1998 OPEL FRONTERA ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 4823 of 6000
6E–166
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
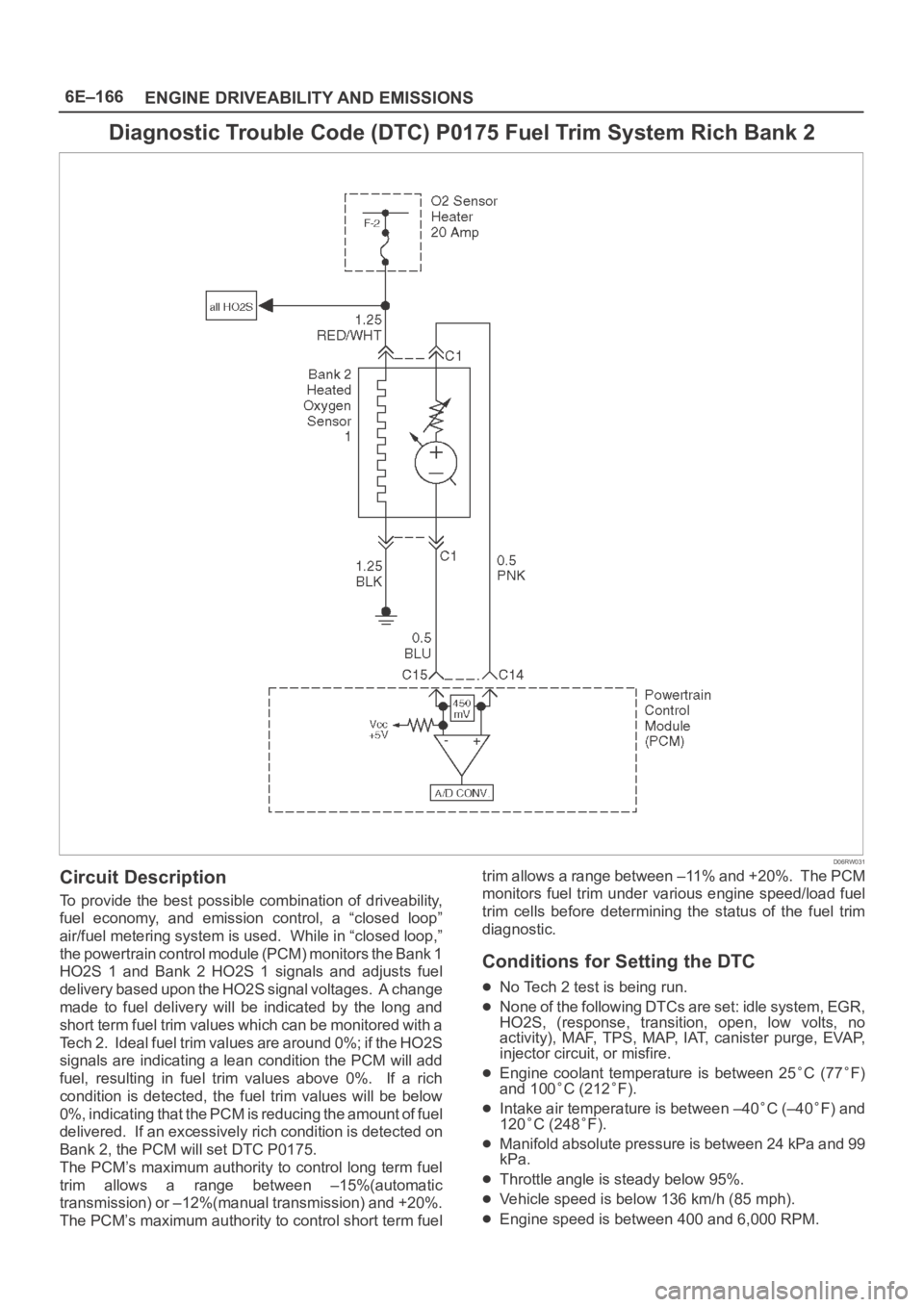
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0175 Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 2
D06RW031
Circuit Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability,
fuel economy, and emission control, a “closed loop”
air/fuel metering system is used. While in “closed loop,”
the powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the Bank 1
HO2S 1 and Bank 2 HO2S 1 signals and adjusts fuel
delivery based upon the HO2S signal voltages. A change
made to fuel delivery will be indicated by the long and
short term fuel trim values which can be monitored with a
Tech 2. Ideal fuel trim values are around 0%; if the HO2S
signals are indicating a lean condition the PCM will add
fuel, resulting in fuel trim values above 0%. If a rich
condition is detected, the fuel trim values will be below
0%, indicating that the PCM is reducing the amount of fuel
delivered. If an excessively rich condition is detected on
Bank 2, the PCM will set DTC P0175.
The PCM’s maximum authority to control long term fuel
trim allows a range between –15%(automatic
transmission) or –12%(manual transmission) and +20%.
The PCM’s maximum authority to control short term fueltrim allows a range between –11% and +20%. The PCM
monitors fuel trim under various engine speed/load fuel
trim cells before determining the status of the fuel trim
diagnostic.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No Tech 2 test is being run.
None of the following DTCs are set: idle system, EGR,
HO2S, (response, transition, open, low volts, no
activity), MAF, TPS, MAP, IAT, canister purge, EVAP,
injector circuit, or misfire.
Engine coolant temperature is between 25C (77F)
and 100C (212F).
Intake air temperature is between –40C (–40F) and
120
C (248F).
Manifold absolute pressure is between 24 kPa and 99
kPa.
Throttle angle is steady below 95%.
Vehicle speed is below 136 km/h (85 mph).
Engine speed is between 400 and 6,000 RPM.
Page 4903 of 6000
6E–246
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
amounts of fuel at idle, but may not be able to supply
enough fuel during heavy acceleration.
Water or alcohol in the fuel may cause low HO2S
voltage during acceleration.
Check for faulty or plugged fuel injector(s).
Check for low fuel.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.4. When the engine is idling or at steady cruise, the
HO2S voltage should vary from between
approximately 100 mV to 900 mV. It is possible to
measure a satisfactory fuel pressure at idle even
though the pressure may drop at high flow
requirements. It may be necessary to watch fuel
pressure at high engine load.
5. Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure
connector to absorb any small amount of fuel
leakage that may occur when installing gauge.
Ignition “ON,” pump pressure should be 280-320
kPa.
DTC P1171 – Fuel System Lean During Acceleration
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any component-related DTCs set?
—
Go to
component
DTC charts
Go to Step 3
31. Check the vehicle’s fuel tank for an adequate
amount of fuel.
2. Add fuel to the vehicle’s fuel tank if the tank is almost
empty.
Was fuel added to the vehicle’s fuel tank?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
41. Place the transmission in park.
2. Using Tech 2, observe HO2S 1 voltage while
running warm engine 75
C-95C (167F-203F) at
1200 RPM.
3. HO2S 1 voltage should vary within the specified
range.
4. Quickly open the throttle halfway for a few seconds.
Did the voltage suddenly rise toward the high end of the
specified range?
100-900 mV
Go to Chart
A-7
Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect the fuel pump relay and crank the
engine to relieve the fuel pressure.
2. Install the fuel pressure gauge.
3. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
4. Disconnect the vacuum line going to the fuel
pressure regulator.
With the engine running, is the fuel pressure within the
specified range?
280-325 kPa
(41-46 psi)
Go to OBD
System
Check
Go to Step 6
6Check for restricted fuel lines or restricted in-line filter.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
Page 4905 of 6000
6E–248
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1380 ABS Rough Road ABS System Fault
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors ABS fault
signal. When PCM receives fault signal, PCM will set
DTC P1380.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Vehicle speed is more than 5 mph.
Load is less than 99%.
Engine revolution is less than 6250 rpm.
PCM receives ABS fault signals from ABS unit.
Ignition on.
Misfire DTCs exist.
100 test failures within 120 test samples.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will store DTC 1380 only, no MIL turn on.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
A history DTC P1380 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm-up cycles have occurred without a fault.
DTC 1380 can be cleared by using Tech-2 or
disconnecting the PCM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
PCM and ABS communication line short circuit to other
line may cause faulty signal. Inspect communication
line.
Follow ABS ECU diagnosis procedure, refer to ABS
procedure page.
DTC P1380 – ABS Rough Road ABS System Fault
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition “ON,” engine “OFF”, review and record
Tech 2 Failure Records Data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Specific DTC” info for DTC
P1380 and Misfire DTCs until the DTC P1380 and
Misfire DTCs test runs. Note the result.
Does the Tech 2 indicates DTC P1380 and Misfire
DTCs failed this ignition?
—
Refer to ABS
diagnosis
After inspect
ABS, unit re-
peat
Step 2
Still problem
exists, go to
Step 3
Clear DTC by
Te c h 2
3Check short circuit among communication line of
PCM/ABS and others.
Was short circuit?
—
Repair wiring
Verify repair
Go to Step 4
4Replace the PCM.
IMPORTANT:The replacement PCM must be
programmed. Refer to
UBS 98model year Immobilizer
Workshop Manual.
Is the action complete?—Verify repair—
Page 4954 of 6000
6E–297 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
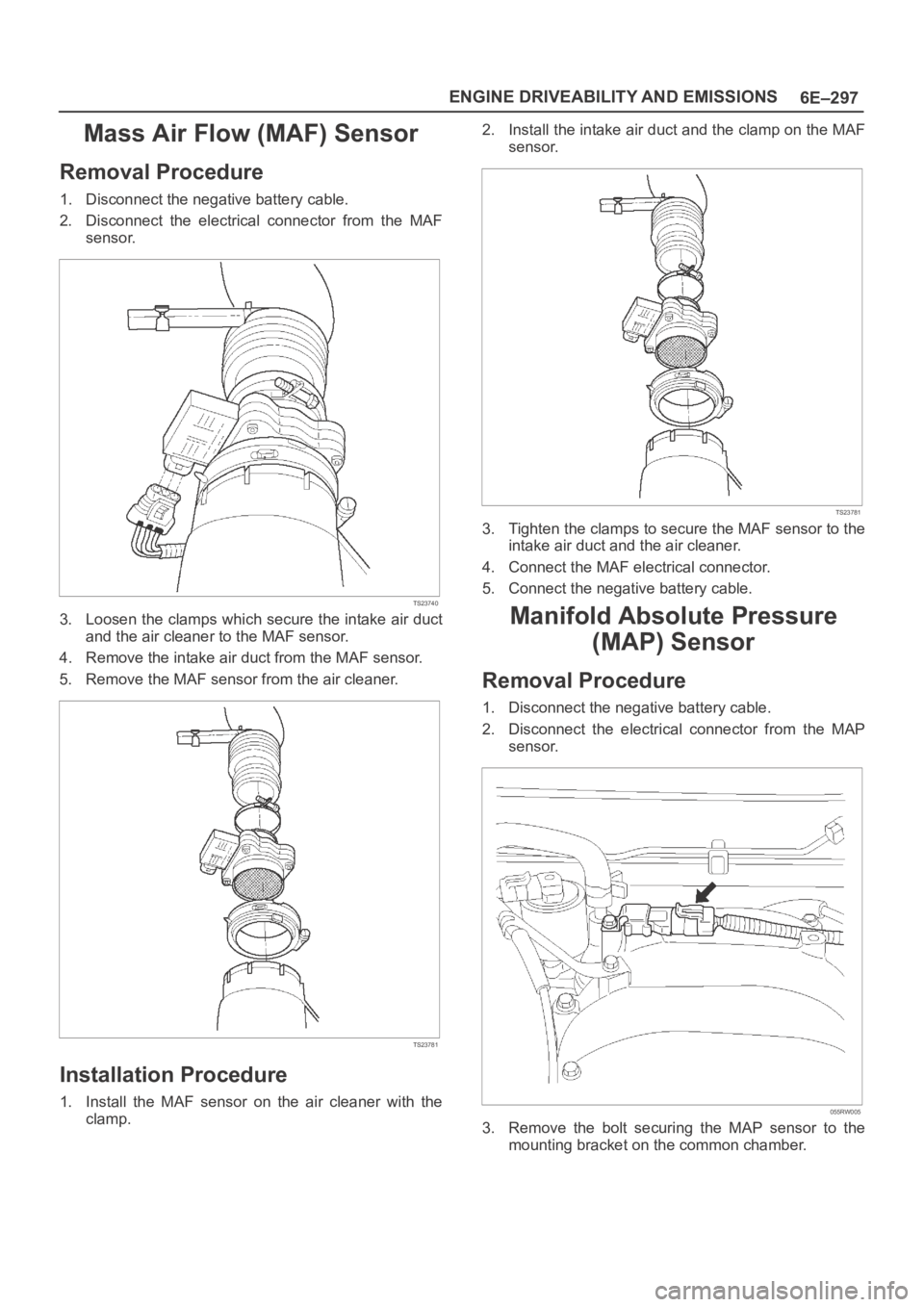
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the electrical connector from the MAF
sensor.
TS23740
3. Loosen the clamps which secure the intake air duct
and the air cleaner to the MAF sensor.
4. Remove the intake air duct from the MAF sensor.
5. Remove the MAF sensor from the air cleaner.
TS23781
Installation Procedure
1. Install the MAF sensor on the air cleaner with the
clamp.2. Install the intake air duct and the clamp on the MAF
sensor.
TS23781
3. Tighten the clamps to secure the MAF sensor to the
intake air duct and the air cleaner.
4. Connect the MAF electrical connector.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) Sensor
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the electrical connector from the MAP
sensor.
055RW005
3. Remove the bolt securing the MAP sensor to the
mounting bracket on the common chamber.
Page 4972 of 6000

6E–315 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Installation Procedure
1. Install the O-ring backup on the fuel injector.
2. Install the new O-ring on the fuel injector.
3. Install the fuel injector on the fuel rail.
055RW009
4. Use new fuel injector retainer clips to retain the fuel
injector to the fuel rail.
5. Coat the end of the fuel injector with engine oil.
6. Install the fuel rail. Refer to
Fuel Rail.
014RW164
7. Install the upper intake manifold. Refer to Common
Chamber in Engine Mechanical.
8. Install the engine cover.
9. Connect the negative battery cable.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
Removal Procedure
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
CAUTION: After relieving the system pressure, a
small amount of fuel may be released when servicing
fuel lines or connections. Reduce the chance of
personal injury by covering the fuel line fittings with
a shop towel before disconnecting the fittings. The
towels will absorb any fuel that may leak out. When
the disconnect is completed, place the towel in an
approved container.
NOTE: Compressed air must never be used to test or
clean a fuel pressure regulator, as damage to the fuel
pressure regulator may result.
NOTE: To prevent damage to the fuel pressure regulator,
do not immerse the pressure regulator in solvent.
1. Depressurize the fuel system. Refer to
Fuel Pressure
Relief Procedure
.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the fuel pump relay. Refer to
Fuel Pump
Relay
.
4. Remove the pressure regulator hose from the fuel
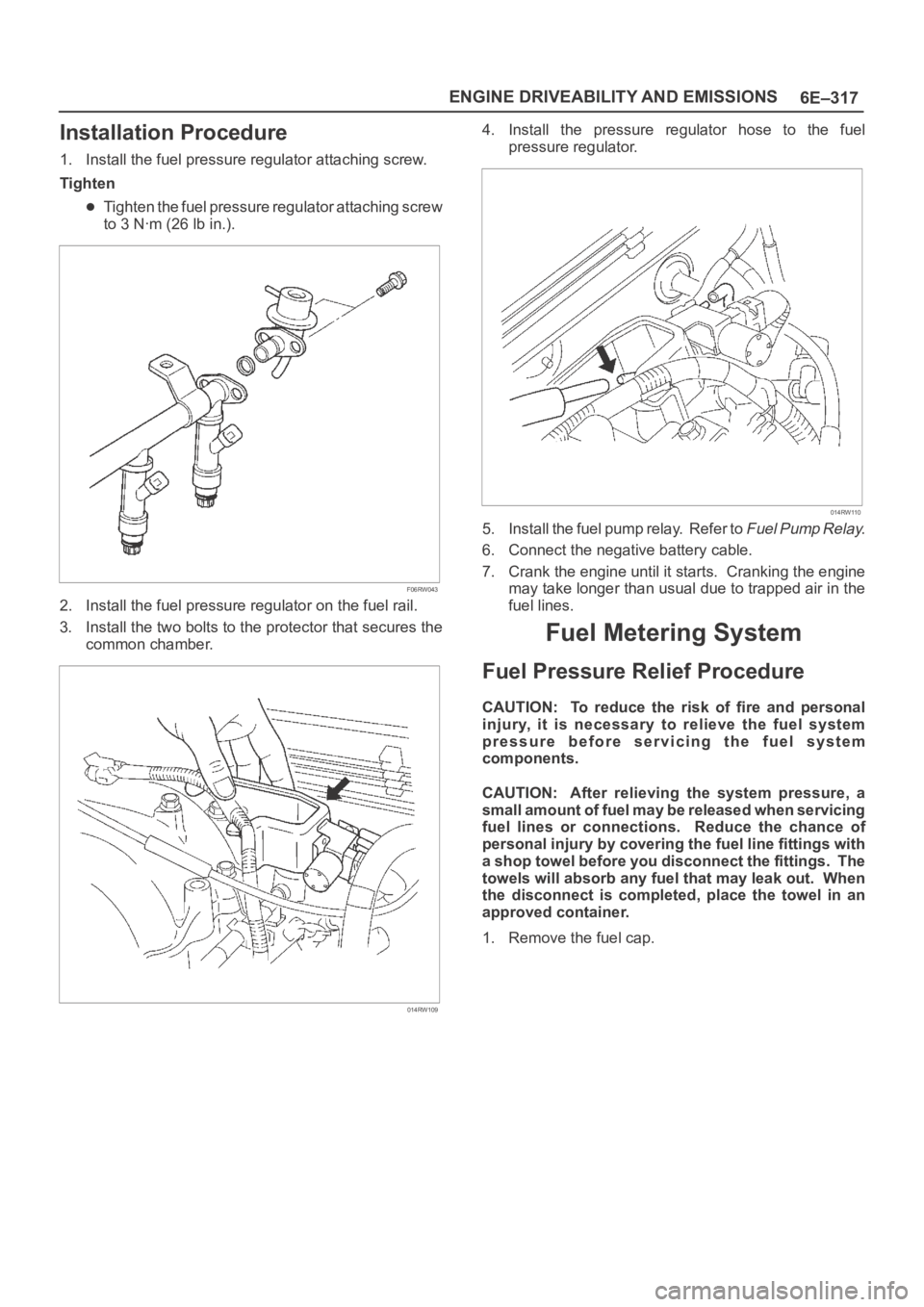
pressure regulator.
014RW110
Page 4974 of 6000
6E–317 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Installation Procedure
1. Install the fuel pressure regulator attaching screw.
Tighten
Tighten the fuel pressure regulator attaching screw
to 3 Nꞏm (26 lb in.).
F06RW043
2. Install the fuel pressure regulator on the fuel rail.
3. Install the two bolts to the protector that secures the
common chamber.
014RW109
4. Install the pressure regulator hose to the fuel
pressure regulator.
014RW110
5. Install the fuel pump relay. Refer to Fuel Pump Relay.
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
7. Crank the engine until it starts. Cranking the engine
may take longer than usual due to trapped air in the
fuel lines.
Fuel Metering System
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
CAUTION: After relieving the system pressure, a
small amount of fuel may be released when servicing
fuel lines or connections. Reduce the chance of
personal injury by covering the fuel line fittings with
a shop towel before you disconnect the fittings. The
towels will absorb any fuel that may leak out. When
the disconnect is completed, place the towel in an
approved container.
1. Remove the fuel cap.
Page 4977 of 6000

6E–320
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
IMPORTANT:An eight-digit identification number is
stamped on the side of the fuel rail. Refer to this number
when you service the fuel rail or when a replacement part
is required.
TS24022
Before removal, the fuel rail assembly may be cleaned
with a spray type engine cleaner. Follow the spray
package instructions. Do not immerse the fuel rails in
liquid cleaning solvent.
1. Depressurize the fuel system. Refer to Fuel Pressure
Relief Procedure in this Section.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the engine cover.
4. Disconnect the accelerator pedal cable from throttle
body and cable bracket.
5. Disconnect the connectors from manifold absolute
pressure sensor, solenoid valve, electric vacuum
sensing valve.
6. Disconnect the vacuum hose on canister VSV and
positive crankcase ventilation hose.
7. Remove the common chamber. Refer to the common
chamber in Engine Mechanical.
1. Lift up carefully on the fuel injectors. Do not
separate the fuel injectors from the fuel rail.
2. If an injector becomes separated from the fuel
rail, the infector O-ring seals and the retainer clip
must be replaced.
3. Drain residual fuel into an approved container.
014RW164
8. If removal of the fuel pressure regulator is necessary,
refer to
Fuel Pressure Regulator.
9. If removal of the fuel injectors is necessary, refer to
Fuel Injectors.
Installation Procedure
1. If the fuel injectors were removed, install them. Refer
to
Fuel Injectors.
2. If the fuel pressure regulator was removed, install it.
Refer to
Fuel Pressure Regulator.
3. Install the common chamber. Refer to common
chamber in engine Mechanical.
014RW164
Page 4978 of 6000
6E–321 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
4. Connect the vacuum hose on Canister VSV and
positive crankcase ventilation hose.
5. Connect the connectors to manifold absolute
pressure sensor, solenoid valve, electric vacuum
sensing valve.
6. Connect the accelerator pedal cable to throttle body
and cable bracket.
7. Install the engine cover.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
9. Crank the engine until it starts. Cranking the engine
may take longer than usual due to trapped air in the
fuel rail and in the injectors.
Fuel Tank
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Loosen the fuel filler cap.
3. Drain the fuel from the tank into an approved
container.
4. Install and tighten the drain plug.
Tighten
Tighten the drain plug to 20 Nꞏm (14 lb ft.).
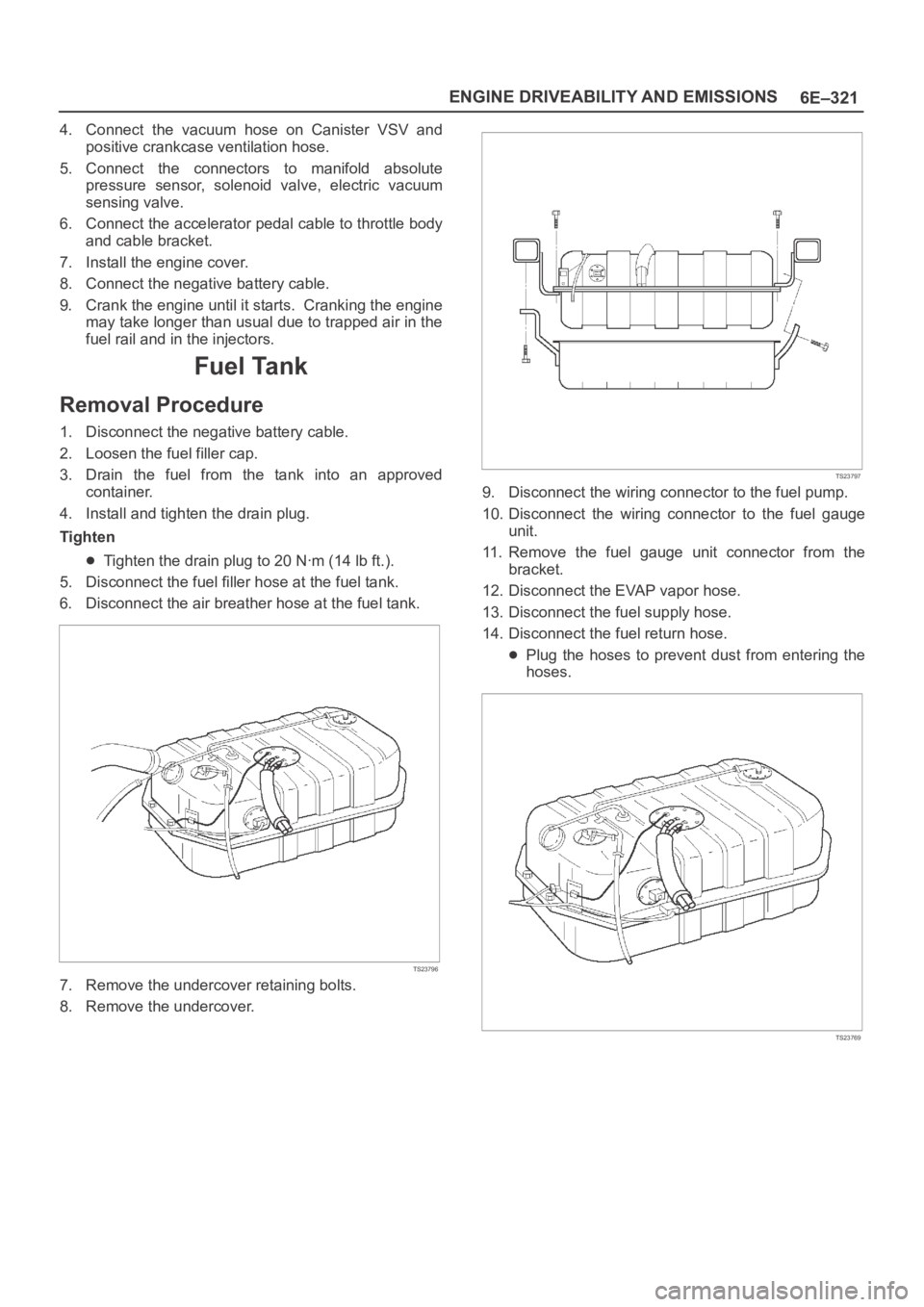
5. Disconnect the fuel filler hose at the fuel tank.
6. Disconnect the air breather hose at the fuel tank.
TS23796
7. Remove the undercover retaining bolts.
8. Remove the undercover.
TS23797
9. Disconnect the wiring connector to the fuel pump.
10. Disconnect the wiring connector to the fuel gauge
unit.
11. Remove the fuel gauge unit connector from the
bracket.
12. Disconnect the EVAP vapor hose.
13. Disconnect the fuel supply hose.
14. Disconnect the fuel return hose.
Plug the hoses to prevent dust from entering the
hoses.
TS23769