1998 OPEL FRONTERA ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 4503 of 6000
6A–7
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Condition CorrectionPossible cause
OthersEngine lacks compressionRefer to “Hard Start”
Valve incorrectly seatedLap valve
Air Cleaner Filter cloggedReplace filter element
Valve timing incorrectReadjust
Idle air control valve brokenReplace
Fast idle solenoid defectiveReplace
Positive Crankcase Ventilation valve
defective or cloggedReplace
Rough Engine Running
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Engine misfires periodicallyIgnition coil layer shortedReplace
Spark plugs foulingClean or install hotter type plug
Spark plug(s) insulator nose leakingReplace
Fuel injector(s) defectiveReplace
Powertrain control module faultyReplace
Engine knocks periodicallySpark plugs running too hotInstall colder type spark plugs
Powertrain control module faultyReplace
Engine lacks powerSpark plugs fouledClean
Fuel injectors defectiveReplace
Mass Airflow Sensor or Intake
Airflow Sensor circuit defectiveCorrect or replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Sensor or Manifold Absolute
Pressure Sensor circuit defectiveCorrect or replace
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
or Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor circuit defectiveCorrect or replace
Powertrain Control Module faultyReplace
Intake Air Temperature Sensor or
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
circuit defectiveCorrect or replace
Throttle Position Sensor or Throttle
Position Sensor circuit defectiveCorrect or replace
Knock Sensor or Knock Sensor
circuits defectiveCorrect or replace
Knock Sensor Module or Knock
Sensor Module circuits defectiveCorrect or replace
Page 4504 of 6000
6A–8
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Hesitation
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Hesitation on accelerationThrottle Position Sensor adjustment
incorrectReplace throttle valve assembly
Throttle Position Sensor circuit open
or shortedCorrect or replace
Excessive play in accelerator linkageAdjust or replace
Mass Airflow Sensor circuit open or
poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Mass Airflow Sensor defectiveReplace
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Sensor circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
MAP Sensor defectiveReplace
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
Knock Sensor (KS) Circuit open or
poor connectionsCorrect or replace
KS defectiveReplace
KS Module circuits open or shortedCorrect or replace
KS Module defectiveReplace
IAT Sensor defectiveReplace
Hesitation at high speedsFuel tank strainer cloggedClean or replace
(Fuel pressure too low)Fuel pipe cloggedClean or replace
Fuel filter cloggedReplace
Defective fuel pump systemCheck and replace
Fuel Pressure Control Valve leakingReplace
Hesitation at high speeds
(Fuel injector not working normally)Power supply or ground circuit for
Multiport Fuel Injection System
shorted or openCheck and correct or replace
Fuel Injector defectiveReplace
Cable of Multiport Fuel Injection
System circuit open or poor
connectionsCorrect or replace
Page 4506 of 6000

6A–10
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Engine Lacks Power
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Trouble in fuel systemFuel Pressure Control Valve not
working normallyReplace
Fuel injector cloggedClean or replace
Fuel pipe cloggedClean
Fuel filter clogged or fouledReplace
Fuel pump drive circuit not working
normallyCorrect or replace
Fuel tank not sufficiently breathing
due to clogged Evaporative
Emission Control System circuitClean or replace
Water in fuel systemClean
Inferior quality fuel in fuel systemUse fuel of specified octane rating
Powertrain Control Module supplied
poor voltageCorrect circuit
Throttle Position Sensor cable
broken or poor connectionsCorrect or replace
Throttle Position Sensor defectiveReplace
Mass Airflow Sensor not working
normallyReplace
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
not working normallyReplace
Intake Air Temperature Sensor not
working normallyReplace
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
defectiveReplace
Powertrain Control Module defectiveReplace
Trouble in intake or exhaust systemAir Cleaner Filter cloggedReplace filter element
Air duct kinked or flattenedCorrect or replace
Ignition failure————Refer to Hard Start Troubleshooting
Guide
Heat range of spark plug inadequateInstall spark plugs of adequate heat
range
Ignition coil defectiveReplace
Page 4509 of 6000
6A–13
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Condition CorrectionPossible cause
Engine knockingPreignition due to use of spark plugs
of inadequate heat rangeInstall Spark Plugs of adequate heat
range
Carbon deposits in combustion
chambersClean
Fuel too low in octane ratingReplace fuel
Wide Open Throttle enrichment
system failureRefer to Section 6E
Selection of transmission gear
incorrectCaution operator of incorrect gear
selection
Engine overheatingRefer to “Engine Lacks Power”
OthersWater pump defectiveReplace
Drive belt slippingReplace auto tentioner or drive belt
Abnormal Combustion
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Trouble in fuel systemFuel pressure control valve defectiveReplace
Fuel filter cloggedReplace
Fuel pump cloggedClean or replace
Fuel tank or fuel pipe cloggedClean or replace
Fuel injector cloggedClean or replace
Fuel pump relay defectiveReplace
Power supply cable for fuel pump
broken or poor connectionsReconnect, correct or replace
Mass Airflow (MAF) sensor circuit
open or defectiveCorrect or replace
MAF Sensor defectiveReplace
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
defectiveReplace
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
Sensor circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
ECT Sensor defectiveReplace
Throttle Position Sensor adjustment
incorrectReadjust
Throttle Position Sensor defectiveReplace
Throttle Position Sensor connector
poor connectionsReconnect
Vehicle Speed Sensor cable poor
connections or defectiveCorrect or replace
Vehicle Speed Sensor loosely fixedFix tightly
Vehicle Speed Sensor in wrong
contact or defectiveReplace
Powertrain Control Module cable
poor connections or defectiveCorrect or replace
Page 4513 of 6000

6A–17
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
The instrument panel “CHECK ENGINE” Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminates by self diagnosticsystem when the system checks the starting of engine, or
senses malfunctions.
Condition
Possible causeCorrection
“CHECK ENGINE” MIL does not
illuminate at the starting of engine
Bulb defectiveReplace
illuminate at the starting of engineMIL circuit openCorrect or replace
Command signal circuit to operate
self diagnostic system shortedCorrect or replace
Engine Control Module (PCM) cable
loosely connected, disconnected or
defectiveCorrect or replace
PCM defectiveReplace
“CHECK ENGINE” MIL illuminates,
and stays onDeterioration of heated oxygen
sensor internal elementReplace
Heated oxygen sensor connector
terminal improper contactReconnect properly
Heated oxygen sensor lead wire
shortedCorrect
Heated oxygen sensor circuit openCorrect or replace
Deterioration of engine coolant
temperature sensor internal elementReplace
Engine coolant temperature sensor
connector terminal improper contactReconnect properly
Engine coolant temperature sensor
lead wire shortedCorrect
Engine coolant temperature sensor
circuit openCorrect or replace
Throttle position sensor open or
shorted circuitsCorrect or replace
Deterioration of crankshaft position
sensorReplace
Crankshaft position sensor circuit
open or shortedCorrect or replace
Vehicle speed sensor circuit openCorrect or replace
Manifold absolute pressure sensor
circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
Intake air temperature sensor circuit
open or shortedCorrect or replace
Fuel injector circuit open or shortedCorrect or replace
PCM driver transistor defectiveReplace PCM
Malfunctioning of PCM RAM
(Random Access Memory) or ROM
(Read Only Memory)Replace PCM
Page 4514 of 6000
6A–18
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Cylinder Head Cover LH
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Drain engine coolant from faucet bottom of radiator.
3. Remove engine cover from the dowels on the
common chamber.
F06RW018
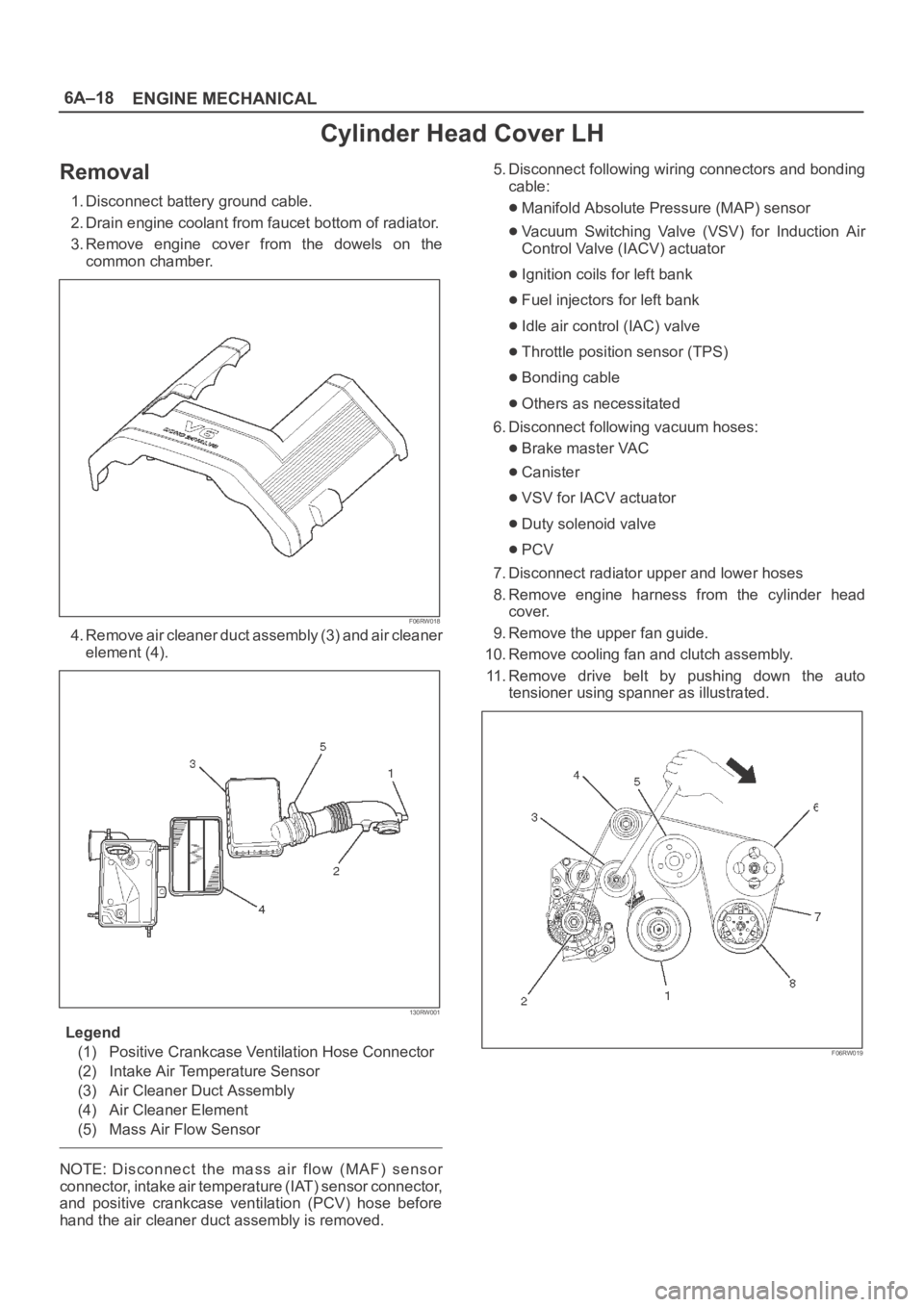
4. Remove air cleaner duct assembly (3) and air cleaner
element (4).
130RW001
Legend
(1) Positive Crankcase Ventilation Hose Connector
(2) Intake Air Temperature Sensor
(3) Air Cleaner Duct Assembly
(4) Air Cleaner Element
(5) Mass Air Flow Sensor
NOTE: Disconnect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor
connector, intake air temperature (IAT) sensor connector,
and positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) hose before
hand the air cleaner duct assembly is removed.5. Disconnect following wiring connectors and bonding
cable:
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
Vacuum Switching Valve (VSV) for Induction Air
Control Valve (IACV) actuator
Ignition coils for left bank
Fuel injectors for left bank
Idle air control (IAC) valve
Throttle position sensor (TPS)
Bonding cable
Others as necessitated
6. Disconnect following vacuum hoses:
Brake master VAC
Canister
VSV for IACV actuator
Duty solenoid valve
PCV
7. Disconnect radiator upper and lower hoses
8. Remove engine harness from the cylinder head
cover.
9. Remove the upper fan guide.
10. Remove cooling fan and clutch assembly.
11. Remove drive belt by pushing down the auto
tensioner using spanner as illustrated.
F06RW019
Page 4520 of 6000

6A–24
ENGINE MECHANICAL
Common Chamber
Removal
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Remove air cleaner duct assembly.
130RW001
Legend
(1) Positive Crankcase Ventilation Hose Connector
(2) Intake Air Temperature Sensor
(3) Air Cleaner Duct Assembly
(4) Air Cleaner Element
(5) Air Flow Sensor
3. Disconnect accelerator pedal cable from throttle body
and cable bracket.
4. Disconnect vacuum booster hose from common
chamber.
5. Disconnect connector from manifold absolute
pressure sensor, idle air control valve, throttle
position sensor, solenoid valve, electric vacuum
sensing valve, and EGR valve.
6. Disconnect vacuum hose on canister VSV and
positive crankcase ventilation hose, fuel rail
assembly with pressure control valve bracket.
7. Remove ventilation hose from throttle valve and
intake duct and remove water hose.
8. Remove the four throttle body fixing bolts.
9. Remove exhaust gas recirculation valve assembly
fixing bolt and nut on common chamber and remove
EGR valve assembly.
10. Remove two bolts from common chamber rear side
for remove fuel hose bracket.
11. Remove common chamber four bolts and four nuts
then remove the common chamber.
025RW001
Legend
(1) Common Chamber
(2) Throttle Valve Assembly
(3) Bolt
Installation
1. Install common chamber and tighten bolts and nuts to
the specified torque.
To r q u e :
Bolt : 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lb ft)
Nut : 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lb ft)
2. Install fuel hose bracket and tighten bolts to specified
torque.
Torque : 10 Nꞏm (1.0 Kgꞏm/89 lb in)
3. Install exhaust gas recirculation valve assembly and
tighten bolt and nut to the specified torque.
Torque : 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lb ft)
4. Install throttle body and tighten bolts to the specified
torque.
Torque : 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lb ft)
5. Install ventilating hose to throttle valve and intake
duct.
6. Connect vacuum hoses on canister VSV and positive
crankcase ventilation hose. Tighten bolts for fuel rail
assembly with pressure control valve bracket.
Torque : 25 Nꞏm (2.5 Kgꞏm/18 lb ft)
7. Connect each connector without fail.
8. Connect vacuum booster hose.
9. Connect accelerator pedal cable.
Accelerator pedal cable adjustment
1. Loosen the adjusting nut and screw cap.
2. Pull outer cable while fully closing the throttle
valve.
Page 4610 of 6000

6C–3
ENGINE FUEL
Adhere to all Notices and Cautions.
All gasoline engines are designed to use only unleaded
gasoline. Unleaded gasoline must be used for proper
emission control system operation.
Its use will also minimize spark plug fouling and extend
engine oil life. Using leaded gasoline can damage the
emission control system and could result in loss of
emission warranty coverage.
All cars are equipped with an Evaporative Emission
Control System. The purpose of the system is to minimize
the escape of fuel vapors to the atmosphere.
Fuel Metering
The Engine Control Module (ECM) is in complete control
of this fuel delivery system during normal driving
conditions.
The intake manifold function, like that of a diesel, is used
only to let air into the engine. The fuel is injected by
separate injectors that are mounted over the intake
manifold.
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load and speed changes, which the MAP
sensor converts to a voltage output.
This sensor generates the voltage to change
corresponding to the flow of the air drawn into the engine.
The changing voltage is transformed into an electric
signal and provided to the ECM.
With receipt of the signals sent from the MAP sensor,
Intake Air Temperature sensor and others, the ECM
determines an appropriate fuel injection pulse width
feeding such information to the fuel injector valves to
effect an appropriate air/fuel ratio.
The Multiport Fuel Injection system utilizes an injection
system where the injectors turn on at every crankshaft
re vol u tion . Th e EC M con tro ls t he in je cto r on tim e so t ha t
the correct amount of fuel is metered depending on
driving conditions.
Two interchangeable “O” rings are used on the injector
that must be replaced when the injectors are removed.
The fuel rail is attached to the top of the intake manifold
and supplies fuel to all the injectors.
Fuel is recirculated through the rail continually while the
engine is running. This removes air and vapors from the
fuel as well as keeping the fuel cool during hot weather
operation.
The fuel pressure control valve that is mounted on the fuel
rail maintains a pressure differential across the injectors
under all operating conditions. It is accomplished by
controlling the amount of fuel that is recirculated back to
the fuel tank based on engine demand.
See Section “Driveability and Emission” for more
information and diagnosis.