1998 OPEL FRONTERA oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 2316 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–71
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical
D07RW010
Circuit Description
The PCM allows current to flow through the solenoid coil
according to the duty cycle (percentage of “on” and “off”
time). This current flow through the solenoid coil creates
a magnetic field that magnetizes the solid core. The
magnetized core attracts the check ball to seat against
spring pressure. This blocks the exhaust for the TCC
signal fluid and allows 2–3 drive fluid to feed to TCC signal
circuit. The TCC signal fluid pressure acts on the TCC
regulator valve to regulate line pressure and to apply fluid
pressure to the torque converter clutch shift valve. When
the TCC shift valve is in the apply position, regulated
apply fluid pressure is directed through the TCC valve to
apply the torque converter clutch. The TCC solenoid is
used in conjunction with the TCC solenoid to regulate fluid
to the torque converter. The TCC solenoid is attached to
the valve body within the transmission.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground or
ignition in the TCC circuit or the TCC solenoid. This is a
type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
No shift solenoid A DTC P0753.
No shift solenoid B DTC P0758.
Ignition is “on”, Engine “run”.
The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains low (zero volts).
The PCM commands the solenoid “off” and the
voltage remains high (B+).
All conditions met for 0.25 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Inhibit TCC engagement.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The MIL/DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
3. This test checks for voltage to the solenoid.
4. This test checks the ability of the PCM and wiring to
control the ignition circuit.
9. This test checks the resistance of the TCC solenoid
and the internal wiring harness.
Page 2386 of 6000
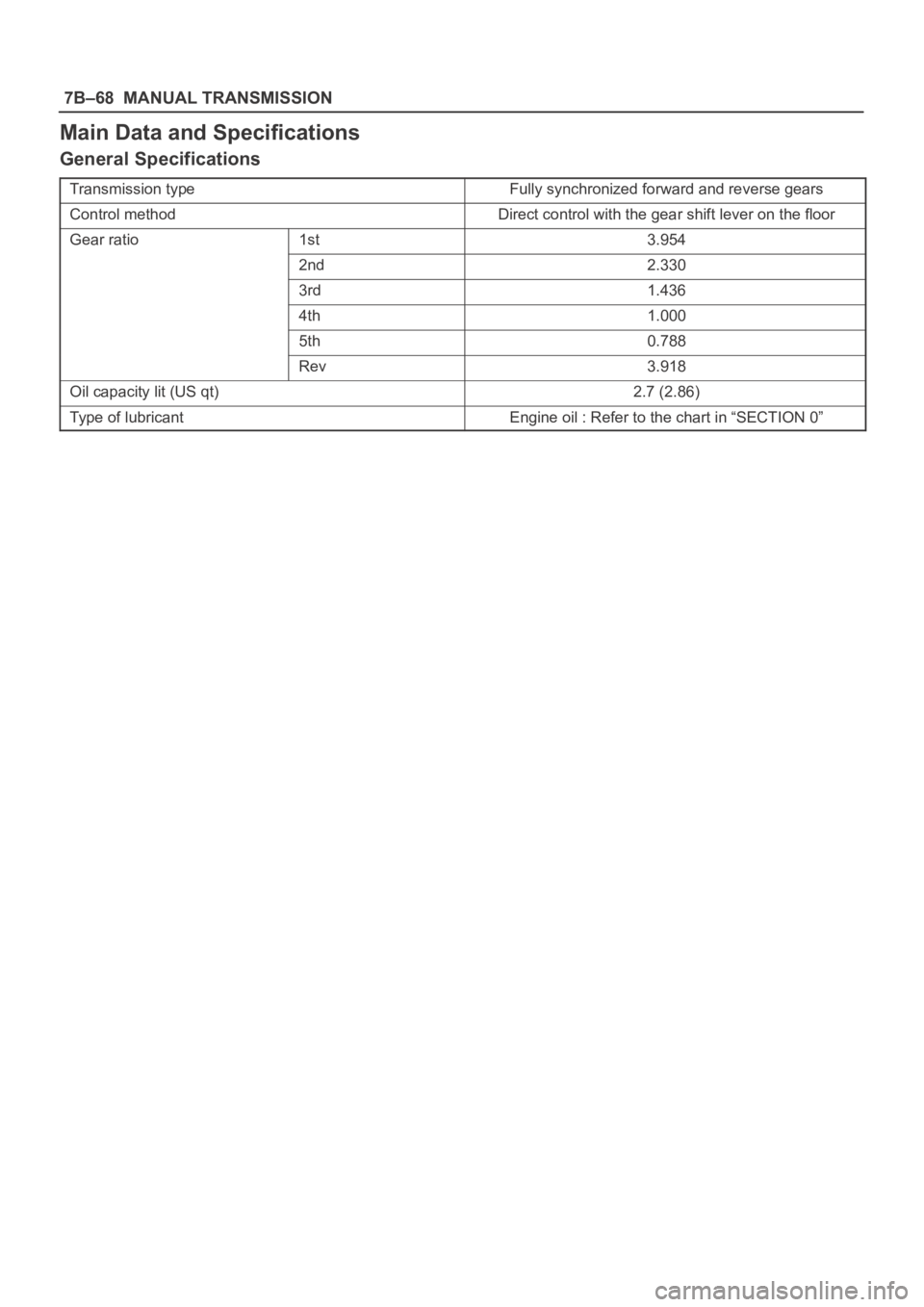
7B–68MANUAL TRANSMISSION
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Transmission typeFully synchronized forward and reverse gears
Control methodDirect control with the gear shift lever on the floor
Gear ratio1st3.954
2nd2.330
3rd1.436
4th1.000
5th0.788
Rev3.918
Oil capacity lit (US qt)2.7 (2.86)
Type of lubricantEngine oil : Refer to the chart in “SECTION 0”
Page 2524 of 6000

CLUTCH7C–15
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points:
1. Install flywheel assembly and crankshaft bearing.
Use the installer 5-8840-0125-0 (J-26516-A) and
driver handle 5-8840-0007-0 (J-8092) to install the
crankshaft bearing then clean and lubricate with
grease.
015RW054
2. Install new flywheel fixing bolts in the order illustrated
and tighten them to the specified torque.
Torque:
6VE1: 54 Nꞏm (5.5 kgꞏm/40 lb ft)
4JX1: 60 Nꞏm (6.1 kgꞏm/44 lb ft)+60
NOTE: Do not reuse the bolt and do not apply oil or thread
lock to the bolt.
015RS047
3. Install the front cover (5) to the transmission case.
4. Tighten eight front cover bolts to the specified torque.
Torque: 17 Nꞏm (1.7 kgꞏm/12 lb ft)
220RW088
5. Apply molybednum disulfide type grease to the pin
hole inner circumferences and thrust surfaces.
6. Attach the shift fork to the front cover and insert the
pin from below of the front cover.
7. Install the washer and snap pin.
201RW019
Page 2557 of 6000

8A–18LIGHTING SYSTEM
Lighting Switch (Combination Switch)
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Remove the instrument panel driver lower cover(5).
Refer to the Instrument Panel Assembly in Body
Structure section.
3. Remove seven screws to remove the steering
cowl(4).
4. Disconnect the SDM (air bag controller) connector
located at lower of the instrument panel driver lower
cover.
5. Remove four fixing screws and disconnect the driver
inflator module connector to remove the driver inflator
module(3).
CAUTION: When carrying a live inflator module,
make sure the bag opening is pointed away from
y o u . I n c a s e o f a n a c c i d e n t a l d e p l o y m e n t , t h e b a g w i l l
then deploy with minimal chance of injury. Never
carry the inflator module by the wires or connector
on the underside of the module.
When placing a live inflator module on a bench or
other surface, always face the bag and trim cover up,
away from the surface. This is necessary so that a
free space is provided to allow the air bag to expand
in the unlikely event of accidental deployment.
6. Remove the steering wheel(2).
Refer to the Steering Wheel in Steering section.
7. Disconnect the SRS coil assembly connector,
remove four fixing screws to remove the SRS coil
assembly(1).
8. Disconnect the lighting switch connector, remove four
fixing screws to remove the lighting switch(6).
825RS039
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points.1. Check to see if the vehicle is in the straight driving
condition and turn the rotary section of the SRS coil
assembly provided to the upper surface of the lighting
switch (combination switch) counterclockwise fully
until it stops.
Then from where it stops, turn it back about 3
rotations to set the alignment marks(7) together
before installing the steering wheel.
825RW099
2. Tighten the steering shaft nut to the specified torque.
Torque: 34 Nꞏm (3.5 kgꞏm/25 lb ft)
3. When connect the double lock type of inflator module
connector, insert the connector completely and lock
at outside.
Imperfect locking may cause malfunction of SRS
system circuit.
4. When installing the steering cowl(11), be sure to pass
the harnesses through the route as shown in the
figure so that the starter switch harness(8), the
combination switch harness(9) and inflator module
harness(10) will not get caught.
431RW014
Page 3445 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–8
the deployment loops, high resistance or opens in the
“Driver Side High”, “Driver Side Low”, “Passenger Side
High” and “Passenger Side Low” circuits and measures
the resistance of the inflator assembly consisting of 1)
Initiators, 2) SRS coil assembly (driver side only), 3)
Connectors and associated wiring.
Normal Operating Voltage Range
The voltage measured between the SDM “Ignition 1”
terminals and “Ground” terminals is between 9 and 16
volts.
Passenger Current Source
An output of the SDM which applies current into the
passenger air bag assembly circuit during the “Initiator
Assembly Resistance Test”.
Passenger Air Bag Assembly
An assembly located in the right side of the instrument
panel consisting of an inflatable bag, an inflator and an
initiator.
Scan Tool
An external computer used to read diagnostic information
from on–board computers via the data link connector.
SDM
Sensing and Diagnostic Module which provides reserve
energy to the deployment loops, deploys the air bags
when required and performs diagnostic monitoring of all
SRS components.
Serial Data
Information representing the status of the SRS.
SRS
Supplemental Restraint System.
SRS Coil Assembly
An assembly of two current–carrying coils in the driver
deployment loop that allows the rotation of the steering
wheel while maintaining the continuous contact of the
driver deployment loop to the driver air bag assembly.
SRS Wiring Harness
The wires and connectors that electrically connect the
components in the SRS.
“Turn–ON”
Test which the SDM performs on the SRS once during
each ignition cycle immediately after “Ignition 1” voltage
is applied to the SDM and before “Continuous
Monitoring”.
Diagnosis
WARNING: TO AVOID DEPLOYMENT WHEN
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS A
BATTERY–POWERED OR AC–POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC., OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A
NONPOWERED PROBE–TYPE TESTER.
INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE
FOLLOWED CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL
INJURY MAY RESULT.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” must always be the
starting point of any SRS diagnosis. The “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” checks for proper “AIR BAG”
warning lamp operation and checks for SRS diagnostic
trouble codes using the scan tool.
1. Current diagnostic trouble codes – Malfunctions that
are presently being detected. Current diagnostic
trouble codes are stored in RAM (Random Access
Memory).
2. History diagnostic trouble codes – All malfunctions
detected since the last time the history memory was
cleared. History diagnostic trouble codes are stored
in EEPROM.
Scan Tool Diagnostics
A scan tool is used to read current and history diagnostic
trouble codes and to clear all diagnostic trouble codes
after a repair is completed. The scan tool must be
updated to communicate with the SRS through a
replaceable cartridge before it can be used for SRS
diagnostics. To use the scan tool, connect it to the data
link connector and turn the ignition switch “ON”. The scan
tool reads serial data from the SDM “Serial Data” line
terminal “24” to the data link connector terminal “9”.
Use Of Special Tools
WARNING: TO AV O I D D E P L O Y M E N T W H E N
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS A
BATTERY–POWERED OR AC–POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC, OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A NON
POWERED PROBE–TYPE TESTER. INSTRUCTIONS
IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE FOLLOWED
CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL INJURY MAY
RESULT. YOU SHOULD BE FAMILIAR WITH THE
TOOLS LISTED IN THIS SECTION UNDER THE
HANDLING SRS SPECIAL TOOLS.
You should be able to measure voltage and resistance.
You should be familiar with proper use of a scan tool such
as the Tech 2 Diagnostic Computer, SRS
Driver/Passenger Load Tool 5–8840–2421–0, Connector
Test Adapter Kit 5–8840–0385–0, and the DVM (Digital
Multimeter) 5–8840–0285–0.
Page 3463 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–26
Special Tools
WARNING: TO AVOID DEPLOYMENT WHEN
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS A
BATTERY–POWERED OR AC–POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC., OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A
NONPOWERED PROBE–TYPE TESTER.
INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE
FOLLOWED CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL
INJURY MAY RESULT.
5–8840–2421–0 SRS Driver/Passenger
Load Tool
901RS146The SRS Driver/Passenger Load Tool 5–8840–2421–0 is
used only when called for in this section. It is used as a
diagnostic aid and safety device to prevent inadvertent air
bag assembly deployment.
The load tool has three yellow connectors attached to its
case.
The three small connectors are electrically functional and
serve as resistive load substitutions.
No more than two connectors are used at any time. One
of the small connectors is used to substitute for the load of
the driver air bag assembly when it is connected at the top
of the column to the SRS coil assembly. Another small
connector is used to substitute for the load of the driver air
bag assembly and the SRS coil assembly when it is
connected at the base of the column to the SRS wiring
harness. The third small connector is used to substitute
for the load of the passenger air bag assembly and
pretensioner seat belt assembly when connected to the
passenger air bag assembly and pretensioner seat belt
assembly harness connector.
By substituting the resistance of the load tool when called
for, a determination can be made as to whether an inflator
circuit component is causing system malfunction and
which component is causing the malfunction. The loadtool should be used only when specifically called for in the
diagnostic procedures.
NOTE: If comand to use 5–8840–2421–0 load tool when
repair the pretensioner seat belt, connect load tool
connector to use for driver air bag and/or passenger air
bag connector.
5–8840–0285–0 DVM
901RS153The 5–8840–0285–0 DVM is the preferred DVM for use in
SRS diagnosis and repair. However, 5–8840–0366–0
may be used if 5–8840–0285–0 is not available. No other
DVMs are approved for SRS diagnosis and repair.
Scan Tool
901RW176The Tech 2 is used to read and clear SRS Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs). Refer to the Tech 2 Operators,
Manual for specific information on how to use the Tech 2.
Page 3467 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–30
Service Precautions for SRS
Component Service
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which they
were removed. If a fastener needs to be replaced, use
the correct part number fastener for that application.
If the correct part number fastener is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or stronger) may
be used. fasteners that are not reused, and those
requiring thread locking compound will be called
out. The correct torque value must be used when
installing fasteners that require it. If the above
conditions are not followed, parts or system damage
could result.
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
AROUND SRS COMPONENTS OR SRS WIRING,
FOLLOW THE PROCEDURES LISTED BELOW TO
TEMPORARILY DISABLE THE SRS. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW PROCEDURES COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL
INJURY OR OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS REPAIRS.
The SDM in Driver–Passenger SRS can maintain
sufficient voltage to cause a deployment for up to 15
seconds after the ignition switch is turned “OFF,” the
battery is disconnected, or the fuse powering the SDM is
removed.
Many of the service procedures require removal of the
“C–21” fuse, and disconnection of the air bag assembly
from the deployment loop to avoid an accidental
deployment. If the air bag assembly is disconnected from
the deployment loop as noted in the “Disabling the SRS”
procedure that follows, service can begin immediately
without waiting for the 15 second time period to expire.
Disabling The SRS
Removal
Turn the ignition switch to “OFF” and turn the steering
wheel so that the vehicle’s wheels are pointing straight
ahead.
1. Remove SRS fuse “C–21” from left dash side lower
fuse block or disconnect battery.
2. Disconnect yellow 2–pin connector at the base of
steering column.
3 . R e m o v e g l o v e b o x a s s e m b l y ; R e f e r t o “ P a s s e n g e r a i r
bag assembly replacement” in this section.
4. Disconnect passenger air bag assembly yellow 2–pin
connector behind the glove box assembly.
CAUTION: W i t h t h e “ C – 2 1 ” f u s e r e m o v e d a n d
ignition switch “ON,” the “AIR BAG” warning lamp
will be “ON.” This is normal operation and does not
indicate an SRS malfunction.
Enabling The SRS
Installation
Turn ignition switch to “LOCK” and remove key.
1. Connect yellow 2–pin connector passenger air bag
assembly.2. Install glove box assembly. Refer to “Passenger Air
Bag Assembly Replacement” in this section.
3. Connect yellow 2–pin connector at the base of the
steering column.
4. Install “AIR BAG” fuse “C–21” to left dash side lower
fuse block or connect battery.
Turn ignition switch to “ON” and verify that the “AIR BAG”
warning lamp turn on 3.5 seconds and then turns “OFF.” If
it does not operate as described, perform the “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” in this section.
Handling / Installation / Diagnosis
1. Air bag assembly should not be subjected to
temperatures above 93
C (200F).
2. Air bag assembly, and SDM should not be used if they
have been dropped from a height of 100 centimeters
(3.28 feet) or more.
3. When a SDM is replaced, it must be oriented with the
arrow on the SDM pointing toward the front of the
vehicle. It is very important for the SDM to be located
flat on the mounting surface, parallel to the vehicle
datum line. It is important that the SDM mounting
surface is free of any dirt or other foreign material.
4. Do not apply power to the SRS unless all components
are connected or a diagnostic chart requests it, as
this will set a diagnostic trouble code.
5. The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” must be the
starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” will verify proper “AIR
BAG” warning lamp operation and will lead you to the
correct chart to diagnose any SRS malfunctions.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis, and incorrect
parts replacements.
Inspections Required After An Accident
CAUTION: C e r t a i n S R S c o m p o n e n t s m u s t b e
replaced after a frontal crash involving air bag
deployment.
In all types of accidents regardless of “Air Bag”
deployment, visually inspect all of the following
components and replace as required:
— Driver air bag assembly
— Passenger air bag assembly
— Driver pretensioner assembly
— Passenger pretensioner assembly
— Steering wheel
— SRS coil assembly
— Steering column
— Knee bolster and instrument panel mounting
attachments
— Driver seat and belt
— Passenger seat and belt
—SDM
SDM always should be checked according to “SDM
Replacement Guidelines.”
Page 3765 of 6000
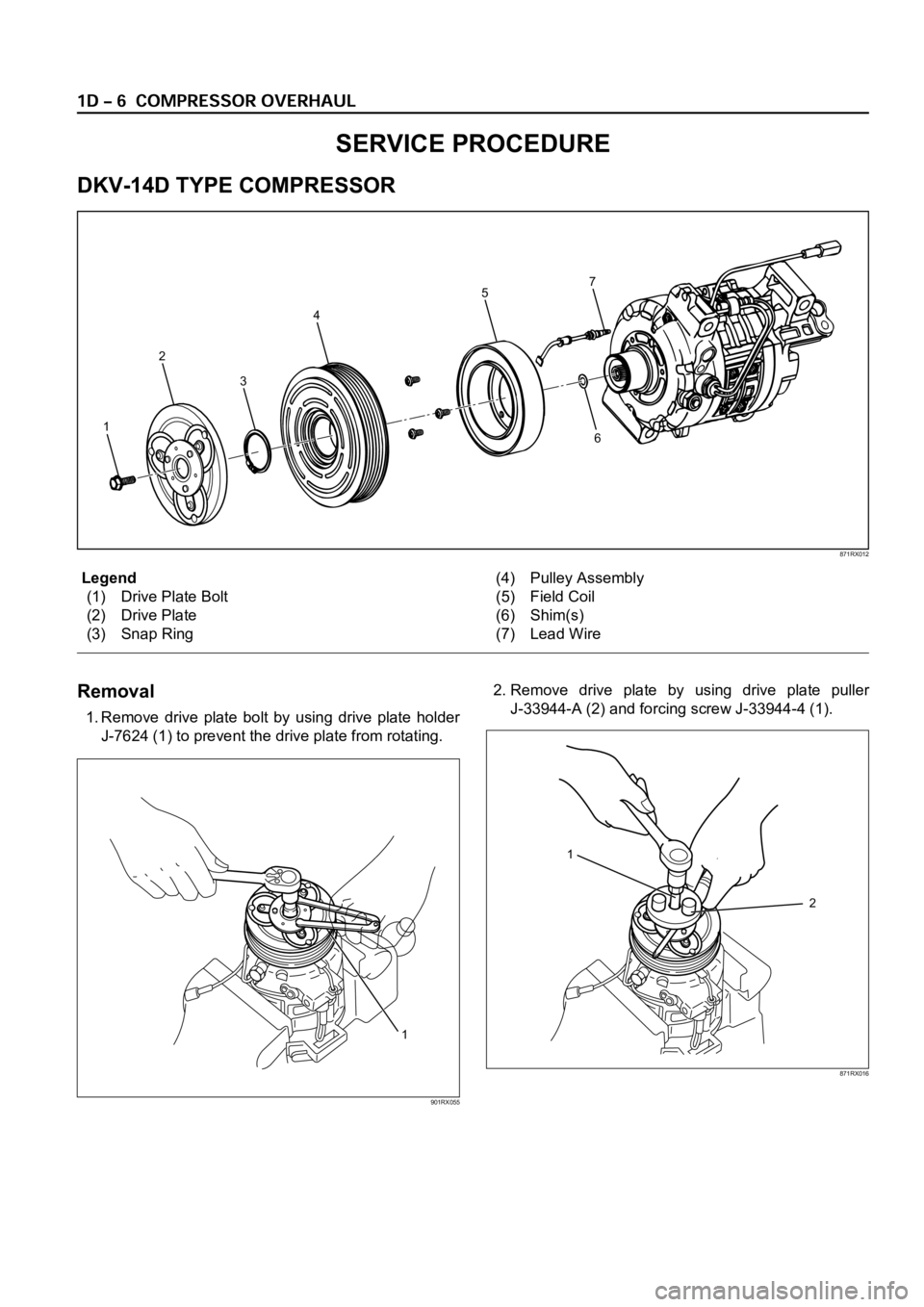
Legend
(1) Drive Plate Bolt
(2) Drive Plate
(3) Snap Ring(4) Pulley Assembly
(5) Field Coil
(6) Shim(s)
(7) Lead Wire
Removal
1. Remove drive plate bolt by using drive plate holder
J-7624 (1) to prevent the drive plate from rotating.2. Remove drive plate by using drive plate puller
J-33944-A (2) and forcing screw J-33944-4 (1).
SERVICE PROCEDURE
DKV-14D TYPE COMPRESSOR
1
2
3
4
5
67
871RX012
1
901RX055
1
2
871RX016