1998 OPEL FRONTERA Gas
[x] Cancel search: GasPage 2173 of 6000

7A–19 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 13: Shudder Only During Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Applying
StepActionYe sNo
11. TCC shudder is one of the most commonly misdiagnosed
conditions in an automatic transmission. The key to
diagnosing TCC shudder is to note when it happens and under
what conditions. Once the TCC has been fully applied, it is
nearly impossible to make it shudder. TCC shudder (short
burst of noise normally less than 1 second) will only occur
during clutch applying. It is not a steady state condition.
2. Drive until whole drivetrain is at normal operating temperature.
– On 4WD vehicles, the test must be performed with transfer
case selector lever in “2H” position.
– Shudder is a short burst of noise normally less than 1 second
in duration, and can be induced by the following maneuver:
3. From coast condition at 50 mph in “D” range (Normal mode),
depress the throttle to 1/4-1/3 throttle. If present, shudder will
occur within 5 seconds together with TCC application.(The
scan tool may be used to determine the exact time of TCC
applying)
Was the problem found?
Replace
transmission fluid
and filter (remove
both pans) and
flush cooler lines.
Replace
converter
assembly and
O-ring on turbine
shaft
Perform
mechanical
inspection of
other drivetrain
components.
Chart 14: Possible Causes Of Transmission Noise
CAUTION: Before checking transmission for what
is believed to be transmission noise, ensure
presence and positioning of insulating plugs, pads
etc. Also make sure that noise does not come from
other drivetrain components.
Condition
Possible causeCorrection
Whine or BuzzOil level lowFill with ATF, check for external
leaks.
Plugged or restricted oil filterInspect oil filter.
Replace oil filter or ATF as necessary.
Damaged oil filter gasketReplace oil filter gasket.
Knocking noise from front of
transmission
Loose bolts (Converter to flex plate)Tighten to specifications.
transmission.Cracked or broken flex plateReplace flex plate.
Converter damagedReplace converter.
Knocking noise while driving, mostly
on acceleration.Transmission mount loose or brokenTighten mount bolts or replace
transmission mount.
Cooler line mounts loose or brokenTighten or replace cooler line
mounts.
Cooler lines touching body or frameRepair or replace as necessary.
Knocking noise when vehicle is
stationary
Loose flex plate mounting boltsTighten to specifications.
stationary.Cracked or broken flex plateReplace flex plate.
Damaged converterReplace converter.
Page 2174 of 6000

7A–20
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 15a: Possible Causes of Low Line Pressure
StepActionYe sNo
1Check oil level.
Was the problem found?
Fill with ATFGo to Step 2
2Check for defective throttle position sensor.
Was the problem found?Replace throttle
position sensor
Go to Step 3
3Check for plugged, loose, or damaged oil filter (79).
Was the problem found?Inspect oil filter,
tighten bolts or
replace oil filter
(79)
Go to Step 4
4Check for a stuck force motor plunger (404). (Adapter case valve
body)
Was the problem found?Replace force
motor plunger
(404)
Go to Step 5
5Check for a stuck feed limit valve (412). (Adapter case valve body)
Was the problem found?Replace feed limit
valve (412)
Go to Step 6
6Check for loose converter bolts (4 & 5).
Was the problem found?Tighten converter
bolts (4 & 5)
Go to Step 7
7Check for a stuck pressure regulator valve (208). (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace pressure
regulator valve
(208)
Go to Step 8
8Check for a stuck boost valve (205).(Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace boost
valve (205)
Go to Step 9
9Check for blocked intermediate oil passages to pressure
regulator valve. (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?
Replace oil pumpGo to Step 10
10Check for defective oil pump (9, 201, 202 & 209).
Was the problem found?
Replace oil pumpGo to Step 11
11Check for internal leaks.
– Check balls missing or out of location in valve bodies
– Seals cut or damaged
– Gaskets defective, etc.
Was the problem found?Install balls, or
correct ball
location
Replace seals
Replace gaskets
—
Page 2175 of 6000
7A–21 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 15b: Possible Causes Of High Line Pressure
NOTE: If transmission is operating in backup mode, high
line pressure will be present.
Step
ActionYe sNo
1Check for defective throttle position sensor.
Was the problem found?Replace throttle
position sensor.
Go to Step 2.
2Check for a stuck force motor plunger (404). (Open
circuit/intermittent) (Adapter case valve body)
Was the problem found?Replace force
motor plunger
(404)
Go to Step 3
3Check for a stuck feed limit valve (412). (Adapter case valve body)
Was the problem found?Replace force
motor plunger
(412)
Go to Step 4
4Check converter bolts (4 & 5).
Was the problem found?Tighten converter
bolts (4 & 5)
Go to Step 5
5Check for a stuck pressure regulator valve (208). (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace pressure
regulator valve
(208)
Go to Step 6
6Check for a stuck boost valve (205). (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace boost
valve (205)
Go to Step 7
7Check for internal leaks.
– Check balls missing or out of location in valve bodies
– Seals cut or missing
– Gaskets defective, etc.
Was the problem found?Install balls, or
correct ball
location
Replace seals
Replace gaskets
—
Page 2176 of 6000
7A–22
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 16: Possible Causes Of
Transmission Fluid Leaks
Before attempting to correct an oil leak, the actual source
of the leak must be determined. In many cases, the
source of the leak may be difficult to determine due to
“wind flow” around the engine and transmission.
The suspected area should be wiped clean before in-
specting for the source of the leak.Oil leaks around the engine and transmission are gener-
ally carried toward the rear of the vehicle by the air
stream. In determining the source of an leak, the following
two checks should be made:
1. With the engine running, check for external line
pressure leaks.
2. With the engine off, check for oil leaks due to the
raised oil level caused by drainback of converter oil
into the transmission.
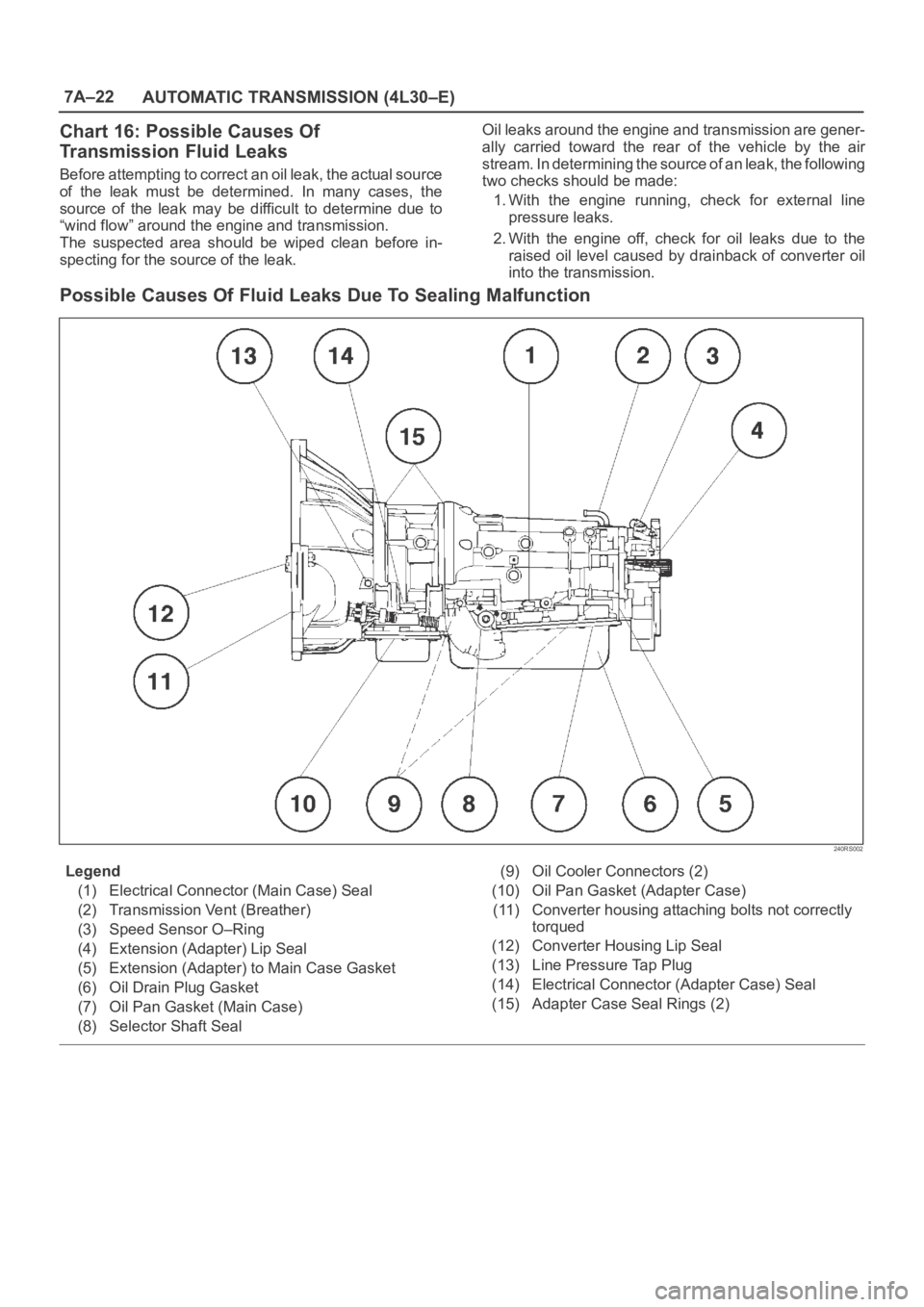
Possible Causes Of Fluid Leaks Due To Sealing Malfunction
240RS002
Legend
(1) Electrical Connector (Main Case) Seal
(2) Transmission Vent (Breather)
(3) Speed Sensor O–Ring
(4) Extension (Adapter) Lip Seal
(5) Extension (Adapter) to Main Case Gasket
(6) Oil Drain Plug Gasket
(7) Oil Pan Gasket (Main Case)
(8) Selector Shaft Seal(9) Oil Cooler Connectors (2)
(10) Oil Pan Gasket (Adapter Case)
(11) Converter housing attaching bolts not correctly
torqued
(12) Converter Housing Lip Seal
(13) Line Pressure Tap Plug
(14) Electrical Connector (Adapter Case) Seal
(15) Adapter Case Seal Rings (2)
Page 2181 of 6000

7A–27 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Changing Transmission Fluid
There is no need to change the transmission fluid unless
the transmission is used under one or more of the
following heavy duty conditions.
A. Repeated short trips
B. Driving on rough roads
C. Driving on dusty roads
D. Towing a trailer
If the vehicle is used under these conditions, change the
fluid every 20,000 miles (32,000 km.)
More over, the remaining life percentage of ATF can be
estimated by using Tech 2 as an auxiliary tool to judge the
right time for ATF replacement.
The remaining life percentage is calculated from ATF’S
heat history. When it is close to 0%, ATF replacement is
recommended.
1. Place a large drain pan under the oil pan.
2. Remove the transmission oil drain screw (2) and drain
fluid.
3. Tighten drain screw (2).
Torque: 38 N
m (3.9 kgꞏm/28 lb ft)
4. Remove the transmission overfill screw (1) and fill
transmission through overfill screw opening, using
DEXRON
–III ATF.
NOTE: Add transmission fluid until it flows out over the
overfill screw opening.
5. Let engine idle until a fluid temperature between 32
C
(90
F) and 57C (135F) is reached.6. Add transmission fluid until it flows out over the overfill
screw opening, then close the overfill screw (1).
To r q u e : 3 8 N
m (3.9 kgꞏm/28 lb ft)
NOTE: To prevent fluid leaks, the overfill screw and oil
drain screws gasket must be replaced each time these
screws are removed.
NOTE: Check transmission fluid temperature with
service scan tool.
242RW003
Selector Lever
Inspection
1. Make sure that when the shifter control lever is shifted
from “P” to “L”, a “clicking” can be felt at each shift
position. Make sure that the gear corresponds to that
of the position plate indicator.
2. Check to see if the shifter lever can be shifted as
shown in illustration.
C07RW009
Page 2190 of 6000

7A–36
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Solenoid (Main Case Valve Body)
Removal
1. Raise the vehicle and support it on jack stands.
2. Disconnect battery ground cable.
3. Remove transfer and exhaust protectors.
4. Drain fluid.
5. Remove exhaust pipe and disconnect oxygen sensor
connector.
6. Support transfer case with a jack and remove third
crossmember.
7. Remove sixteen 10 mm screws, main case oil pan,
magnet, and gasket.
8. Remove three 13 mm screws, oil filter.
9. Disconnect wiring harness from band control
solenoid and shift solenoids. Pull only on connectors,
not on wiring harness.
10. Remove spring pin for shift solenoid A, shift solenoid
B, and band control solenoid respectively, using
suitable pliers taking care not to damage solenoids.
210RW010
244RW003
11. Remove shift solenoid A, shift solenoid B, band
control solenoid, and gaskets from main case valve
body. Do not pull on wiring harness. Remove
solenoids by grasping the metal tip.
Installation
1. Install shift solenoid A, shift solenoid B, band control
solenoid with new gaskets to main case valve body
respectively.
2. Carefully install spring pin with hammer to avoid
damage to valve body, etc.
243RW004
3. Connect wiring harness to solenoids.
4. Install oil filter with a new gasket and the three 13 mm
screws. Tighten the screws to the specified torque.
To r q u e : 2 0 N
m (2.0 kgꞏm/15 lb ft)
5. Install magnet, main case oil pan with new gasket,
sixteen 10 mm screws. Tighten the screws to the
specified torque.
To r q u e : 11 N
m (1.1 kgꞏm/96 lb in)
6. Install third crossmember and rear mount nuts.
Tighten the nuts and bolts to the specified torque.
Third crossmember bolt: 50 N
m
(5.1 kgꞏm/37 lb ft)
Rear mount nut: 50 N
m (5.1 kgꞏm/37 lb ft)
7. Install exhaust pipe and connect oxygen sensor
connector. Tighten the bolts to the specified torque.
Exhaust pipe flange bolt torque:
43 N
m(4.4kgꞏm/32lbft)
8. Install the transfer and exhaust protectors. Tighten
the bolts to the specified torque.
Torque: 37 N
m (3.8 kgꞏm/27 lb ft)
9. Fill transmission through the overfill screw hole of oil
pan, using ATF DEXRON
–III. Refer to Changing
Transmission Fluid in this section.
10. Connect the battery ground cable.
Page 2191 of 6000
7A–37 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Solenoid (Adapter Case Valve Body)
Removal
1. Raise the vehicle and support it on jack stands.
2. Disconnect battery ground cable.
3. Drain fluid.
4. Remove transfer and exhaust protectors.
5. Remove exhaust pipe and disconnect oxygen sesnor
connector.
6. Remove adapter case oil pan twelve fixing 10 mm
screws, adapter case oil pan, and gasket.
NOTE: Oil pan still contains transmission fluid. Place a
large drain container under the oil pan and drain the fluid
carefully.
7. Disconnect wiring harness from force motor solenoid
and converter clutch solenoid. Pull only on
connectors, not on wiring harness.
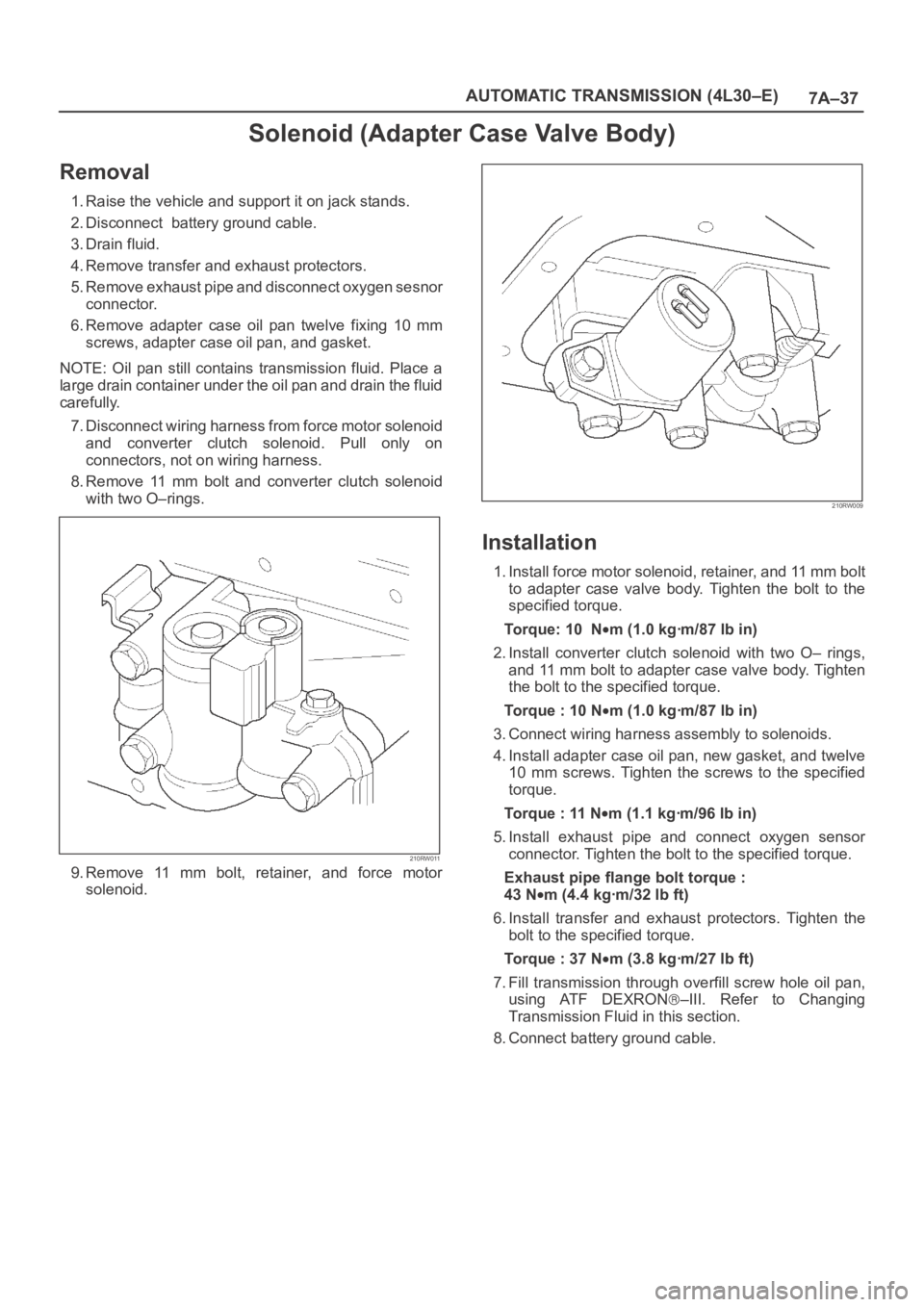
8. Remove 11 mm bolt and converter clutch solenoid
with two O–rings.
210RW011
9. Remove 11 mm bolt, retainer, and force motor
solenoid.
210RW009
Installation
1. Install force motor solenoid, retainer, and 11 mm bolt
to adapter case valve body. Tighten the bolt to the
specified torque.
To r q u e : 1 0 N
m (1.0 kgꞏm/87 lb in)
2. Install converter clutch solenoid with two O– rings,
and 11 mm bolt to adapter case valve body. Tighten
the bolt to the specified torque.
Torque : 10 N
m (1.0 kgꞏm/87 lb in)
3. Connect wiring harness assembly to solenoids.
4. Install adapter case oil pan, new gasket, and twelve
10 mm screws. Tighten the screws to the specified
torque.
Torque : 11 N
m (1.1 kgꞏm/96 lb in)
5. Install exhaust pipe and connect oxygen sensor
connector. Tighten the bolt to the specified torque.
Exhaust pipe flange bolt torque :
43 N
m(4.4kgꞏm/32lbft)
6. Install transfer and exhaust protectors. Tighten the
bolt to the specified torque.
Torque : 37 N
m(3.8kgꞏm/27lbft)
7. Fill transmission through overfill screw hole oil pan,
using ATF DEXRON
–III. Refer to Changing
Transmission Fluid in this section.
8. Connect battery ground cable.
Page 2192 of 6000

7A–38
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Valve Body Assembly (Main Case)
Removal
1. Raise the vehicle and support it on jack stands.
2. Disconnect battery ground cable.
3. Remove transfer and exhaust protectors.
4. Drain fluid.
5. Remove exhaust pipe and disconnect oxygen sensor
connector.
6. Support transfer case with a jack and remove third
crossmember.
7. Remove sixteen 10 mm screws, main case oil pan,
magnet and gasket.
8. Remove three 13 mm oil filter fixing screws, then
remove oil filter.
9. Remove two 13 mm manual detent fixing screws,
then remove roller and spring assembly.
10. Disconnect wiring harness from band control
solenoid and shift solenoids. Pull only on connectors,
not on wiring harness.
11. Remove four 13 mm servo cover fixing screws, then
remove servo cover and gasket.
12. Remove seven 13 mm valve body fixing screws.
Disconnect the ground wire from the main case
valve body.
13. Remove main case valve body with manual valve link
and transfer plate. Note the position of the link (long
end into valve, short end into range selector lever).
14. Remove transfer plate gasket from main case.
15. Remove two check balls from main case.
Installation
1. Install two check balls to main case.
244RW002
2. Inspect electrical 4 pin connector and seal of main
case. Replace if necessary.3. Use two 5–8840–0022–0 (J–25025–B) guide pin to
install main case.
Install valve body assembly and manual valve link.
NOTE: Valve must be extended as the short end of
manual valve link is connected to the range selector lever.
Long end of link goes into valve.
4. Install seven 13 mm screws, and tighten them to the
specified torque.
To r q u e : 2 0 N
m (2.0 kgꞏm/15 lb ft)
243RS008
5. Install 8.5 mm connector of ground wire the head of
this valve body bolt and reinstall it. Tighten the bolt to
the specified torque.
To r q u e : 2 0 N
m (2.0 kgꞏm/15 lb ft)
244RW001
6. Remove two guide pins from main case.
7. Install servo cover gasket, cover, and four 13 mm
screws. Tighten the screws to the specified torque.
To r q u e : 2 5 N
m (2.6 kgꞏm/18 lb ft)