1998 OPEL FRONTERA Electrical
[x] Cancel search: ElectricalPage 2209 of 6000
7A–55 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
242RW008
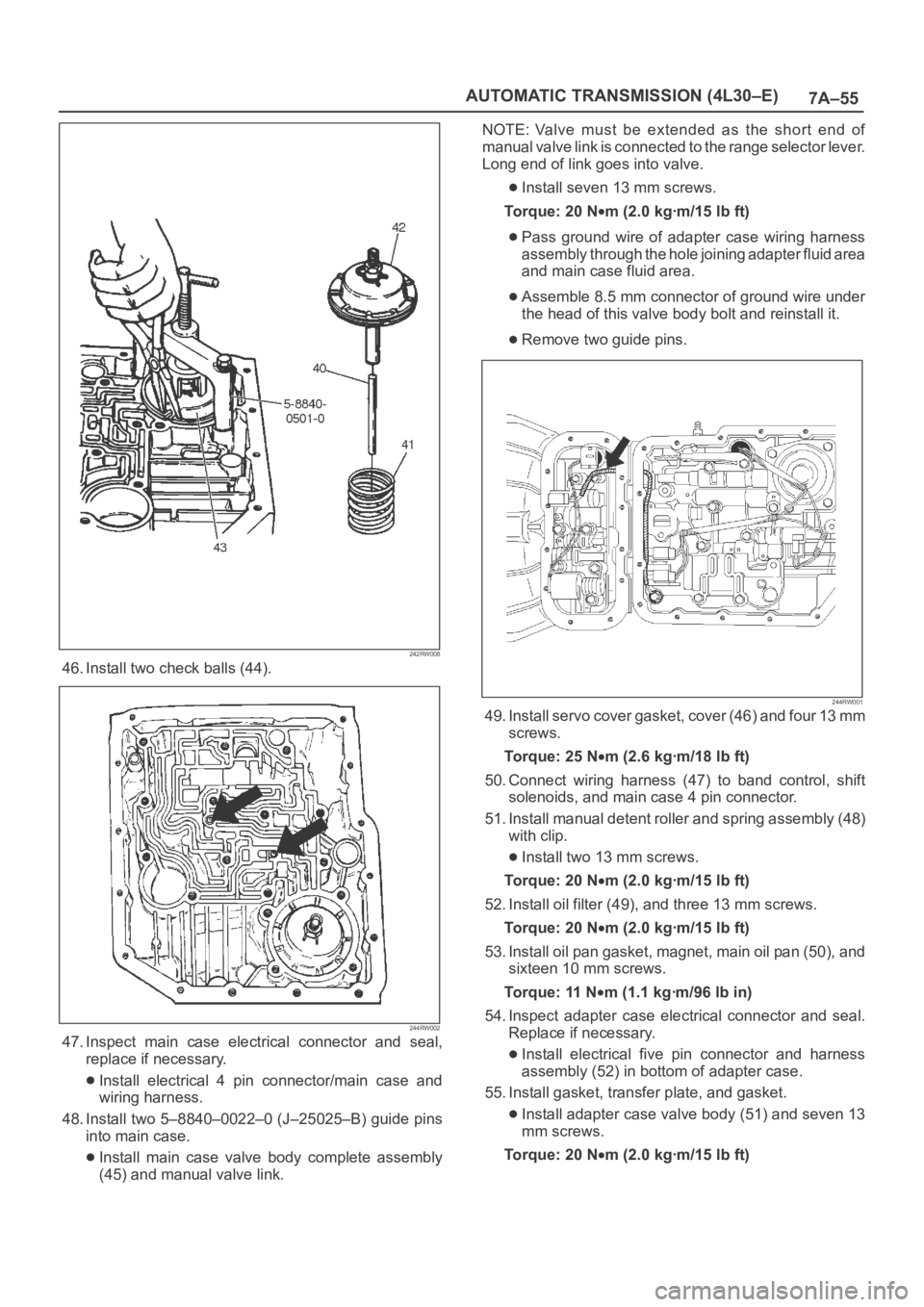
46. Install two check balls (44).
244RW002
47. Inspect main case electrical connector and seal,
replace if necessary.
Install electrical 4 pin connector/main case and
wiring harness.
48. Install two 5–8840–0022–0 (J–25025–B) guide pins
into main case.
Install main case valve body complete assembly
(45) and manual valve link.NOTE: Valve must be extended as the short end of
manual valve link is connected to the range selector lever.
Long end of link goes into valve.
Install seven 13 mm screws.
To r q u e : 2 0 N
m (2.0 kgꞏm/15 lb ft)
Pass ground wire of adapter case wiring harness
assembly through the hole joining adapter fluid area
and main case fluid area.
Assemble 8.5 mm connector of ground wire under
the head of this valve body bolt and reinstall it.
Remove two guide pins.
244RW001
49. Install servo cover gasket, cover (46) and four 13 mm
screws.
To r q u e : 2 5 N
m (2.6 kgꞏm/18 lb ft)
50. Connect wiring harness (47) to band control, shift
solenoids, and main case 4 pin connector.
51. Install manual detent roller and spring assembly (48)
with clip.
Install two 13 mm screws.
To r q u e : 2 0 N
m (2.0 kgꞏm/15 lb ft)
52. Install oil filter (49), and three 13 mm screws.
To r q u e : 2 0 N
m (2.0 kgꞏm/15 lb ft)
53. Install oil pan gasket, magnet, main oil pan (50), and
sixteen 10 mm screws.
To r q u e : 11 N
m (1.1 kgꞏm/96 lb in)
54. Inspect adapter case electrical connector and seal.
Replace if necessary.
Install electrical five pin connector and harness
assembly (52) in bottom of adapter case.
55. Install gasket, transfer plate, and gasket.
Install adapter case valve body (51) and seven 13
mm screws.
Torque: 20 N
m (2.0 kgꞏm/15 lb ft)
Page 2238 of 6000
7A–84
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
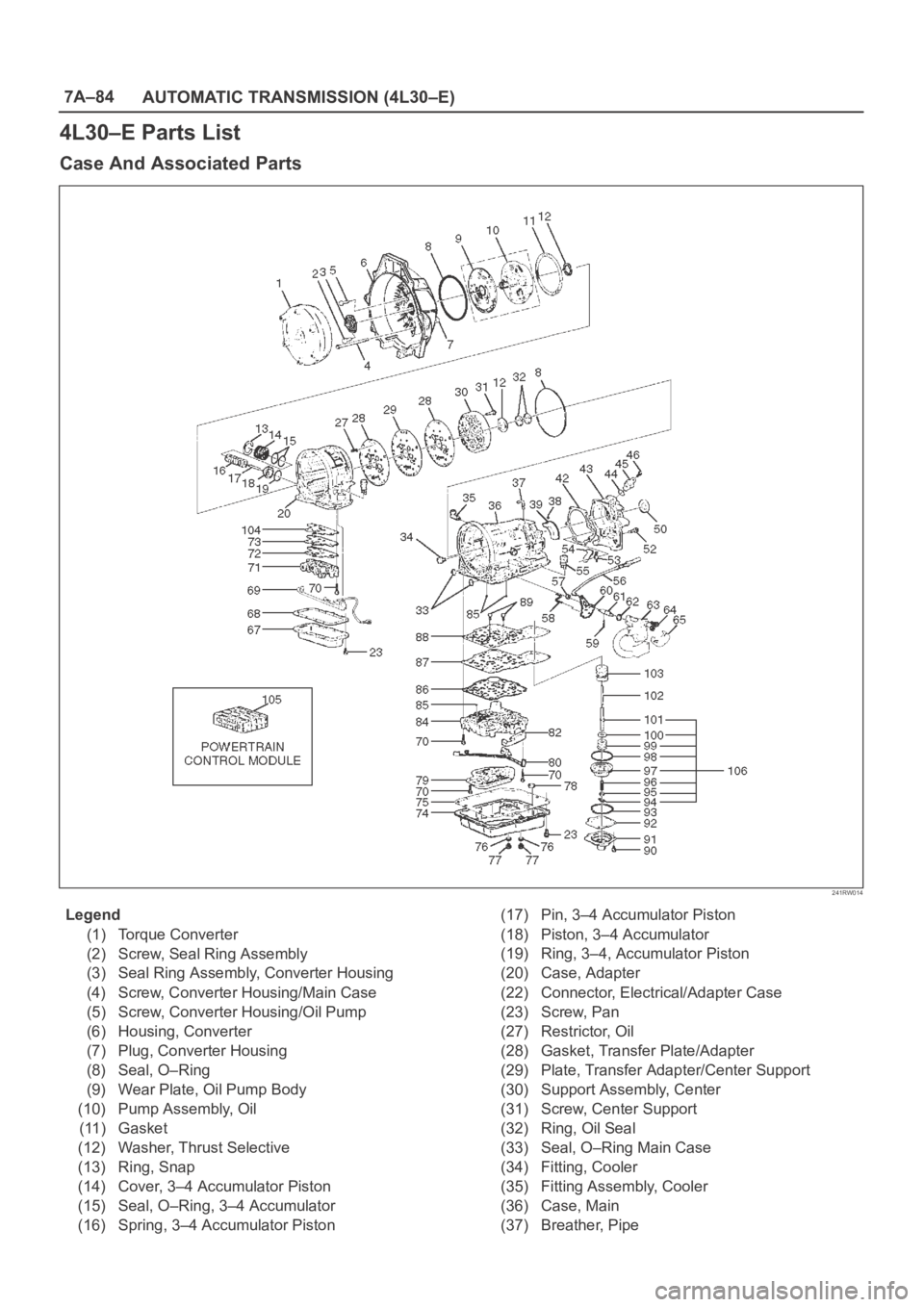
4L30–E Parts List
Case And Associated Parts
241RW014
Legend
(1) Torque Converter
(2) Screw, Seal Ring Assembly
(3) Seal Ring Assembly, Converter Housing
(4) Screw, Converter Housing/Main Case
(5) Screw, Converter Housing/Oil Pump
(6) Housing, Converter
(7) Plug, Converter Housing
(8) Seal, O–Ring
(9) Wear Plate, Oil Pump Body
(10) Pump Assembly, Oil
(11) Gasket
(12) Washer, Thrust Selective
(13) Ring, Snap
(14) Cover, 3–4 Accumulator Piston
(15) Seal, O–Ring, 3–4 Accumulator
(16) Spring, 3–4 Accumulator Piston(17) Pin, 3–4 Accumulator Piston
(18) Piston, 3–4 Accumulator
(19) Ring, 3–4, Accumulator Piston
(20) Case, Adapter
(22) Connector, Electrical/Adapter Case
(23) Screw, Pan
(27) Restrictor, Oil
(28) Gasket, Transfer Plate/Adapter
(29) Plate, Transfer Adapter/Center Support
(30) Support Assembly, Center
(31) Screw, Center Support
(32) Ring, Oil Seal
(33) Seal, O–Ring Main Case
(34) Fitting, Cooler
(35) Fitting Assembly, Cooler
(36) Case, Main
(37) Breather, Pipe
Page 2239 of 6000
7A–85 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
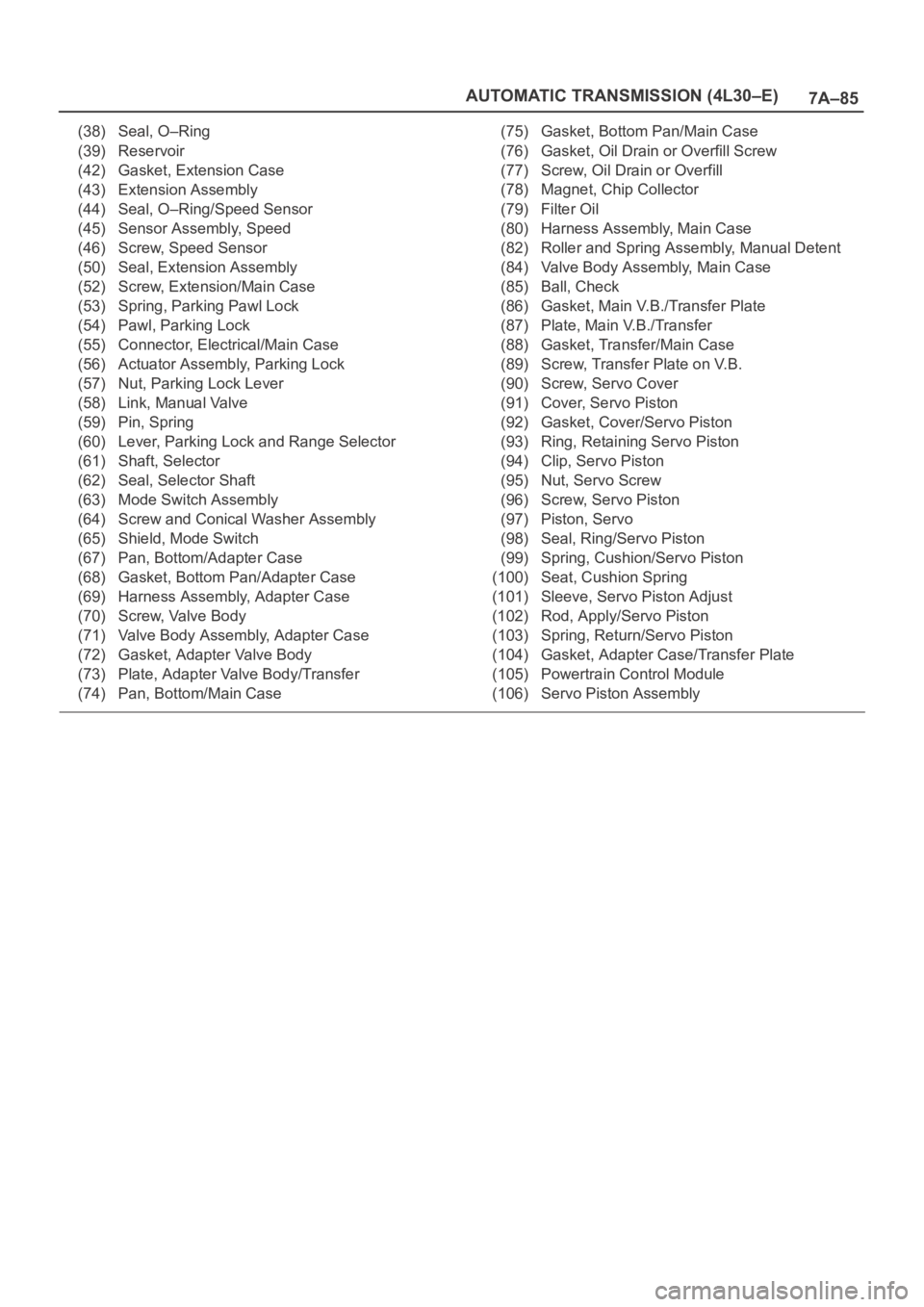
(38) Seal, O–Ring
(39) Reservoir
(42) Gasket, Extension Case
(43) Extension Assembly
(44) Seal, O–Ring/Speed Sensor
(45) Sensor Assembly, Speed
(46) Screw, Speed Sensor
(50) Seal, Extension Assembly
(52) Screw, Extension/Main Case
(53) Spring, Parking Pawl Lock
(54) Pawl, Parking Lock
(55) Connector, Electrical/Main Case
(56) Actuator Assembly, Parking Lock
(57) Nut, Parking Lock Lever
(58) Link, Manual Valve
(59) Pin, Spring
(60) Lever, Parking Lock and Range Selector
(61) Shaft, Selector
(62) Seal, Selector Shaft
(63) Mode Switch Assembly
(64) Screw and Conical Washer Assembly
(65) Shield, Mode Switch
(67) Pan, Bottom/Adapter Case
(68) Gasket, Bottom Pan/Adapter Case
(69) Harness Assembly, Adapter Case
(70) Screw, Valve Body
(71) Valve Body Assembly, Adapter Case
(72) Gasket, Adapter Valve Body
(73) Plate, Adapter Valve Body/Transfer
(74) Pan, Bottom/Main Case(75) Gasket, Bottom Pan/Main Case
(76) Gasket, Oil Drain or Overfill Screw
(77) Screw, Oil Drain or Overfill
(78) Magnet, Chip Collector
(79) Filter Oil
(80) Harness Assembly, Main Case
(82) Roller and Spring Assembly, Manual Detent
(84) Valve Body Assembly, Main Case
(85) Ball, Check
(86) Gasket, Main V.B./Transfer Plate
(87) Plate, Main V.B./Transfer
(88) Gasket, Transfer/Main Case
(89) Screw, Transfer Plate on V.B.
(90) Screw, Servo Cover
(91) Cover, Servo Piston
(92) Gasket, Cover/Servo Piston
(93) Ring, Retaining Servo Piston
(94) Clip, Servo Piston
(95) Nut, Servo Screw
(96) Screw, Servo Piston
(97) Piston, Servo
(98) Seal, Ring/Servo Piston
(99) Spring, Cushion/Servo Piston
(100) Seat, Cushion Spring
(101) Sleeve, Servo Piston Adjust
(102) Rod, Apply/Servo Piston
(103) Spring, Return/Servo Piston
(104) Gasket, Adapter Case/Transfer Plate
(105) Powertrain Control Module
(106) Servo Piston Assembly
Page 2246 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–1
TRANSMISSION
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 7A1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 7A1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Shift Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Band Apply Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Converter Clutch Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . .
Line Pressure Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
On–Board Diagnostic System 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . .
Fail Safe Mechanism 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Torque Management Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . .
ATF Warning Control 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ABS Control (If equipped) 7A1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Winter Drive Mode 7A1–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Backup Mode 7A1–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functions of Input / Output Components 7A1–10. .
Diagnosis 7A1–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Check Trans Indicator 7A1–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Check 7A1–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
“Check Trans” Check 7A1–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tech2 OBD II Connection 7A1–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OBD II Diagnostic Management System 7A1–18. .
16 – Terminal Data Link Connector (DLC) 7A1–19.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 7A1–20. . . . . . . .
Types Of Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTCs) 7A1–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clear DTC 7A1–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC Check 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Precaution 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Information On PCM 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Intermittent Conditions 7A1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission And PCM Identification 7A1–22. . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
Identification 7A1–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over
Temperature 7A1–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Conditions For Setting The DTC 7A1–25. . . . . . . . .
Action Taken When The DTC Sets 7A1–25. . . . . . .
Conditions For Clearing The DTC 7A1–25. . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Aids 7A1–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Description 7A1–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction 7A1–27. . .
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch
(Mode Switch) Illegal Position 7A1–30. . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0706 Transmission Range Switch
(Mode Switch) Performance 7A1–33. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature
(TFT) Sensor Circuit Low Input 7A1–36. . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature
(TFT) Sensor Circuit High Input 7A1–39. . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High
(Stuck On) 7A1–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0722 Transmission Output Speed
Sensor (OSS) Low Input 7A1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0723 Transmission Output Speed
Sensor (OSS) Intermittent 7A1–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0730 Transmission Incorrect
Gear Ratio 7A1–51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid
(PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit Electrical 7A1–54. . . . .
DTC P0753 Shift Solenoid A Electrical 7A1–56. . . . .
DTC P0758 Shift Solenoid B Electrical 7A1–59. . . . .
DTC P1790 ROM Transmission Side Bad
Check Sum 7A1–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1792 EEPROM Transmission Side
Bad Check Sum 7A1–64. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1835 Kickdown Switch Always On 7A1–65. . .
DTC P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid
Malfunction 7A1–67. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical 7A1–71. . . . . . .
Page 2266 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–21
NOTE: To use the DTC again to identify a problem, you
will need to reproduce the fault or the problem. This may
require a new test drive or just turning the ignition on (this
depends on the nature of the fault).
1. IF you have a Tech2:
1. Connect the Tech2 if it is still not connected
GOTHROUGH Tech2 OBD II CONNECTION.
2. Push “F4” and answer “Yes” to the question “Do
you really want to clear the codes?”
a. When a malfunction remains as it is the Tech2
displays “4L30E CODES NOT CLEARED”. This
means that the problem is still there or that the
recovery was not done. Please GOTO DTC
CHECK.
b. When a malfunction has been repaired and the
recovery is done. The Tech2 displays “4L30E
CODES CLEARED”.
2. IF you have no Tech2:
To clear the DTC, remove Fuse “Stop, A/T CONT”
(C–14, 15A) for at least 10 seconds.
DTC Check
1. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) have been identified
by Tech2.
2. You have written the list of the DTCs. The order of the
malfunctions has no meanings for this PCM. Usually
only one or two malfunctions should be set for a given
problem.
3. Check directly the DTCs you identified. The DTCs are
sorted by number. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) Identification in this section.
PCM Precaution
The PCM can be damaged by:
1. Electrostatic discharge
2. The short circuit of some terminals to voltage or to
ground.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage Description:
1. Electronic components used to control systems are
often designed to carry very low voltage, and are very
susceptible to damage caused by electrostatic
discharge. It is possible for less than 100 volts of
static electricity to cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as
4,000 volts for a person to even feel the zap of a static
discharge.2. There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction. An example of
charging by friction is a person sliding across a car
seat, in which a charge of as much as 25,000 volts
can build up. Charging by induction occurs when a
person with well insulated shoes stands near a highly
charged object and momentarily touches ground.
Charges for the same polarity are drained off, leaving
the person highly charged with the opposite polarity.
Static charges of either type can cause damage,
therefore, it is important to use care when handling
and testing electronic components.
NOTICE: To prevent possible electrostatic
discharge damage:
1. Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
2. Be sure to follow the guidelines listed below if
servicing any of these electronic components:
3. Do not open the replacement part package until it is
time to install the part.
4. Avoid touching electrical terminals of the part.
5. Before removing the part from its package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
6. Always touch a known good ground before handling
the part. This step should be repeated before
installing the part if the part has been handled while
sliding across the seat, while sitting down from a
standing position or while walking some distance.
Information On PCM
1. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is located in
the center console and is the control center of the
electronic transmission control system.
2. The PCM must be maintained at a temperature below
185
F (85C) at all times. This is most essential if the
vehicle is put through a paint baking process. The
PCM will become inoperative if its temperature
exceeds 85
C (185F). Therefore, it is
recommended that the PCM be removed or that
temporary insulation be placed around the PCM
during the time the vehicle is in a paint oven or other
high temperature process.
3. The PCM is designed to process the various inputs
and then respond by sending the appropriate
electrical signals to control transmission upshift,
downshift, shift feel and torque converter clutch
engagement.
4. The PCM constantly interprets information from the
various sensors, and controls the systems that affect
transmission and vehicle performance. By analyzing
operational problems, the PCM is able to perform a
diagnostic function by displaying DTC(s) and aid the
technician in making repairs.
Intermittent Conditions
If the Tech2 displays a diagnostic trouble code as
intermittent, or if after a test drive a DTC does not
reappear though the detection conditions for this DTC are
present, the problem is most likely a faulty electrical
Page 2267 of 6000

7A1–22
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
connection or loose wiring. Terminals and grounds should
always be the prime suspect. Intermittents rarely occur
inside sophisticated electronic components such as the
PCM.
Use the DTC information to understand which wires and
sensors are involved.
When an intermittent problem is encountered, check
suspect circuits for:
1. Poor terminal to wire connection.
2. Terminals not fully seated in the connector body
(backed out).
3. Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
4. Loose, dirty, or corroded ground connections:
HINT: Any time you have an intermittent in more than
one circuit, check whether the circuits share a
common ground connection.
5. Pinched or damaged wires.
6. Electro–Magnetic Interference (EMI):
HINT: Check that all wires are properly routed away
from spark plug wires, distributor wires, coil, and
generator. Also check for improperly installed
electrical options, such as lights, 2–way radios, etc.Use the F3 SNAPSHOT mode of the Tech2 to help isolate
the cause of an intermittent fault. The snapshot mode will
record information before and after the problem occurs.
Set the snapshot to “trigger” on the suspect DTC. If you
notice the reported symptom during the test drive, trigger
the snapshot manually.
After the snapshot has been triggered, command the
Tech2 to play back the flow of data recorded from each of
the various sensors. Signs of an intermittent fault in a
sensor circuit are sudden unexplainable jump in data
values out of the normal range.
Transmission And PCM Identification
The chart below contains a list of all important information
concerning rear axle ratio, Powertrain Control Module
(PCM), and transmission identification.
VEHICLE
Rr axlePCMTRANSMISSION
Ty p eEngine
Rr axle
RatioISUZU Parts No.Calibration
CodeIsuzu Part No.Model Code
Isuzu /
Trooper3.2L V64.555
8–16254–949–0
8–16254–749–0
8–16253–989–0
G208–96018–272–3FP (4X4)
Page 2269 of 6000

7A1–24
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
Identification
DTC NUM-
BERDTC NAMEDTC TYPE“CHECK
TRANS”
P0218Transmission Fluid Over TemperatureD
P0560System Voltage MalfunctionCFlash
P0705Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Illegal PositionD
P0706Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) PerformanceD
P0712Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input
(TFT)D
P0713Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit High
InputD
P0719TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck ON)D
P0722Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Low InputCFlash
P0723Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) IntermittentCFlash
P0730Transmission Incorrect Gear Ratio FlashCFlash
P0748Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (FORCE MOTOR) Circuit
ElectricalCFlash
P0753Shift Solenoid A ElectricalCFlash
P0758Shift Solenoid B ElectricalCFlash
P1790ROM Transmission Side Bad Check SumCFlash
P1792EEPROM Transmission Side Bad Check SumCFlash
P1835Kickdown Switch Always OND
P1850Brake Band Apply Solenoid MalfunctionD
P1860TCC Solenoid ElectricalD
DTC TYPEDEFINITION
CFlashing Check Trans on 1st failure
DNo lamps
NOTE: On the following charts, refer to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) section for the Wiring System, and
the Body and Accessories section for circuit diagram
details, parts location, and connector configuration.
Page 2270 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–25
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature
D07RW029
Circuit Description
The Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) sensor is a
thermister that controls the signal voltage to the PCM.
The PCM supplies a 5–volt reference to the sensor on
circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED. When the transmission fluid
is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the PCM will
sense high signal voltage. As the fluid temperature
warms to a normal transmission operating temperature of
100
C (212F), the sensor resistance becomes less and
the voltage decreases to 1.5 to 2.0 volts.
This DTC detects a high transmission temperature for a
long period of time. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
No TFT DTCs P0712 or P0713.
TFT is greater than 135C (275F).
All conditions met for 21 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Hot mode TCC Shift Pattern.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
ATF Lamp ON. (TFT is greater than 145C (293F).)
Disable E–side TCC OFF request.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warm–up cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed, or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well.
Also check for a chafed wire that could short to bare
metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire inside
the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Check harness routing for a potential short to ground
in circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED.
Scan tool TFT sensor temperature should rise
steadily to about 100
C (212F), then stabilize.
Check for a “skewed” (mis–scaled) sensor by
comparing the TFT sensor temperature to the
ambient temperature after a vehicle cold soak. A
“skewed” sensor can cause delayed garage shifts or
TCC complaints.
Check for a possible torque converter stator problem.
Verify customer driving habits, trailer towing, etc.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart.
3. This test checks for a “skewed” sensor or shorted
circuit.
4. This test simulates a TFT DTC P0713.