1998 OPEL FRONTERA Electrical
[x] Cancel search: ElectricalPage 2273 of 6000

7A1–28
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction
StepActionYe sNo
11. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”. Note: If any other DTCs
are present, refer to their applicable diagnostic charts before
continuing.
4. Using the J–39200 DVOM, measure the battery voltage
across the battery terminals. Record the measurement for
future reference.
Is the voltage higher than 10.5 volts?
Go to Step 2
Go to Engine
Electrical in
Engine section
2Start the engine and warm to normal operating temperature.
Is the generator/check engine light “on”?Go to Starting
and Charging
System in Engine
section
Go to Step 3
31. Increase the engine speed to 1,000–1,500 rpm.
2. Observe scan tool system voltage.
Is the system voltage within 13–15 volts.
Go to Step 4
Go to Starting
and Charging
System in Engine
section
41. Turn the ignition switch “off”.
2. Disconnect the J1(RED) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connector
(additional DTCs will set).
3. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
4. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the battery voltage input at
PCM connector terminals J1–A4 and J3–E16.
Is there a voltage variance between the voltage measured at the
battery (taken in Step 1) and at terminals J1–A4 and J3–E16 that
is greater than 0.5 volts?
Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair the high resistance condition in circuit WHT.
Was the circuit repaired?
Go to Step 10—
61. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Measure the ignition voltage input at PCM connector terminals
J3–E16 and J3–F16.
Is there a voltage variance between the voltage measured at the
battery (taken in Step 1) and at terminals J3–E16 and J3–F16 that
is greater than 0.5 volts?
Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Repair the high resistance condition is circuit RED/BLU.
Was the circuit repaired?
Go to Step 10—
8Check PCM connector terminals J1–A4, J3–E16 and J3–F16 for
bent, damaged, or backed out connector pins. Also check for
weak terminal tension.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 10Go to Step 9
Page 2275 of 6000

7A1–30
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Illegal Position
D07RW031
Circuit Description
The range switch supplies the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) with information regarding the selector
lever position: P, R, N, D 3, 2 or L. The selector lever
position is indicated by the state of four ON/OFF
contracts. The range switch is located on one side of
the transmission. It is on the transmission manual
shaft and is fixed to the main case.
The range switch is also used to provide the
information P or N to the engine crank wiring. The
engine can be cranked only if connector M–25
terminal 4(H) is connected to terminal 1(E) which is
connected to ground.
The range switch is also used to provide the backup
lamp power in reverse. This is why the range switch is
supplied through a 10A fuse (C–3). This fuse can
burn due to a short circuit in the backup lamp.
This DTC detects when a fuse is open or the range switch
circuit does not work. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Range switch illegal positions met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Default to D position.
Inhibit torque management.
Maximum line pressure.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Refer to accompanying chart for the normal range
signals and the illegal combinations.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 8–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Page 2279 of 6000
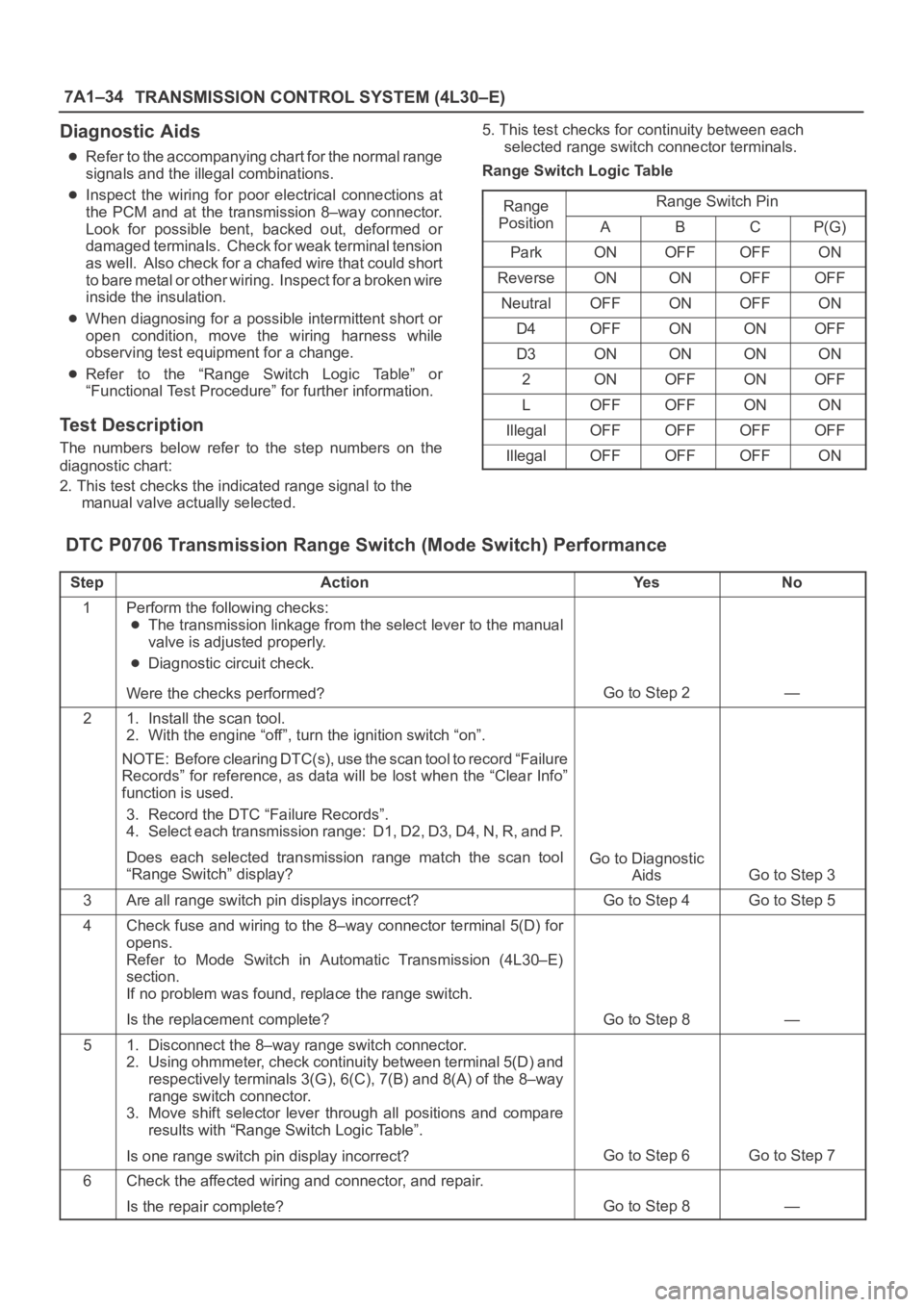
7A1–34
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Diagnostic Aids
Refer to the accompanying chart for the normal range
signals and the illegal combinations.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 8–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well. Also check for a chafed wire that could short
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Refer to the “Range Switch Logic Table” or
“Functional Test Procedure” for further information.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks the indicated range signal to the
manual valve actually selected.5. This test checks for continuity between each
selected range switch connector terminals.
Range Switch Logic Table
Range
Range Switch Ping
PositionABCP(G)
ParkONOFFOFFON
ReverseONONOFFOFF
NeutralOFFONOFFON
D4OFFONONOFF
D3ONONONON
2ONOFFONOFF
LOFFOFFONON
IllegalOFFOFFOFFOFF
IllegalOFFOFFOFFON
DTC P0706 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Performance
StepActionYe sNo
1Perform the following checks:
The transmission linkage from the select lever to the manual
valve is adjusted properly.
Diagnostic circuit check.
Were the checks performed?
Go to Step 2—
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
4. Select each transmission range: D1, D2, D3, D4, N, R, and P.
Does each selected transmission range match the scan tool
“Range Switch” display?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 3
3Are all range switch pin displays incorrect?Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Check fuse and wiring to the 8–way connector terminal 5(D) for
opens.
Refer to Mode Switch in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
If no problem was found, replace the range switch.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 8—
51. Disconnect the 8–way range switch connector.
2. Using ohmmeter, check continuity between terminal 5(D) and
respectively terminals 3(G), 6(C), 7(B) and 8(A) of the 8–way
range switch connector.
3. Move shift selector lever through all positions and compare
results with “Range Switch Logic Table”.
Is one range switch pin display incorrect?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
6Check the affected wiring and connector, and repair.
Is the repair complete?
Go to Step 8—
Page 2281 of 6000

7A1–36
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit Low Input
D07RW029
Circuit Description
The TFT sensor is a thermister that controls the signal
voltage to the PCM. The PCM supplies a 5–volt reference
signal to the sensor on circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED.
When the transmission fluid is cold, the sensor resistance
is high. The PCM detects high signal voltage. As the
transmission fluid temperature increases to the normal
operating temperature of 100
C (212F), the sensor
resistance becomes less and the voltage decreases to
1.5 to 2 volts. With transmission fluid over temperature
and DTC P0218 also set, check the transmission cooling
system.
This DTC detects a continuous short to ground in the TFT
signal circuit or the TFT sensor. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
Ignition is “on”.
TFT sensor indicating a voltage less than 0.4 volts.
All conditions met for 20 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Transmission default temperature will be:
80
C (176F) if engine temperature code is set.
100
C (212F) if engine temperature is warm.
80
C (176F) if engine run time is greater than 5
minutes.
21
C (69.8F) if engine run time is less than 5
minutes.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Check harness routing for a potential short to ground
in circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED. Scan tool TFT
display should rise steadily to about 100
C (212F),
then stabilize.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
The temperature to resistance value scale may be
used to test the TFT sensor at the various
temperature levels to evaluate the possibility of a
“skewed” (mis–scaled) sensor.
A “skewed” sensor could result in delayed garage
shifts or TCC complaints.
Verify customer driving habits, trailer towing, etc.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
3. This test checks for a short to ground or a “skewed”
sensor.
4. This test checks for an internal fault within the
transmission by creating an open.
Page 2284 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–39
DTC P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit High Input
D07RW029
Circuit Description
The TFT sensor is a thermistor that controls the signal
voltage to the PCM. The PCM supplies a 5–volt reference
signal to the sensor on circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED.
When the transmission fluid is cold, the sensor resistance
is high and the PCM will sense high signal voltage. As the
transmission fluid temperature warms to the normal
operating temperature of 100
C (212F), the sensor
resistance becomes less and the voltage decreases to
about 1.5 to 2 volts.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to power in
the TFT signal circuit or the TFT sensor. This is a type “D”
DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
Ignition is “on”.
TFT sensor indicating a voltage greater than 4.86
volts.
All conditions met for 20 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Transmission default temperature will be:
80
C (176F) if engine temperature code is set.
100
C (212F) if engine temperature is warm.
80
C (176F) if engine run time is greater than 5
minutes.
21
C (69.8F) if engine run time is less than 5
minutes.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as we ll. A lso ch eck fo r a ch af e d w ire th at cou l d s ho r t
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire
inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Scan tool displays transmission fluid temperature in
degrees. After transmission is operating, the
temperature should rise steadily to about 100
C
(212
F), then stabilize.
The temperature to resistance value scale may be
used to check the TFT sensor at the various
temperature levels to evaluate the possibility of a
“skewed” (mis–scaled) sensor.
A “skewed” sensor could result in hard shifts or TCC
complaints.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
3. This check verifies problem in the TFT sensor circuit.
4. This test simulates a TFT sensor DTC P0712. If the
PCM recognizes the low signal voltage (high
temperature), and the scan tool displays 146
C
(295
F) or greater, the PCM and wiring are OK.
Page 2287 of 6000

7A1–42
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck On)
D07RW032
Circuit Description
The TCC brake switch is used to indicate brake pedal
status. The normally opened brake switch signal voltage
circuit is opened.
Brake switch supplies a B+ signal on circuit GRN/YEL to
the PCM when the brakes are applied. The PCM uses
this signal to deenergize the TCC solenoid when the
brakes are applied.
This DTC detects a closed brake switch during
accelerations. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
No OSS DTCs P0722 or P0723.
The PCM detects a closed brake switch/circuit (12
volts) for 2 seconds, and the following events occur
seven consecutive times: vehicle speed is less than 8
km/h (5 mph); then vehicle speed is between 8 and 32
km/h (5 and 20 mph) for 4 seconds; then vehicle
speed is greater than 32 km/h (20 mph) for 4 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
If throttle opening is greater than 10% and vehicle
speed is greater than 45 km/h (28 mph), then
disregard brake switch contingency for TCC off
mode.
The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and TCC brake switch. Look for possible
bent, backed out, deformed or damaged terminals.
Check for weak terminal tension as well. Also check
for a chafed wire that could short to bare metal or
other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire inside the
insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Check customer driving habits and/or unusual driving
conditions (i.e. stop and go, highway).
Check brake switch for proper mounting and
adjustment.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
3. This test checks for voltage at the brake switch.
6. This test checks the brake switch.
9. This test checks circuit GRN/YEL at the PCM.
Page 2290 of 6000

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–45
DTC P0722 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Low Input
D07RW006
Circuit Description
Output speed information is provided to the PCM by the
OSS, which is a permanent magnet (PM) generator. The
PM generator produces a pulsing AC voltage. The AC
voltage level and number of pulses increases as the
speed of the vehicle increases. The PCM then converts
the pulsing voltage to output speed, which is used for
calculations. The vehicle speed can be displayed with a
scan tool.
This DTC detects a low output speed when there is a high
engine speed in a drive gear range. This is a type “C”
DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
No MAP DTCs P0107 or P0108, P0106, P1106,
P1107.
No TPS DTCs P0122 or P0123.
Not in Park or Neutral.
TP angle is greater than 10%.
Engine vacuum is between 0 and 70kPa.
Engine speed is between 3,000 and 7,000 rpm.
Transmission output speed is less than 0 rpm.
All conditions met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Fixed to 4th gear.
Maximum line pressure.
Inhibit TCC engagement.
The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The MIL/DTC
The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool. The DTC will be cleared from
history when the vehicle has achieved 40 warmup
cycles without a failure reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
An OSS DTC P0722 will set when no output speed is
at detected at start off.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM. Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed
or damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal
tension as well. Also check for a chafed wire that
could short to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a
broken wire inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
5. This test checks the OSS circuit.
6. This test checks the integrity of the OSS.
8. This test checks the 5–volt and ground circuit of the
PCM.
Page 2293 of 6000

7A1–48
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
DTC P0723 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Intermittent
D07RW006
Circuit Description
Output speed information is provided to the PCM by the
OSS, which is a permanent magnet (PM) generator. The
PM generator produces a pulsing AC voltage. The AC
voltage level and number of pulses increases as the
speed of the vehicle increases. The PCM then converts
the pulsing voltage to output speed, which is used for
calculations. The vehicle speed can be displayed with a
scan tool.
This DTC detects a low output speed when there is a high
engine speed in a drive gear range. This is a type “C”
DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
In Park or Neutral:
Transmission output speed change is greater than
10,000 rpm.
Conditions met for 6 seconds.
Engine running time is greater than 2 seconds.
Not in Park or Neutral:
Transmission output speed change is greater than
512 rpm.
Conditions met for 0.075 seconds
Engine running time is greater than 2 seconds.
Engine vacuum is less than 70 kPa.
Output speed is greater than 1,380 rpm for 1 second.
NORAW–NOLAST < 60 rpm for 6 seconds.
NORAW: Latest raw data of output shaft speed.
NOLAST: Filtered pervious data of output speed.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
Fixed to 4th gear.
Maximum line pressure.
Inhibit TCC engagement.
The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The MIL/DTC
The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
The DTC will be cleared from history when the vehicle
has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled “off”
long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
A OSS DTC P0723 will set when output speed has
been detected and is lost.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM. Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed
or damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal
tension as well. Also check for a chafed wire that
could short to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a
broken wire inside the insulation.
When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
5. This test checks the OSS circuit.
6. This test checks the integrity of the OSS.
8. This test checks the 5–volt and ground circuit of the
PCM.