1999 DODGE NEON width
[x] Cancel search: widthPage 762 of 1200

²Exhaust valve seat diameter is 28 mm (1.102
in.)
(6) Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. The intake valve seat must be ser-
viced when the valve seat width is 2.0 mm (0.079 in.)
or greater. The exhaust valve seat must be serviced
when the valve seat width is 2.5 mm (0.098 in.) or
greater. Otherwise the cylinder head must be
replaced.
(7) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 0.75 to 1.25 mm
(0.030 to 0.049 in.) (Fig. 107).
(8) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A
after grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve
tip to 43.51 - 44.57 mm (1.71 - 1.75 in.) for exhaust
valve and 45.01 - 46.07 mm (1.77 - 1.81 in.) for
intake valve over spring seat when installed in thehead (Fig. 108). The valve tip chamfer may need to
be reground to prevent seal damage when the valve
is installed.
CLEANING
Clean all valve guides, valves and valve spring
assemblies thoroughly with suitable cleaning solution
before reassembling.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves using
a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 109). The valve stem
seals should be pushed firmly and squarely over
valve guide.
CAUTION: If oversize valves are used, there is only
one oversize valve available. The same stem seal is
used on both the standard and oversize valve.
(3) Install valve springs and retainers. Compress
valve springs only enough to install locks, taking
care not to misalign the direction of compression.
Nicked valve stems may result from misalignment of
the valve spring compressor.
VALVE SPECIFICATION CHART
Face Angle
Intake and
Exhaust:45 - 45 1/2É
Head Diameter
Intake: 33.12 - 33.37 mm (1.303 - 1.313 in.)
Exhaust: 28.57 - 28.83 mm (1.124 - 1.135 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake: 114.69 - 115.19 mm (4.515 - 4.535 in.)
Exhaust: 116.94 - 117.44 mm (4.603 - 4.623 in.)
Stem Diameter
Intake: 5.934 - 5.952 mm (0.2337 - 0.2344 in.)
Exhaust: 5.906 - 5.924 mm (0.2326 - 0.2333 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake: 1.15 - 1.48 mm (0.0452 - 0.0582 in.)
Exhaust: 1.475 - 1.805 mm (0.0580 - 0.0710 in.)
Fig. 107 Valve Seat Refacing
Fig. 108 Spring Installed Height and Valve Tip to
Spring Seat Dimensions
Fig. 109 Valve Stem Oil Seal Tool
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 49
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 766 of 1200

Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston. . . .0.008 - 0.020 mm (0.0003 -
0.0008 in.)
In Rod (Interference) . . .0.018 - 0.043 mm (0.0007 -
0.0017 in.)
Diameter .20.998 - 21.003 mm (0.8267 - 0.8269 in.)
End Play.............................None
Length.......74.75 - 75.25 mm (2.943 - 2.963 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring Gap Top Compression Ring . . .0.23 - 0.52 mm
(0.009 - 0.020 in.)
Ring Gap 2nd Compression Ring . . .0.49 - 0.78 mm
(0.019 - 0.031 in.)
Ring Gap Oil Control (Steel Rails). .0.23 - 0.66 mm
(0.009 - 0.026 in.)
Ring Side Clearance Both Compression
Rings......0.025 - 0.065 mm (0.0010 - 0.0026 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack) .0.004 - 0.178 mm (0.0002 - 0.0070
in.)
Ring Width Compression Rings. . . .1.17 - 1.19 mm
(0.046 - 0.047 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack) . .2.854 - 3.008 mm (0.1124 - 0.1184
in.)
Connecting Rod
Bearing Clearance......0.026 - 0.059 mm (0.001 -
0.0023 in.)
Piston Pin Bore Diameter......20.96 - 20.98 mm
(0.8252 - 0.8260 in.)
Large End Bore Diameter. . . .50.991 - 51.005 mm
(2.0075 - 2.0081 in.)
Side Clearance . .0.13 - 0.38 mm (0.005 - 0.015 in.)
Total Weight (Less Bearing) . .543 grams (1.20 lbs.)
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal Diameter......47.9924 -
48.0076 mm (1.8894 - 1.8900 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)......0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)............0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical Clearance
No.1-5 ...0.022 - 0.062 mm (0.0008 - 0.0024 in.)
End Play.....0.09 - 0.24 mm (0.0035 - 0.0094 in.)
Main Bearing Journals
Diameter . .51.9924 - 52.0076 mm (2.0469 - 2.0475
in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)......0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)............0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft
Rocker Arm Shaft Diameter . . .19.996 ± 19.984mm
(0.786 ± 0.7867 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft Retainers (Width)
Intake (All)................28.46 mm (1.12 in.)
Exhaust....1 & 5 29.20 mm (1.14in.) 2, 3, and 4 -
40.45 mm (1.59 in.)
Rocker Arm/Hydraulic Lash Adjuster *
Rocker Arm Inside Diameter. . . .20.00 ± 20.02 mm
(0.787 ± 0.788 in.)Rocker Arm Shaft Clearance. . . .0.016 ± 0.054 mm
(0.0006 ± 0.0021 in.)
Body Diameter.....22.949 ± 22.962 mm (0.9035 ±
0.9040 in.)
Plunger Travel Minimum (Dry) .2.2 mm (0.087 in.)
Rocker Arm Ratio....................1.4 to 1
Cylinder Head Camshaft Bearing Diameter
No.1 .....41.20 ± 41.221 mm (1.622 ± 1.6228 in.)
No.2 .......41.6 ± 41.621 mm (1.637 ± 1.638 in.)
No.3 .......42.0 ± 42.021 mm (1.653 ± 1.654 in.)
No.4 .......42.4 ± 42.421 mm (1.669 ± 1.670 in.)
No.5 ......42.8 ± 42.821 mm (1.685 ± 1.6858 in.)
Camshaft Journal Diameter
No. 1 . . . .41.128 ± 41.147 mm (1.619 ± 1.6199 in.)
No.2 .....41.528 ± 41.547 mm (1.634 ± 1.635 in.)
No.3 .....41.928 ± 41.947 mm (1.650 ± 1.651 in.)
No.4 .....42.328 ± 42.374 mm (1.666 ± 1.668 in.)
No. 5 . . . .42.728 ± 42.747 mm (1.682 ± 1.6829 in.)
Diametrical Bearing Clearance . .0.053 ± 0.093 mm
(0.0027 ± 0.003 in.)
Max. Allowable............0.12 mm (0.0047 in.)
End Play...........0.05 ± 0.39 mm (0.0059 in.)
Lift (Zero Lash )
Intake.....................7.2 mm (0.283 in.)
Exhaust..................7.03 mm (0.277 in.)
Valve Timing Exhaust Valve**
Closes (ATDC)..........................5.4É
Opens (BBDC).........................43.7É
Duration............................229.1É
Valve Timing Intake Valve **
Closes (ABDC)........................41.1É
Opens (ATDC).........................13.9É
Duration............................207.2É
Valve Overlap...........................0É
Cylinder Head
Material....................Cast Aluminum
Gasket Thickness (Compressed) . . .1.15 mm (0.045
in.)
Valve Seat
Angle.................................45É
Runout (Max.)...............0.050 mm (0.002)
Width (Finish) Intake and Exhaust. . . .0.75 ± 1.25
mm (0.030 ± 0.049 in.)
Valve Guide Finished
Diameter I.D. . .5.975 ± 6.000 mm (.235 ± .236 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter (Std.)......11.0±11.02 mm
(0.4330 ± 0.4338 in.)
Valves
Face Angle Intake and Exhaust......45±45-1/2É
Head Diameter Intake . .32.12 ± 33.37 mm (1.303 ±
1.313 in.)
Head Diameter Exhaust . .28.57 ± 28.83 mm (1.124
± 1.135 in.)
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 53
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 806 of 1200
²Intake valve seat diameter is 34.37 - 34.63 mm
(1.353 - 1.363 inch.)
²Exhaust valve seat diameter is 29.37 29.63 mm
(1.156 1.166 inch.)
(6)
Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. The intake valve seat must be serviced
when the valve seat width is 2.0 mm (0.079 in.) or
greater. The exhaust valve seat must be serviced when
the valve seat width is 2.5 mm (0.098 in.) or greater.
Otherwise the cylinder head must be replaced. For spec-
ification refer to Valve Specification Chart.
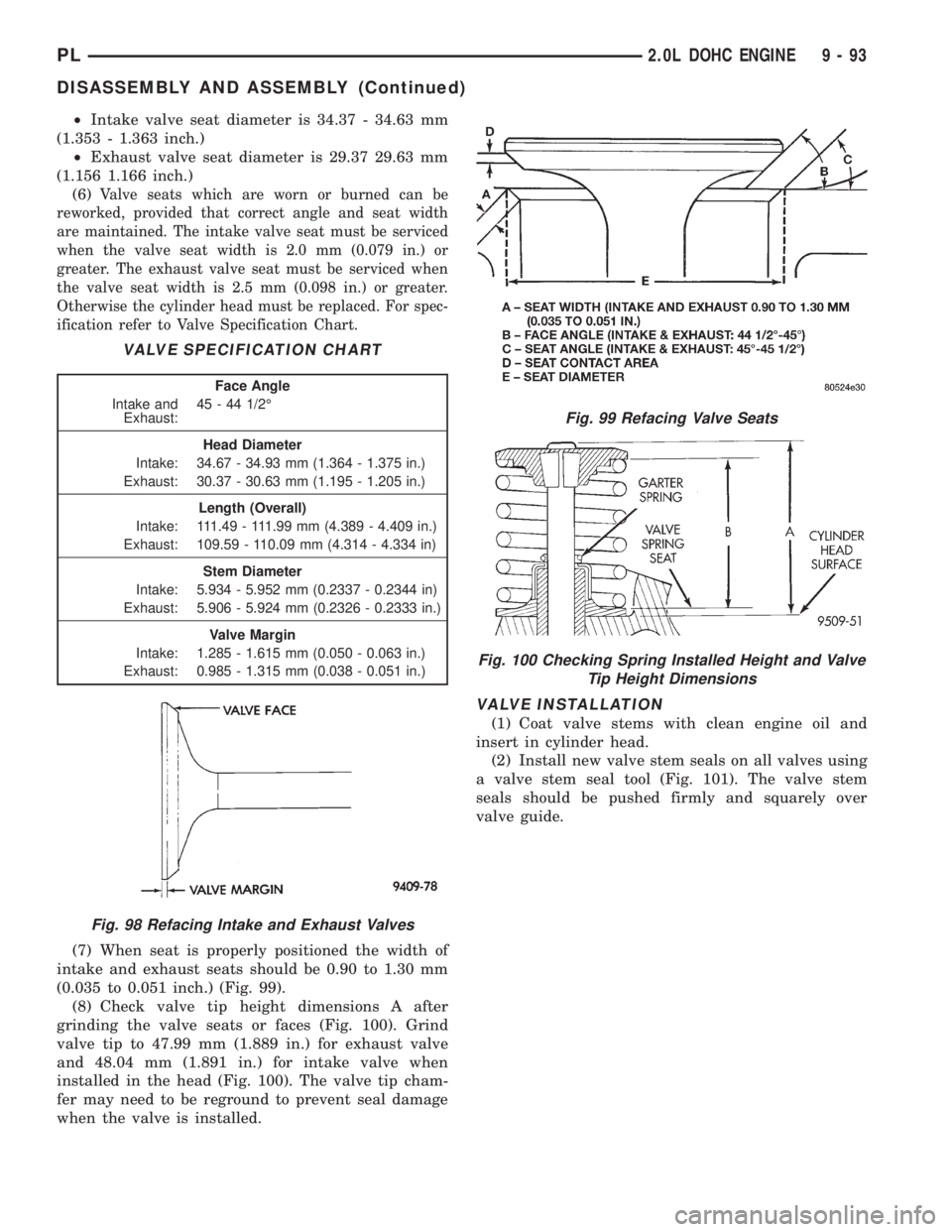
(7) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 0.90 to 1.30 mm
(0.035 to 0.051 inch.) (Fig. 99).
(8) Check valve tip height dimensions A after
grinding the valve seats or faces (Fig. 100). Grind
valve tip to 47.99 mm (1.889 in.) for exhaust valve
and 48.04 mm (1.891 in.) for intake valve when
installed in the head (Fig. 100). The valve tip cham-
fer may need to be reground to prevent seal damage
when the valve is installed.
VALVE INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert in cylinder head.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves using
a valve stem seal tool (Fig. 101). The valve stem
seals should be pushed firmly and squarely over
valve guide.
VALVE SPECIFICATION CHART
Face Angle
Intake and
Exhaust:45 - 44 1/2É
Head Diameter
Intake: 34.67 - 34.93 mm (1.364 - 1.375 in.)
Exhaust: 30.37 - 30.63 mm (1.195 - 1.205 in.)
Length (Overall)
Intake: 111.49 - 111.99 mm (4.389 - 4.409 in.)
Exhaust: 109.59 - 110.09 mm (4.314 - 4.334 in)
Stem Diameter
Intake: 5.934 - 5.952 mm (0.2337 - 0.2344 in)
Exhaust: 5.906 - 5.924 mm (0.2326 - 0.2333 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake: 1.285 - 1.615 mm (0.050 - 0.063 in.)
Exhaust: 0.985 - 1.315 mm (0.038 - 0.051 in.)
Fig. 98 Refacing Intake and Exhaust Valves
Fig. 99 Refacing Valve Seats
Fig. 100 Checking Spring Installed Height and Valve
Tip Height Dimensions
PL2.0L DOHC ENGINE 9 - 93
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 810 of 1200

Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 2 .4.456 - 4.605 mm
(0.175 - 0.181 in.)
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 3 .3.841 - 4.075 mm
(0.151 - 0.160 in.)
Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston. . . .0.008 - 0.020 mm (0.0003 -
0.0008 in.)
In Rod (Interference) . . .0.018 - 0.043 mm (0.0007 -
0.0017 in.)
Diameter .20.998 - 21.003 mm (0.8267 - 0.8269 in.)
End Play.............................None
Length.......74.75 - 75.25 mm (2.943 - 2.963 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring Gap Top Compression Ring . . .0.23 - 0.52 mm
(0.009 - 0.020 in.)
Ring Gap 2nd Compression Ring . . .0.49 - 0.78 mm
(0.019 - 0.031 in.)
Ring Gap Oil Control (Steel Rails). .0.23 - 0.66 mm
(0.009 - 0.026 in.)
Ring Side Clearance Both
Compression Rings. . . .0.025 - 0.065 mm (0.0010 -
0.0026 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack).0.004 - 0.178 mm (0.0002 - 0.0070 in.)
Ring Width Compression Rings. . . .1.17 - 1.19 mm
(0.046 - 0.047 in.)
Oil Ring (Pack).2.854 - 3.008 mm (0.1124 - 0.1184 in.)
Connecting Rod
Bearing Clearance.0.026 - 0.059 mm (0.001 - 0.0023
in.)
Piston Pin Bore Diameter.20.96 - 20.98 mm (0.8252
- 0.8260 in.)
Large End Bore Diameter. . . .50.991 - 51.005 mm
(2.0075 - 2.0081 in.)
Side Clearance . .0.13 - 0.38 mm (0.005 - 0.015 in.)
Total Weight (Less Bearing) . .543 grams (1.20 lbs.)
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal Diameter.47.9924 - 48.0076
mm (1.8894 - 1.8900 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)......0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)............0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical
Clearance No. 1 - 5.0.022 - 0.062 mm (0.0008 - 0.0024
in.)
End Play.....0.09 - 0.24 mm (0.0035 - 0.0094 in.)
Main Bearing Journals
Diameter.51.9924 - 52.0076 mm (2.0469 - 2.0475 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.)......0.0035 mm (0.0001 in.)
Taper (Max.)............0.0038 mm (0.0001 in.)
Camshaft
Bearing Bore Diameter No. 1 - 6.26.020 mm - 26.041
mm (1.024 - 1.025 in.)
Diametrical Bearing Clearance . .0.069 - 0.071 mm
(0.0027 - 0.003 in.)
End Play.......0.05 - 0.15 mm (0.002 - 0.006 in.)Bearing Journal Diameter No. 1 - 6.25.951 - 25.970
mm (1.021 - 1.022 in.)
Lift (Zero Lash) Intake.......8.75 mm (0.344 in.)
Lift (Zero Lash) Exhaust.....8.00 mm (0.314 in.)
Valve Timing @ .5 mm Lift
Intake Valve Closes (ABDC)...............38É
Intake Valve Opens (BTDC)...............1.2É
Intake Valve Duration..................219.2É
Exhaust Valve Closes (BTDC)...............3É
Exhaust Valve Opens (BBDC)..............42É
Exhaust Valve Duration..................219É
Valve Overlap...........................0É
Cylinder Head
Material.....................Cast Aluminum
Gasket Thickness (Compressed).1.15 mm (0.045 in.)
Valve Seat Angle...................44.5 - 45É
Runout (Max.).............0.050 mm (0.002 in.)
Width (Finished) Intake and Exhaust .0.9 - 1.3 mm
(0.035 - 0.051 in.)
Valve Guide Finished Diameter ID.5.975 - 6.000 mm
(0.235 - 0.236 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter (Standard) . .11.0 - 11.02 mm
(0.4330 - 0.4338 in.)
Valves
Head Diameter Intake . .34.67 - 34.93 mm (1.365 -
1.375 in.)
Head Diameter Exhaust .30.37 - 30.36 mm (1.195 -
1.195 in.)
Valve Margin Intake.1.15 - 1.48 mm (0.0452 - 0.0582
in.)
Valve Margin Exhaust . .1.475 - 1.805 mm (0.058 -
0.071 in.)
Length Intake.111.49 -111.99 mm (4.389 - 4.409 in.)
Length Exhaust .109.59 - 110.09 mm (4.314 - 4.334
in.)
Valve Stem Tip Heigth Intake.48.04 mm (1.891 in.)
Valve Stem Tip Heigth Exhaust.47.99 mm (1.889 in.)
Stem Diameter Intake. .5.9034 - 5.952 mm (0.234 -
0.234 in.)
Stem Diameter Exhaust .5.906 - 5.924 mm (0.233 -
0.233 in.)
Stem-to-Guide Clearance Intake .0.023 - 0.066 mm
(0.0009 - 0.0025 in.)
Stem-to-Guide Clearance Exhaust.0.051 - 0.094 mm
(0.002 - 0.0037 in.)
Maximum Allowable Intake . .0.076 mm (0.003 in.)
Maximum Allowable Exhaust .0.101 mm (0.004 in.)
Valve Spring
Free Length (Approx.).........46mm(1.811 in.)
Spring Tension (Valve Closed).246 - 270 N @ 38.0 mm
(55 - 60 lbs. @ 1.496 in.)
Spring Tension (Valve Open).549 - 611 N @ 29.3 mm
(123 - 137 lbs. @ 1.53 in.)
PL2.0L DOHC ENGINE 9 - 97
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 815 of 1200

ENGINE 1.8L SOHC
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter.....82.993 - 83.007 mm
Out-of-Round (Max.)...............0.051 mm
Taper (Max.).....................0.051 mm
Pistons
Clearance from Piston (measured 6.0 mm from
bottom of skirt) to bore.......0.018 - 0.050 mm
Weight.....................296-305grams
Land Clearance (Diametrical) . . 0.753 - 0.799 mm
Piston Length....................54.11 mm
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 1
.........................3.203 - 3.337 mm
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 2
.........................4.406 - 4.272 mm
Piston Ring Groove Depth No. 3
.........................3.932 - 3.798 mm
Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston..........0.009 - 0.021 mm
In Rod (Interference).........0.018 - 0.043 mm
Diameter................20.998 - 21.003 mm
End Play............................None
Length....................74.75 - 75.25 mm
Piston Rings
Ring Gap Top Compression Ring . . 0.23 - 0.38 mm
Ring Gap 2nd Compression Ring . . 0.20 - 0.47 mm
Ring Gap Oil Control (Steel
Rails)......................0.25 - 0.64 mm
Ring Side Clearance Compression Ring
Upper.........................0.03 - 0.07
Ring Side Clearance Compression Ring
Lower.....................0.04 - 0.078 mm
Oil Ring (Pack).............0.056 - 0.186 mm
Ring Width Compression Ring
Top ........................1.19 - 1.17 mm
Ring Width Compression Ring
Lower....................1.490 - 1.472 mm
Oil Ring (Pack).............2.984 - 2.854 mm
9 - 2 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 862 of 1200

GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygen
sensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than .745
volts or less than .1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 21
Page 863 of 1200

ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays. If
the PCM does not receive both signals within approx-
imately one second, it will not energize the ASD
relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel pump
relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump, fuel
injectors, ignition coil and heated oxygen sensors.
²The PCM energizes all four injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within664 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If
the PCM does not detect a minimum difference
between the two values, it sets a MAP diagnostic
trouble code into memory.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine RPM
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch
²Battery voltage²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²Both O2 sensors
²All diagnostics
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content
²A/C control positions
²Power steering pressure switch
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor
²Purge system monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to Group 25 for
On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 864 of 1200

below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Power steering pressure switch
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C pressure transducer
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Power steering pressure switch
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in respones to MAP
sensor feedback
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
If decel fuel shutoff is detected, downstream oxy-
gen sensor diagnostics is performed.
WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
²Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to Group 25,
On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The PCM can test many of its own input and out-
put circuits. If the PCM senses a fault in a major
system, the PCM stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) in memory.
For DTC information, refer to Group 25, Emission
Control Systems. See On-Board Diagnostics.
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
The power distribution center (PDC) is located next
to the battery (Fig. 1). The PDC contains the starter
relay, radiator fan relay, A/C compressor clutch relay,
auto shutdown relay, fuel pump relay and several
fuses.
Fig. 1 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 23
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)