1998 PONTIAC BONNEVILLE tire type
[x] Cancel search: tire typePage 187 of 395

0
0
0
0
Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder, and
start your left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane
to pass. When you are far enough
ahead
of the passed vehicle to see its front in your
inside mirror, activate your right lane change signal and
move back into the right lane. (Remember that
your right outside mirror is convex. The vehicle you
just passed may seem to be farther away from you
than it really is.)
Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time
on two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle
too rapidly.
Even though
the brake lamps are not flashing, it may
be slowing down or
starting to turn.
If you’re being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes, steering and acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the
tires meet the road to do what the driver has asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to steer and
constantly
seek an escape route or area of less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most
skids by taking reasonable
care
suited to existing conditions, and by not “overdriving”
those conditions. But skids are always possible.
The
three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling.
In the steering or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip and
lose cornering force. And
in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes
the driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.
If you have the traction control system, remember: It
helps avoid only the acceleration skid.
If you do not have traction control, or if the system is
off, then an acceleration skid is also best handled by
easing your foot
off the accelerator pedal.
4-14
Page 207 of 395
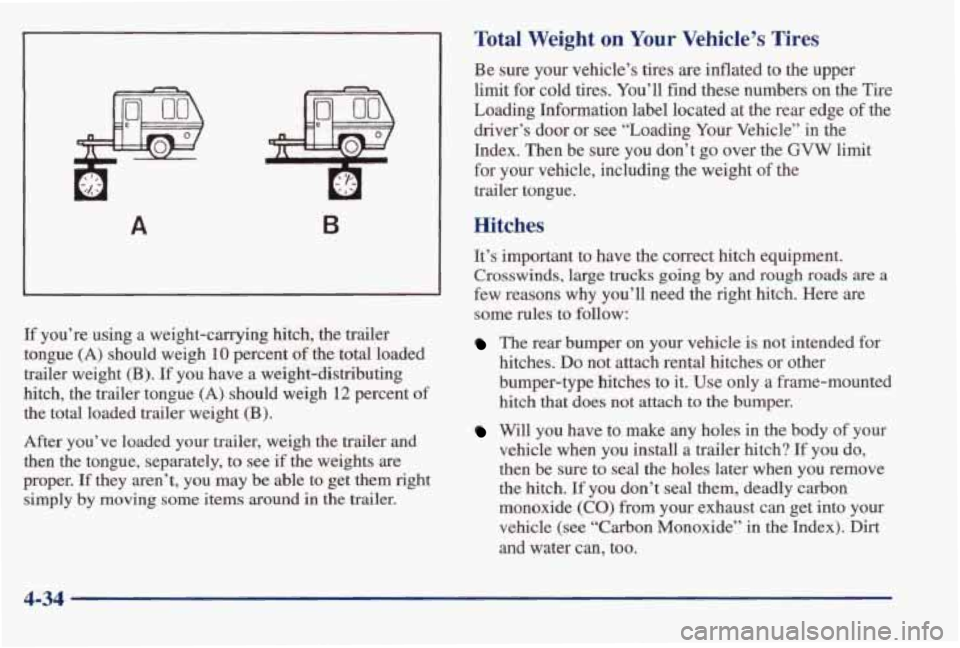
A B
If you’re using a weight-carrying hitch, the trailer
tongue
(A) should weigh 10 percent of the total loaded
trailer weight
(B). If you have a weight-distributing
hitch, the trailer tongue
(A) should weigh 12 percent of
the total loaded trailer weight (B).
After you’ve loaded your trailer, weigh the trailer and
then the tongue, separately, to
see if the weights are
proper.
If they aren’t, you may be able to get them right
simply by moving some
items around in the trailer.
Total Weight on Your Vehicle’s Tires
Be sure your vehicle’s tires are inflated to the upper
limit for cold tires.
You’ll find these numbers on the Tire
Loading Information label located at the rear edge of the
driver’s door or see “Loading Your Vehicle’’
in the
Index. Then be sure you don’t go over the
GVW limit
for
your vehicle, including the weight of the
trailer tongue.
Hitches
It’s important to have the correct hitch equipment.
Crosswinds, large trucks going
by and rough roads are a
few reasons why you’ll need the right hitch. Here are
some rules to follow:
The rear bumper on your vehicle is not intended for
hitches.
Do not attach rental hitches or other
bumper-type hitches
to it. Use only a frame-mounted
hitch that
does not attach to the bumper.
Will you have to make any holes in the body of your
vehicle when you install a trailer hitch?
If you do,
then be sure to seal the holes later when you remove
the hitch. If you don’t seal them, deadly carbon
monoxide
(CO) from your exhaust can get into your
vehicle (see “Carbon Monoxide” in the Index).
Dirt
and water can, too.
4-34
Page 221 of 395

Towing Your Vehicle
Try to have a dealer or a professional towing service tow
your vehicle. See “Roadside Assistance” in the Index.
If your vehicle has been changed or modified since it
was factory-new by adding aftermarket items like fog
lamps, aero skirting,
or special tires and wheels, these
instructions and illustrations may not be correct.
Before you do anything, turn on the hazard
warning flashers.
When you call, tell the towing service:
0
0
0
0
0
That, if you have the SSE model, your
vehicle cannot be towed from the front with
sling-type equipment.
That your vehicle has front-wheel drive.
The make, model and year
of your vehicle.
Whether you can still move
the shift lever.
If there was an accident, what was damaged.
When the towing service arrives, let the tow operator
know that this manual contains detailed towing
instructions and illustrations. The operator may want to
see them.
I A CAUTION:
To help avoid injury to you or others:
0 Never let passengers ride in a vehicle that is
0 Never tow faster than safe or posted speeds.
0 Never tow with damaged parts not fully secured.
0 Never get under your vehicle after it has
been
lifted by the tow truck.
0 Always secure the vehicle on each side with
separate safety chains when towing
it.
0 Never use J-hooks. Use T-hooks instead. being towed.
5-8
Page 292 of 395
For the proper windshield wiper blade replacement length and type, see “Normal Maintenance Replacement
Parts” in the Index.
Tires
Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by
a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions
about your tire warranty and where to obtain service, see
your Pontiac Warranty booklet for details.
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
0 Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result of too much friction.
You could have an airout and a serious
accident. See “Loading Your Vehicle” in
the Index.
CAUTION: (Continued)
0
a
0
Underinflated tires pose the same danger as
overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check
all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked when your tires are cold.
Overinflated tires are more likely to be
cut, punctured or broken
by a sudden
impact
-- such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires
at the recommended pressure.
Worn, old tires can cause accidents.
If your
tread
is badly worn, or if your tires have
been damaged, replace them.
Inflation -- Tire Pressure
The Tire-Loading Information label, which is on the
rear edge
of the driver’s door shows the correct inflation
pressures for your tires when they’re cold. “Cold”
means your vehicle has been sitting for at least three
hours or driven no more than
1 mile (1.6 km).
6-41
Page 293 of 395

NOTICE:
Don’t let anyone tell you that underinflation or
overinflation is
all right. It’s not. If your tires
don’t have enough air (underinflation),
you can
get the following:
0 Too much flexing
0 Too much heat
Tire overloading
Bad wear
Bad handling
0 Bad fuel economy.
If your tires have too much air (overinflation),
you can get the following:
Unusual wear
Bad handling
0 Rough ride
0 Needless damage from road hazards. When
to Check
Check your tires once a month or more.
Don’t forget your compact spare tire. It should
be at
60 psi (420 Wa).
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure.
You can’t tell if your tires are properly inflated
simply by looking at them. Radial tires may look
properly inflated even when they’re underinflated.
Be sure to put the valve caps back on the valve
stems.
They help prevent leaks by keeping out dirt
and moisture.
6-42
Page 295 of 395

When It’s Time for New Tires
One way to tell when it’s
time for
new tires is to
check the treadwear
indicators, which will
appear when your tires have
only 1/16 inch
(1.6 mm) or
less of tread remaining.
You need a
new tire if any of the following statements
are true:
0 You can see the indicators at three or more places
0 You can see cord or fabric showing through the tire’s
The tread or sidewall is cracked, cut or snagged deep
around the tire.
rubber.
enough to show cord or fabric.
0 The tire has a bump, bulge or split.
0 The tire has a puncture, cut or other damage that
can’t be repaired well because of the size or location
of the damage.
Buying New Tires
To find out what kind and size of tires you need, look at
the Tire-Loading Information label.
The tires installed on
your vehicle when it was new had
a Tire Performance Criteria Specification
(TPC Spec)
number on each tire’s sidewall. When you get new tires,
get
ones with that same TPC Spec number. That way
your vehicle will continue to have tires that are designed
to give proper endurance, handling, speed rating,
traction, ride and other things during normal service on
your vehicle.
If your tires have an all-season tread
design,
the TPC number will be followed by an “MS”
(for mud and snow).
If
you ever replace your tires with those not having a
TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size,
load range, speed rating and construction type (bias,
bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
6-44
Page 296 of 395
Mixing tires could cause you to lose control while
driving.
If you mix tires of different sizes or types
(radial and bias-belted tires), the vehicle may not
handle properly, and you could have
a crash.
Using tires
of different sizes may also cause
damage to your vehicle. Be sure to use the same
size and type tires on all wheels.
It’s all right to drive with your compact spare,
though.
It was developed for use on your vehicle.
I a CAUTION:
If you use bias-ply tires on your vehicle, the
wheel rim flanges could develop cracks after
many miles
of driving. A tire and/or wheel could
fail suddenly, causing a crash. Use only radial-ply
tires with the wheels on your vehicle.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
The following information relates to the system
developed by the United States National Highway
Traffic Safety Administration, which grades tires by
treadwear, traction
and temperature performance. (This
applies only to vehicles sold
in the United States.) The
grades are molded on the sidewalls
of most passenger
car tires. The Uniform Tire Quality Grading system does
not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver or temporary use spare tires, tires with
nominal
rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm),
or to some limited-production tires.
While the tires available on General Motors passenger cars and light
trucks may vary with respect to these
grades, they
must also conform to Federal safety
requirements and additional General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria
(PC) standards.
6-45
Page 299 of 395
NOTICE:
The wrong wheel can also cause problems with
bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or
odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper
height, vehicle ground clearance and tire or tire
chain clearance to the body and chassis.
See “Changing a Flat Tire” in the Index for more
information.
Used Replacement Wheels
I
A CAUTION:
Putting a used wheel on your vehicle is
dangerous. You can’t know how it’s been used or
how far it’s been driven. It could fail suddenly
and cause an accident.
If you have to replace a
wheel, use a new GM original equipment wheel.
Tire Chains
I
NOTICE:
Use tire chains only where legal and only when
you must. Use only
SAE Class “S” type chains
that are the proper size for your tires. Install
them on the front tires and tighten them as
tightly
as possible with the ends securely
fastened. Drive slowly and follow the chain
manufacturer’s instructions.
If you can hear the
chains contacting your vehicle, stop and retighten
them.
If the contact continues, slow down until it
stops. Driving too fast or spinning the wheels
with chains on will damage your vehicle.
6-48