
be done away from the place of disassembly
and assembly.
(2) Partial cleaning will do, depending on the
extent of disassembly (such as when disassem-
bly is limited to some certain parts).
4) Disassembly, assembly and cleaning
(1) Disassemble and assemble the transmis-
sion while inspecting the parts in accordance
with the Diagnostics.
(2) During job, do not use gloves. Do not clean
the parts with rags: Use chamois or nylon cloth.
(3) Pay special attention to the air to be used
for cleaning. Get the moisture and the dust rid
of the air as much as possible. Be careful not to
scratch or dent any part while checking for
proper operation with an air gun.
(4) Complete the job from cleaning to comple-
tion of assembly as continuously and speedily
as possible in order to avoid occurrence of sec-
ondary troubles caused by dust. When stopping
the job unavoidably cover the parts with clean
chamois or nylon cloth to keep them away from
any dust.
(5) Use kerosene, white gasoline or the equiva-
lent as washing fluid. Use always new fluid for
cleaning the automatic transmission parts and
never reuse. The used fluid is usable in disas-
semble and assemble work of engine and
manual transmission.
(6) Although the cleaning should be done by
dipping into the washing fluid or blowing of the
pressurized washing fluid, the dipping is more
desirable. (Do not rub with a brush.) Assemblethe parts immediately after the cleaning without
exposure to the air for a while. Besides in case
of washing rubber parts, perform the job quickly
not to dip them into the washing fluid for long
time.
(7) Apply the automatic transmission fluid
(ATF) onto the parts immediately prior to
assembly, and the specified tightening torque
should be observed carefully.
(8) Use vaseline if it is necessary to hold parts
in the position when assembling.
(9) Drain ATF and differential gear oil into a
saucer so that the conditions of fluid and oil can
be inspected.
(10) Do not support axle drive shaft, stator
shaft, input shaft or various pipes when moving
transmission from one place to another.
(11) Always discard old oil seals and O-ring,
and install new ones.
(12) Always discard old oil seals and O-ring,
and install new ones.
(13) Be sure to replace parts which are
damaged, worn, scratched, discolored, etc.
B: INSPECTION
1. ATF LEVEL
1) Raise ATF temperature to 60 to 80ÉC (140 to
176ÉF) from 40 to 60ÉC (104 to 140ÉF) (when cold)
by driving a distance of 5 to 10 km (3 to 6 miles).
NOTE:
The level of ATF varies with fluid temperature. Pay
attention to the fluid temperature when checking oil
level.
B3M1020A
2) Make sure the vehicle is level. After selecting all
positions (P, R, N, D, 3, 2, 1), set the selector lev-
eler in ªPº range. Measure fluid level with the
engine idling.
NOTE:
After running, idle the engine for one or two min-
utes before measurement.
3) If the fluid level is below the center between
upper and lower marks, add the recommended
ATF until the fluid level is found within the specified
27
[W1B1]3-2SERVICE PROCEDURE
1. General
Page 553 of 1456

range (above the center between upper and lower
marks). When the transmission is hot, the level
should be above the center of upper and lower
marks, and when it is cold, the level should be
found below the center of these two marks.
CAUTION:
IUse care not to exceed the upper limit level.
IATF level varies with temperature. Remem-
ber that the addition of fluid to the upper limit
mark when the transmission is cold will result
in the overfilling of fluid.
4) Fluid temperature rising speed
IBy idling the engine
Time for temperature rise to 60ÉC (140ÉF) with
atmospheric temperature of 0ÉC (32ÉF): More than
25 minutes
Time for temperature rise to 30ÉC (86ÉF) with
atmospheric temperature of 0ÉC (32ÉF): Approx. 8
minutes
IBy running the vehicle
Time for temperature rise to 60ÉC (140ÉF) with
atmospheric temperature of 0ÉC (32ÉF): More than
10 minutes
5) Method for checking fluid level upon delivery or
at periodic inspection
Check fluid level after a warm-up run of approx. 10
minutes. During the warm-up period, the automatic
transmission functions can also be checked.
2. DIFFERENTIAL GEAR OIL LEVEL
1) Ensure the vehicle is in safe condition.
NOTE:
Do not check the oil level nor add oil to the case
with the front end of the vehicle jacked-up; this will
result in an incorrect reading of the oil level.
2) Check whether the oil level is between the
upper (F) and lower (L) marks. If it is below the
lower limit mark, add oil until the level reaches the
upper mark.
G3M0283
3. OIL LEAKAGE
It is difficult to accurately determine the precise
position of a oil leak, since the surrounding area
also becomes wet with oil. The places where oil
seals and gaskets are used are as follows:
1) Jointing portion of the case
ITransmission case and oil pump housing joint-
ing portion
ITorque converter clutch case and oil pump
housing jointing portion
ITransmission case and extension case jointing
portion
B3M1021
2) Torque converter clutch case
IEngine crankshaft oil seal
ITorque converter clutch impeller sleeve oil seal
IATF cooler pipe connector
ITorque converter clutch
ITorque converter clutch case
IAxle shaft oil seal
IO-ring on the outside diameter of axle shaft oil
seal holder
IO-ring on the differential oil gauge
IDifferential oil drain plug
ILocation of steel balls
B3M1022
28
3-2[W1B2]SERVICE PROCEDURE
1. General
Page 571 of 1456

8. Time Lag Test
A: INSPECTION
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
If the shift lever is shifted while the engine is idling,
there will be a certain time elapse or lag before the
shock can be felt. This is used for checking the
condition of the low clutch, reverse clutch, low &
reverse brake and one-way clutch.
CAUTION:
IPerform the test at normal operation fluid
temperature 60 to 80ÉC (140 to 176ÉF).
IBe sure to allow a one minute interval
between tests.
IMake three measurements and take the aver-
age value.
2. TEST METHODS
1) Fully apply the parking brake.
2) Start the engine.
Check idling speed (A/C OFF).
ªNº range: 800±100 rpm
3) Shift the shift lever from ªNº to ªDº range.
Using a stop watch, measure the time it takes from
shifting the lever until the shock is felt.
Time lag: Less than 1.2 seconds
4) In same manner, measure the time lag for ªNº
®ªRº.
Time lag: Less than 1.5 seconds
3. EVALUATION
1) If ªNº®ªDº time lag is longer than specified:
ILine pressure too low
ILow clutch worn
IOne-way clutch not operating properly
2) If ªNº®ªRº time lag is longer than specified:
ILine pressure too low
IReverse clutch worn
ILow & reverse brake worn
9. Line Pressure Test
A: MEASUREMENT
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
If the clutch or the brake shows a sign of slippage
or shifting sensation is not correct, the line pres-
sure should be checked.
IExcessive shocks during upshifting or shifting
takes place at a higher point than under normal
circumstances, may be due to the line pressure
being too high.
ISlippage or inability to operate the vehicle may,
in most cases, be due to loss of oil pressure for the
operation of the clutch, brake or control valve.
1) Line pressure measurement (under no load)
CAUTION:
IBefore measuring line pressure, jack-up all
wheels.
IMaintain temperature of ATF at approxi-
mately 50ÉC (122ÉF) during measurement.
(ATF will reach the above temperature after
idling the engine for approximately 30 minutes
with select lever in ªNº or ªPº.)
2) Line pressure measurement (under heavy load)
CAUTION:
IBefore measuring line pressure, apply both
foot and parking brakes with all wheels
chocked (Same as for ªstallº test conditions).
IMeasure line pressure when select lever is in
ªRº, ª2º with engine under stall conditions.
IMeasure line pressure within 5 seconds after
shifting the select lever to each position. (If line
pressure needs to be measured again, allow
the engine to idle and then stop. Wait for at
least one minute before measurement.)
IMaintain the temperature of ATF at approxi-
mately 50ÉC (122ÉF) during measurement. (ATF
will reach the above temperature after idling
the engine for approximately 30 minutes with
the select lever in ªNº or ªPº.)
43
[W9A1]3-2SERVICE PROCEDURE
9. Line Pressure Test
Page 572 of 1456

8. Time Lag Test
A: INSPECTION
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
If the shift lever is shifted while the engine is idling,
there will be a certain time elapse or lag before the
shock can be felt. This is used for checking the
condition of the low clutch, reverse clutch, low &
reverse brake and one-way clutch.
CAUTION:
IPerform the test at normal operation fluid
temperature 60 to 80ÉC (140 to 176ÉF).
IBe sure to allow a one minute interval
between tests.
IMake three measurements and take the aver-
age value.
2. TEST METHODS
1) Fully apply the parking brake.
2) Start the engine.
Check idling speed (A/C OFF).
ªNº range: 800±100 rpm
3) Shift the shift lever from ªNº to ªDº range.
Using a stop watch, measure the time it takes from
shifting the lever until the shock is felt.
Time lag: Less than 1.2 seconds
4) In same manner, measure the time lag for ªNº
®ªRº.
Time lag: Less than 1.5 seconds
3. EVALUATION
1) If ªNº®ªDº time lag is longer than specified:
ILine pressure too low
ILow clutch worn
IOne-way clutch not operating properly
2) If ªNº®ªRº time lag is longer than specified:
ILine pressure too low
IReverse clutch worn
ILow & reverse brake worn
9. Line Pressure Test
A: MEASUREMENT
1. GENERAL INFORMATION
If the clutch or the brake shows a sign of slippage
or shifting sensation is not correct, the line pres-
sure should be checked.
IExcessive shocks during upshifting or shifting
takes place at a higher point than under normal
circumstances, may be due to the line pressure
being too high.
ISlippage or inability to operate the vehicle may,
in most cases, be due to loss of oil pressure for the
operation of the clutch, brake or control valve.
1) Line pressure measurement (under no load)
CAUTION:
IBefore measuring line pressure, jack-up all
wheels.
IMaintain temperature of ATF at approxi-
mately 50ÉC (122ÉF) during measurement.
(ATF will reach the above temperature after
idling the engine for approximately 30 minutes
with select lever in ªNº or ªPº.)
2) Line pressure measurement (under heavy load)
CAUTION:
IBefore measuring line pressure, apply both
foot and parking brakes with all wheels
chocked (Same as for ªstallº test conditions).
IMeasure line pressure when select lever is in
ªRº, ª2º with engine under stall conditions.
IMeasure line pressure within 5 seconds after
shifting the select lever to each position. (If line
pressure needs to be measured again, allow
the engine to idle and then stop. Wait for at
least one minute before measurement.)
IMaintain the temperature of ATF at approxi-
mately 50ÉC (122ÉF) during measurement. (ATF
will reach the above temperature after idling
the engine for approximately 30 minutes with
the select lever in ªNº or ªPº.)
43
[W9A1]3-2SERVICE PROCEDURE
9. Line Pressure Test