1998 OPEL FRONTERA low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 2172 of 6000

7A–18
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 9c: Coastdown Harsh Shift Or Clunk At 3–2 Downshift
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15b:
Possible Causes
of High Line
Pressure in this
section
2Does DTC P1850 set?
Diagnose P1850
first
Replace band
apply solenoid
(PWM) (323)
Chart 10: Intermittent 4TH TO 2ND Gear Downshift At Steady Speed
StepActionYe sNo
1Check for consistent speed sensor reading with scan tool.
Was the reading correct?Replace mode
switch for
intermittent
contact.
Go to Step 2
21. Check for wiring harness damage or short to ground. If OK, go
to (2).
2. Check transmission speed sensor connections. If OK, go to
(3).
3. Replace transmission speed sensor.
Was the replacement complete?
—
Replace speed
sensor.
Chart 11: Engine Flare At Shifting During Turning Only (Usually With Warm Engine)
StepActionYe sNo
1Check for oil leaks at transmission.
Was the problem found?Replace
transmission oil
filter and gasket
—
Chart 12: Engine Flare During 1–2 Or 2–3 Shift
StepActionYe sNo
1Check line pressure. Refer to Line Pressure Test in this section.
Was line pressure normal?
Go to Step 2
Use Chart 15a:
Possible Causes
of Low Line
Pressure in this
section
21. Check for a stuck 1–2 accumulator valve (320).
2. Check for servo piston (106) leaks.
3. Check for a stuck band apply solenoid (323).
Was line pressure normal?
Repair or replace—
Page 2174 of 6000

7A–20
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 15a: Possible Causes of Low Line Pressure
StepActionYe sNo
1Check oil level.
Was the problem found?
Fill with ATFGo to Step 2
2Check for defective throttle position sensor.
Was the problem found?Replace throttle
position sensor
Go to Step 3
3Check for plugged, loose, or damaged oil filter (79).
Was the problem found?Inspect oil filter,
tighten bolts or
replace oil filter
(79)
Go to Step 4
4Check for a stuck force motor plunger (404). (Adapter case valve
body)
Was the problem found?Replace force
motor plunger
(404)
Go to Step 5
5Check for a stuck feed limit valve (412). (Adapter case valve body)
Was the problem found?Replace feed limit
valve (412)
Go to Step 6
6Check for loose converter bolts (4 & 5).
Was the problem found?Tighten converter
bolts (4 & 5)
Go to Step 7
7Check for a stuck pressure regulator valve (208). (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace pressure
regulator valve
(208)
Go to Step 8
8Check for a stuck boost valve (205).(Oil pump)
Was the problem found?Replace boost
valve (205)
Go to Step 9
9Check for blocked intermediate oil passages to pressure
regulator valve. (Oil pump)
Was the problem found?
Replace oil pumpGo to Step 10
10Check for defective oil pump (9, 201, 202 & 209).
Was the problem found?
Replace oil pumpGo to Step 11
11Check for internal leaks.
– Check balls missing or out of location in valve bodies
– Seals cut or damaged
– Gaskets defective, etc.
Was the problem found?Install balls, or
correct ball
location
Replace seals
Replace gaskets
—
Page 2176 of 6000
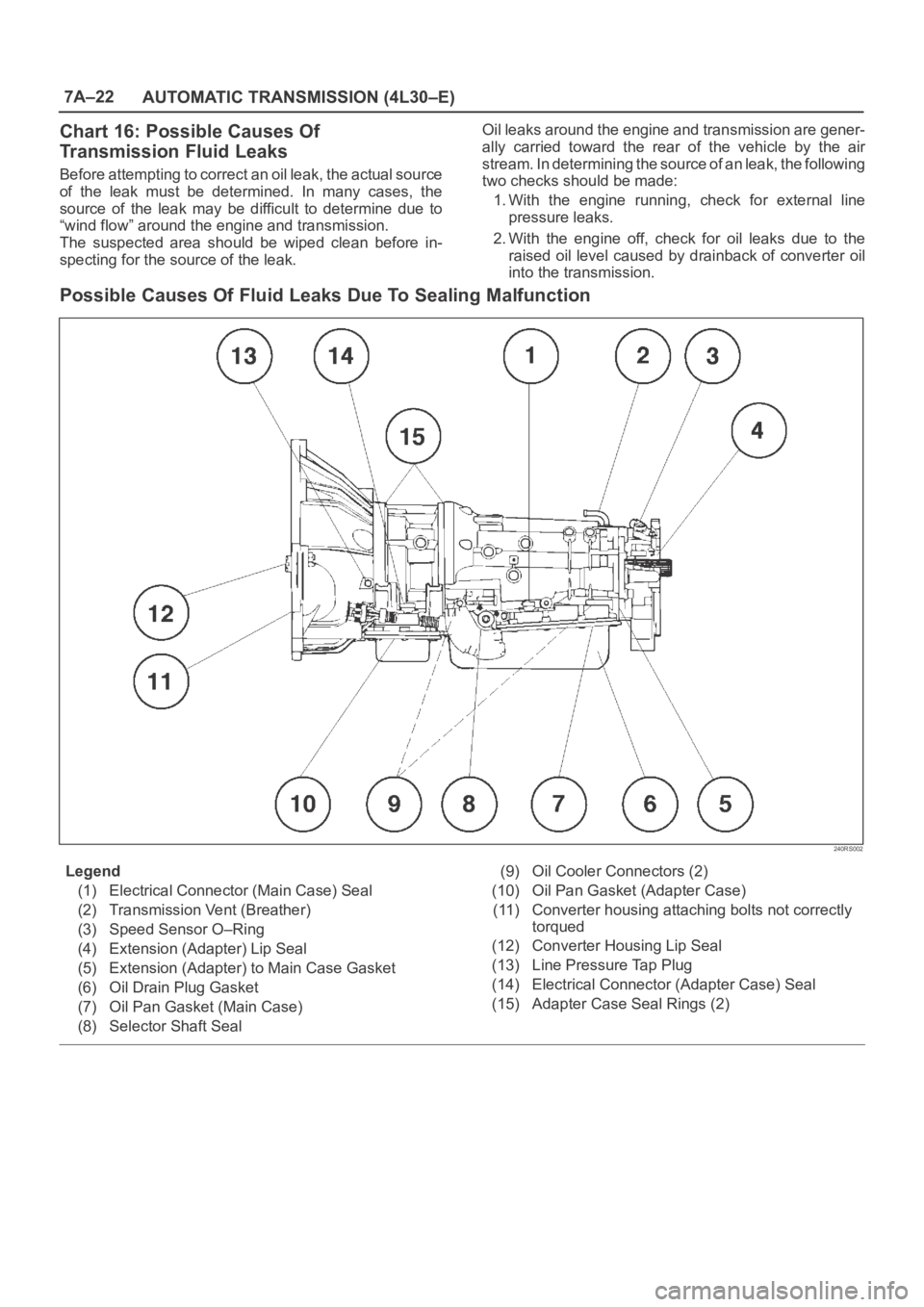
7A–22
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Chart 16: Possible Causes Of
Transmission Fluid Leaks
Before attempting to correct an oil leak, the actual source
of the leak must be determined. In many cases, the
source of the leak may be difficult to determine due to
“wind flow” around the engine and transmission.
The suspected area should be wiped clean before in-
specting for the source of the leak.Oil leaks around the engine and transmission are gener-
ally carried toward the rear of the vehicle by the air
stream. In determining the source of an leak, the following
two checks should be made:
1. With the engine running, check for external line
pressure leaks.
2. With the engine off, check for oil leaks due to the
raised oil level caused by drainback of converter oil
into the transmission.
Possible Causes Of Fluid Leaks Due To Sealing Malfunction
240RS002
Legend
(1) Electrical Connector (Main Case) Seal
(2) Transmission Vent (Breather)
(3) Speed Sensor O–Ring
(4) Extension (Adapter) Lip Seal
(5) Extension (Adapter) to Main Case Gasket
(6) Oil Drain Plug Gasket
(7) Oil Pan Gasket (Main Case)
(8) Selector Shaft Seal(9) Oil Cooler Connectors (2)
(10) Oil Pan Gasket (Adapter Case)
(11) Converter housing attaching bolts not correctly
torqued
(12) Converter Housing Lip Seal
(13) Line Pressure Tap Plug
(14) Electrical Connector (Adapter Case) Seal
(15) Adapter Case Seal Rings (2)
Page 2177 of 6000

7A–23 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
Stall Test
The stall test allows you to check the transmission for
internal abrasion and the one way clutch for slippage.
Torque converter performance can also be evaluated.
The stall test results together with the road test results will
identify transmission components requiring servicing or
adjustment.
Stall Test Procedure:
1. Check the level of the engine coolant, the engine oil,
and the automatic transmission fluid. Replenish if
necessary.
2. Block the wheels and set the parking brake.
3. Connect a tachometer to the engine.
4. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the engine
coolant temperature reaches 70 – 80
C (158 –
176
F).
5. Hold the brake pedal down as far as it will go.
6. Place the selector in the “D” range.
7. Gradually push the accelerator pedal to the floor.
The throttle valve will be fully open.
Note the engine speed at which the tachometer
needle stabilizes.
Stall Speed : 2,100
150 rpm
NOTE: Do not continuously run this test longer than 5
seconds.
8. Release the accelerator pedal.
9. Place the selector in the “N” range.
10. Run the engine at 1,200 rpm for one minute.
This will cool the transmission fluid.
11. Repeat Steps 7 – 10 for the “3”, “2”, “L” and “R”
ranges.
Line Pressure Test
The line pressure test checks oil pump and control valve
pressure regulator valve function. It will also detect oil
leakage.
Line Pressure Test Procedure:
1. Check the level of the engine coolant, the engine oil,
and the automatic transmission fluid.
Replenish if required.
2. Block the wheels and set the parking brake.
3. Remove the pressure detection plug at the left side of
the transmission case.
Set 5–8840–0004–0 pressure gauge and adapter to
the pressure detection plug hole.
241RS001
4. Start the engine and allow it to idle until the engine
coolant temperature reaches 70 – 80
C (158 –
176
F).
5. Hold the brake pedal down as far as it will go.
6. Place the selector in the “D” range.
7. Note the pressure gauge reading with the engine
idling.
8. Gradually push the accelerator pedal to the floor. The
throttle valve will be fully open.
Note the pressure gauge reading with the accelerator
pedal fully depressed.
NOTE: Do not continuously run this test longer than 5
seconds.
9. Release the accelerator pedal.
10. Place the selector in the “N” range.
11. Run the engine at 1,200 rpm for one minute.
This will cool the transmission fluid.
12. Repeat Steps 7 – 11 for the “3”, “2”, “L”, and “R”
ranges.
13. Install a pressure detection plug to the transmission
case, applying recommended thread locking agent
(LOCTITE 242) or its equivalent to thread of plug.
Make sure that thread is cleaned before applying
locking agents.
14. Tighten the pressure detection plug to the specified
torque.
Torque:9–14Nꞏm(0.9–1.4kgꞏm/7–10lbft)
Page 2214 of 6000

7A–60
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION (4L30–E)
10. Remove retainer (13), 2–3 shift valve (14), and spring
(15).
11. Remove spring pin (16), plug (17), spring (18), and
low pressure control valve (19).
12. Remove spring pin (20), plug (21), and band control
screen assembly (22).
13. Remove spring pin (23), plug (24), 1–2 accumulator
valve (25), and 1–2 accumulator control valve (26).
14. Remove check ball (27) from valve body (28).
Inspection And Repair
Inspect for the following, and replace any damaged or
worn parts:
1. Damage or wear to each valve.
2. Damage in oil passeges.
3. Cracks or damage to valve body.
4. Valve operations.
5. Spring fatigue.
Reassembly
1. Install 1–2 accumulator control valve (26), 1–2
accumulator valve (25), plug (24), and spring pin (23).
2. Install band control screen assembly (22), plug (21),
and spring pin (20).
3. Install low pressure control valve (19), spring (18),
plug (17), and spring pin (16).
4. Install spring (15), 2–3 shift valve (14), retainer (13),
solenoid B (12), and spring pin (11).
5. Install spring (10), 1–2/3–4 shift valve (9), retainer (8),
solenoid A (7), and spring pin (6).
6. Install waved washer (5), band control solenoid (3),
and pin (4).
7. Install manual valve (2).
8. Install check ball (27) to valve body (28).
9. Install gasket (valve body/transfer plate) and transfer
plate using two 5–8840–2270–0 (J–3387–2) guide
pins.
Install two 11mm bolts.
Torque: 13 N
m (1.3 kgꞏm/113 lb in)
244RW004
Install gasket (transfer plate/main case).
Page 2251 of 6000

7A1–6
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Shift Control
The transmission gear is shifted according to the shift
pattern selected by the driver. In shifting gears, the gear
ratio is controlled by the ON/ OFF signal using the shift
solenoid A and the shift solenoid B.
Band Apply Control
The band apply is controlled when in the 3–2 downshift
(engine overrun prevention) and the garage shift (shock
control).
The band apply solenoid is controlled by the signal from
the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to regulate the flow of
the oil.
Torque Converter Clutch Control
The clutch ON/OFF is controlled by moving the converter
clutch valve through shifting Torque Converter Clutch
(TCC) solenoid using the ON/OFF signal.
Line Pressure Control
The throttle signal allows the current signal to be sent to
the force motor. After receiving the current signal, the
force motor activates the pressure regulator valve to
regulate the line pressure.
On–Board Diagnostic System
Several malfunction displays can be stored in the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) memory, and read out
of it afterward.The serial data lines, which are required for the testing of
the final assembly and the coupling to other electronic
modules, can be regulated by this function.
Fail Safe Mechanism
If there is a problem in the transmission system, the PCM
will go into a “backup” mode.
The vehicle can still be driven, but the driver must use the
select lever to shift gears.
Torque Management Control
The transmission control side sends the absolute spark
advance signal to the engine control side while the
transmission is being shifted. This controls the engine
spark timing in compliance with the vehicle running
condition to reduce the shocks caused by the change of
speed.
ATF Warning Control
The oil temperature sensor detects the ATF oil
temperature to control the oil temperature warning, TCC,
and the winter mode.
ABS Control (If equipped)
When the select lever is at “L” or “R” range, a signal is sent
to the ABS controller as one of the ABS control
conditions.
Page 2255 of 6000

7A1–10
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Functions of Input / Output Components
ComponentsFunction
Speed sensor
(fixed to transmission
(T/M))Senses rotation of output shaft and feeds the data to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
Throttle position sensor
(TPS)
(fixed to engine)Senses the extent of throttle valve opening and the speed of the throttle valve
lever motion to open the valve. Feeds the data to PCM.
I
N
Brake Switch (SW)
(fixed to brake pedal)Senses whether the driver has pressed the brake pedal or not and feeds the
information to PCM.
N-
P
U
Kickdown SW
(fixed to accelerator pedal)Senses whether the driver has pushed the accelerator pedal fully or not, and
feeds the information to PCM.
U
TMode SW (fixed to T/M)Senses the select lever position, and feeds the information to PCM.
S
I
Power drive SW
(fixed to front console)Senses whether the driver has selected the power mode, and feeds the informa-
tion to PCM.
I
G-T/M oil temp. sensorSenses the T/M oil temperature and feeds the data to PCM
N
A
L
Engine coolant tempera-
ture sensorSenses the engine coolant temperature, and feeds the data to PCM.
LEngine speed signalFeeds the signals monitoring engine speed to PCM from crank angle sensor.
Air conditioning informationSenses whether the air conditioner has been switched on or not, and feeds the
information to PCM.
Winter switch (fixed to front
console)Senses whether the driver has selected the winter mode, and feeds the informa-
tion to PCM.
Cruise controller * (Over-
drive OFF signal)Downshift takes place when Overdrive OFF signal is received from auto cruise
control unit.
S
Shift solenoid A, BSelects shift point and gear position suited to the vehicle running condition on
the basis of PCM output.
O
S
O-
L
Band apply solenoidControls oil flow suited to the vehicle running condition on the basis of PCM out-
put.
O
U
T-
P
E-
N
O
Torque Converter
Clutch solenoidControls clutch engagement/disengagement suited to the vehicle running condi-
tion on the basis of PCM output.
P
U
T
O
I
DForce motor
(Pressure regulator
valve)Adjusts the oil pump delivery pressure to line pressure suited to the vehicle run-
ning condition on the basis of PCM output.
S
I
Power drive mode lampInforms the driver whether the vehicle is in power mode or not.
I
G-Winter drive mode lampInforms the driver whether the vehicle is in winter mode or not.G
N
A
L
T/M monitor lamp
(“CHECK TRANS”)Informs the driver of failure in the system.
LATF warning lampLights when ATF oil temperature rises.
ABS signal *When the select lever is at “Reverse” or “L” range, sends a signal to the ABS
controller as one of the ABS control conditions.
* If equipped
Page 2300 of 6000
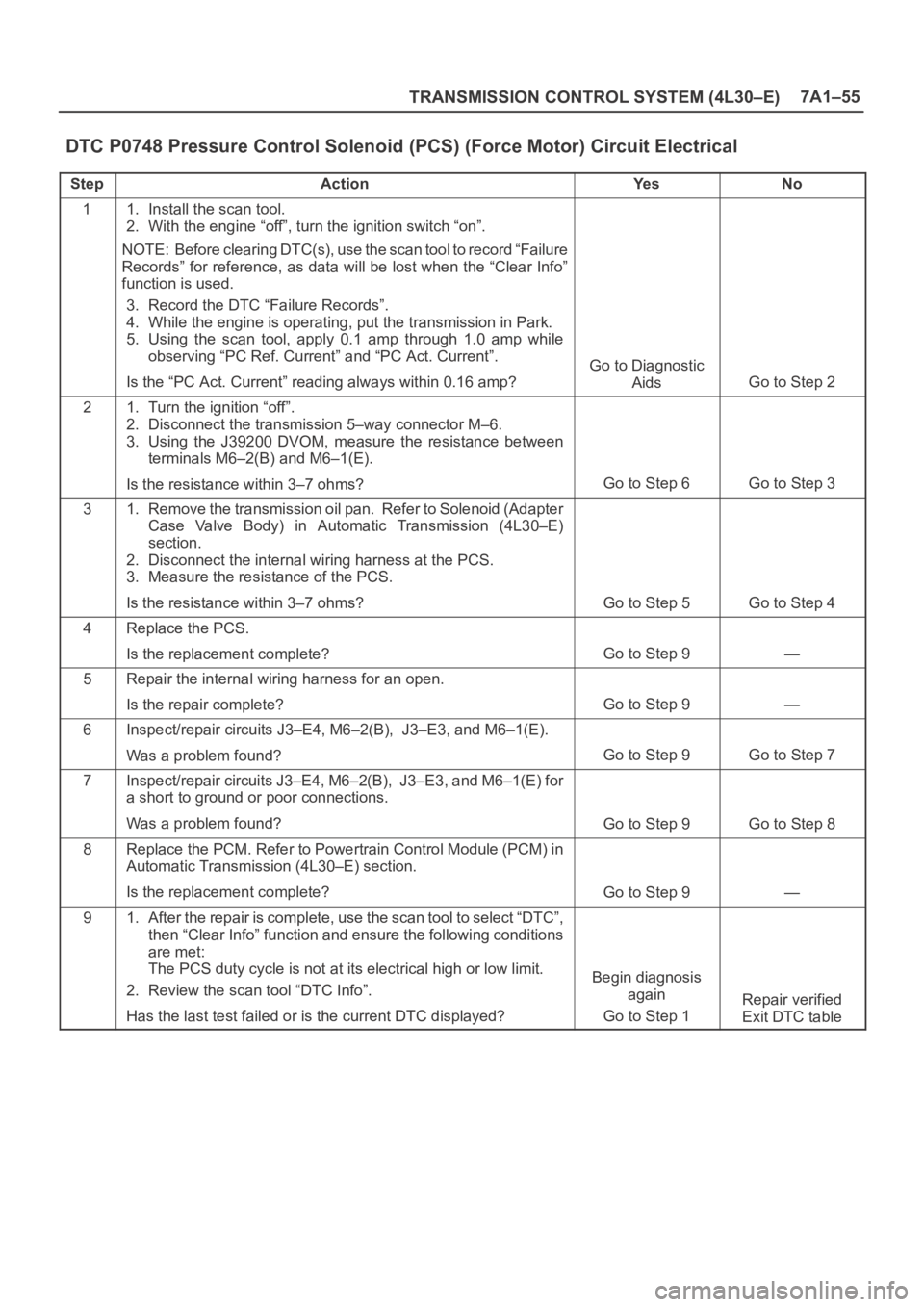
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (4L30–E)7A1–55
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit Electrical
StepActionYe sNo
11. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine “off”, turn the ignition switch “on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record “Failure
Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the “Clear Info”
function is used.
3. Record the DTC “Failure Records”.
4. While the engine is operating, put the transmission in Park.
5. Using the scan tool, apply 0.1 amp through 1.0 amp while
observing “PC Ref. Current” and “PC Act. Current”.
Is the “PC Act. Current” reading always within 0.16 amp?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
Go to Step 2
21. Turn the ignition “off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 5–way connector M–6.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M6–2(B) and M6–1(E).
Is the resistance within 3–7 ohms?
Go to Step 6Go to Step 3
31. Remove the transmission oil pan. Refer to Solenoid (Adapter
Case Valve Body) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
2. Disconnect the internal wiring harness at the PCS.
3. Measure the resistance of the PCS.
Is the resistance within 3–7 ohms?
Go to Step 5Go to Step 4
4Replace the PCS.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 9—
5Repair the internal wiring harness for an open.
Is the repair complete?
Go to Step 9—
6Inspect/repair circuits J3–E4, M6–2(B), J3–E3, and M6–1(E).
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9Go to Step 7
7Inspect/repair circuits J3–E4, M6–2(B), J3–E3, and M6–1(E) for
a short to ground or poor connections.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9Go to Step 8
8Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete?
Go to Step 9—
91. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select “DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
The PCS duty cycle is not at its electrical high or low limit.
2. Review the scan tool “DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified
Exit DTC table