1998 OPEL FRONTERA battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 5649 of 6000

6E–220
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Installation Procedure
1. Install the EVRV.
035RW064
2. Connect the EVRV hose and the EVRV connector.
035RW065
3. Connect the negative battery cable.
Wiring and Connectors
Wiring Harness Service
The ECM harness electrically connects the ECM to the
various solenoids, switches and sensors in the vehicle
engine compartment and passenger compartment.
Replace wire harnesses with the proper part number
replacement.
Because of the low amperage and voltage levels utilized
in powertrain control systems, it is essential that all wiring
in environmentally exposed areas be repaired with crimp
and seal splice sleeves.The following wire harness repair information is intended
as a general guideline only. Refer to
Chassis Electrical f o r
all wire harness repair procedures.
Connectors and Terminals
Use care when probing a connector and when replacing
terminals. It is possible to short between opposite
terminals. Damage to components could result. Always
use jumper wires between connectors for circuit
checking. NEVER probe through Weather-Pack seals.
Use an appropriate connector test adapter kit which
contains an assortment of flexible connectors used to
probe terminals during diagnosis. Use an appropriate
fuse remover and test tool for removing a fuse and to
adapt the fuse holder to a meter for diagnosis.
Open circuits are often difficult to locate by sight because
oxidation or terminal misalignment are hidden by the
connectors. Merely wiggling a connector on a sensor, or
in the wiring harness, may temporarily correct the open
circuit. Intermittent problems may also be caused by
oxidized or loose connections.
Be certain of the type of connector/terminal before
making any connector or terminal repair. Weather-Pack
and Com-Pack III terminals look similar, but are serviced
differently.
Wire Harness Repair: Twisted
Shielded Cable
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the outer jacket.
2. Unwrap the aluminum/mylar tape. Do not remove the
mylar.
047
Page 5655 of 6000

6E–226
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
0018
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the ECM varies from below 2 volts at idle
(high vacuum) to above 4 volts.
The MAP sensor is used to determine the following:
Boost pressure for injector control.
Barometric pressure (BARO).
If the ECM detects a voltage that is lower than the
possible range of the MAP sensor, DTC P0107 will be set.
A signal voltage higher than the possible range of the
sensor will set DTC P0108. An intermittent low or high
voltage will set DTC P1107 or DTC P1106, respectively.
The ECM can detect a shifted MAP sensor. The ECM
compares the MAP sensor signal to a calculated MAP
based on throttle position and various engine load factors.
If the ECM detects a MAP signal that varies excessively
above or below the calculated value, DTC P0106 will set.
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located in the engine
room.
The ECM constantly observes the information from
various sensors. The ECM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize
operational problems, alert the driver through the MIL
(Service Engine Soon lamp), and store diagnostic trouble
codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the problem areas to aid the
technician in making repairs.
ECM Function
The ECM supplies 5, 12 and 110 volts to power various
sensors or switches. The power is supplied through
resistances in the ECM which are so high in value that a
test light will not light when connected to the circuit. In
some cases, even an ordinary shop voltmeter will not give
an accurate reading because its resistance is too low.
Therefore, a digital voltmeter with at least 10 megohms
input impedance is required to ensure accurate voltage
readings. The ECM controls output circuits such as theinjectors, glow relays, etc., by controlling the ground or
the power feed circuit through transistors or through
either of the following two devices:
Output Driver Module (ODM)
Quad Driver Module (QDM)
ECM Components
The ECM is designed to maintain exhaust emission levels
to government mandated standards while providing
excellent driveability and fuel efficiency. The ECM
monitors numerous engine and vehicle functions via
electronic sensors such as the crankshaft position (CKP)
sensor, and vehicle speed sensor (VSS). The ECM also
controls certain engine operations through the following:
Fuel injector control
Rail pressure control
ECM Voltage Description
The ECM supplies a buffered voltage to various switches
and sensors. It can do this because resistance in the
ECM is so high in value that a test light may not illuminate
when connected to the circuit. An ordinary shop
voltmeter may not give an accurate reading because the
voltmeter input impedance is too low. Use a 10-megohm
input impedance digital voltmeter to assure accurate
voltage readings.
The input/output devices in the ECM include
analog-to-digital converters, signal buffers, counters,
and special drivers. The ECM controls most components
with electronic switches which complete a ground circuit
when turned “ON.” These switches are arranged in
groups of 4 and 7, called either a surface-mounted quad
driver module (QDM), which can independently control up
to 4 output terminals, or QDMs which can independently
control up to 7 outputs. Not all outputs are always used.
ECM Input/Outputs
Inputs – Operating Conditions Read
Air Conditioning “ON” or “OFF”
Engine Coolant Temperature
Crankshaft Position
Electronic Ignition
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Battery Voltage
Intake Throttle Position
Vehicle Speed
Fuel Temperature
Oil Temperature
Intake Air Temperature
EGR boost pressure
Oil rail pressure
Camshaft Position
Accelerator position
Outputs – Systems Controlled
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Injector Control
QWS
Page 5656 of 6000

6E–227 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
QOS
Diagnostics
– Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Service Engine
Soon lamp)
– Data Link Connector (DLC)
– Data Output
ECM Service Precautions
The ECM is designed to withstand normal current draws
associated with vehicle operation. Avoid overloading any
circuit. When testing for opens and shorts, do not ground
or apply voltage to any of the ECM’s circuits unless
instructed to do so. These circuits should only be tested
using digital voltmeter. The ECM should remain
connected to the ECM or to a recommended breakout
box.
Intake Throttle Position (ITP) Sensor
ITP sensor is a potentiometer type and installed to the
intake throttle valve body. A voltage of 5V is applied
constantly from ECM to ITP sensor thereby to determine
by change in voltage the opening of the intake throttle
valve during warming up.
Transmission Range Switch
IMPORTANT:The vehicle should not be driven with the
transmission range switch disconnected; idle quality will
be affected.
The four inputs from the transmission range switch
indicate to the ECM which position is selected by the
transmission selector lever.
For more information on the transmission on the
transmission range switch, refer to
Automatic
Tr a n s m i s s i o n
.
Accelerator Position Sensor (AP)
AP sensor is a potentiometer type and installed to
accelerator pedal bracket. A voltage of 5V constantly
applied from ECM to the sensor thereby to determine the
accelerator pedaling angle by change in voltage. Further,
this sensor is provided with an accelerator switch, which
is set off only when the accelerator pedal is stepped on.
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment is
defined as any equipment which connects to the vehicle’s
electrical or vacuum systems that is installed on a vehicle
after it leaves the factory. No allowances have been
made in the vehicle design for this type of equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle’s electrical system at the battery
(power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the powertrain system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such asportable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any powertrain problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be diagnosed
in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
TS23793
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and induction.
An example of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
Charge by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentary touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered
components on the ECM circuit board.
Do not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
Before removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
If the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
Page 5663 of 6000

6F – 4 ENGINE EXHAUST
REMOVAL
1. Battery negative cable.
2. Raise the vehicle and support with suitable safety
stands.
3. Remove front exhaust pipe fixing nuts from engine
side.
4. Remove fixing nuts between front exhaust pipe and
center exhaust pipe, remove front exhaust pipe.
5. Disconnect center exhaust pipe and silencer,
remove center exhaust pipe.
6. Remove fixing nuts from connection part of tail pipe,
remove mounting rubber and remove silencer
bracket, silencer.
7. Remove mounting rubber for tail pipe, remove tail
pipe.
INSTALLATION
1. Install front exhaust pipe and tighten it temporarily.
2. Tighten fixing nuts of front exhaust pipe to the
specified torque. (for engine side)
Torque: 67 Nꞏm (6.8 kgꞏm/50 lb ft)
3. Tighten fixing nuts of front exhaust pipe to the
specified torque. (for center pipe side)
Torque: 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
4. Install silencer and tighten silencer bracket nuts to
the specified torque.
Torque: 16 Nꞏm (1.6 kgꞏm/12 lb ft)
5. Install tail pipe and tighten it.
Torque: 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
6. Install mounting rubbers.
Page 5664 of 6000
ENGINE EXHAUST 6F – 5
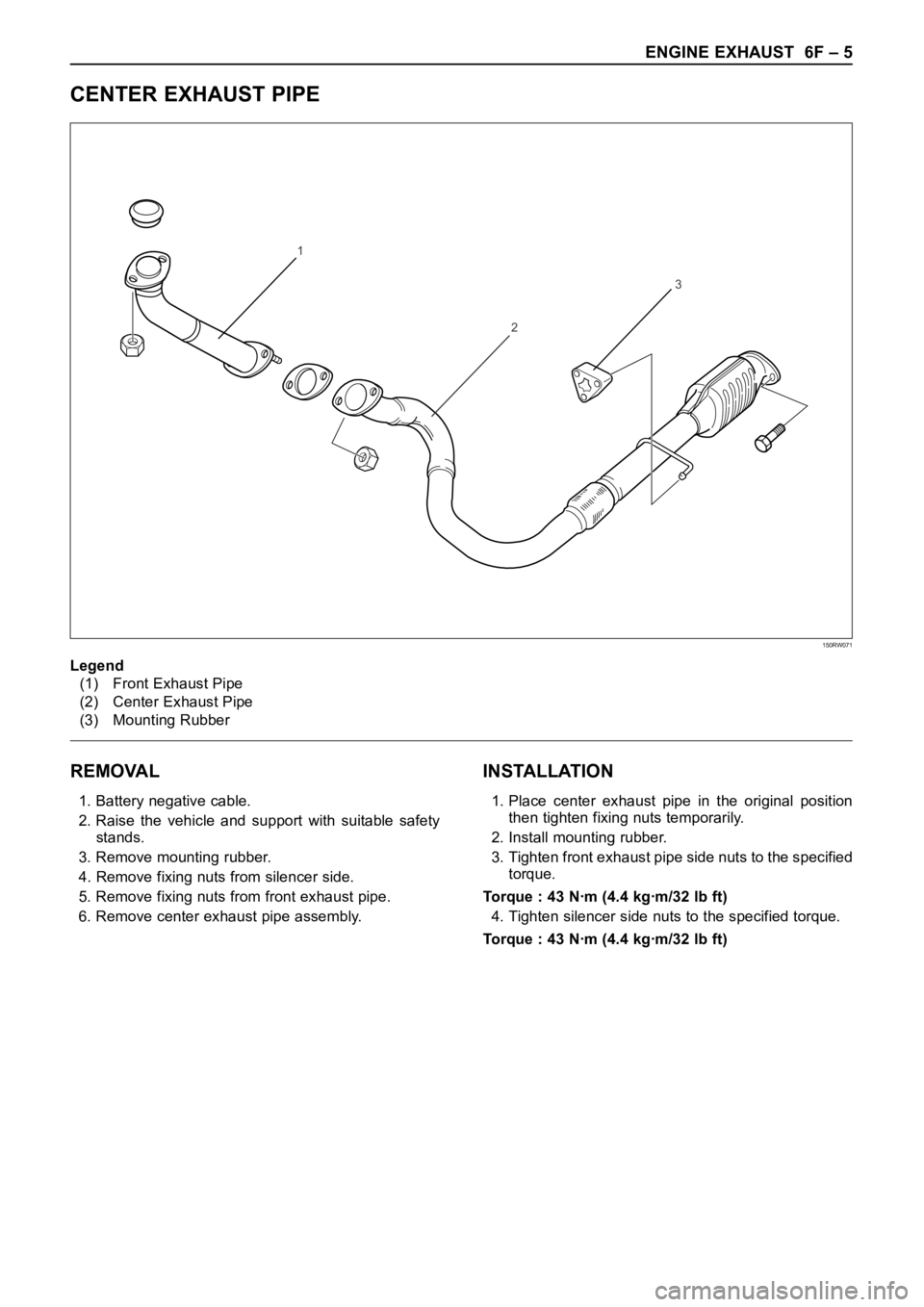
CENTER EXHAUST PIPE
REMOVAL
1. Battery negative cable.
2. Raise the vehicle and support with suitable safety
stands.
3. Remove mounting rubber.
4. Remove fixing nuts from silencer side.
5. Remove fixing nuts from front exhaust pipe.
6. Remove center exhaust pipe assembly.
INSTALLATION
1. Place center exhaust pipe in the original position
then tighten fixing nuts temporarily.
2. Install mounting rubber.
3. Tighten front exhaust pipe side nuts to the specified
torque.
Torque : 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
4. Tighten silencer side nuts to the specified torque.
Torque : 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
3
2 1
Legend
(1) Front Exhaust Pipe
(2) Center Exhaust Pipe
(3) Mounting Rubber
150RW071
Page 5665 of 6000

6F – 6 ENGINE EXHAUST
EXHAUST SILENCER
REMOVAL
1. Battery negative cable.
2. Raise the vehicle and support with suitable safety
stands.
3. Remove mounting rubber from silencer.
4. Remove silencer mounting bracket.
5. Remove fixing nuts between center exhaust pipe
and silencer.
6. Remove fixing nuts from tail pipe flange.
7. Remove silencer assembly.
INSTALLATION
1. Place silencer assembly in the original installation
position, tighten both side (front and rear) nuts
temporarily.
2. Tighten silencer mounting bracket to the specified
torque.
Torque : 16 Nꞏm (1.6 kgꞏm/12 lb ft)
3. Tighten center exhaust pipe side nuts to the
specified torque.
Torque : 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
4. Tighten tail pipe side nuts to the specified torque.
Torque : 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
5. Install silencer mounting rubber.
6
3
4
2
1
5
Legend
(1) Mounting Rubber
(2) Post Silencer
(3) Silencer(4) Mounting Bracket
(5) Mounting Rubber
(6) Tail Pipe
150RW072
Page 5666 of 6000

ENGINE EXHAUST 6F – 7
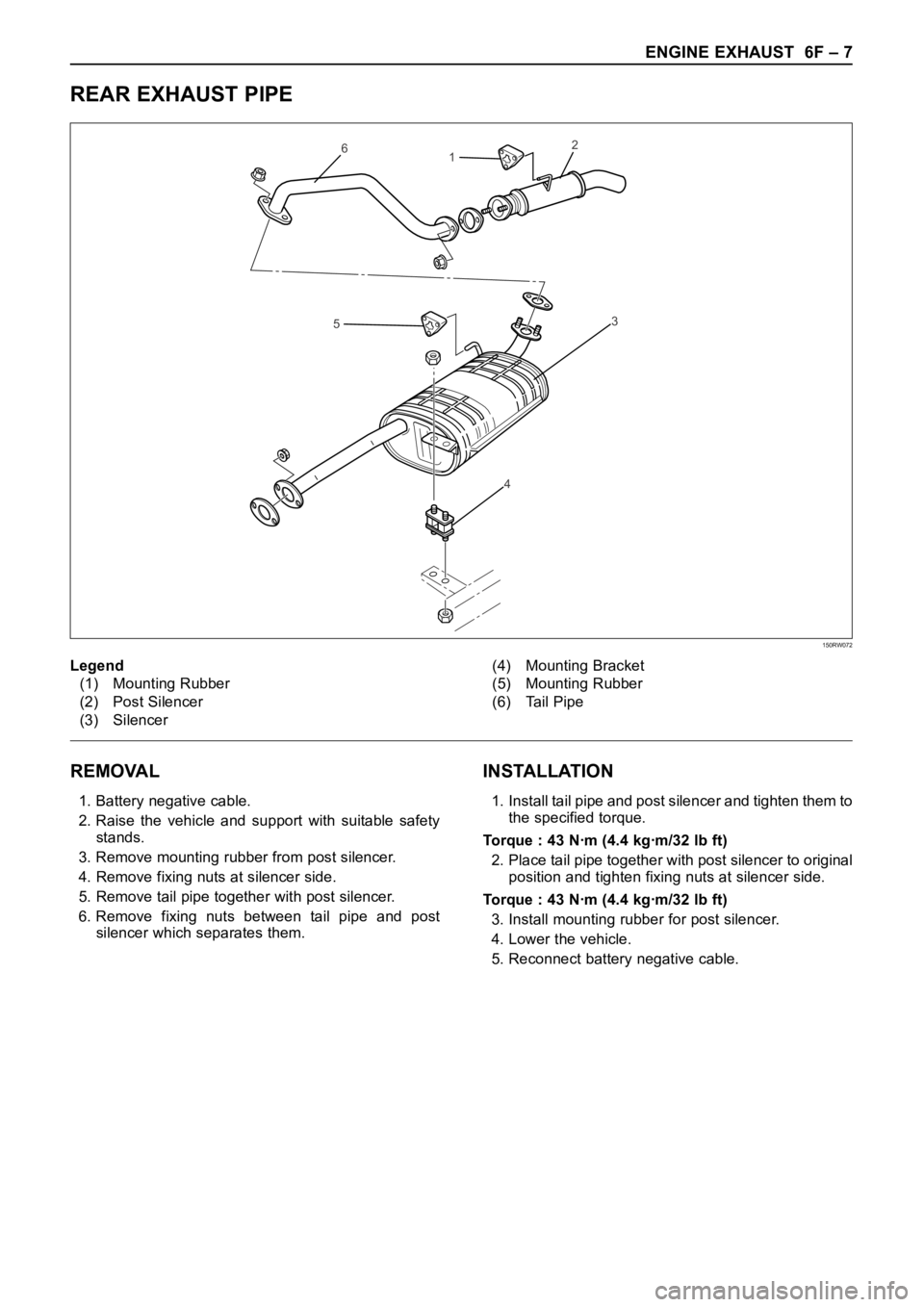
REAR EXHAUST PIPE
REMOVAL
1. Battery negative cable.
2. Raise the vehicle and support with suitable safety
stands.
3. Remove mounting rubber from post silencer.
4. Remove fixing nuts at silencer side.
5. Remove tail pipe together with post silencer.
6. Remove fixing nuts between tail pipe and post
silencer which separates them.
INSTALLATION
1. Install tail pipe and post silencer and tighten them to
the specified torque.
Torque : 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
2. Place tail pipe together with post silencer to original
position and tighten fixing nuts at silencer side.
Torque : 43 Nꞏm (4.4 kgꞏm/32 lb ft)
3. Install mounting rubber for post silencer.
4. Lower the vehicle.
5. Reconnect battery negative cable.
6
3
4
2
1
5
Legend
(1) Mounting Rubber
(2) Post Silencer
(3) Silencer(4) Mounting Bracket
(5) Mounting Rubber
(6) Tail Pipe
150RW072
Page 5672 of 6000

ENGINE LUBRICATION 6G – 5
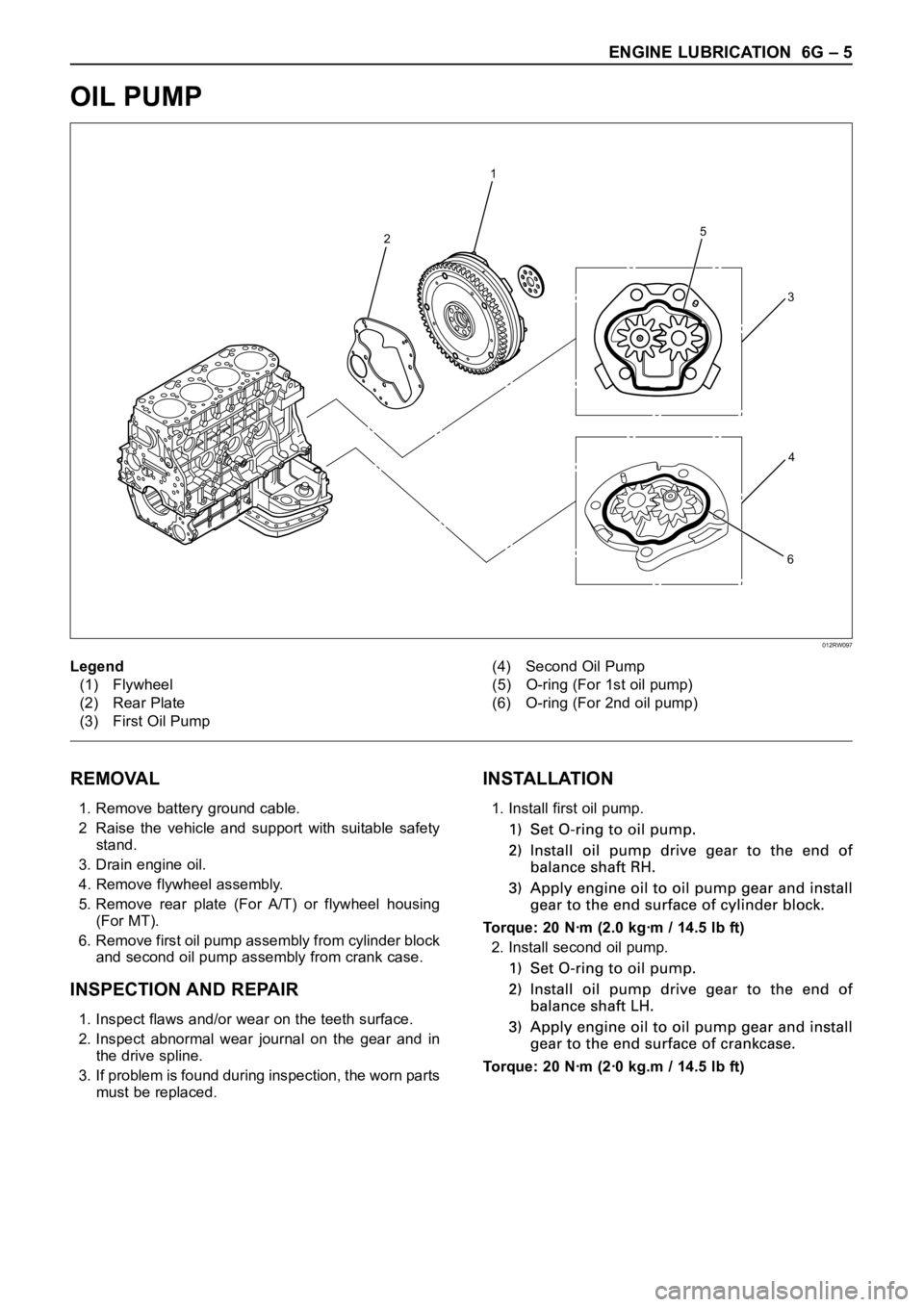
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
1. Remove battery ground cable.
2 Raise the vehicle and support with suitable safety
stand.
3. Drain engine oil.
4. Remove flywheel assembly.
5. Remove rear plate (For A/T) or flywheel housing
(For MT).
6. Remove first oil pump assembly from cylinder block
and second oil pump assembly from crank case.
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
1. Inspect flaws and/or wear on the teeth surface.
2. Inspect abnormal wear journal on the gear and in
the drive spline.
3. If problem is found during inspection, the worn parts
must be replaced.
INSTALLATION
1. Install first oil pump.
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2.0 kgꞏm / 14.5 lb ft)
2. Install second oil pump.
Torque: 20 Nꞏm (2ꞏ0 kg.m / 14.5 lb ft)
2
1
5
6
3
4
Legend
(1) Flywheel
(2) Rear Plate
(3) First Oil Pump(4) Second Oil Pump
(5) O-ring (For 1st oil pump)
(6) O-ring (For 2nd oil pump)
012RW097