1998 JAGUAR X308 inlet manifold
[x] Cancel search: inlet manifoldPage 43 of 2490

Safety Standard
Canister PurgeCANPControls pu
rging of the EVAP canister
Carbon dioxideCO2Colorless gas with
a density of a
pproximately 1.5 ti mes that of air
Carbon mon
oxide
COPoi
sonous gas produced as the re
sult of incomplete combustion
Case G
round
CSE GNDControl modu
le casing ground
Catal
ytic converter
In
-line exhaust system device used to reduce the level of engine exhaust
emissions
Ce
lsius
CSI ter
m for the Centigrade scale, with
freezing point at zero and boiling point
at 100°
Central
Processor Unit
CPUTh
e section of a computer that contai
ns the arithmetic, logic and control
circuits. It performs arithm etic operations, controls instruction processing, and
provides timing signals and other housekeeping operations
Cl
osed Loop
CL
Cl
osed Loop System
CLSControl
system with one
or more feedback loops
Col
umn/Mirror Control
Module
C/MC
M
Control ModuleCMA
self-contained group of electrical/electronic components, designed as a
single replaceable un it, and controlling one or more processes
Controll
er Area Network
CANA
communication system which allows control modules to be linked together
in a network.
Crankshaft Posi
tion
Sensor
CKPSGenerates crankshaft positi on informa
tion in conjunct
ion with the CKPTR (also
generates speed information in certain applications)
Crankshaft Posi
tion
Timing Ring
CKPT
R
Toothe
d ring which
triggers the CKPS
Crankcase Ventila
tion
System
CVSys
tem which scavenges camshaft cover and crankcase emissions and feeds
them into the inlet manifold
Cubic ce nt
imeter
cm
3
Curb weightWe
ight of vehicle with fuel, lubrican
ts and coolant, but excluding driver,
passengers or payload
D
Dat
a Link Connector
DLCConne
ctor providing access and/or control of the vehicle information,
operating conditions, and diagnostic information
De
gree
deg, °Angle or tempe
rature
D
epartment of
Transportation (US)
DO
T
D
epartment of Transport
(UK)
DTp
De
utsche In
stitut für
Normung
DINGerman stand
ards regulation body
Di
agnostic Module
DMSuppl
emental Restraint System (non-c
ontrolling) module for diagnostics
overview
Di
agnostic Test Mode
DTMA le
vel of capability in an OBD system.
May include different functional states
to observe signals, a base level to re ad DTCs, a monitor level which includes
information on signal levels, bi-directional control with on /off board aids, and
the ability to interface with remote diagnosis
Diagnostic Trouble CodeDTCAn al
pha/numeric identifier for a fault
condition identified by the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) system
D
ial test indicator
DTIA mechan
ical measuring
instrument, with a rotary indicating pointer
connected to a linear operating probe
D
ifferential pressure
Pressure di
fference betwee
n two regions e.g. between intake manifold and
atmospheric pressures
D
ifferential Pressure
Feedback EGR
DP
FE
An
EGR system that monito
rs differential EGR pressure across a remote orifice
to control EGR flow
D
irect current
dcCurrent which f
lows in on
e direction only, though it may have appreciable
pulsations in its magnitude
Du
al linear switch
DLSJ
-gate switch connected to the TCM on SC vehicles
E
EGR
Temperature EGRT
Sensor
EGRTSens
ing EGR function based on temperature change
EGR Vacu
um Regulator
EVRControls EGR
flow by changi
ng vacuum to the EGR valve
EGR Valve
Position
EVPAn EGR
system that direct
ly monitors EGR valve position to control EGR flow
Electrically E
rasable
Programmable Read-Only
Memory
EEP
ROM
Page 45 of 2490

High
tension (electrical)
ht
Hourh
Hydro
carbon
HC
I
Idl
e Air Control
IACEl
ectrical control of throttle bypass air
Idl
e Air Control Valve
IACVStepper motor dri
ven device which vari
es the volume of air by-passing the
throttle to maintain the programmed idle speed
Ignitionign
Ignition am
plifier
IAD
evice which amplifies the i
gniti
on system output
Ignition groundIGN GND
In
ertia Fuel Shut-off
IFSAn
inertia system that shuts off the fuel supply when activated by pre-
determined force limits brough t about by (e.g.) collision
In
ertia Fuel Shut-off
Switch
IFSSShut
s down fuel and ignition systems in the event of a vehicle impact
Inta
ke air
Air drawn t
hrough a cleaner and distri
buted to each cylinder for use in
combustion
InputI/PAn
electrical input signal to a controlling device
Inta
ke Air Temperature
IATTem
perature of intake air
Inta
ke Air Temperature
Sensor
IATSDe
vice used to measure IAT
Inta
ke Air Temperature
Sensor Ignition
IATSITherm
istor which signals the ECM to retard
the ignition timing in response to
high inlet air temperatures
Inta
ke Air Temperature
Sensor Injection
IATSFTher
mistor which inputs air density information to the ECM
Internal diameteri.
dia
Inte
rnational Standards
Organization
ISO
K
Kilogramme (mass)kg
Kilogram
me (force)
kg
f
Ki
logramme force per
square centimeter
kg
f/cm2
Kilom
eter
km
Ki
lometer per hour
km
/h
Kilopasc
al
kP
a
KilovoltkV
Knock
Sensor
KSSens
or which detects the onset of detonation, and signals the ECM to retard
the ignition
L
Le
ft-hand
LH
Left-hand drive veh
icle
LHD
Le
ft-hand thread
LH Thd
Ligh
t Emitting Diode
LEDLigh
t-emitting semiconductor diode used
in alphanumeric displays and as an
indicator lamp
Liqu
id Crystal Display
LCDOp
tical digital display system, applied voltage to which varies the way the
crystals reflect light, thereby modifying the display
LiterL
Low ten
sion
ltPrim
ary circuit of the ignition system, linking the battery to the primary
winding in the ignition coil
M
Malfu
nction Indicator
Lamp
MILA
required on-board indicator to aler
t the driver of an emission related
malfunction
Mani
fold Absolute
Pressure
MAPAbsolute pressure o
f the intake manifold air
Mani
fold Absolute
Pressure Sensor
MAPSSensor loca
ted in the ECM and
ported to the intake manifold
Manifol
d Surface
Temperature
MST
Mass Ai
r Flow
MAFSy
stem which provides inform
ation on the mass flow rate of the intake air to
the engine
Mass Ai
r Flow Sensor
MAFSHot-wi
re sensor which monitors air flow
into the intake manifold for fueling
and ignition control
Maxim
um
max.
Page 527 of 2490

E
ngine Management System Components
Electronic Throt
tle
The
electronic throttle assembly, in resp
onse to signals from both the driver and the ECM, adjusts idle speed, sets the
throttle valve to the position requested by the driver's accelerator / throttle pedal, cruise and traction control, power
limitation and catalyst warm-up.
Mass
Air Flow Meter
The sensor i
s located in the air flow mete
r assembly and outputs an analogue voltag e to the ECM. This sensor measures air
flow into the engine inlet system and is calibrated to measure kg / hour.
In
take Air Temperature
Th
e intake air temperature sensor is loca
ted in the air flow meter assembly and outputs an analogue voltage to the ECM.
The ECM will substitute a default value eq ual to 50°C should this sensor fail.
Fuel Injectors
The eigh
t bottom fed fuel injectors are located in the fuel rails. Th
e fuel injectors are electromagnetic solenoid valves
controlled by the ECM. The pulse time for the injector combined with the fuel pr essure determines the volume of fuel
injected to the manifold.
Fue
l Delivery
The fu
el pump provides fuel to the fuel rail where the circulat
ing pressure is controlled by a pressure regulator valve; excess
fuel is returned to the fuel tank.
The pressure regulator valve is controlled by manifold depression so that fuel delivery pressure is maintained at
approximately 3 bar above manifold pressure.
Fuel Pump
Relay
The ECM controls thi
s component for normal
engine running. The security system may disable this relay via communication
with the ECM.
Fuel Lev
el Sensing
The tank fuel
is measured by the fuel le
vel sensor . This signal is used by the ECM as an in put to certain diagnostics.
Eva
porative Valve
Excess vapour
formed in the fuel tank is
absorbed into the evaporative emission pu rge control canister. While the engine is
running, the fuel absorbed in the canister is gradually purged back into the engine. The rate of purging is governed by
engine operating conditions and vapour concentration level. Operating conditions which affect the purge rate are:
2—Purge
valve
3—Engine
torque reduction
4—E
lectronic throttle assembly
5—Coo
ling fans
6—Ignition amplifier driver
7—Engine overspeed
8—Cli
mate control compressor clutch
9—O
BDII information (J1962, CAN, ISO)
10—F
uel pump relay
11—Heat
ed oxygen sensor
12—Vari
able valve timing
13—MIL sw
itching
ECM Out
puts
It
em
Par
t Number
De
scription
1—Exhaus
t gas recirculation
Page 529 of 2490

Thi
s sensor uses a piezo-electric sensing element to detect kn
ock which may occur under acceleration at critical conditions.
Should detonation be present the ECM will retard ignition timing of individual cylinders.
Exhaust G
as Recirculation
The EGR
valve (where fitted) reduces NOx
emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the inlet
manifold.
Heated Oxyg
en Sensors
The h
eated oxygen sensors, one per bank, are situated upstream of the catalysts. Integral
to the sensors are heaters
(under ECM control) which allow the sensor s to reach their operating temperature as soon as possible after engine start. A
comparison between the level of oxygen in the exhaust gas to that in the atmosphere produces an output signal. This signal
is used by the engine closed loop fuel strategy to make fuelling corrections and so control overall emission levels.
Oxygen Sensors
Thes
e sensors, one per bank, are situated downstream of the
catalyst. The comparison of upstream and downstream signals
allows determination of cata lyst conversion efficiency.
Knock Sensor
Page 611 of 2490

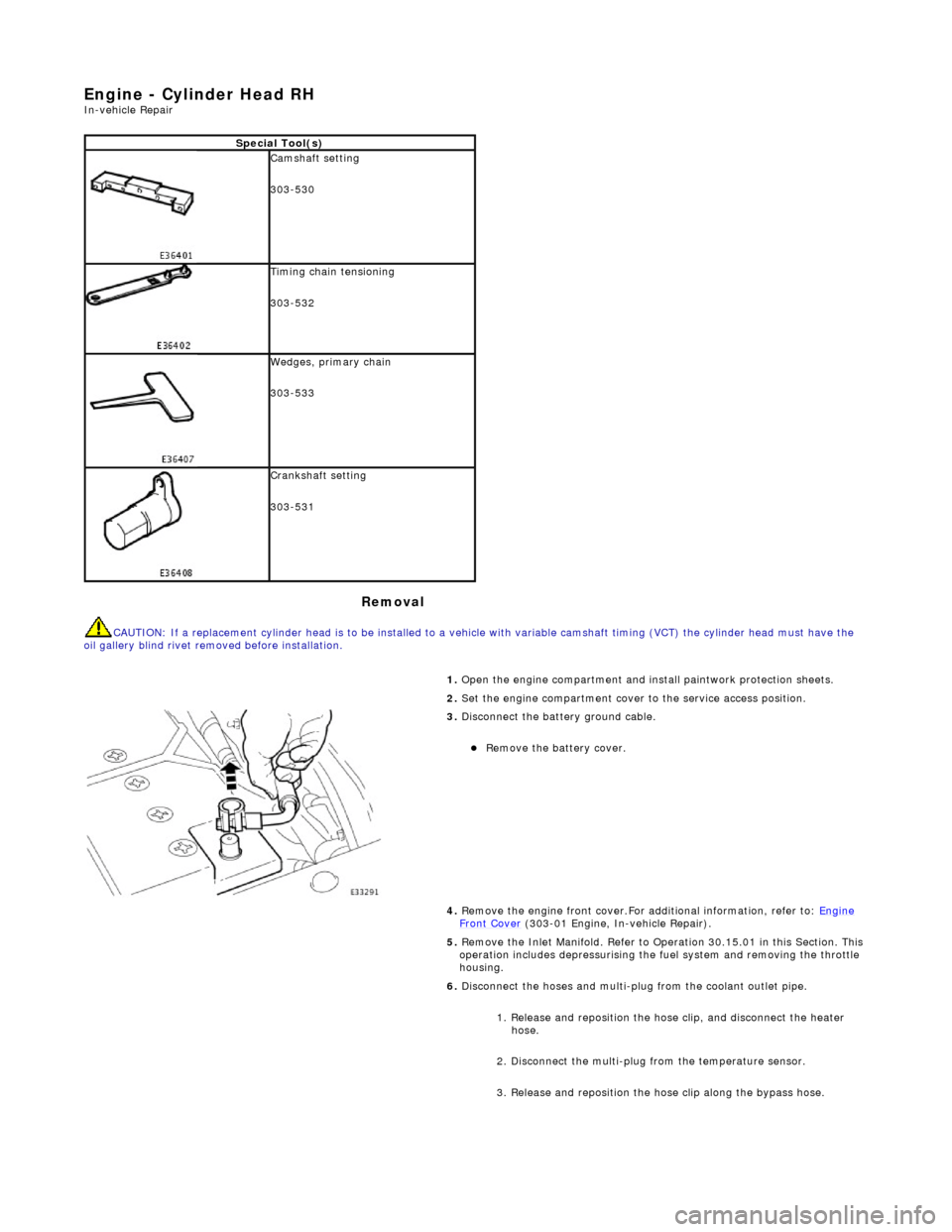
E
ngine - Cylinder Head LH
In-ve
hicle Repair
Remova
l
CAU
TION: If a replacement cylinder head is to be installed to a
vehicle with variable camshaft timing (VCT) the cylinder head m ust have the
oil gallery blind rivet removed before installation.
Spe
cial Tool(s)
Cams
haft setting
303-530
Ti
ming chain tensioning
303-532
Wedges, prim
ary chain
303-533
Cr
ankshaft setting
303-531
1.
Open the engine compartment and install paintwork protection sheets.
2. Set the engine compartment cover to the service access position.
3.
Disconnect the battery ground cable.
Re
move the battery cover.
4. Remove the engine fron cover.For additional information, refer to: Engine
Front Cover (303-01 Engi
ne, In-vehicle Repair).
5. Remove the Inlet Manifold. Refer to Operation 30.15.01 in this Section. This operation includes depressurising the fuel system and removing the throttle
housing.
6. Disconnect the hoses and multi-plug from the coolant outlet pipe.
1. Release and reposition the hose clip, and disconnect the heater hose.
2. Disconnect the multi-plug from the temperature sensor.
3. Release and reposition the hose clip along the bypass hose.
Page 625 of 2490
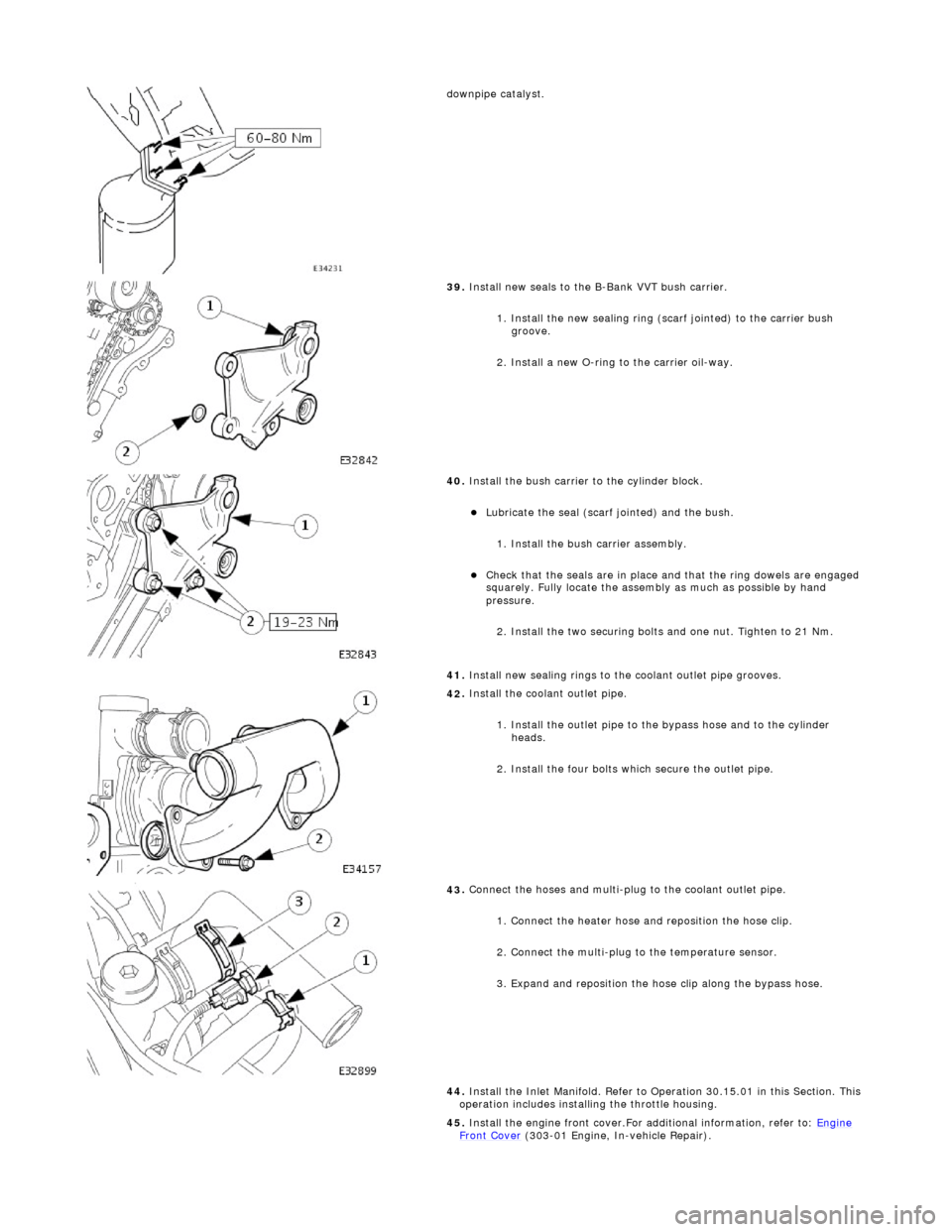
d
ownpipe catalyst.
39
.
Install new seals to the B-Bank VVT bush carrier.
1. Install the new sealing ring (scarf jointed) to the carrier bush groove.
2. Install a new O-ring to the carrier oil-way.
40
.
Install the bush carrier to the cylinder block.
Lu
bricate the seal (scarf
jointed) and the bush.
1. Install the bush carrier assembly.
Chec
k that the seals are
in place and that the ri ng dowels are engaged
squarely. Fully locate the assembly as much as possible by hand
pressure.
2. Install the two securing bolts and one nut. Tighten to 21 Nm.
41. Install new sealing rings to the coolant outlet pipe grooves.
42
.
Install the coolant outlet pipe.
1. Install the outlet pipe to the bypass hose and to the cylinder heads.
2. Install the four bolts which secure the outlet pipe.
43
.
Connect the hoses and multi-plug to the coolant outlet pipe.
1. Connect the heater hose and reposition the hose clip.
2. Connect the multi-plug to the temperature sensor.
3. Expand and reposition the hose clip along the bypass hose.
44. Install the Inlet Manifold. Refer to Operation 30.15.01 in this Section. This
operation includes installing the throttle housing.
45. Install the engine front cover.For additional information, refer to: Engine
Front Cover (303-01 Engi
ne, In-vehicle Repair).
Page 627 of 2490
E
ngine - Cylinder Head RH
In-ve
hicle Repair
Remova
l
CAU
TION: If a replacement cylinder head is to be installed to a
vehicle with variable camshaft timing (VCT) the cylinder head m ust have the
oil gallery blind rivet removed before installation.
Spe
cial Tool(s)
Cams
haft setting
303-530
Ti
ming chain tensioning
303-532
Wedges, prim
ary chain
303-533
Cr
ankshaft setting
303-531
1.
Open the engine compartment and install paintwork protection sheets.
2. Set the engine compartment cover to the service access position.
3.
Disconnect the battery ground cable.
Re
move the battery cover.
4. Remove the engine front cover.For additional information, refer to: Engine
Front Cover (303-01 Engi
ne, In-vehicle Repair).
5. Remove the Inlet Manifold. Refer to Operation 30.15.01 in this Section. This operation includes depressurising the fuel system and removing the throttle
housing.
6. Disconnect the hoses and multi-plug from the coolant outlet pipe.
1. Release and reposition the hose clip, and disconnect the heater hose.
2. Disconnect the multi-plug from the temperature sensor.
3. Release and reposition the hose clip along the bypass hose.
Page 641 of 2490

2.
Connect the multi-plug to the temperature sensor.
3. Expand and reposition the hose clip along the bypass hose.
43. Install the Inlet Manifold. Refer to Operation 30.15.01 in this Section. This
operation includes installing the throttle housing.
44. Install the engine front cover.For additional information, refer to: Engine
Front Cover (303-01 Engi
ne, In-vehicle Repair).
45. Move the engine compartment cover from the service position and connect
the gas struts.
46. Remove the paint protection sheets and close the cover.
47. Connect the battery and install th e battery cover.For additional
information, refer to: Battery Connect
(414
-01 Battery, Mounting and
Cables, General Procedures).