1998 OPEL FRONTERA light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 655 of 6000

DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD) 4B2–84
Chart Hlighting switch circuit
Function of circuitReads in the status of lighting switch and reduces the indicator brightness at night.
Fail conditionEven if the lighting switch is pressed on and off, brightness does not change.
Indicator lamp status
Transfer positionAll position (example TOD mode)
D04RW056
Page 656 of 6000

4B2–85 DRIVE LINE CONTROL SYSTEM (TOD)
StepActionYe sNo
11. Disconnect ECU terminal.
2. Turn on the starter switch.
Is battery voltage observed between ECU terminals (B–68)1 and
(B–67)11?
Go to Step 2
Wirers are broken
lighting SW
circuit. Repair
the circuit.
Go to Step 4
2Turn lighting SW “ON”.
Is 0 V observed between ECU terminal (B–68)1 and (B–67)11?
Go to Step 3
Lighting SW
circuit battery
short. Repair the
circuit.
Go to Step 4
3Connect ECU terminal.
While the lighting switch is pressed on and off, does the
brightness of the indicator change?The phenomenon
is not
reproduced.
Refer to
“Troubles
intermittently
observed”
Go to Step 4
The ECU has
failed. Replace
the ECU.
Go to Step 4
4Check that all the parts are mounted.
Is this step complete?Repeat the
“Diagnosis Flow”.
Return to Step 4
Page 671 of 6000
4C–5 DRIVE SHAFT SYSTEM
7.Remove the parking brake cable mounting
bolts(Behind the back plate)(1).
311RS001
8. Remove the bearing holder mounting nuts.
9. Remove axle shaft assembly.
NOTE: Be sure not to damage the oil seal.
10. Remove snap ring.
11. Using a bearing remover 5–8840–2295–0 and press,
remove retainer together with the bearing holder.
420RW024
12. Remove bearing.
13. Remove bearing holder.
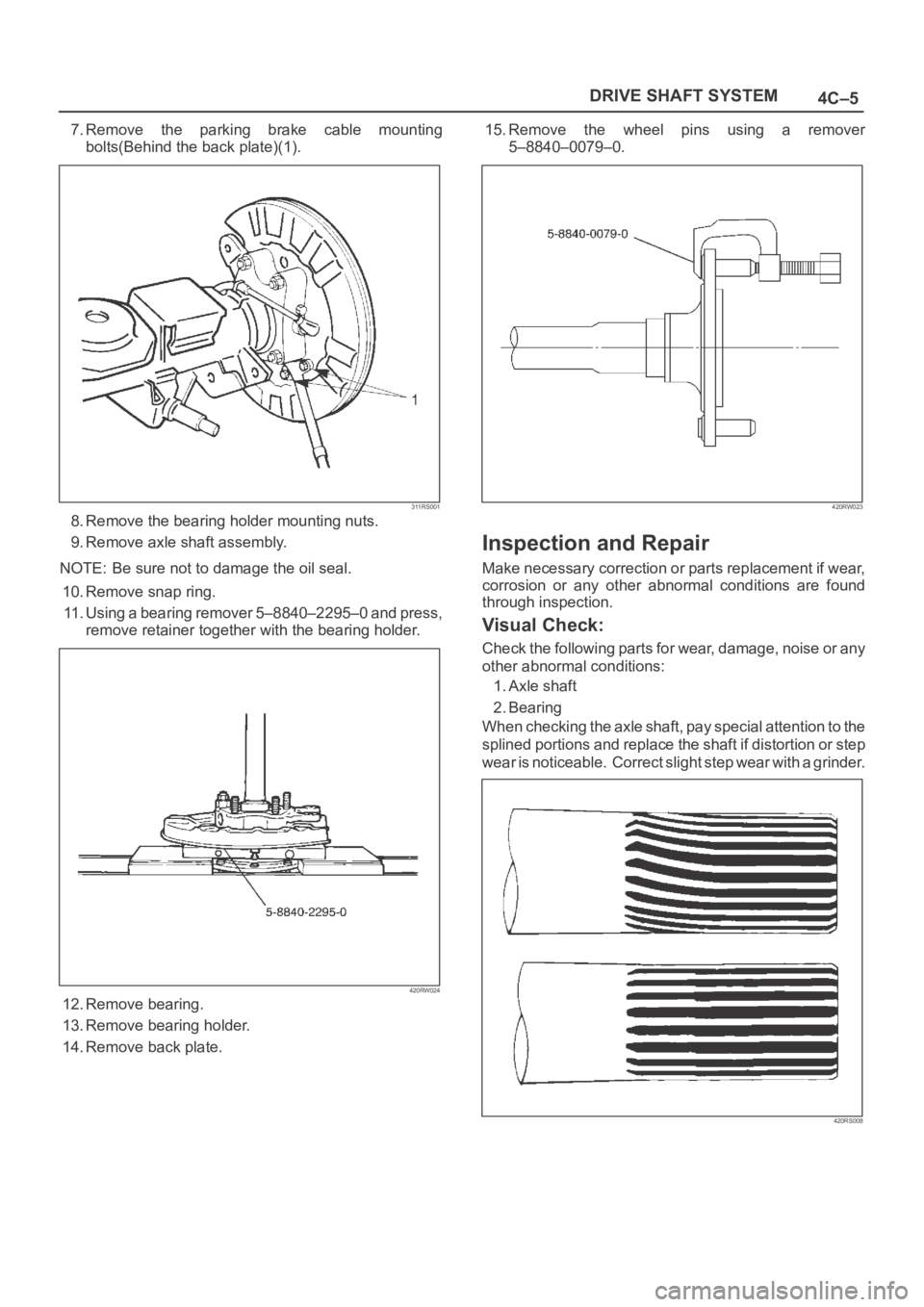
14. Remove back plate.15. Remove the wheel pins using a remover
5–8840–0079–0.
420RW023
Inspection and Repair
Make necessary correction or parts replacement if wear,
corrosion or any other abnormal conditions are found
through inspection.
Visual Check:
Check the following parts for wear, damage, noise or any
other abnormal conditions:
1. Axle shaft
2. Bearing
When checking the axle shaft, pay special attention to the
splined portions and replace the shaft if distortion or step
wear is noticeable. Correct slight step wear with a grinder.
420RS008
Page 728 of 6000

TRANSFER CASE (STANDARD TYPE)
4D1–7
A/T, WO/Shift On The Fly, WO/4WD Switch, model
A07RW055
The transfer case is used to provide a means of providing
power flow to the front axle. The transfer case also
provides a means of disconnecting the front axle,
providing better fuel economy and quieter operation when
the vehicle is driven on improved roads where four wheel
drive is not required. In addition, the transfer case
provides an additional gear reduction when placed in low
range, which is useful when difficult off–road conditions
are encountered.
A floor mounted shift lever is used to select the high–low
range. When four wheel drive switch has been turned on,
the four wheel drive indicator light is designed to come on
when the front axle has been engaged.
Page 755 of 6000

4D1–34
TRANSFER CASE (STANDARD TYPE)
2. If the measured value exceeds the specified limit, the
gear must be replaced.
Gear inside diameter
Standard : 48.000–48.013 mm (1.8898–1.8903 in)
Limit : 48.10 mm (1.894 in)
226RS040
Clutch Hub Spline Play
1. Set a dial indicator to the clutch hub to measured.
2. Move the clutch hub as far as possible to both the right
and the left.
Note the dial indicator reading.
3. If the measured value exceeds the specified limit, the
clutch hub must be replaced.
Clutch hub spline play
Standard : 0–0.1 mm (0–0.004 in)
Limit : 0.2 mm (0.008 in)
226RS042
Bearings
1. Inspect the condition of all the needles and ball
bearings. Wash bearings thoroughly in a cleaning
solvent. Apply compressed air to the bearings.
NOTE: Do not allow the bearings to spin. Turn them
slowly by hand. Spinning bearings may damage the
rollers.
2. Lubricate the bearings with a light oil and check them
for roughness by slowly turning the race by hand.
Ball Bearing Play
1. Use a dial indicator to measure the ball bearing play.
2. If the measured value exceeds the specified limit, the
ball bearing must be replaced.
Limit : 0.2 mm (0.008 in)
226RS043
Synchronizers
The synchronizer hubs and sliding sleeves are a selected
assembly and should be kept together as originally
assembled.
Clean synchronizer components with clean solvent and
air dry.
Inspect the components for the following:
Teeth for wear, scuffs, nicks, burrs or breaks.
Keys and springs for wear, cracks or distortion,
replace if these conditions are present.
If scuffed, nicked or burred conditions cannot be
corrected with a soft stone or crocus cloth, replace the
component.
Block Ring and Insert Clearance
1. Use a vernier caliper to measure the clearance
between the block ring and the insert.
2. If the measured value exceeds the specified limit, the
block ring and the insert must be replaced.
Block ring and insert clearance
Standard : 2.46–2.74 mm (0.097–0.108 in)
Page 811 of 6000

5A–1 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
BRAKES
CONTENTS
Brake Control System 5A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Anti–lock Brake System 5B. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Power–Assisted Brake System 5C. . . . . . . . . . . .
Parking Brakes 5D. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 5A–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 5A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Components 5A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) 5A–3.
ABS Warning Light 5A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wheel Speed Sensor 5A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
G-Sensor 5A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Normal and Anti-lock Braking 5A–4. . . . . . . . . . .
Brake Pedal Travel 5A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Acronyms and Abbreviations 5A–4. . . . . . . . . . . .
General Diagnosis 5A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Information 5A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS Service Precautions 5A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Computer System Service Precautions 5A–5. . .
General Service Precautions 5A–5. . . . . . . . . . . .
Note on Intermittents 5A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Driving ABS Complaint Vehicles 5A–6. . . . .
“ABS” Warning Light 5A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Normal Operation 5A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Diagnostic Flow Chart 5A–6. . . . . . . . . . . .
Basic Inspection Procedure 5A–7. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech 2 Scan Tool 5A–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Getting Started 5A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Procedure 5A–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Data List 5A–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EHCU Connector Pin-out Checks 5A–12. . . . . . . .
Circuit Diagram (LHD model / 6VD1 and
4JG2) 5A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Diagram (LHD model / 4JG2) 5A–14. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (LHD model / 4JG2) 5A–15. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (LHD model / 6VD1) 5A–16. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (LHD model / 6VD1) 5A–17. . . . .
Connector List (LHD model) 5A–18. . . . . . . . . . . .
Part Location (LHD model) 5A–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 6VD1 and
4JG2) 5A–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 4JG2) 5A–22. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 4JG2) 5A–23. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 6VD1) 5A–24. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 6VD1) 5A–25. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 6VE1 and
4JX1) 5A–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 4JX1) 5A–27. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 4JX1) 5A–28. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 6VE1) 5A–29. . . . .
Circuit Diagram (RHD model / 6VE1) 5A–30. . . . .
Connector List (RHD model) 5A–31. . . . . . . . . . . .
Part Location (RHD model) 5A–34. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 5A–35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart A–1 ABS Works Frequently But
Vehicle Does Not Decelerate 5A–35. . . . . . . . . . .
Chart TA-1 ABS Works Frequently But
Vehicle Does Not Decelerate (Use
TECH 2) 5A–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart A-2 Uneven Braking Occurs While
ABS Works 5A–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart A-3, TA-3 The Wheels Are Locked 5A–36.
Chart A-4 Brake Pedal Feed Is Abnormal 5A–37.
Chart A-5, TA-5 Braking Sound (From
EHCU) Is Heard While Not Braking 5A–38. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Codes 5A–39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnosis By “ABS” Warning Light
Illumination Pattern 5A–40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) 5A–40. . . . . . .
Chart B-1 With the key in the ON position
(Before starting the engine). Warning light
(W/L) is not activated. 5A–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-2 EHCU Abnormality (DTC 14) 5A–43. . .
Chart B-3 Power Voltage Drop (DTC 15) 5A–44. .
Chart B-4 CLASS-2 Communication Line
Abnormality (DTC 16) 5A–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-5 G-Sensor Circuit (DTC 21) 5A–45. . . . .
Chart B-6 Abnormal Transmission Input
(DTC 23) 5A–46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-7 Transfer Monitor (DTC 24) 5A–47. . . . .
Chart B-8 EHCU Pump Motor And Motor
Relay Circuit (DTC 32) 5A–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-9 EHCU Pump Valve And Valve
Relay Circuit (DTC 35) 5A–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-10 FL Isolation Solenoid Valve
Abnormality (DTC 41) 5A–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-11 FL Dump Solenoid Valve
Abnormality (DTC 42) 5A–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-12 FR Isolation Solenoid Valve
Abnormality (DTC 43) 5A–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-13 FR Dump Solenoid Valve
Abnormality (DTC 44) 5A–49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-14 Rear Isolation Solenoid Valve
Abnormality (DTC 45) 5A–49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B-15 Rear Dump Solenoid Valve
Abnormality (DTC 46) 5A–49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 813 of 6000

5A–3 BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
General Description
The Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) works on all four
wheels. A combination of wheel speed sensor and
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU) can determine
when a wheel is about to stop turning and adjust brake
pressure to maintain best braking.This system helps the driver maintain greater control of
the vehicle under heavy braking conditions.
C05RW027
Legend
(1) With P&B Valve Model
(2) With LSPV Model
(3) Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU)
(4) Front Wheel Speed Sensor
(5) Rear Wheel Speed Sensor(6) G-Sensor
(7) Proportioning and Bypass (P&B) Valve
(8) Load Sensing Proportioning Valve (LSPV)
(9) Electronic Line
(10) Hydraulic Line
System Components
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU), four Wheel
Speed Sensors, Warning Light, and G-sensor.
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU)
T h e E H C U c o n s i s t s o f A B S c o n t r o l c i r c u i t s , f a u l t d e t e c t o r,
and a fail-safe. It drives the hydraulic unit according to the
signal from each sensor, cancelling ABS to return to
Page 814 of 6000

5A–4
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
normal braking when a malfunction has occurred in the
ABS.
The EHCU has a self-diagnosing function which can
indicate faulty circuits during diagnosis.
The EHCU is mounted on the engine compartment front
right side. It consists of a Motor, Plunger Pump, Solenoid
Valves and Check Valve.
On the outside, the relay box containing a motor relay and
a valve relay is installed.
Solenoid Valves: Reduces or holds the caliper fluid
pressure for each front disc brake or both rear disc brakes
according to the signal sent from the EHCU.
Reservoir: Temporarily holds the brake fluid that returns
from the front and rear disc brake caliper so that pressure
of front disc brake caliper can be reduced smoothly.
Plunger Pump: Feeds the brake fluid held in the reservoir
to the master cylinder.
Motor: Drives the pump according to the signal from
EHCU.
Check Valve: Controls the brake fluid flow.
ABS Warning Light
821RW033Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System have
an amber “ABS” warning light in the instrument panel.
The “ABS” warning light will illuminate if a malfunction in
the Anti-lock Brake System is detected by the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU). In case of an electronic
malfunction, the EHCU will turn “ON” the “ABS” warning
light and disable the Anti-lock braking function.
The “ABS” light will turn “ON” for approximately three
seconds after the ignition switch is to the “ON” position.
If the “ABS” light stays “ON” after the ignition switch is the
“ON” position, or comes “ON” and stays “ON” while
driving, the Anti-lock Brake System should be inspected
for a malfunction according to the diagnosis procedure.
Wheel Speed Sensor
It consists of a sensor and a rotor. The sensor is attached
to the knuckle on the front wheels and to the axle shaft
bearing holder on the rear wheels.
The rotor is press-fit in the axle shaft.The flux generated from electrodes magnetized by a
magnet in the sensor varies due to rotation of the rotor,
and the electromagnetic induction generates alternating
voltage in the coil. This voltage draws a “sine curve” with
the frequency proportional to rotor speed and it allows
detection of wheel speed.
G-Sensor
The G-sensor installed inside the center console detects
the vehicle deceleration speed and sends a signal to the
EHCU. In 4WD operation, all four wheels may be
decelerated in almost the same phase, since all wheels
are connected mechanically.
This tendency is noticeable particularly on roads with low
friction coefficient, and the ABS control is adversely
affected.
The G-sensor judges whether the friction coefficient of
road surface is low or high, and changes the EHCU’s
operating system to ensure ABS control.
Normal and Anti-lock Braking
Under normal driving conditions, the Anti-lock Brake
System functions the same as a standard power assisted
brake system. However, with the detection of wheel
lock-up, a slight bump or kick-back will be felt in the brake
pedal. This pedal “bump” will be followed by a series of
short pedal pulsations which occurs in rapid succession.
The brake pedal pulsation will continue until there is no
longer a need for the anti-lock function or until the vehicle
is stopped. A slight ticking or popping noise may be heard
during brake applications when the Anti-lock features is
being used.
When the Anti-lock feature is being used, the brake pedal
may rise even as the brakes are being applied. This is
also normal. Maintaining a constant force on the pedal
will provide the shortest stopping distance.
Brake Pedal Travel
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System may
be stopped by applying normal force to the brake pedal.
Although there is no need to push the pedal beyond the
point where it stops or holds the vehicle, by applying more
force the pedal will continue to travel toward the floor.
This extra brake pedal travel is normal.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly used
throughout this section:
ABS
Anti-lock Brake System
CKT
Circuit
DLC
Data Link Connector
EHCU
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit
FL
Front Left