1998 OPEL FRONTERA ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 4754 of 6000

6E–97 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Check
D06RW106
Circuit Description
A properly operation exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
system will directly affect the air/fuel requirements of the
engine. Since the exhaust gas introduced into the air/fuel
mixture is an inert gas (contains very little or no oxygen),
less fuel is required to maintain a correct air/fuel ratio.
Introducing exhaust gas into the combustion chamber
lowers combustion temperatures and reduces the
formation of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) in the exhaust gas.
Lower combustion temperatures also prevent detonation.
If the EGR pintle were to stay closed, the inert exhaust
gas would be replaced with air and the air/fuel mixture
would be leaner. The powertrain control module (PCM)
would compensate for the lean condition by adding fuel,
resulting in higher long term fuel trim values.
Diagnostic Aids
The EGR valve chart is a check of the EGR system. An
EGR pintle constantly in the closed position could cause
detonation and high emissions of NOx. It could also result
in high long term fuel trim values in the open throttle cell,
but not in the closed throttle cell. An EGR pintle
constantly in the open position would cause a rough idle.
Also, an EGR mounted incorrectly (rotated 180
) could
cause rough idle. Check for the following items:
EGR passages – Check for restricted or blocked EGR
passages.
Manifold absolute pressure sensor – A manifold
absolute pressure sensor may shift in calibration
enough to affect fuel delivery. Refer to
Manifold
Absolute Pressure Output Check.
Page 4756 of 6000
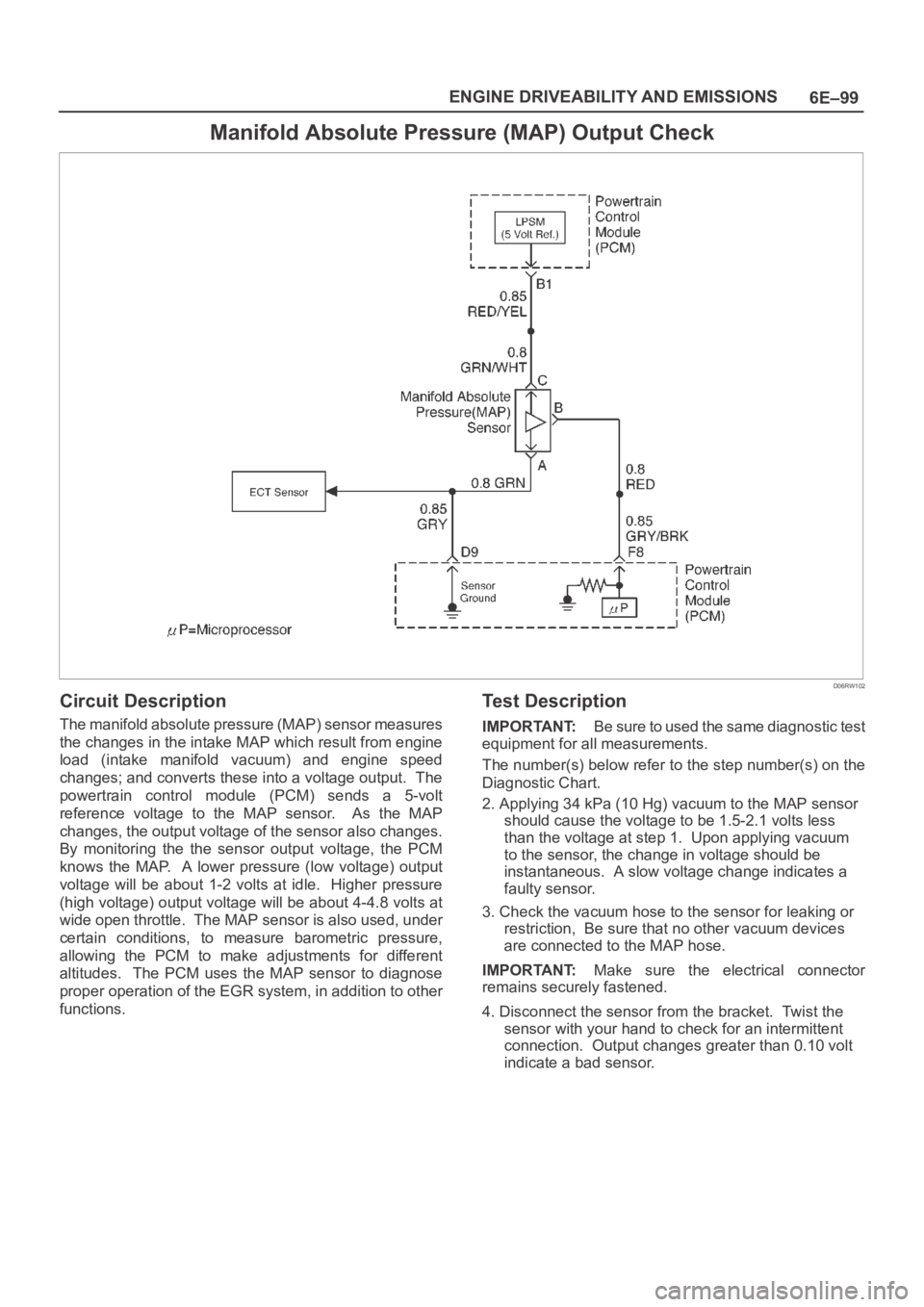
6E–99 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Output Check
D06RW102
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake MAP which result from engine
load (intake manifold vacuum) and engine speed
changes; and converts these into a voltage output. The
powertrain control module (PCM) sends a 5-volt
reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the MAP
changes, the output voltage of the sensor also changes.
By monitoring the the sensor output voltage, the PCM
knows the MAP. A lower pressure (low voltage) output
voltage will be about 1-2 volts at idle. Higher pressure
(high voltage) output voltage will be about 4-4.8 volts at
wide open throttle. The MAP sensor is also used, under
certain conditions, to measure barometric pressure,
allowing the PCM to make adjustments for different
altitudes. The PCM uses the MAP sensor to diagnose
proper operation of the EGR system, in addition to other
functions.
Test Description
IMPORTANT:Be sure to used the same diagnostic test
equipment for all measurements.
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Applying 34 kPa (10 Hg) vacuum to the MAP sensor
should cause the voltage to be 1.5-2.1 volts less
than the voltage at step 1. Upon applying vacuum
to the sensor, the change in voltage should be
instantaneous. A slow voltage change indicates a
faulty sensor.
3. Check the vacuum hose to the sensor for leaking or
restriction, Be sure that no other vacuum devices
are connected to the MAP hose.
IMPORTANT:Make sure the electrical connector
remains securely fastened.
4. Disconnect the sensor from the bracket. Twist the
sensor with your hand to check for an intermittent
connection. Output changes greater than 0.10 volt
indicate a bad sensor.
Page 4757 of 6000
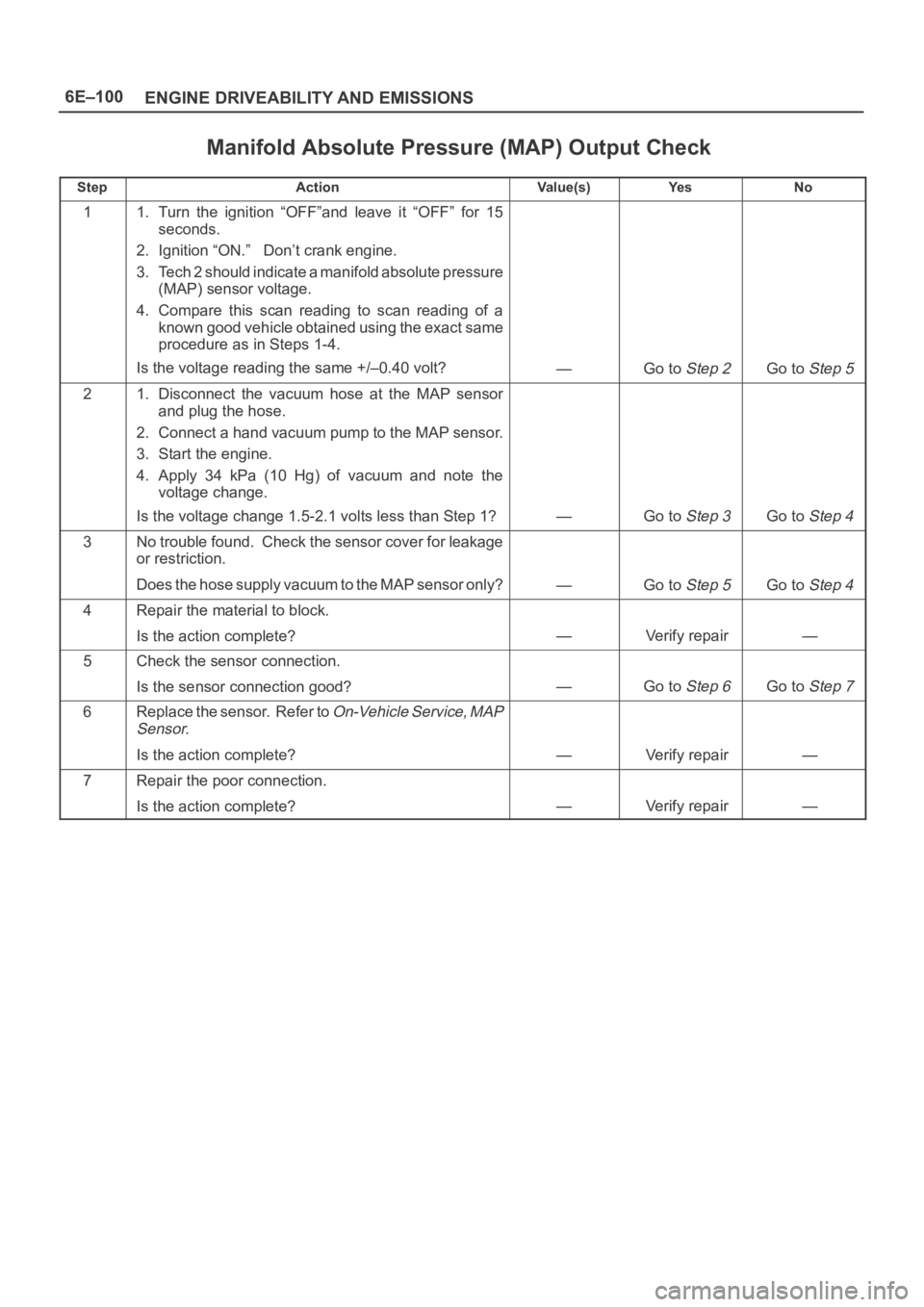
6E–100
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Output Check
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
11. Turn the ignition “OFF”and leave it “OFF” for 15
seconds.
2. Ignition “ON.” Don’t crank engine.
3. Tech 2 should indicate a manifold absolute pressure
(MAP) sensor voltage.
4. Compare this scan reading to scan reading of a
known good vehicle obtained using the exact same
procedure as in Steps 1-4.
Is the voltage reading the same +/–0.40 volt?
—Go to Step 2Go to Step 5
21. Disconnect the vacuum hose at the MAP sensor
and plug the hose.
2. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the MAP sensor.
3. Start the engine.
4. Apply 34 kPa (10 Hg) of vacuum and note the
voltage change.
Is the voltage change 1.5-2.1 volts less than Step 1?
—Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3No trouble found. Check the sensor cover for leakage
or restriction.
Does the hose supply vacuum to the MAP sensor only?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
4Repair the material to block.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
5Check the sensor connection.
Is the sensor connection good?
—Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
6Replace the sensor. Refer to On-Vehicle Service, MAP
Sensor.
Is the action complete?—Verify repair—
7Repair the poor connection.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 4769 of 6000
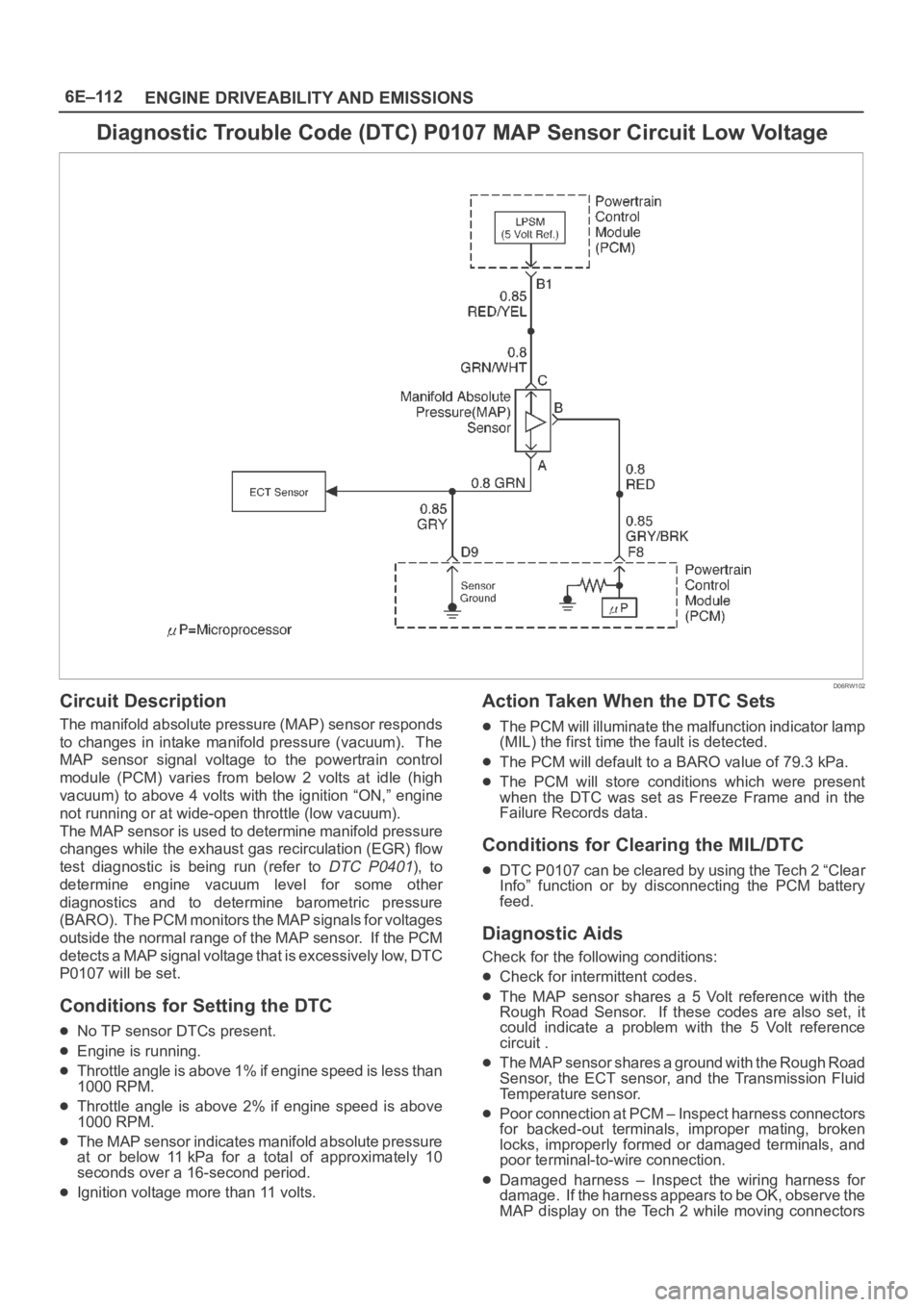
6E–112
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0107 MAP Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
D06RW102
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the powertrain control
module (PCM) varies from below 2 volts at idle (high
vacuum) to above 4 volts with the ignition “ON,” engine
not running or at wide-open throttle (low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine manifold pressure
changes while the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow
test diagnostic is being run (refer to
DTC P0401), to
determine engine vacuum level for some other
diagnostics and to determine barometric pressure
(BARO). The PCM monitors the MAP signals for voltages
outside the normal range of the MAP sensor. If the PCM
detects a MAP signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC
P0107 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No TP sensor DTCs present.
Engine is running.
Throttle angle is above 1% if engine speed is less than
1000 RPM.
Throttle angle is above 2% if engine speed is above
1000 RPM.
The MAP sensor indicates manifold absolute pressure
at or below 11 kPa for a total of approximately 10
seconds over a 16-second period.
Ignition voltage more than 11 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0107 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check for intermittent codes.
The MAP sensor shares a 5 Volt reference with the
Rough Road Sensor. If these codes are also set, it
could indicate a problem with the 5 Volt reference
circuit .
The MAP sensor shares a ground with the Rough Road
Sensor, the ECT sensor, and the Transmission Fluid
Temperature sensor.
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
Page 4772 of 6000
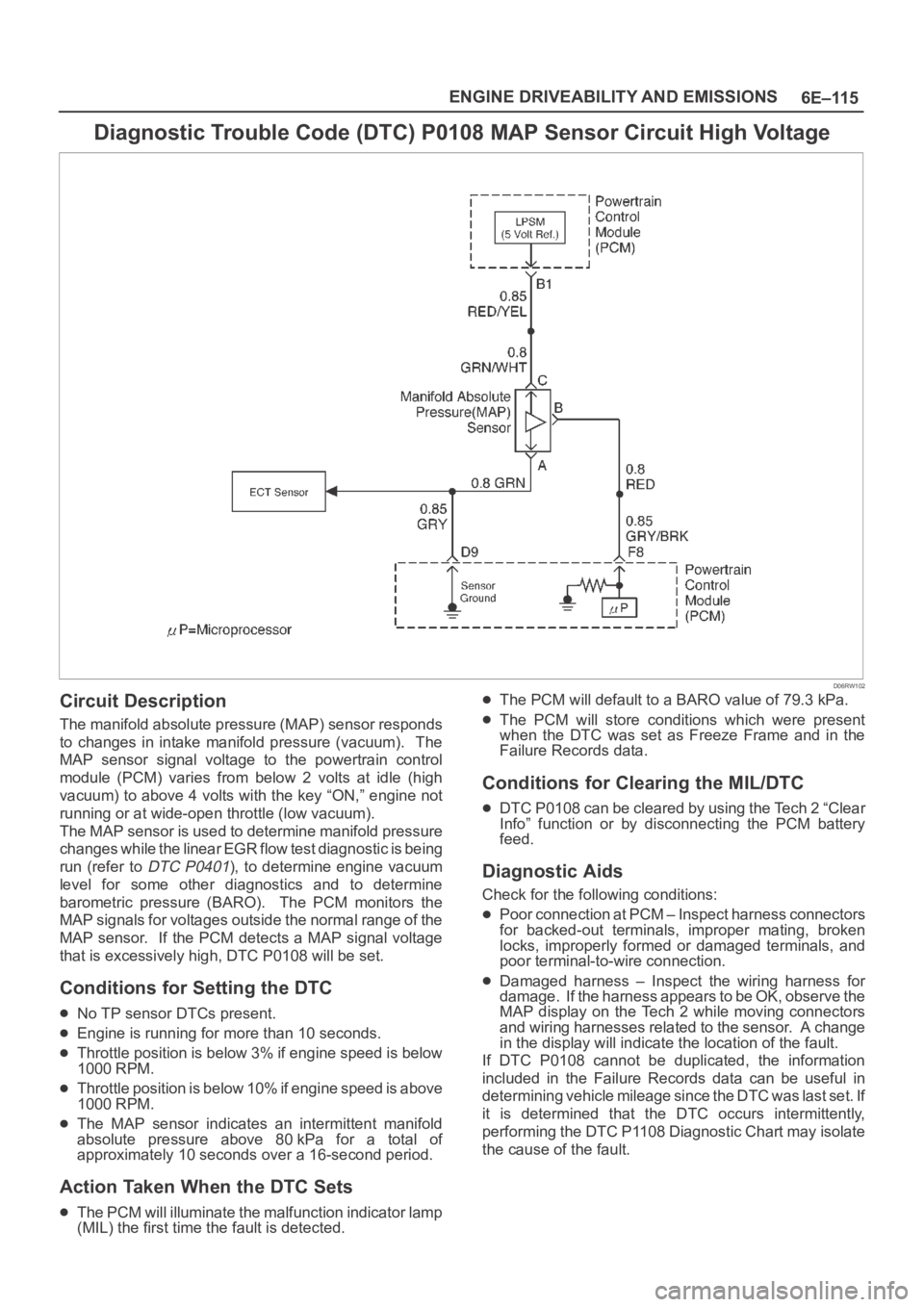
6E–115 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0108 MAP Sensor Circuit High Voltage
D06RW102
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the powertrain control
module (PCM) varies from below 2 volts at idle (high
vacuum) to above 4 volts with the key “ON,” engine not
running or at wide-open throttle (low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine manifold pressure
changes while the linear EGR flow test diagnostic is being
run (refer to
DTC P0401), to determine engine vacuum
level for some other diagnostics and to determine
barometric pressure (BARO). The PCM monitors the
MAP signals for voltages outside the normal range of the
MAP sensor. If the PCM detects a MAP signal voltage
that is excessively high, DTC P0108 will be set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No TP sensor DTCs present.
Engine is running for more than 10 seconds.
Throttle position is below 3% if engine speed is below
1000 RPM.
Throttle position is below 10% if engine speed is above
1000 RPM.
The MAP sensor indicates an intermittent manifold
absolute pressure above 80kPa for a total of
approximately 10 seconds over a 16-second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
The PCM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0108 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0108 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. If
it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1108 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 4811 of 6000
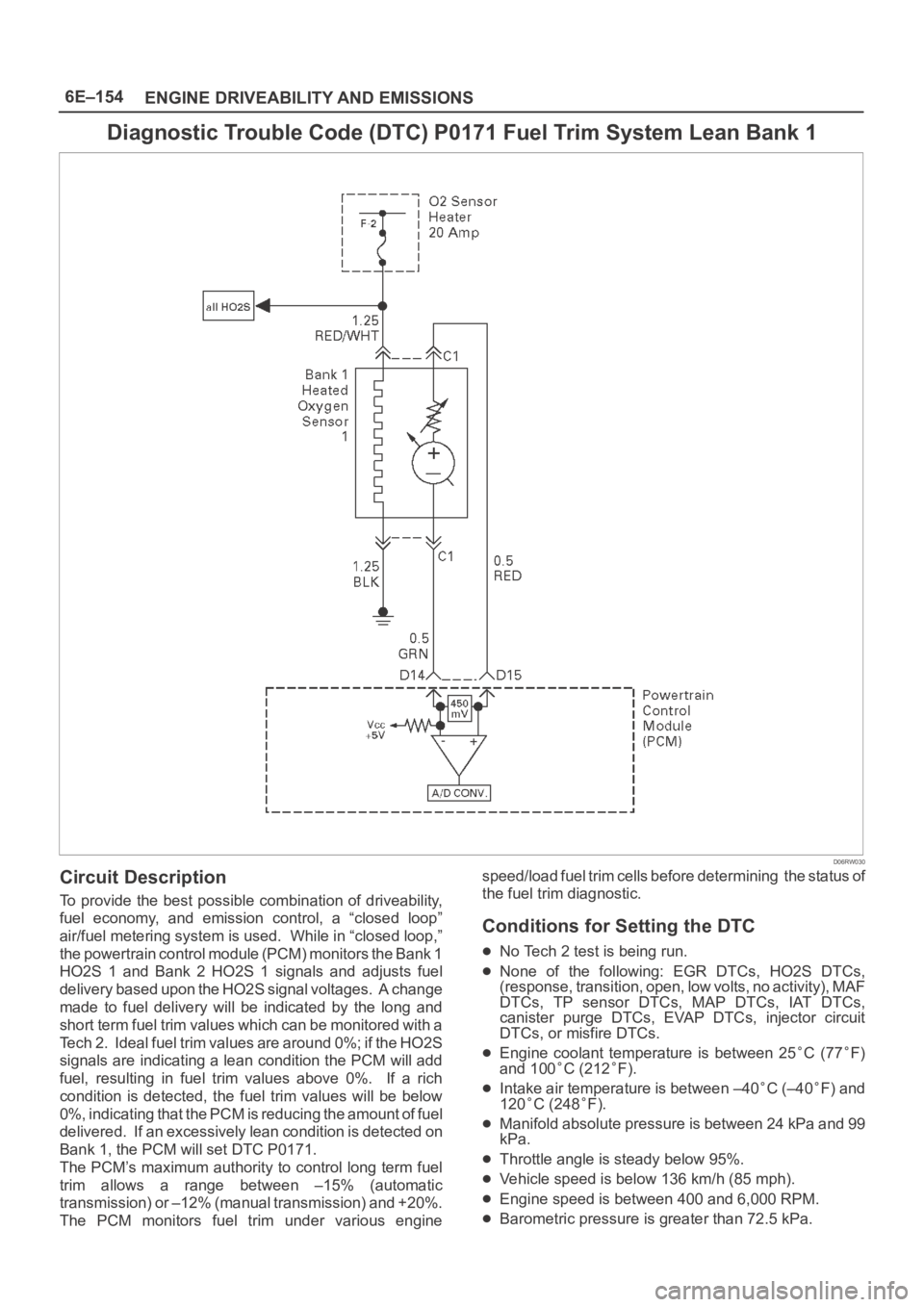
6E–154
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0171 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 1
D06RW030
Circuit Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability,
fuel economy, and emission control, a “closed loop”
air/fuel metering system is used. While in “closed loop,”
the powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the Bank 1
HO2S 1 and Bank 2 HO2S 1 signals and adjusts fuel
delivery based upon the HO2S signal voltages. A change
made to fuel delivery will be indicated by the long and
short term fuel trim values which can be monitored with a
Tech 2. Ideal fuel trim values are around 0%; if the HO2S
signals are indicating a lean condition the PCM will add
fuel, resulting in fuel trim values above 0%. If a rich
condition is detected, the fuel trim values will be below
0%, indicating that the PCM is reducing the amount of fuel
delivered. If an excessively lean condition is detected on
Bank 1, the PCM will set DTC P0171.
The PCM’s maximum authority to control long term fuel
trim allows a range between –15% (automatic
transmission) or –12% (manual transmission) and +20%.
The PCM monitors fuel trim under various enginespeed/load fuel trim cells before determining the status of
the fuel trim diagnostic.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No Tech 2 test is being run.
None of the following: EGR DTCs, HO2S DTCs,
(response, transition, open, low volts, no activity), MAF
DTCs, TP sensor DTCs, MAP DTCs, IAT DTCs,
canister purge DTCs, EVAP DTCs, injector circuit
DTCs, or misfire DTCs.
Engine coolant temperature is between 25C (77F)
and 100C (212F).
Intake air temperature is between –40C (–40F) and
120C (248F).
Manifold absolute pressure is between 24 kPa and 99
kPa.
Throttle angle is steady below 95%.
Vehicle speed is below 136 km/h (85 mph).
Engine speed is between 400 and 6,000 RPM.
Barometric pressure is greater than 72.5 kPa.
Page 4815 of 6000
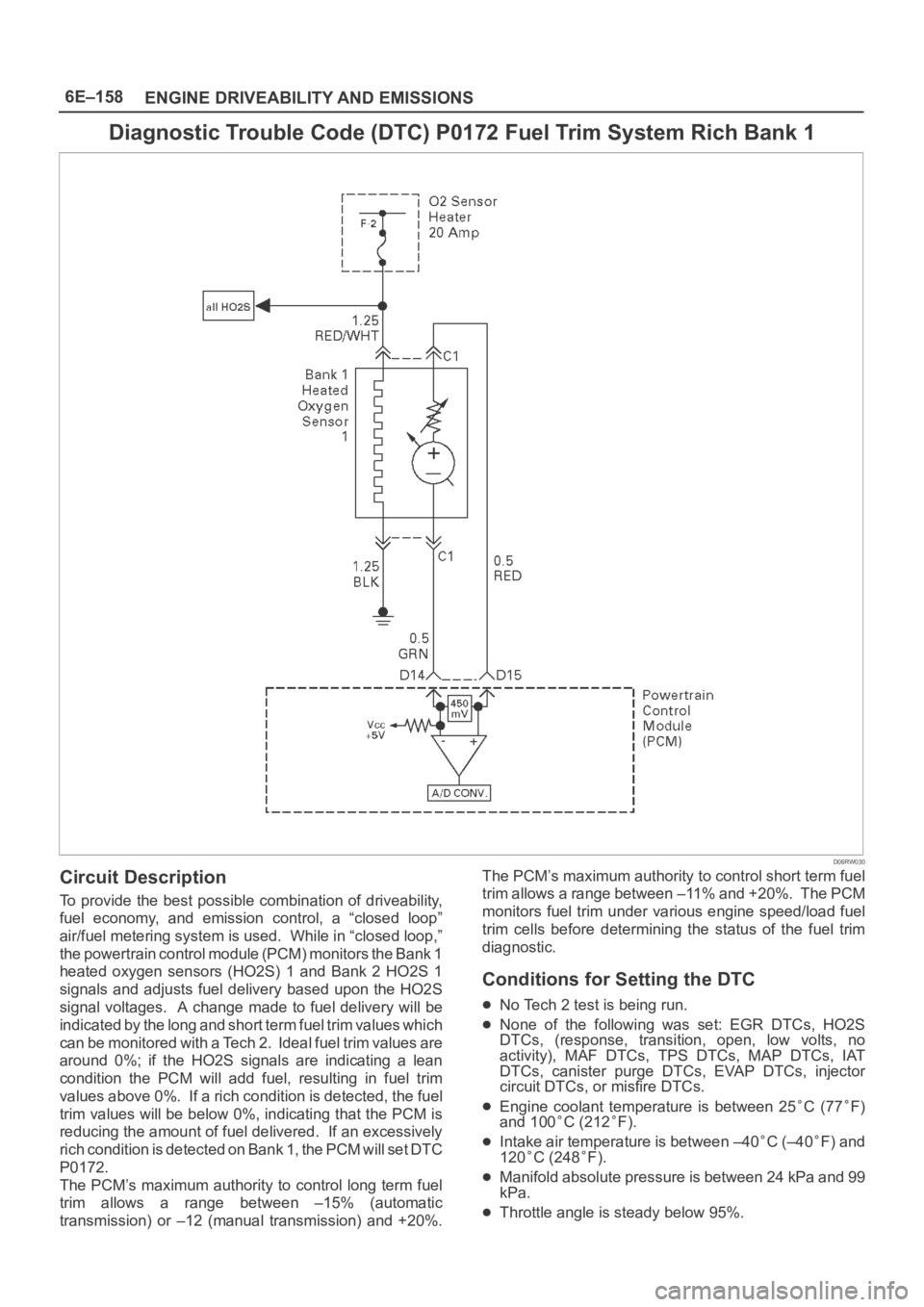
6E–158
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0172 Fuel Trim System Rich Bank 1
D06RW030
Circuit Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability,
fuel economy, and emission control, a “closed loop”
air/fuel metering system is used. While in “closed loop,”
the powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the Bank 1
heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) 1 and Bank 2 HO2S 1
signals and adjusts fuel delivery based upon the HO2S
signal voltages. A change made to fuel delivery will be
indicated by the long and short term fuel trim values which
can be monitored with a Tech 2. Ideal fuel trim values are
around 0%; if the HO2S signals are indicating a lean
condition the PCM will add fuel, resulting in fuel trim
values above 0%. If a rich condition is detected, the fuel
trim values will be below 0%, indicating that the PCM is
reducing the amount of fuel delivered. If an excessively
rich condition is detected on Bank 1, the PCM will set DTC
P0172.
The PCM’s maximum authority to control long term fuel
trim allows a range between –15% (automatic
transmission) or –12 (manual transmission) and +20%.The PCM’s maximum authority to control short term fuel
trim allows a range between –11% and +20%. The PCM
monitors fuel trim under various engine speed/load fuel
trim cells before determining the status of the fuel trim
diagnostic.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No Tech 2 test is being run.
None of the following was set: EGR DTCs, HO2S
DTCs, (response, transition, open, low volts, no
activity), MAF DTCs, TPS DTCs, MAP DTCs, IAT
DTCs, canister purge DTCs, EVAP DTCs, injector
circuit DTCs, or misfire DTCs.
Engine coolant temperature is between 25C (77F)
and 100C (212F).
Intake air temperature is between –40C (–40F) and
120
C (248F).
Manifold absolute pressure is between 24 kPa and 99
kPa.
Throttle angle is steady below 95%.
Page 4819 of 6000
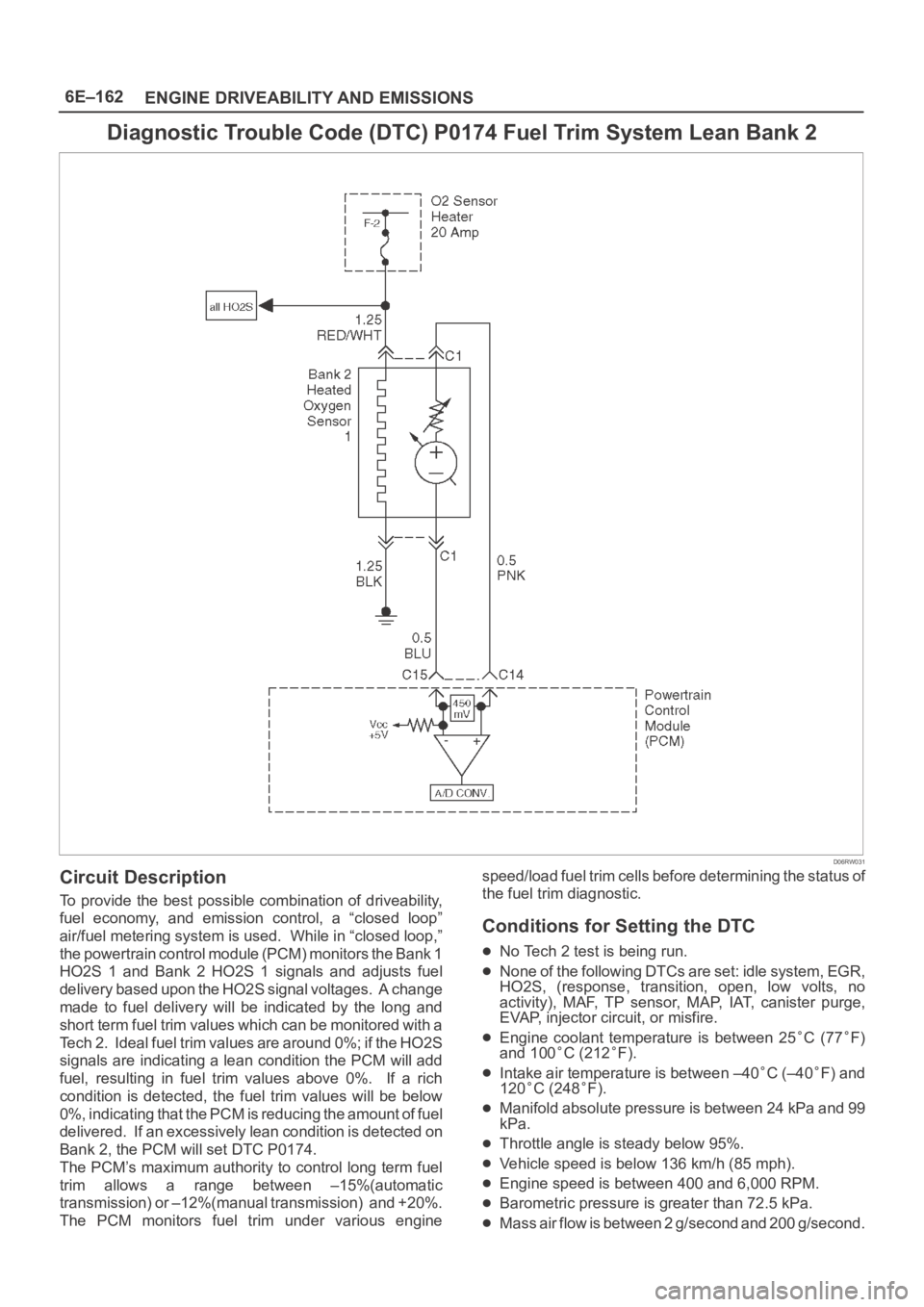
6E–162
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0174 Fuel Trim System Lean Bank 2
D06RW031
Circuit Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability,
fuel economy, and emission control, a “closed loop”
air/fuel metering system is used. While in “closed loop,”
the powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the Bank 1
HO2S 1 and Bank 2 HO2S 1 signals and adjusts fuel
delivery based upon the HO2S signal voltages. A change
made to fuel delivery will be indicated by the long and
short term fuel trim values which can be monitored with a
Tech 2. Ideal fuel trim values are around 0%; if the HO2S
signals are indicating a lean condition the PCM will add
fuel, resulting in fuel trim values above 0%. If a rich
condition is detected, the fuel trim values will be below
0%, indicating that the PCM is reducing the amount of fuel
delivered. If an excessively lean condition is detected on
Bank 2, the PCM will set DTC P0174.
The PCM’s maximum authority to control long term fuel
trim allows a range between –15%(automatic
transmission) or –12%(manual transmission) and +20%.
The PCM monitors fuel trim under various enginespeed/load fuel trim cells before determining the status of
the fuel trim diagnostic.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No Tech 2 test is being run.
None of the following DTCs are set: idle system, EGR,
HO2S, (response, transition, open, low volts, no
activity), MAF, TP sensor, MAP, IAT, canister purge,
EVAP, injector circuit, or misfire.
Engine coolant temperature is between 25C (77F)
and 100C (212F).
Intake air temperature is between –40C (–40F) and
120C (248F).
Manifold absolute pressure is between 24 kPa and 99
kPa.
Throttle angle is steady below 95%.
Vehicle speed is below 136 km/h (85 mph).
Engine speed is between 400 and 6,000 RPM.
Barometric pressure is greater than 72.5 kPa.
Mass air flow is between 2 g/second and 200 g/second.