1998 JAGUAR X308 ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 2382 of 2490

Health and Safety
It is the duty of both employer and employee to ensure safe working conditions and practices. Correct safety procedures
and equipment must be applied to any potential hazards that are notified, or identified by an operator.
Employees must observe local legislation go verning working conditions and practices at all times and must always act in a
responsible manner in the workplace. In the event of personal injury resulting from any workshop activity, medical help
should be obtained as soon as poss ible. Self-treatment other than by first aid, should not be attempted.
WARNING: READ AND UNDERSTAND WORKING PRACTICE S CONCERNING CLIMATE CONTROL SYSTEMS, SECTION
412, WITH SPECIAL REGARD TO: REFRIGERANT MUST NEVE R BE DIRECTLY VENTED TO ATMOSPHERE. ALWAYS USE
JAGUAR APPROVED RECOVERY / RECYCLE / RECHARGE EQUI PMENT, WEAR SUITABLE EYE AND SKIN PROTECTION AND
OBSERVE ALL APPLICABLE SAFETY REQUIREMENTS.
With the constant introduction of new materials in the manufacture of vehicles, an awareness of the potential risks and
appropriate precauti ons is important.
Notification of Hazards
Symbols, which convey important information, will be positioned at the beginning of any specific operation or text. Standard symbols will be used where repairs or service procedures ar e detailed. All symbols will conform to standard ANSI Z535.3
(American National Standards Institute). The surround shape of the symbol will indicate the basis of the message to be
conveyed (see top three elements of ?) The icon depicting the message will be within the surrounding shape. Once
nominated the icon will retain its meaning.
POTENTIAL RISKS
Paint
Organic solvents, found in paints, may caus e damage or severe irritation to liver, kidneys, digestive tracts and respiratory
system if inhaled over long pe riods of time. Prolonged exposure to isocyanate s can cause lung sensitization with asthma-like symptoms developing on subsequent exposure to even low concentrations of isocyanates. Solvent inhalation can cause
dizziness or loss of consciousness and inhalation of spray dust and sanding debris may cause lung damage.
Spillage or splashes of solvents, paint ac tivators and additives can cause dermatitis or eye injury. Contact with peroxide or
acid catalysts can cause serious burns.
Applied Heat (Welding)
There is considerable risk of damage to eyes and skin if welding or flame cutting is attempted without using the correct
protective equipment. Many materials or fluids within vehicles are highly flammable and toxic and dangerous fumes may
also be liberated if heat is applied to expanded foam, corr osion protection, trim and seat materials, paints containing
isocyanates, and adhesive and sealing compounds.
When heated to a temperature of 300°C, polyurethane based compounds may liberate small quantities of isocyanate. Many
types of nitrogen containing chemicals ma y be liberated as breakdown products which can contain isocyanates, oxides of
nitrogen and hydrogen cyanide.
Potentially toxic or asphyxiant fumes and gases produced when welding include zinc oxide from zinc coated panels, and
ozone gas from the MIG process.
Metal Repair
There is considerable risk of damage to eyes, ears and skin wh en cutting, forming, or dressing metal. Soldering operations
can also be hazardous due to heat generated fumes and the risk of skin contact with hot materials.
PRECAUTIONS
Page 2383 of 2490

Paint
The inhalation of sprays, fumes, or dust during paint application or sanding processes should always be avoided. Ensure
that there is efficient ventilation / extrac tion at all times. Paint spraying should be confined as far as possible to spray
booths. Personnel with a history of asth ma should not be employed in any process involving the use of isocyanates.
Operators working in a spray booth where isocyanate material is present must use air-fed breathing equipment with air
supplied to the visor at the re commended pressure and filtered to remove oil, water, and fumes. Operators involved in
handling mixing or spraying should wear protective clothing including gloves and goggles, to avoid skin and eye contact.
Particle masks or canister type respir atosr should be worn when sanding.
Applied Heat
When welding, flame cutting, brazing etc, the operator shou ld use as appropriate, goggles, mask / fume extractor and
flameproof protective clothing. It is especially important when working with polyurethane compounds to use air-fed
breathing equipment. Appropriat e fire fighting equipment and personnel trai ned in its use must always be available.
Metal Repair
Appropriate eye and hand protection should be worn when sanding, drilling, cutting, chiselling, flatting or welding. Face
masks or air-fed visors should also be wo rn when sanding or flatting either body solder or fillers. On completion of a
soldering operation, swarf must be re moved from the work area and the operat or must wash his hands thoroughly.
GENERAL REPAIR NOTES
The following advice should be noted before any repair work is carried out.
Disconnect the vehicle battery gr ound lead (disconnect the alternator where electric welding is used) and take note of the
reconnection procedures as detailed in 86.15.15.
Where structural parts are straightened or renewed, a body alignment / straightening jig must be used. The application of
heat, especially excessive heat, reduces the strength of steels, where appropriate therefore, structural sections should be
straightened by cold processes.
Repairs may only be carried out successful ly, and any warranties protected, if genuine Jaguar replacement parts and Jaguar
approved materials are used.
The correct tools, procedures and facilities must always be us ed. The quality of the work must not be compromised by using
inappropriate methods or equipment.
All trim and electrical components in the locality of the repair must be removed or disconnected prior to panel removal /
replacement; this is especially important where hollow sectio ns may contain harnesses, tubes or foam, see section A4.3.5.
WARNING: DO NOT WORK IN THE VICINITY OF A LIVE AIR BAG, REMOVE IT COMPLETELY. READ WORKING
PRACTICES AIR BAG, SECTION 20. ANY SEAT BELT WHICH HAS BEEN WORN IN AN ACCIDENT MUST BE RENEWED.
CAUTION: Electric arc welding should not be used on Jaguar vehicles. The high voltages produced by this process will
cause irreparable damage to the electric al control and microprocessor systems.
The following welding and gas processes are the only ones recommended by Jaguar Cars Ltd.
Welding and Gas Processes
Resistance spot welding, MIG welding and all gas processes may only be carried out on bare, unpainted or unplated metal.
The flanges of panels to be welded toge ther, must be clean, corrosion free and tr eated as appropriate, with either weld-
through primer or inter-weld sealer. Only materials and processes specified in the 'Body Sealing and Preservation Manual'
should be used in the relevant application areas detailed in this section. Refer to 'Zinc Coated Panels' Section
Page 2394 of 2490
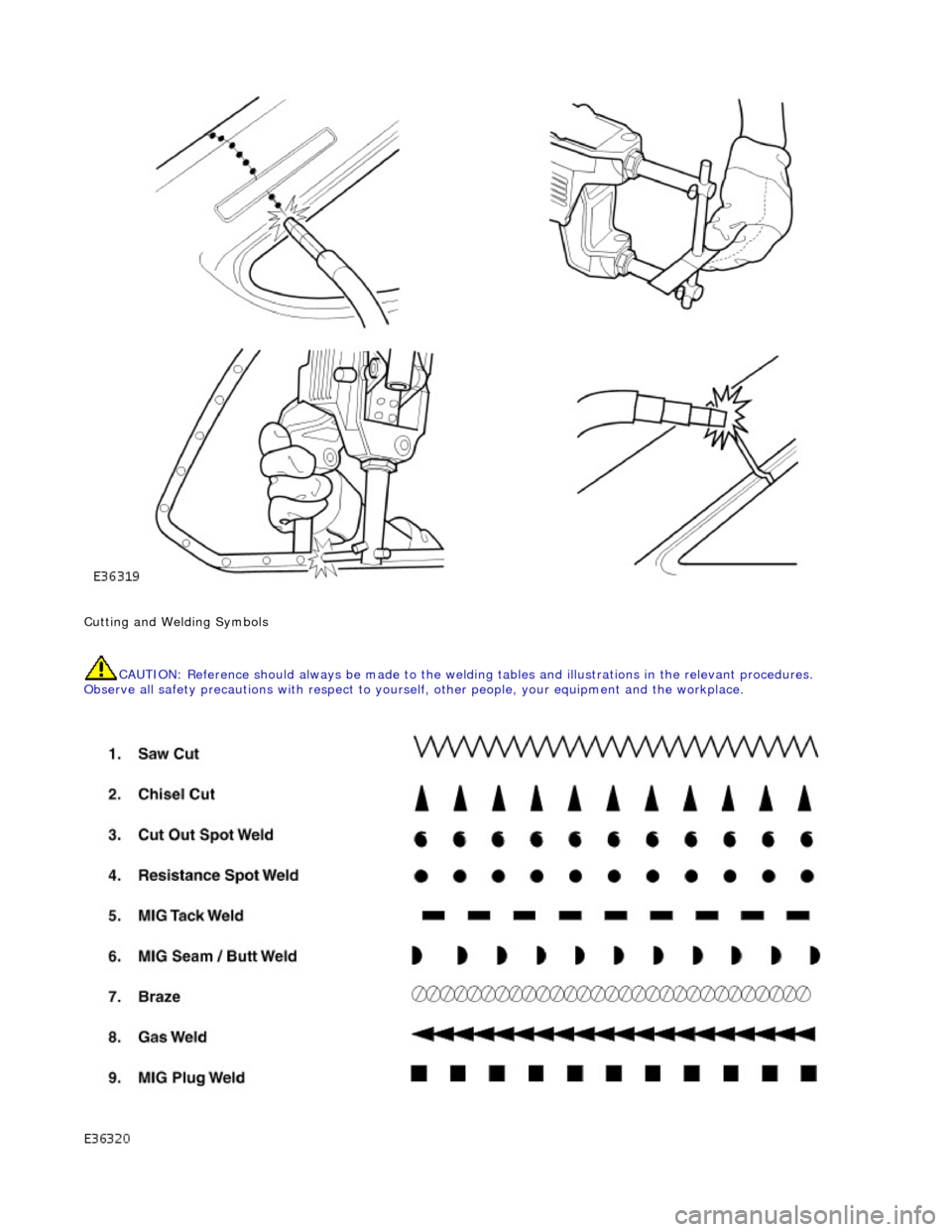
Cutting and Welding Symbols CAUTION: Reference should always be made to the welding tables and illust rations in the relevant procedures.
Observe all safety precautions with respect to yourself, ot her people, your equipment and the workplace.
Page 2420 of 2490

lever mechanism driven by an electric motor. A sliding roof control module (SRCM) controls the motor in response to
selections made on the roof console switch , or input from the security system for automatic closing. Both the motor and the SRCM are accessed by removing the roof console.In the event of an electrical failure the sliding roof can be manually
operated. This is achieved by inserting a wide bladed screwdriver into a slot in the motor drive gear and turning clockwise to open or counter clockwise to close the sliding roof.
• NOTE: The drive gear becomes disengaged from the motor during manual operation. Before restoring electrical operation
the drive gear must be rotated one quarter turn in the reverse direction to re-engage the motor.
The SRCM is held in position by clips and has two electrical connectors in terfacing with the motor and the roof console
switch/security system. Prior to installing a new SRCM, the sun ro of must be in a neutral closed position. This provides the
SRCM with a sliding roof datum, to ensure accurate and consistent operation. Obstacle sensin g operates on closing in the
slide mode only. If the sliding roof lid encounters an ob struction between 4mm and 200mm from the closed position, the
SRCM detects increased motor load and reve rses the motor, driving the sliding roof to the fully open position. The sliding
roof lid surround seal has a metal inner sect ion which will deform on removal. If removed, this seal must be discarded and a
new seal must be installed on the lid using a Jaguar approved crimping tool.
Page 2489 of 2490
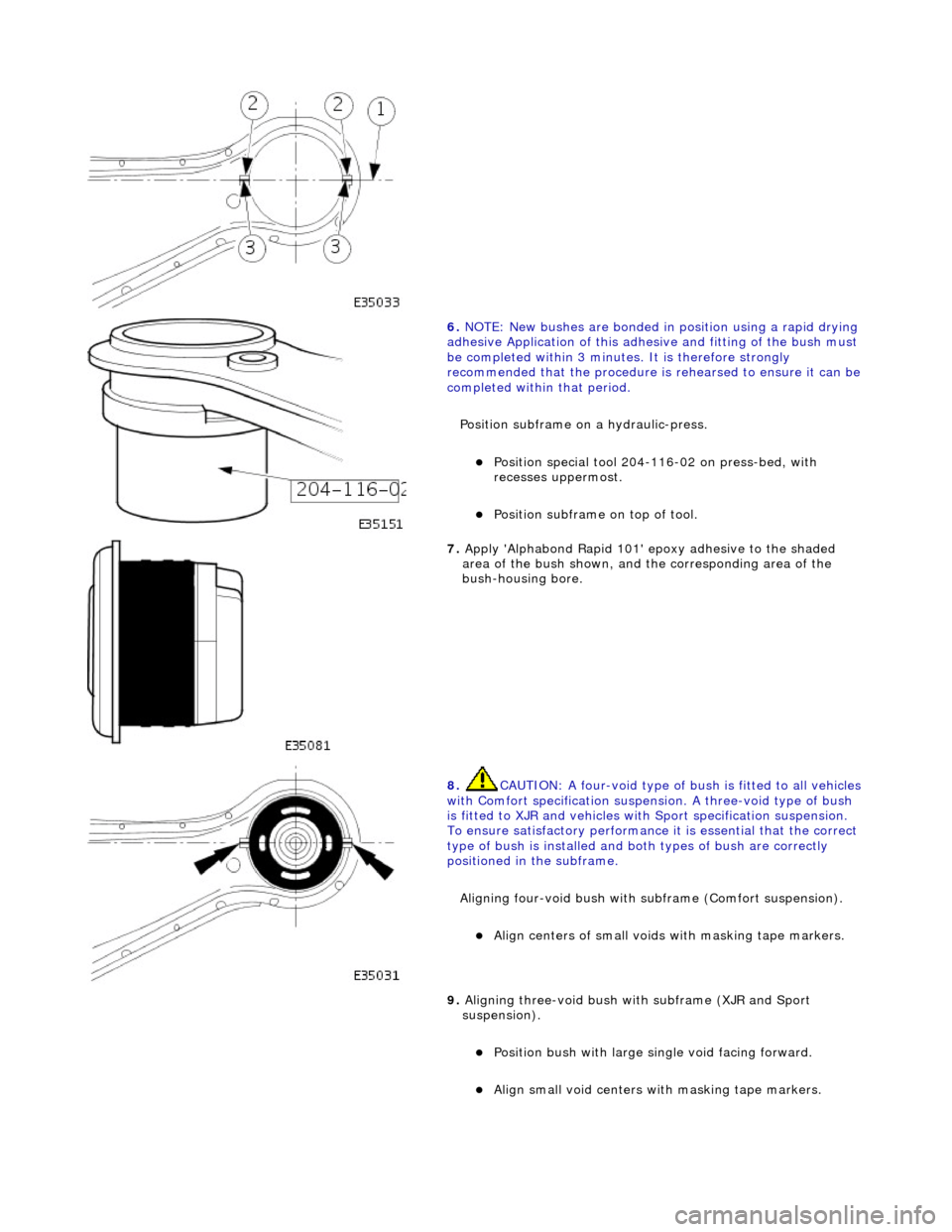
6. NOTE: New bushes are bonded in position using a rapid drying
adhesive Application of this adhesive and fitting of the bush must
be completed within 3 minutes. It is therefore strongly
recommended that the procedure is rehearsed to ensure it can be
completed within that period.
Position subframe on a hydraulic-press.
Position special tool 204-116-02 on press-bed, with
recesses uppermost.
Position subframe on top of tool.
7. Apply 'Alphabond Rapid 101' epoxy adhesive to the shaded
area of the bush shown, and the corresponding area of the
bush-housing bore.
8. CAUTION: A four-void type of bu sh is fitted to all vehicles
with Comfort specification suspension. A three-void type of bush
is fitted to XJR and vehicles with Sport specification suspension.
To ensure satisfactory performance it is essential that the correct
type of bush is installed and bo th types of bush are correctly
positioned in the subframe.
Aligning four-void bush with su bframe (Comfort suspension).
Align centers of small voids with masking tape markers.
9. Aligning three-void bush wi th subframe (XJR and Sport
suspension).
Position bush with large single void facing forward.
Align small void centers with masking tape markers.