1999 DODGE RAM heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 1457 of 1691

* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check engine vacuum
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check oxygen sensor heater
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check engine mechanical condition
* Check evaporative system
* Check EGR system
* Check Intake Air Temperature (IAT) motor operation
* Check Park/Neutral Position (PNP) switch.
POOR FUEL ECONOMY
Check the following:
* Check secondary ignition system
* Check PCM power and ground circuits
* Check engine vacuum
* Check fuel pressure
* Check Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor calibration
* Check Throttle Position (TP) sensor calibration
* Check Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) calibration
* Check minimum idle airflow
* Check oxygen sensor switching
* Check oxygen sensor heater
* Check Idle Air Control (IAC) motor operation
* Check engine mechanical condition
* Check evaporative system
* Check EGR system
* Check Intake Air Temperature (IAT) motor operation
* Check Park/Neutral Position (PNP) switch.
INTERMITTENTS
INTERMITTENT PROBLEM DIAGNOSIS
Intermittent fault testing requires duplicating circuit or
component failure to identify the problem. These procedures may lead
to PCM setting a Diagnostic Trouble Code (FTC) which may help in
diagnosis.
If problem vehicle does not produce FTC, monitor voltage or
resistance values using a DVOM while attempting to reproduce
conditions causing intermittent fault. A status change on DVOM
indicates a fault has been located.
Use a DVOM to pinpoint faults. When monitoring voltage,
ensure ignition switch is in ON position or engine is running. Ensure
ignition switch is in OFF position or negative battery cable is
disconnected when monitoring circuit resistance. Status changes on
DVOM during test procedures indicate area of fault.
TEST PROCEDURES
Intermittent Simulation
To reproduce the conditions creating an intermittent fault,
use the following methods:
Page 1462 of 1691

* Charging System
* Cruise Control System
* Intake Manifold Air Heater
* Tachometer
* Torque Convertor Clutch Engagement (A/T Only)
* Transmission Overdrive Solenoid (A/T Only) Components are
grouped into 2 categories. The first category covers INPUT
DEVICES, which control or produce voltage signals monitored
by the PCM. The second category covers OUTPUT SIGNALS, which
are components controlled by the PCM. See PCM INPUT SIGNALS
and ECM/PCM OUTPUT SIGNALS.
ECM INPUT SIGNALS
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS)
APPS sensor is mounted on top left of engine. See Fig. 2.
Sensor provides DC voltage input signal to Engine Control Module (ECM)\
to indicate throttle position. On previous engines, there were
linkages between accelerator pedal, throttle position sensor and
injection pump. On this engine, no linkage exists between accelerator
pedal and injection pump. ECM uses input signals from APPS sensor to
determine proper fuel delivery. ECM also outputs this signal to PCM.
Battery Voltage
Battery voltage input signal provides operating voltage to
Engine Control Module (ECM). This input signal keeps ECM memory alive
and informs ECM what generator output voltage is when engine is
running. ECM memory is used to store Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs),
store APPS sensor voltages from previous key cycles and provide a
speed control adaptive memory.
Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP)
Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is a hall effect sensor (0-5
volts switched), located below injection pump in rear face of timing
gear cover. Sensor is not used for fuel control. Sensor is used only
for diagnostic purposes.
CCD Bus Circuits
These circuits are connected between Engine Control Module
(ECM) and Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to allow communication
between modules.
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor delivers input signal (35
tooth wheel with gap) to Engine Control Module (ECM) to indicate
engine speed and crankshaft position. ECM uses CKP signal along with
other input signals for controlling injector firing sequence and
timing. Sensor is located below fuel transfer pump, on side of engine
block. See Fig. 2.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
Data Link Connector (DLC) provides an input signal to Engine
Control Module (ECM) when using scan tool to retrieve Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs) from ECM. Input signal may also be used when
performing various tests on the ECM and electronic control system.
Data link connector is a 16-pin connector located at lower edge of
driver's side of instrument panel, just above accelerator pedal.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor delivers input signal to
Engine Control Module (ECM) to indicate engine coolant temperature.
ECM uses input signal for controlling fuel control and timing. Engine
coolant temperature sensor is located on front of head, near
Page 1463 of 1691

thermostat housing. See Fig. 2.
Fuel Injection Pump Control Module (FPCM)
Fuel Pump Control Module (FPCM) controls fuel pump using
inputs from Engine Control Module (ECM). FPCM is integral to top of
fuel pump. ECM and FPCM are interconnected together for fuel injection
control.
Fuel Temperature Sensors
There are 2 fuel temperature sensors. One sensor is located
inside injection pump, and will set FTC under high temperature
conditions. Engine Control Module (ECM) will lower engine power if FTC\
is set. Other sensor is an integral part of fuel heater. See FUEL
HEATER.
Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Intake manifold air temperature sensor is a variable
thermistor sensor located on top of intake manifold, behind intake
manifold air heater. See Fig. 4. Intake manifold air temperature
sensor delivers an input signal to Engine Control Module (ECM) to
indicate intake manifold air temperature. ECM uses input signal for
controlling intake manifold air heater, fuel control and timing.
Fig. 4: Locating Intake Manifold Air Temperature Sensor & MAP Sensor
Courtesy of Chrysler Corp.
Manifold Air Pressure (MAP) Sensor (Boost Pressure)
Manifold Air Pressure (MAP) sensor, located at rear of intake\
Page 1464 of 1691

manifold, sends input signal to Engine Control Module (ECM). ECM uses
input signal for controlling fuel control, timing and engine
protection. ECM will lower engine power if boost is too high.
Oil Pressure Sensor
Oil pressure sensor signal is input to Engine Control Module
(ECM). ECM converts signal to pressure value. Value is sent on CCD Bus\
to instrument panel gauge/light. Oil pressure sensor is located on
side of engine block, below ECM. See Fig. 2.
Power Take Off (PTO)
This input is used on vehicles equipped with a Power Take Off
(PTO) unit. When PTO is engaged, Engine Control Module (ECM) will
disable some OBD-II functions.
Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor
WIF sensor is located in bottom of fuel filter/water
separator. See Fig. 2. WIF sensor delivers input signal to Engine
Control Module (ECM) when water exists in the fuel filter/water
separator. As water level increases, resistance across WIF sensor
decreases. ECM compares decrease in resistance to a high water
standard value. When resistance is 30,000-40,000 ohms, ECM will turn
on WATER-IN-FUEL warning light. WATER-IN-FUEL warning light is located
on instrument panel, just below tachometer. ECM monitors input signal
when ignition switch is in the ON position and continues to monitor
input signal until intake manifold air heater post-heat cycle is
complete.
PCM INPUT SIGNALS
A/C Switch
When A/C switch is in ON position, an input signal is
delivered from A/C switch to Engine Control Module (ECM) to indicate
that A/C operation has been requested. Once A/C operation has been
requested, an A/C request signal is delivered to ECM from A/C high-
pressure switch and A/C low-pressure switch. The A/C request signal
indicates evaporator pressure is within proper range for A/C
operation. ECM uses A/C request signal to cycle A/C compressor clutch
by using an A/C clutch relay. A/C clutch relay may also be referred to
as A/C compressor clutch relay. If A/C high-pressure switch or A/C
low-pressure switch opens, A/C request signal will not be delivered to
the ECM. ECM will then open ground circuit for A/C clutch relay and
A/C compressor clutch will be disengaged.
The A/C clutch relay is located in power distribution center
at driver's side front corner of engine compartment, near the battery.
The A/C high-pressure switch is located on discharge line, near A/C
compressor. The A/C low-pressure switch is located on top of
accumulator.
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) Output From ECM
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) is mounted on top
left of engine. See Fig. 2. Sensor provides DC voltage input signal to
Engine Control Module (ECM) to indicate throttle position. On previous\
engines, there were linkages between accelerator pedal, throttle
position sensor and injection pump. On this engine, no linkage exists
between accelerator pedal and injection pump. APPS signal is sent on
CCD Bus circuit from ECM to PCM.
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Relay
A 12-volt input signal is delivered from ASD relay to Engine
Control Module (ECM) when ASD relay is energized. If ECM does not
receive a 12-volt input signal when ASD relay is energized, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (FTC) will be stored in ECM. ASD relay is
Page 1467 of 1691

brakelines are attached to and is mounted in the engine compartment.
ECM OUTPUT SIGNALS
APPS & CKP Output To PCM
See ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (APPS) OUTPUT FROM ECM
under PCM INPUT SIGNALS.
CCD Bus
These circuits are connected between Engine Control Module
(ECM) and Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to allow communication
between modules.
DLC Output
Data Link Connector (DLC) is connected to Engine Control
Module (ECM). Using a scan tool, data can be retrieved (output) from\
ECM.
5-Volt Sensor Supply Output
Engine Control Module (ECM) supplies a 5-volt reference
signal to the following sensors:
* Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
* Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
* Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
* Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
* Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Engine Control Module (ECM) also supplies voltage to the
following sensors:
* Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor (APPS)
* Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
* Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
* Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
* Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
* Water-In-Fuel (WIF) Sensor
Fuel Injection Pump Relay
The Engine Control Module (ECM) energizes the fuel injection
pump and integral Fuel Pump Control Module (FPCM) through the relay.
When ignition is turned on, ECM supplies 12 volts to fuel injection
pump relay, located in Power Distribution Center.
Fuel Pump Control Module (FPCM)
Fuel Pump Control Module (FPCM) controls fuel pump using
inputs from Engine Control Module (ECM). FPCM is integral to top of
fuel pump. ECM and FPCM are interconnected together for fuel injection
control.
Fuel Transfer Pump
Engine Control Module (ECM) supplies power to fuel transfer
pump. Transfer fuel pump supplies fuel under low pressure (14 psi)
while engine is running to fuel injection pump. Fuel transfer pump
supplies an excess of fuel to cool fuel injection pump. Excess fuel is
returned to fuel tank by fuel injection pump.
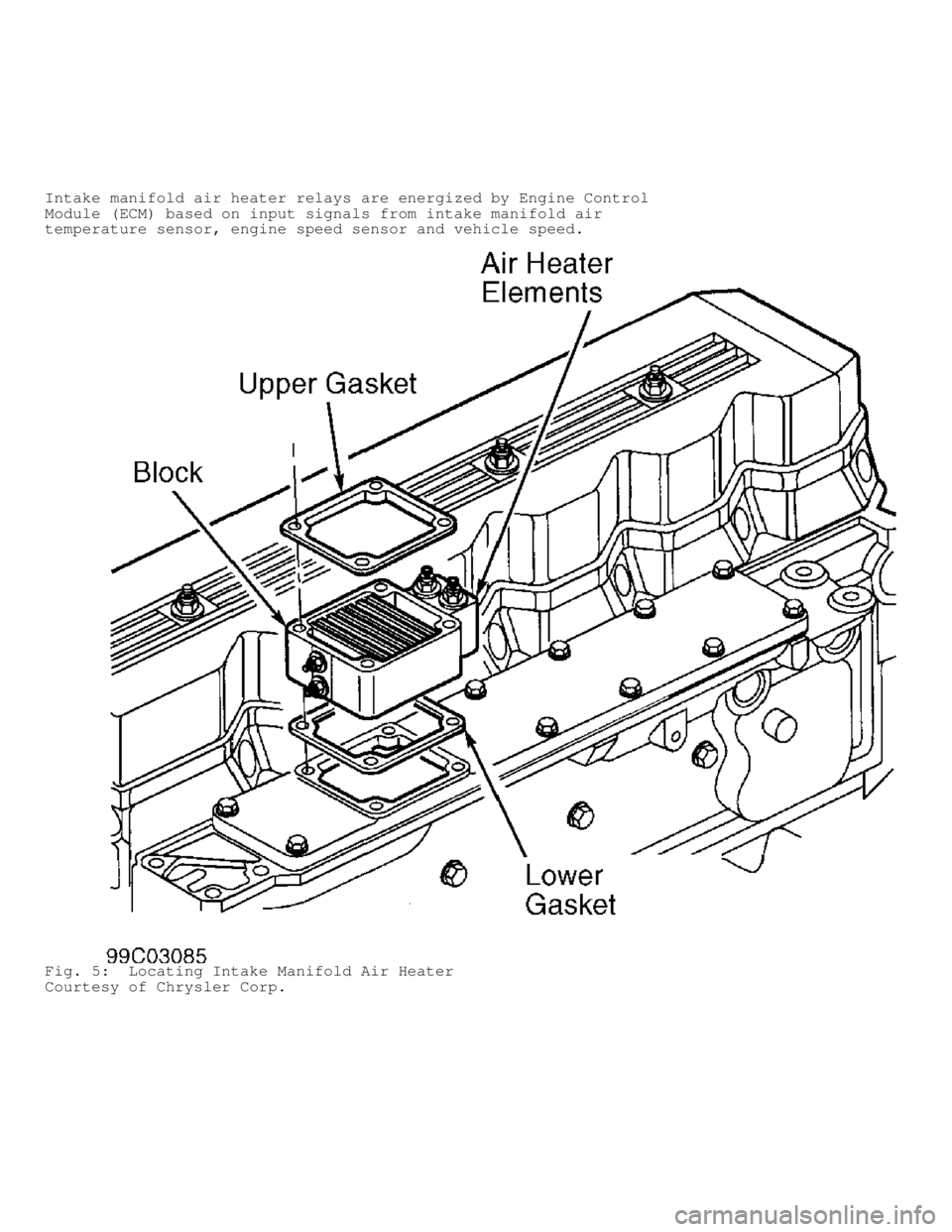
Intake Manifold Air Heater Relays
Intake manifold air heater relays provide voltage to intake
manifold air heater for warming of intake. See Fig. 5. Warming of
intake air aids in engine starting and improved driveability during
cold ambient temperatures. Intake manifold air heater relays are
mounted on inner wheelwell, below driver's side battery. See Fig. 6.
Page 1468 of 1691
Intake manifold air heater relays are energized by Engine Control
Module (ECM) based on input signals from intake manifold air
temperature sensor, engine speed sensor and vehicle speed.
Fig. 5: Locating Intake Manifold Air Heater
Courtesy of Chrysler Corp.
Page 1469 of 1691
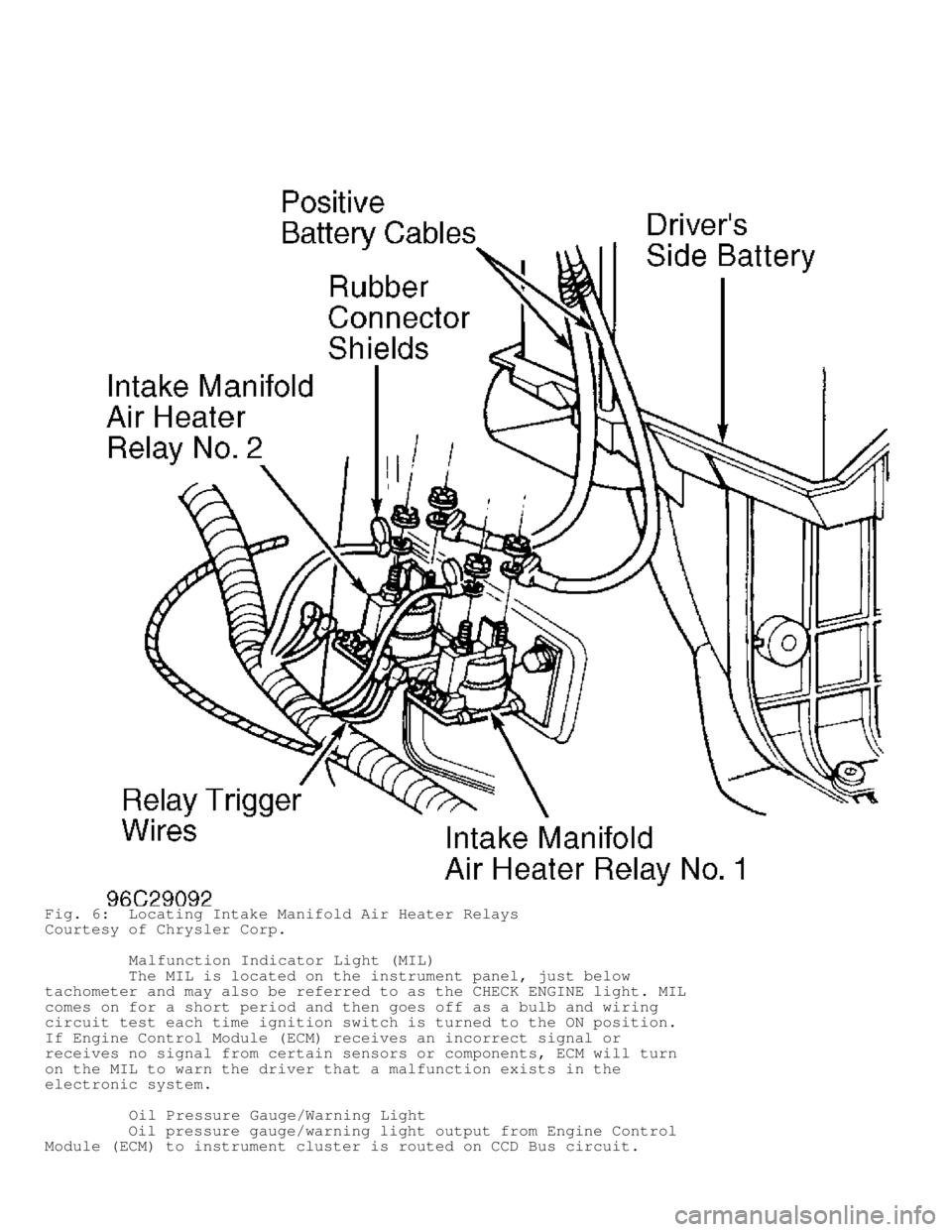
Fig. 6: Locating Intake Manifold Air Heater Relays
Courtesy of Chrysler Corp.
Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL)
The MIL is located on the instrument panel, just below
tachometer and may also be referred to as the CHECK ENGINE light. MIL
comes on for a short period and then goes off as a bulb and wiring
circuit test each time ignition switch is turned to the ON position.
If Engine Control Module (ECM) receives an incorrect signal or
receives no signal from certain sensors or components, ECM will turn
on the MIL to warn the driver that a malfunction exists in the
electronic system.
Oil Pressure Gauge/Warning Light
Oil pressure gauge/warning light output from Engine Control
Module (ECM) to instrument cluster is routed on CCD Bus circuit.
Page 1470 of 1691

WAIT-TO-START Warning Light
WAIT-TO-START warning light is located on instrument panel,
just below the speedometer. WAIT-TO-START warning light will come on
for a short period and then go off as a bulb and wiring circuit test
each time ignition switch is turned to the ON position. If Engine
Control Module (ECM) determines intake manifold air temperature is
less than 59
�F (15�C) by input signal received from intake manifold
air temperature sensor, ECM delivers output signal to operate WAIT-TO-
START warning light and intake manifold air heater for a preheat
cycle.
WAIT-TO-START warning light will remain on until intake
manifold air heater preheat cycle is complete. WAIT-TO-START warning
light will flash on and off if intake manifold air temperature sensor
signal to ECM is not within a specified value and Diagnostic Trouble
Code (FTC) will be stored in ECM memory.
WATER-IN-FUEL Warning Light
WATER-IN-FUEL warning light is located on instrument panel,
just below tachometer. WATER-IN-FUEL warning light will come on for a
short period and then go off as a bulb and wiring circuit test each
time ignition switch is turned to the ON position. If Engine Control
Module (ECM) determines water exists in fuel/water separator by input
signal from Water-In-Fuel (WIF) sensor, ECM will deliver output signal\
to turn on the WATER-IN-FUEL warning light.
ECM/PCM OUTPUT SIGNALS
A/C Clutch Relay
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls A/C compressor
operation by controlling ground circuit for A/C clutch relay. ECM de-
energizes A/C clutch relay if engine coolant temperature is more than
257
�F (125�C). The A/C clutch relay is located in power distribution
center at driver's side front corner of engine compartment, near the
battery.
Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Relay
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls ASD operation by
controlling ground circuit for ASD relay. ASD provides voltage to
operate generator field control for charging system. ASD relay is
located in power distribution center at driver's side front corner of
engine compartment, near the battery. Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay
may also be referred to as Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay.
CCD Bus
These circuits are connected between Engine Control Module
(ECM) and Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to allow communication
between modules.
Cruise Control System
Engine Control Module (ECM) regulates cruise control system
operation by controlling vacuum at cruise control servo. Vacuum is
controlled by use of vacuum and vent solenoids in cruise control
servo.
Data Link Connector
Engine Control Module (ECM) provides output information at
Data Link Connector (DLC) when using scan tool to perform various
tests on the ECM and electronic control system. Data link connector is
a 16-pin connector located at lower edge of driver's side of
instrument panel, just above the accelerator pedal.
5-Volt Sensor Supply Output
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) supplies a 5-volt reference