1998 OPEL FRONTERA low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 4908 of 6000

6E–251 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1508 IAC System Low RPM
T321115
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls engine
idle speed by adjusting the position of the idle air control
(IAC) motor pintle. The IAC is a bi-directional stepper
motor driven by two coils. The PCM applies current to the
IAC coils in steps (counts) to extend the IAC pintle into a
passage in the throttle body to decrease air flow. The
PCM reverses the current to retract the pintle, increasing
air flow. This method allows highly accurate control of idle
speed and quick response to changes in engine load. If
the PCM detects a condition where too low of an idle
speed is present and the PCM is unable to adjust idle
speed by increasing the IAC counts, DTC P1508 will set,
indicating a problem with the idle control system.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No Tech 2 test is being run.
None of these DTCs are set: TP sensor, VSS, ECT,
EGR, fuel system, MAF, MAP, IAT, canister purge,
injector control or ignition control.
Barometric pressure is above 75 kPa.
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) is above 50C
(120
F).
Engine speed is more than 100-200 RPM lower than
desired idle, based upon coolant temperature.
The engine has been running for at least 125 seconds.
Vehicle speed is less than 1 mph.
Canister purge duty cycle is above 10%.
Ignition voltage is between 9.5 volts and 16.7 volts.
The throttle is closed.
Engine speed is lower than desired idle.
All of the above conditions are met for 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1508 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM or IAC motor – Inspect
harness connectors for backed-out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal-to-wire
connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring for damage.
Restricted air intake system – Check for a possible
collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter element,
or foreign objects blocking the air intake system.
Throttle body – Check for objects blocking the IAC
passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC
Page 4911 of 6000

6E–254
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1509 IAC System High RPM
T321115
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls engine
idle speed by adjusting the position of the idle air control
(IAC) motor pintle. The IAC is a bi-directional stepper
motor driven by two coils. The PCM applies current to the
IAC coils in steps (counts) to extend the IAC pintle into a
passage in the throttle body to decrease air flow. The
PCM reverses the current to retract the pintle, increasing
air flow. This method allows highly accurate control of idle
speed and quick response to changes in engine load. If
the PCM detect a condition where too high of an idle
speed is present and the PCM is unable to adjust idle
speed by increasing the IAC counts, DTC P1509 will set,
indicating a problem with the idle control system.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No Tech 2 test is being run.
None of these DTCs are set: TP sensor, VSS, ECT,
EGR, fuel system, MAF, MAP, IAT, canister purge,
injector control or ignition control.
Barometric pressure is above 75 kPa.
Engine coolant temperature is above 50C (120F).
Engine speed is more than 100-200 RPM lower than
desired idle, based upon coolant temperature.
The engine has been running for at least 125 seconds.
Vehicle speed is less than 1 mph.
Canister purge duty cycle is above 10%.
Ignition voltage is between 9.5 volts and 16.7 volts.
Engine speed is lower than desired idle.
All of the above conditions are met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
The PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1509 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the PCM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at PCM or IAC motor – Inspect
harness connectors for backed-out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal-to-wire
connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring for damage.
Vacuum leak – Check for a condition that causes a
vacuum leak, such as disconnected or damaged
h o s e s , l e a k s a t t h e E G R v a l v e a n d t h e E G R p i p e t o t h e
intake manifold, leaks at the throttle body, faulty or
incorrectly installed PCV valve, leaks at the intake
manifold, etc.
Page 4925 of 6000
6E–268
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
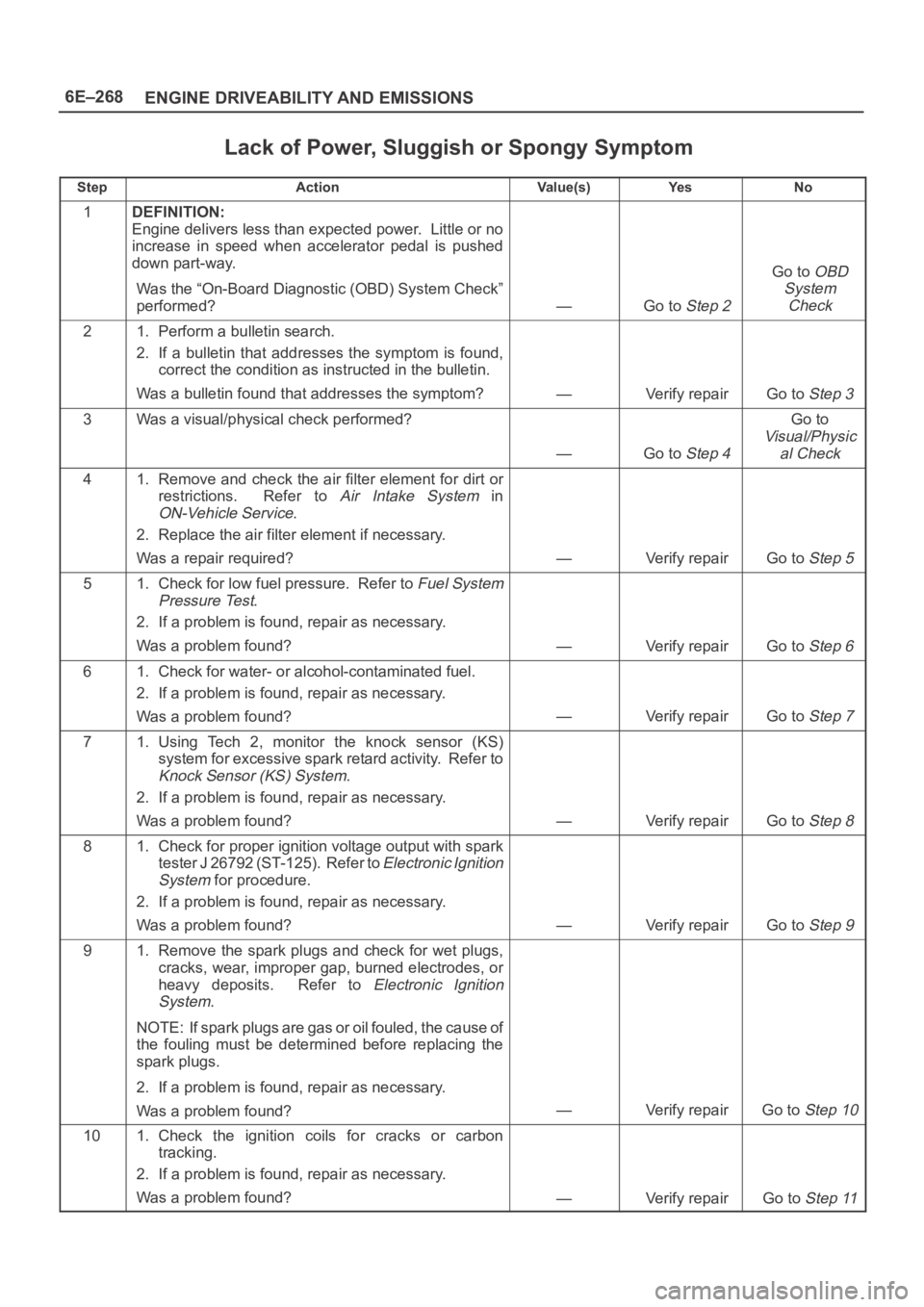
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Engine delivers less than expected power. Little or no
increase in speed when accelerator pedal is pushed
down part-way.
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
41. Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or
restrictions. Refer to
Air Intake System in
ON-Vehicle Service.
2. Replace the air filter element if necessary.
Was a repair required?
—Verify repairGo to Step 5
51. Check for low fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System
Pressure Test
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 6
61. Check for water- or alcohol-contaminated fuel.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Using Tech 2, monitor the knock sensor (KS)
system for excessive spark retard activity. Refer to
Knock Sensor (KS) System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Remove the spark plugs and check for wet plugs,
cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or
heavy deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
101. Check the ignition coils for cracks or carbon
tracking.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 11
Page 4930 of 6000
6E–273 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
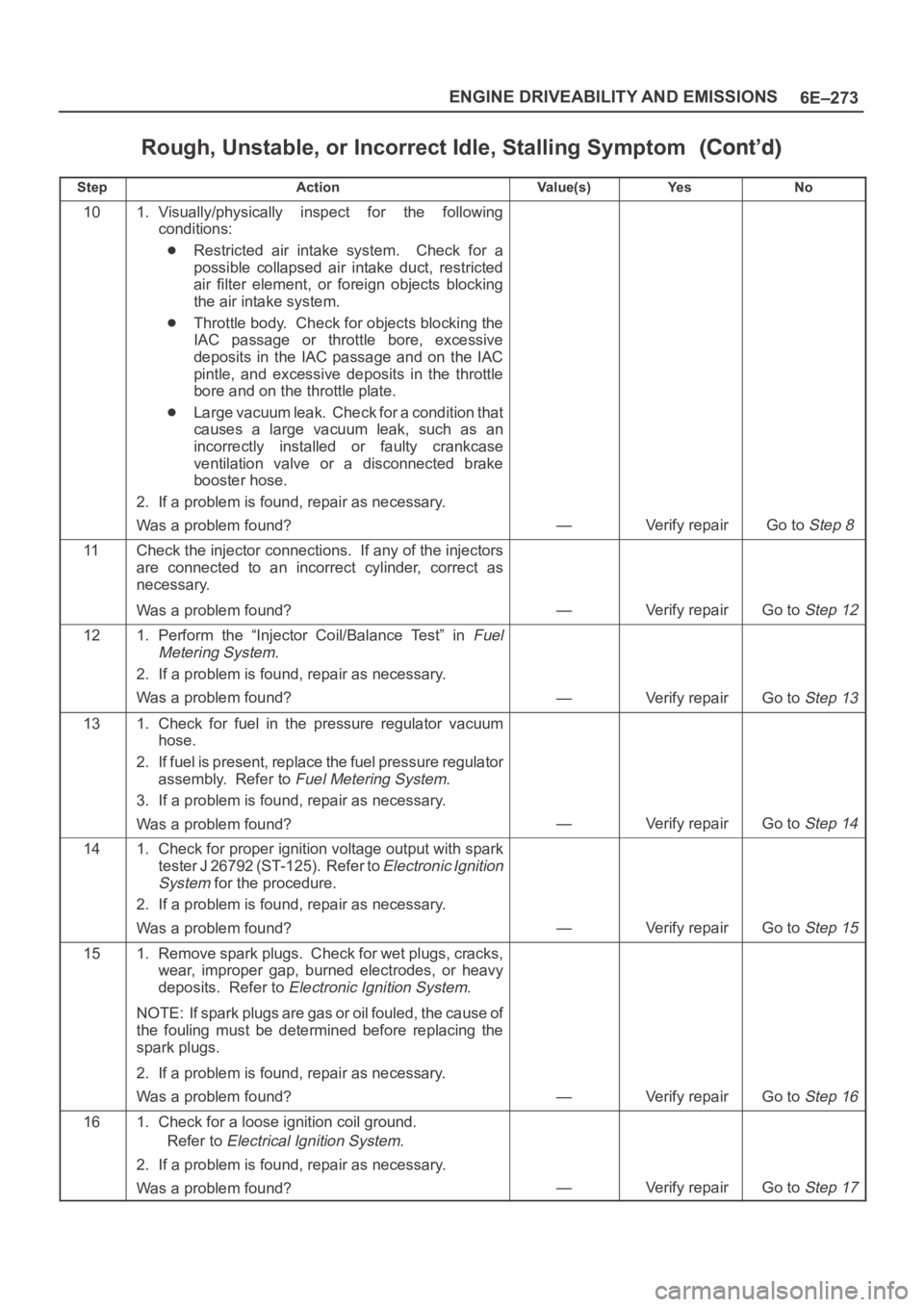
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the
IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive
deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC
pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle
bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that
causes a large vacuum leak, such as an
incorrectly installed or faulty crankcase
ventilation valve or a disconnected brake
booster hose.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
11Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Perform the “Injector Coil/Balance Test” in Fuel
Metering System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check for fuel in the pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
2. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator
assembly. Refer to
Fuel Metering System.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for the procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Check for a loose ignition coil ground.
Refer to
Electrical Ignition System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
Page 4932 of 6000
6E–275 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
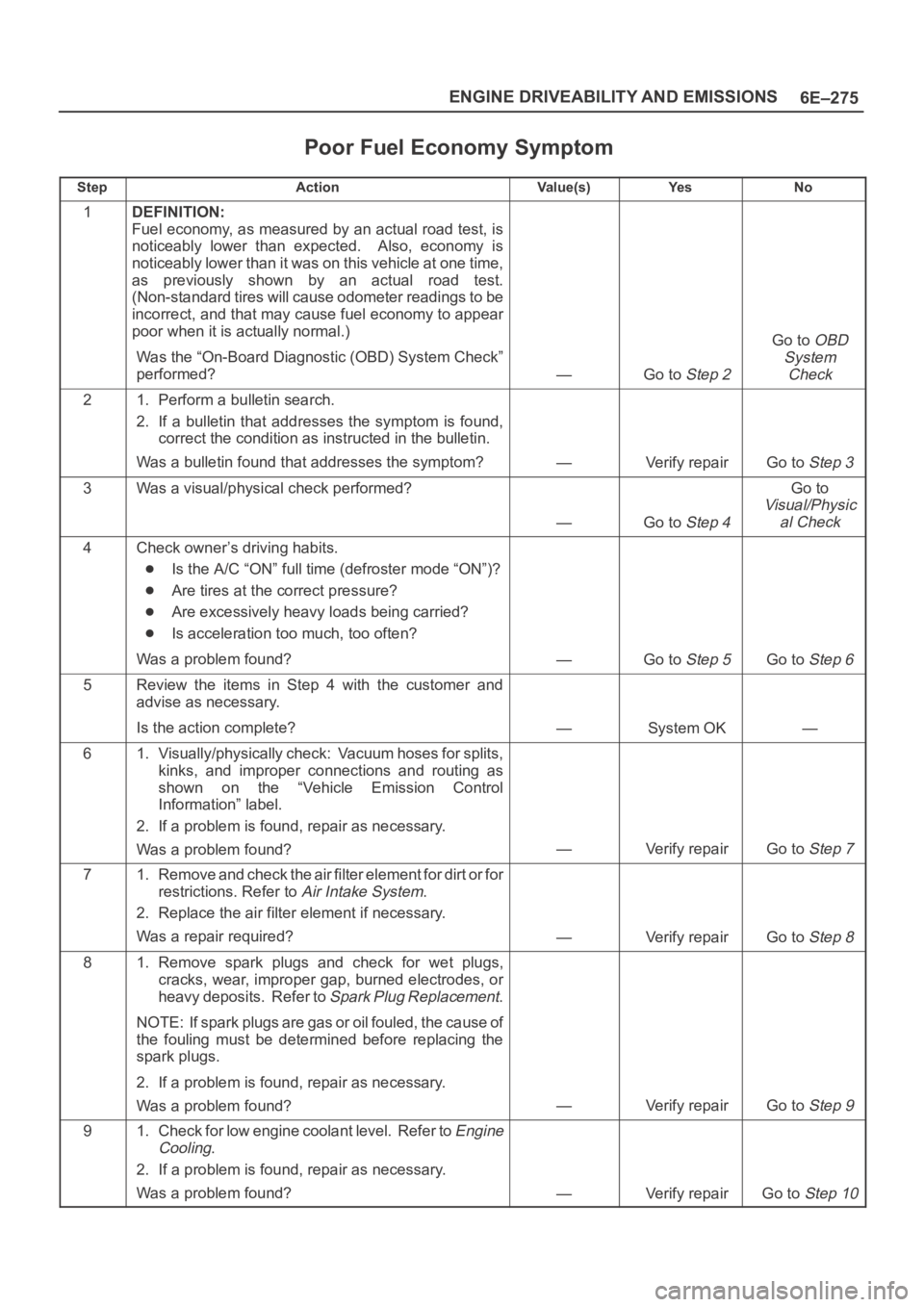
Poor Fuel Economy Symptom
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1DEFINITION:
Fuel economy, as measured by an actual road test, is
noticeably lower than expected. Also, economy is
noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one time,
as previously shown by an actual road test.
(Non-standard tires will cause odometer readings to be
incorrect, and that may cause fuel economy to appear
poor when it is actually normal.)
Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom?
—Verify repairGo to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to
Visual/Physic
al Check
4Check owner’s driving habits.
Is the A/C “ON” full time (defroster mode “ON”)?
Are tires at the correct pressure?
Are excessively heavy loads being carried?
Is acceleration too much, too often?
Was a problem found?
—Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Review the items in Step 4 with the customer and
advise as necessary.
Is the action complete?
—System OK—
61. Visually/physically check: Vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and improper connections and routing as
shown on the “Vehicle Emission Control
Information” label.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 7
71. Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or for
restrictions. Refer to
Air Intake System.
2. Replace the air filter element if necessary.
Was a repair required?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
81. Remove spark plugs and check for wet plugs,
cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or
heavy deposits. Refer to
Spark Plug Replacement.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 9
91. Check for low engine coolant level. Refer to Engine
Cooling
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 10
Page 4940 of 6000
6E–283 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
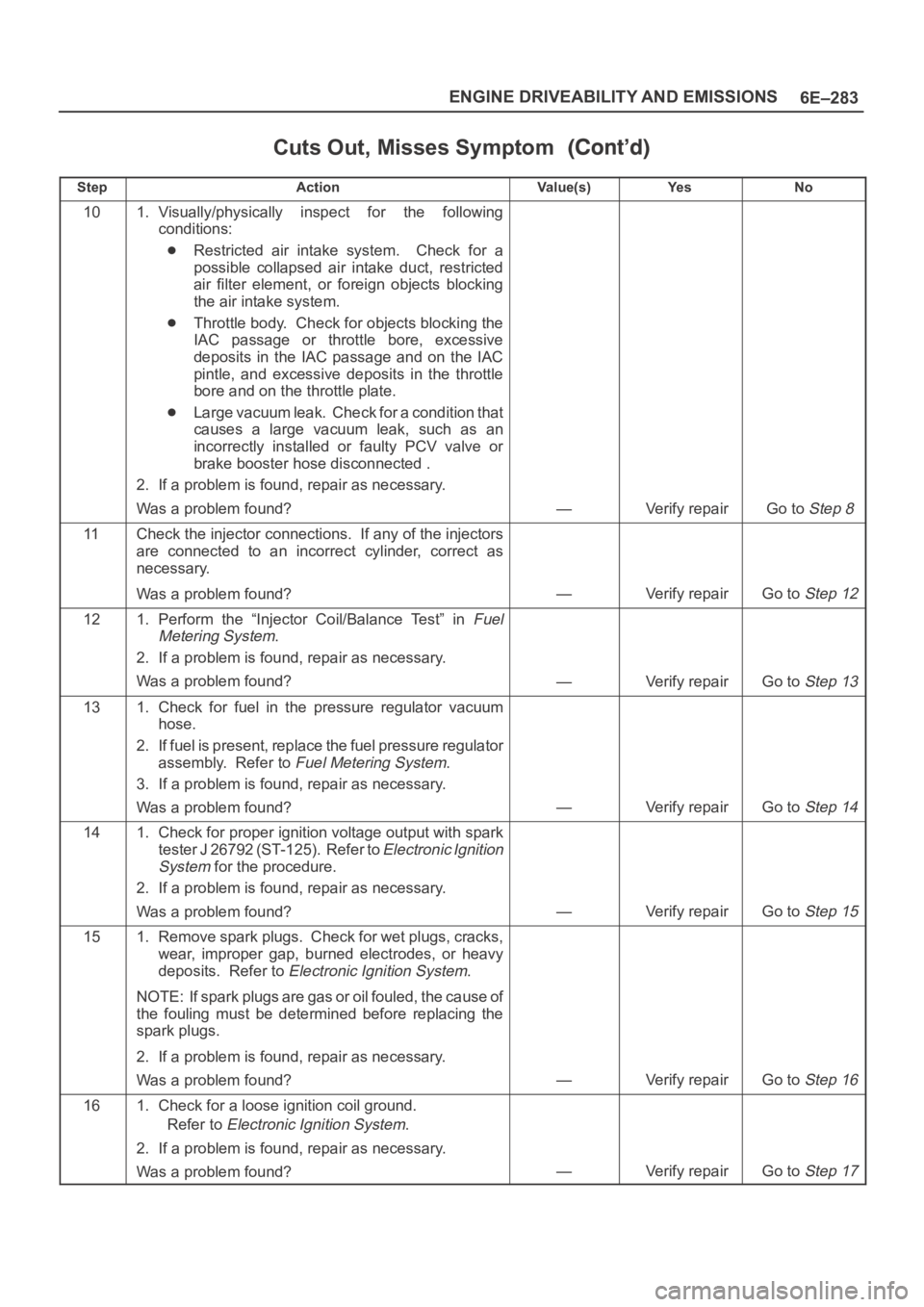
Cuts Out, Misses Symptom
StepNo Ye s Va l u e ( s ) Action
101. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
Restricted air intake system. Check for a
possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted
air filter element, or foreign objects blocking
the air intake system.
Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the
IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive
deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC
pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle
bore and on the throttle plate.
Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that
causes a large vacuum leak, such as an
incorrectly installed or faulty PCV valve or
brake booster hose disconnected .
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 8
11Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 12
121. Perform the “Injector Coil/Balance Test” in Fuel
Metering System
.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 13
131. Check for fuel in the pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
2. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator
assembly. Refer to
Fuel Metering System.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 14
141. Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792 (ST-125). Refer to
Electronic Ignition
System
for the procedure.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 15
151. Remove spark plugs. Check for wet plugs, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
deposits. Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
NOTE: If spark plugs are gas or oil fouled, the cause of
the fouling must be determined before replacing the
spark plugs.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 16
161. Check for a loose ignition coil ground.
Refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
—Verify repairGo to Step 17
Page 5006 of 6000

6E–349 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Damage during re-gapping can happen if the gapping
tool is pushed against the center electrode or the
insulator around it, causing the insulator to crack.
When re-gapping a spark plug, make the adjustment
by bending only the ground side terminal, keeping the
tool clear of other parts.
”Heat shock” breakage in the lower insulator tip
generally occurs during several engine operating
conditions (high speeds or heavy loading) and may be
caused by over-advanced timing or low grade fuels.
Heat shock refers to a rapid increase in the tip
temperature that causes the insulator material to
crack.
Spark plugs with less than the recommended amount of
service can sometimes be cleaned and re-gapped , then
returned to service. However, if there is any doubt about
the serviceability of a spark plug, replace it. Spark plugs
with cracked or broken insulators should always be
replaced.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation
A 12-volt signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the
PCM when the A/C is selected through the A/C control
switch.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is controlled through the
PCM. This allows the PCM to modify the idle air control
position prior to the A/C clutch engagement for better idle
quality. If the engine operating conditions are within their
specified calibrated acceptable ranges, the PCM will
enable the A/C compressor relay. This is done by
providing a ground path for the A/C relay coil within the
PCM. When the A/C compressor relay is enabled,
battery voltage is supplied to the compressor clutch coil.
The PCM will enable the A/C compressor clutch
whenever the engine is running and the A/C has been
requested. The PCM will not enable the A/C compressor
clutch if any of the following conditions are met:
The throttle is greater than 90%.
The engine speed is greater than 6315 RPM.
The ECT is greater than 119C (246F).
The IAT is less than 5C (41F).
The throttle is more than 80% open.
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose
The A/C compressor operation is controlled by the
powertrain control module (PCM) for the following
reasons:
It improvises idle quality during compressor clutch
engagement.
It improvises wide open throttle (WOT) performance.
It provides A/C compressor protection from operation
with incorrect refrigerant pressures.
The A/C electrical system consists of the following
components:
The A/C control head.
The A/C refrigerant pressure switches.
The A/C compressor clutch.
The A/C compressor clutch relay.
The PCM.
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the PCM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control head. The PCM uses this to adjust the
idle speed before turning on the A/C clutch. The A/C
compressor will be inoperative if this signal is not
available to the PCM.
Refer to
A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis for A/C wiring
diagrams and diagnosis for A/C electrical system.
General Description (Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System)
EGR Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is use to
reduce emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx
emission levels are caused by a high combustion
temperature. The EGR system lowers the NOx emission
levels by decreasing the combustion temperature.
057RW002
Linear EGR Valve
The main element of the system is the linear EGR valve.
The EGR valve feeds small amounts of exhaust gas back
into the combustion chamber. The fuel/air mixture will be
diluted and combustion temperatures reduced.
Linear EGR Control
The PCM monitors the EGR actual positron and adjusts
the pintle position accordingly. The uses information from
the following sensors to control the pintle position:
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
Throttle position (TP) sensor.
Mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
Linear EGR Valve Operation and Results
of Incorrect Operation
The linear EGR valve is designed to accurately supply
EGR to the engine independent of intake manifold
vacuum. The valve controls EGR flow from the exhaust
Page 5276 of 6000
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 3
SERVICE INFORMATION
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATION
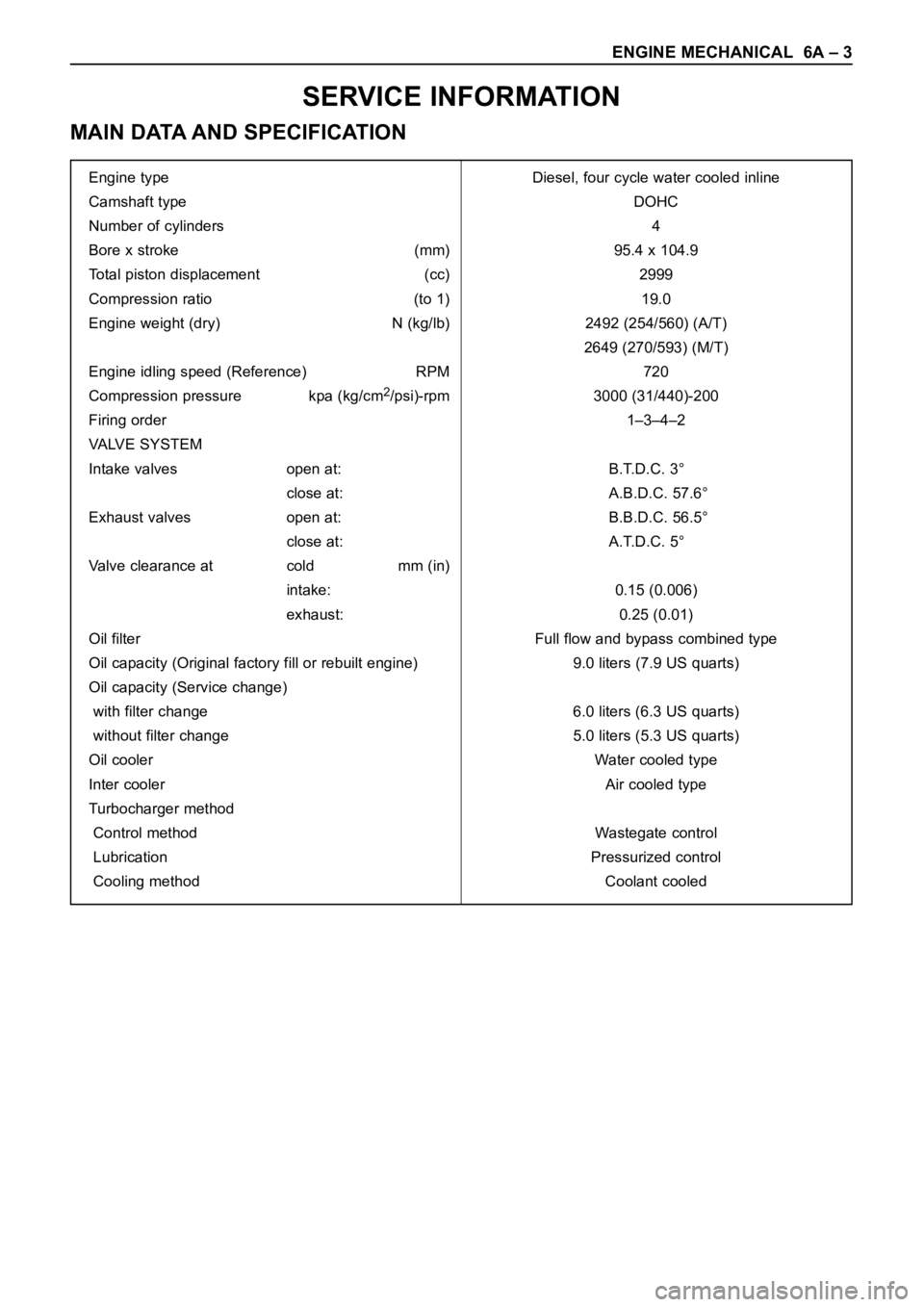
Engine type Diesel, four cycle water cooled inline
Camshaft type DOHC
Number of cylinders 4
Bore x stroke (mm) 95.4 x 104.9
Total piston displacement (cc) 2999
Compression ratio (to 1) 19.0
Engine weight (dry) N (kg/lb) 2492 (254/560) (A/T)
2649 (270/593) (M/T)
Engine idling speed (Reference) RPM 720
Compression pressure kpa (kg/cm
2/psi)-rpm 3000 (31/440)-200
Firing order 1–3–4–2
VALVE SYSTEM
Intake valves open at: B.T.D.C. 3°
close at: A.B.D.C. 57.6°
Exhaust valves open at: B.B.D.C. 56.5°
close at: A.T.D.C. 5°
Valve clearance at cold mm (in)
intake: 0.15 (0.006)
exhaust: 0.25 (0.01)
Oil filter Full flow and bypass combined type
Oil capacity (Original factory fill or rebuilt engine) 9.0 liters (7.9 US quarts)
Oil capacity (Service change)
with filter change 6.0 liters (6.3 US quarts)
without filter change 5.0 liters (5.3 US quarts)
Oil cooler Water cooled type
Inter cooler Air cooled type
Turbocharger method
Control method Wastegate control
Lubrication Pressurized control
Cooling method Coolant cooled