1999 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 294 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
REPAIRS 17-2-61
Air Manifold - RH - Secondary Air
Injection (SAI)
$% 17.25.18
Remove
1.Remove SAI control valve.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8,
REPAIRS, Control Valve - Secondary Air
Injection (SAI).
2.Remove heater feed pipe.
+ HEATING AND VENTILATION,
REPAIRS, Pipe - Heater - Feed.
3.Disconnect 2 air manifold unions from adapters
in cylinder head.
CAUTION: Take care that air manifold pipes
are not damaged during removal of union
nuts.
4.Remove nut securing air manifold bracket to
inlet manifold.
5.Remove air manifold.Refit
1.Clean air manifold and cylinder head adaptors.
2.Apply a small amount of engine oil to top of air
manifold union nuts and around air manifold
pipes.
3.Position air manifold and finger tighten both
union nuts.
CAUTION: Finger tighten union nuts as far
as possible, damage to air manifold pipes or
adapters may result if this is not done.
4.Tighten air manifold unions to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
CAUTION: Ensure that air manifold pipes
are not distorted during tightening
operation.
5.Fit nut securing air manifold to inlet manifold
and tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
6.Fit heater feed pipe.
+ HEATING AND VENTILATION,
REPAIRS, Pipe - Heater - Feed.
7.Fit SAI control valve.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8,
REPAIRS, Control Valve - Secondary Air
Injection (SAI).
M17 0223
43
3
5
Page 296 of 1529

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
REPAIRS 17-2-63
8.Remove 2 nuts securing air injection pipe to air
intake plenum.
9.Release pipe from clip on rear of air intake
plenum.
10.Release 3 clips securing harness to engine bay
bulkhead.
11.Position container to collect any coolant
spillage.
12.Release clips securing heater hoses to heater.
13.Release hoses from heater.
14.With assistance, manoeuvre air injection pipe
from engine bay.Refit
1.With assistance, manoeuvre air injection pipe
into engine bay and secure onto clip at rear of
air intake plenum.
2.Connect heater hoses to heater and secure
with clips.
3.Reposition harness along engine bay bulkhead
and secure with clips.
4.Fit and tighten nuts securing air injection pipe to
air intake plenum.
5.Connect multiplug to SAI vacuum solenoid.
6.Connect air pump hose to air injection pipe and
secure with clip.
7.Connect LH and RH SAI control valve hoses to
air injection pipe and secure with clips.
8.Remove container.
9.Top up engine coolant.
+ MAINTENANCE, PROCEDURES,
Cooling system.
M17 0231
M17 0232
M17 0233
Page 308 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-9
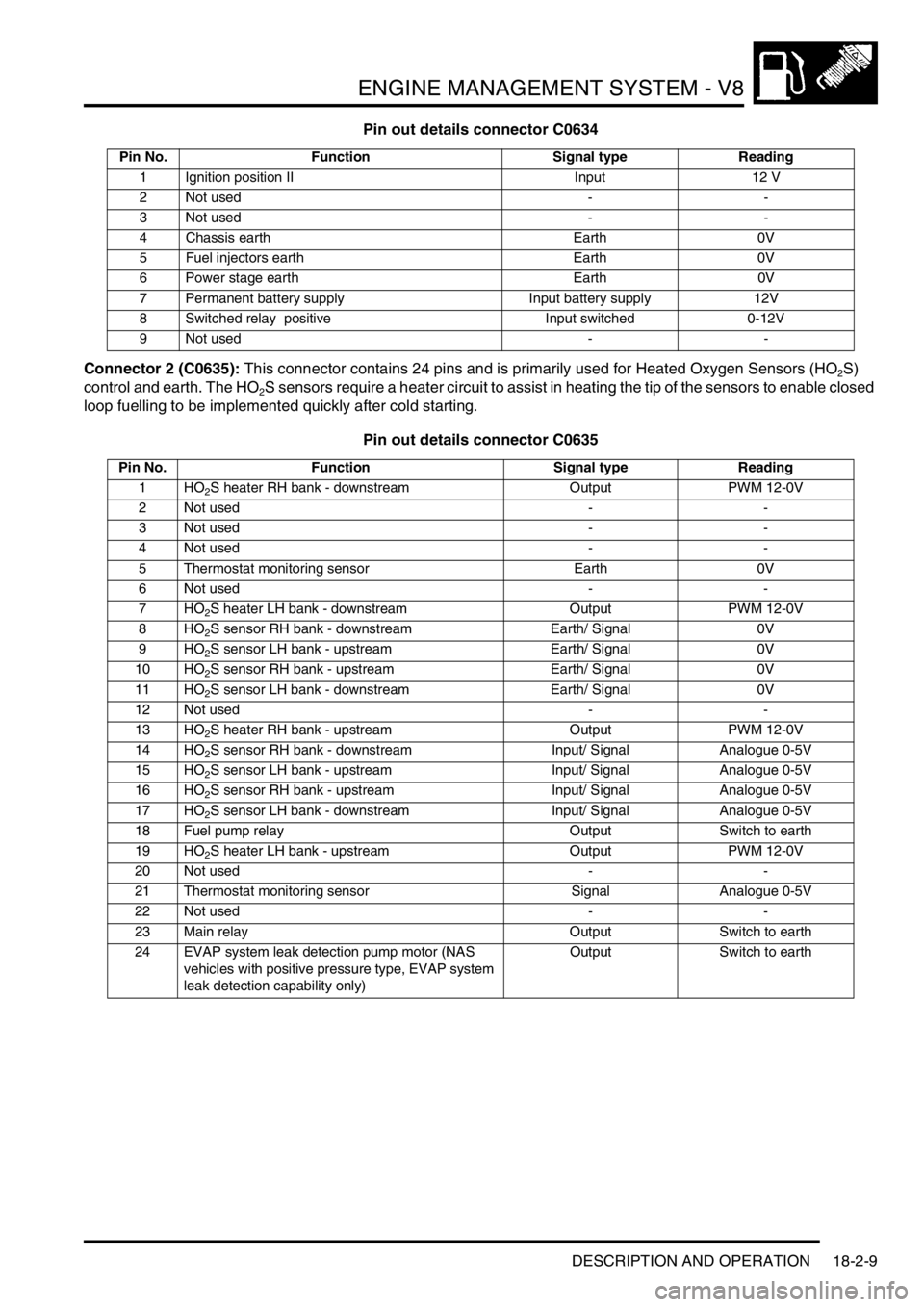
Pin out details connector C0634
Connector 2 (C0635): This connector contains 24 pins and is primarily used for Heated Oxygen Sensors (HO
2S)
control and earth. The HO
2S sensors require a heater circuit to assist in heating the tip of the sensors to enable closed
loop fuelling to be implemented quickly after cold starting.
Pin out details connector C0635
Pin No. Function Signal type Reading
1 Ignition position II Input 12 V
2 Not used - -
3 Not used - -
4 Chassis earth Earth 0V
5 Fuel injectors earth Earth 0V
6 Power stage earth Earth 0V
7 Permanent battery supply Input battery supply 12V
8 Switched relay positive Input switched 0-12V
9 Not used - -
Pin No. Function Signal type Reading
1HO
2S heater RH bank - downstream Output PWM 12-0V
2 Not used - -
3 Not used - -
4 Not used - -
5 Thermostat monitoring sensor Earth 0V
6 Not used - -
7HO
2S heater LH bank - downstream Output PWM 12-0V
8HO
2S sensor RH bank - downstream Earth/ Signal 0V
9HO
2S sensor LH bank - upstream Earth/ Signal 0V
10 HO
2S sensor RH bank - upstream Earth/ Signal 0V
11 HO
2S sensor LH bank - downstream Earth/ Signal 0V
12 Not used - -
13 HO
2S heater RH bank - upstream Output PWM 12-0V
14 HO
2S sensor RH bank - downstream Input/ Signal Analogue 0-5V
15 HO
2S sensor LH bank - upstream Input/ Signal Analogue 0-5V
16 HO
2S sensor RH bank - upstream Input/ Signal Analogue 0-5V
17 HO
2S sensor LH bank - downstream Input/ Signal Analogue 0-5V
18 Fuel pump relay Output Switch to earth
19 HO
2S heater LH bank - upstream Output PWM 12-0V
20 Not used - -
21 Thermostat monitoring sensor Signal Analogue 0-5V
22 Not used - -
23 Main relay Output Switch to earth
24 EVAP system leak detection pump motor (NAS
vehicles with positive pressure type, EVAP system
leak detection capability only)Output Switch to earth
Page 311 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Connector 4 (C0637): This connector contains 40 pins and facilitates use of TestBook via the Diagnostic connector.
Also contained in this connector is the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), this instrument panel lamp informs the driver
of concerns within the engine management system.
Pin out details connector C0637
Pin No. Function Signal type Reading
1 Not used - -
2 Not used - -
3 Not used - -
4 Not used - -
5 Not used - -
6 Not used - -
7 Not used - -
8 Low fuel level Input, signal Active high
9 Fuel tank pressure sensor (NAS vehicles with
vacuum type, EVAP system leak detection
capability only)Output, reference 5V
10 Not used - -
11 Not used - -
12 Analogue fuel level (NAS vehicles with positive
pressure type, EVAP system leak detection only)Input, signal 0-5V
13 Not used - -
14 Fuel tank pressure sensor (NAS vehicles with
vacuum type, EVAP system leak detection
capability only)Input, signal Analogue 0-5V
15 Not used - -
16 ATC compressor request Input, signal Active low
17 Engine speed output Output, signal PWM 0-5V
18 Not used - -
19 Not used - -
20 Malfunction indicator lamp 'ON' Output Switched earth
21 Not used - -
22 Vehicle speed signal (VSS) Input, signal PWM 0-12V
23 Not used - -
24 Not used - -
25 Not used - -
26 Not used - -
27 Not used - -
28 Not used - -
29 ATC compressor relay Output Switched earth
30 Not used - -
31 Positive pressure type EVAP system heater (02MY
vehicles only)Output, drive Switched earth
32 Diagnostic connector K-line Bi-directional Serial 0-12V
33 Immobiliser serial W link Input, signal Serial 0-12V
34 Rough road signal Input, signal PWM 0-12V
35 Not used - -
36 CAN data bus 'high line' Bi-directional 5-2.5V
37 CAN data bus 'low line' Bi-directional 0-2.5V
38 ATC stand by Input, signal Active low
39 Not used - -
40 Not used - -
Page 329 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Heated Oxygen Sensors (HO2S) (C0642)
The market requirement dictates how many HO
2S are fitted to the vehicle.
l4 sensors are fitted to all NAS and EU-3 vehicles.
l2 sensors fitted to all UK, European, Australia and Japanese pre EU-3 specification vehicles.
lNo sensors fitted to ROW vehicles.
The HO
2S monitor the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. By positioning the sensors one for each bank upstream
of the catalytic converter in the exhaust pipe, the ECM can control fuelling on each bank independently of the other.
This allows greater control of the air:fuel ratio and maintains optimum catalyst efficiency. On NAS vehicles the ECM
also uses two HO
2S positioned downstream of the catalytic converters in the exhaust pipe to monitor catalytic
converter efficiency. The ECM is able to achieve this by comparing the values of the upstream HO
2S and the down
stream sensor for the same bank. These comparative values form part of the ECM OBD strategy.
The HO
2S uses zirconium contained in a galvanic cell surrounded by a gas permeable ceramic, this produces an
output voltage proportional to the ratio difference between the oxygen in the exhaust gases and to the ambient
oxygen.
The HO
2S operates at approximately 350 °C (662 °F). To achieve this temperature the HO2S incorporate a heating
element which is controlled by a PWM signal from the ECM. The elements are activated immediately after engine
starts and also under low engine load conditions when the exhaust gas temperature is insufficient to maintain the
required HO
2S temperature. If the heater fails, the ECM will not allow closed loop fuelling to be implemented until the
sensor has achieved the required temperature.
This value equates to an HO
2S output of 450 to 500 mV. A richer mixture can be shown as λ = 0.97, this pushes the
HO
2S output voltage towards 1000 mV. A leaner mixture can be shown as λ = 1.10, this pushes the HO2S output
voltage towards 100 mV.
From cold start, the ECM runs an open loop fuelling strategy. The ECM keeps this strategy in place until the HO
2S is
at a working temperature of 350 °C (662 °F). At this point the ECM starts to receive HO
2S information and it can then
switch into closed loop fuelling as part of its adaptive strategy. The maximum working temperature of the tip of the
HO
2S is 930 °C (1706 °F), temperatures above this will damage the sensor.
HO
2S age with use, this increases their response time to switch from rich to lean and from lean to rich. This can lead
to increased exhaust emissions over a period of time. The switching time of the upstream sensors are monitored by
the ECM. If a pre-determined threshold is exceeded, a failure is detected and the MIL illuminated.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Exhaust Emission Control System.
Input/Output
The upstream and downstream HO
2S are colour coded to prevent incorrect fitting. The tips of the upstream sensors
are physically different to the tips of the downstream sensors.
The HO
2S are colour coded as follows:
lUpstream sensors (both banks) - orange.
lDownstream sensors (both banks) - grey.
The four HO
2S have a direct battery supply to the heater via fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box.
Page 330 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-31
The heater is driven by the ECM providing an earth path for the circuit as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 19 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 13 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 7 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 1 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S output signal is measured by the ECM as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 15 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 16 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 17 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 14 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S earth path for the signal is supplied by the ECM as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 9 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 10 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 11 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 8 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S voltage is difficult to measure using a multimeter, the output can be monitored using TestBook. A rich
mixture would read 500 to 1000 mV, a weak mixture would read 100 mV to 500 mV, the reading should switch from
rich to weak. The open loop default voltage is 450 mV, this is used by the ECM to set the air/ fuel ratio until the tip of
the HO
2S reaches operating temperature.
The HO
2S can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lSensor disconnected.
lStoichiometric ratio outside the correct operating band.
lContamination from leaded fuel.
lAir leak into the exhaust system.
lWiring loom damage.
lSensors fitted incorrectly or cross wired.
In the event of a HO
2S signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDefault to open loop fuelling on defective bank.
lIf the sensors are crossed over (LH bank to RH bank), the engine will run normally after initial start up, but
performance will become progressively worse as the sensors go towards maximum rich for one bank of cylinders
and maximum lean for the other. The ECM will eventually default into open loop fuelling.
lHigh CO reading.
lExcess emissions.
lStrong hydrogen sulphide (H
2S) smell until the ECM defaults to open loop fuelling. .
lMIL illuminated (NAS market only).
A number of diagnostic tests are performed by the ECM with regards to the HO
2sensors:
lHO
2 sensor and system diagnostics
lHO
2 sensor heater diagnostics
lHO
2 sensor switching period (ageing) diagnostics
lRear HO
2 sensor adaption diagnostic (NAS only)
lCatalyst monitoring diagnostic
For further details of the heated oxygen sensors and exhaust emission control, refer to the V8 Emission Control
section of this manual.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Exhaust Emission Control System.
Page 331 of 1529
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-32 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
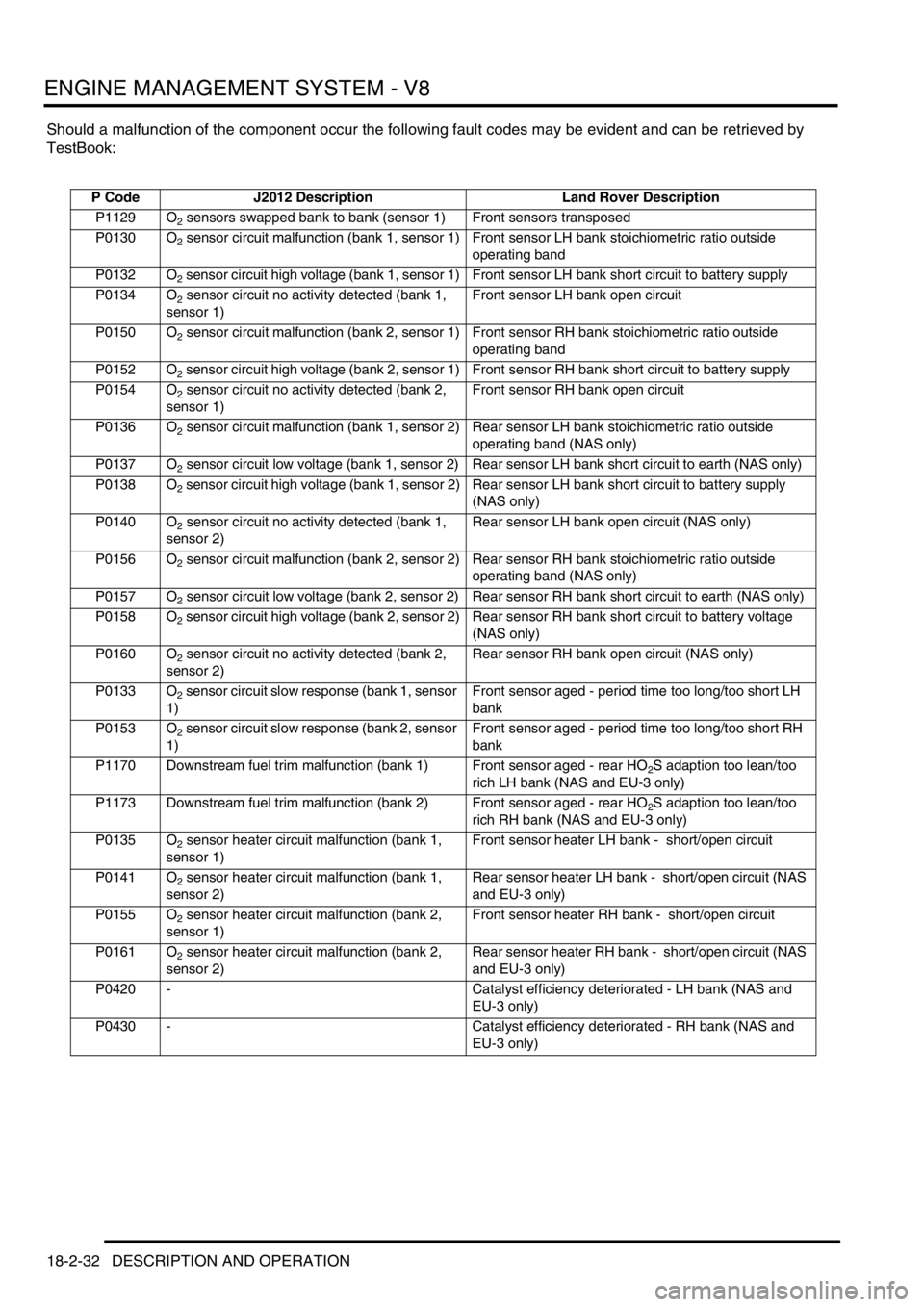
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1129 O
2 sensors swapped bank to bank (sensor 1) Front sensors transposed
P0130 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 1, sensor 1) Front sensor LH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band
P0132 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 1, sensor 1) Front sensor LH bank short circuit to battery supply
P0134 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 1,
sensor 1)Front sensor LH bank open circuit
P0150 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 2, sensor 1) Front sensor RH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band
P0152 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 2, sensor 1) Front sensor RH bank short circuit to battery supply
P0154 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 2,
sensor 1)Front sensor RH bank open circuit
P0136 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band (NAS only)
P0137 O
2 sensor circuit low voltage (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank short circuit to earth (NAS only)
P0138 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 1, sensor 2) Rear sensor LH bank short circuit to battery supply
(NAS only)
P0140 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 1,
sensor 2)Rear sensor LH bank open circuit (NAS only)
P0156 O
2 sensor circuit malfunction (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank stoichiometric ratio outside
operating band (NAS only)
P0157 O
2 sensor circuit low voltage (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank short circuit to earth (NAS only)
P0158 O
2 sensor circuit high voltage (bank 2, sensor 2) Rear sensor RH bank short circuit to battery voltage
(NAS only)
P0160 O
2 sensor circuit no activity detected (bank 2,
sensor 2)Rear sensor RH bank open circuit (NAS only)
P0133 O
2 sensor circuit slow response (bank 1, sensor
1)Front sensor aged - period time too long/too short LH
bank
P0153 O
2 sensor circuit slow response (bank 2, sensor
1)Front sensor aged - period time too long/too short RH
bank
P1170 Downstream fuel trim malfunction (bank 1) Front sensor aged - rear HO
2S adaption too lean/too
rich LH bank (NAS and EU-3 only)
P1173 Downstream fuel trim malfunction (bank 2) Front sensor aged - rear HO
2S adaption too lean/too
rich RH bank (NAS and EU-3 only)
P0135 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 1,
sensor 1)Front sensor heater LH bank - short/open circuit
P0141 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 1,
sensor 2)Rear sensor heater LH bank - short/open circuit (NAS
and EU-3 only)
P0155 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 2,
sensor 1)Front sensor heater RH bank - short/open circuit
P0161 O
2 sensor heater circuit malfunction (bank 2,
sensor 2)Rear sensor heater RH bank - short/open circuit (NAS
and EU-3 only)
P0420 - Catalyst efficiency deteriorated - LH bank (NAS and
EU-3 only)
P0430 - Catalyst efficiency deteriorated - RH bank (NAS and
EU-3 only)
Page 358 of 1529

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-59
⇒ Drive cycle C:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 60°C (140°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 8 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 3 minutes.
9Allow engine to idle for 3 minutes.
10Connect TestBook and with the engine still running, check for fault codes.
NOTE: The following areas have an associated readiness test which must be flagged as complete, before a problem
resolution can be verified:
lcatalytic converter fault;
lEvaporative loss system fault;
lHO
2 sensor fault;
lHO
2 sensor heater fault.
When carrying out a drive cycle C to determine a fault in any of the above areas, select the readiness test icon to
verify that the test has been flagged as complete.
⇒ Drive cycle D:
1Switch ignition on for 30 seconds.
2Ensure engine coolant temperature is less than 35°C (95°F).
3Start the engine and allow to idle for 2 minutes.
4Perform 2 light accelerations (0 to 35 mph (0 to 60 km/h) with light pedal pressure).
5Perform 2 medium accelerations (0 to 45 mph (0 to 70 km/h) with moderate pedal pressure).
6Perform 2 hard accelerations (0 to 55 mph (0 to 90 km/h) with heavy pedal pressure).
7Cruise at 60 mph (100 km/h) for 5 minutes.
8Cruise at 50 mph (80 km/h) for 5 minutes.
9Cruise at 35 mph (60 km/h) for 5 minutes.
10Allow engine to idle for 2 minutes.
11Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.
⇒ Drive cycle E:
1Ensure fuel tank is at least a quarter full.
2Carry out Drive Cycle A.
3Switch off ignition.
4Leave vehicle undisturbed for 20 minutes.
5Switch on ignition.
6Connect TestBook and check for fault codes.