Page 1562 of 3573
6A Ð 12 ENGINE MECHANICAL
3. Visually inspect both ends of the push rod for exces-
sive wear and damage. The push rod must be re-
placed if these conditions are discovered during
inspection.
REASSEMBLY
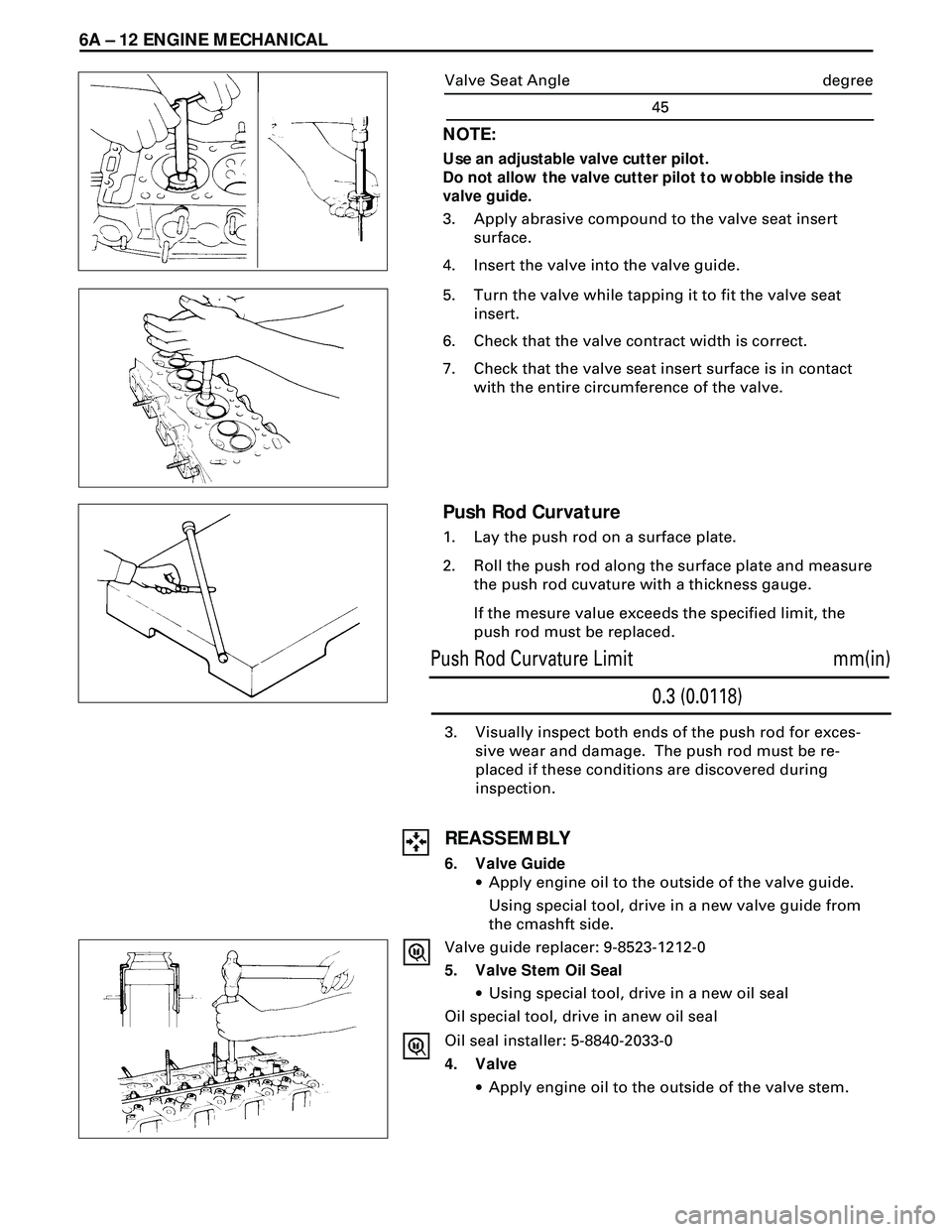
6. Valve Guide
·Apply engine oil to the outside of the valve guide.
Using special tool, drive in a new valve guide from
the cmashft side.
Valve guide replacer: 9-8523-1212-0
5. Valve Stem Oil Seal
·Using special tool, drive in a new oil seal
Oil special tool, drive in anew oil seal
Oil seal installer: 5-8840-2033-0
4. Valve
·Apply engine oil to the outside of the valve stem.
Push Rod Curvature
1. Lay the push rod on a surface plate.
2. Roll the push rod along the surface plate and measure
the push rod cuvature with a thickness gauge.
If the mesure value exceeds the specified limit, the
push rod must be replaced.
NOTE:
Use an adjustable valve cutter pilot.
Do not allow the valve cutter pilot to wobble inside the
valve guide.
3. Apply abrasive compound to the valve seat insert
surface.
4. Insert the valve into the valve guide.
5. Turn the valve while tapping it to fit the valve seat
insert.
6. Check that the valve contract width is correct.
7. Check that the valve seat insert surface is in contact
with the entire circumference of the valve.
mm(in)
0.3 (0.0118) Push Rod Curvature Limit
degree
45 Valve Seat Angle
Page 1577 of 3573
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A Ð 27
NOTE:
Do not allow the crankshaft to rotate.
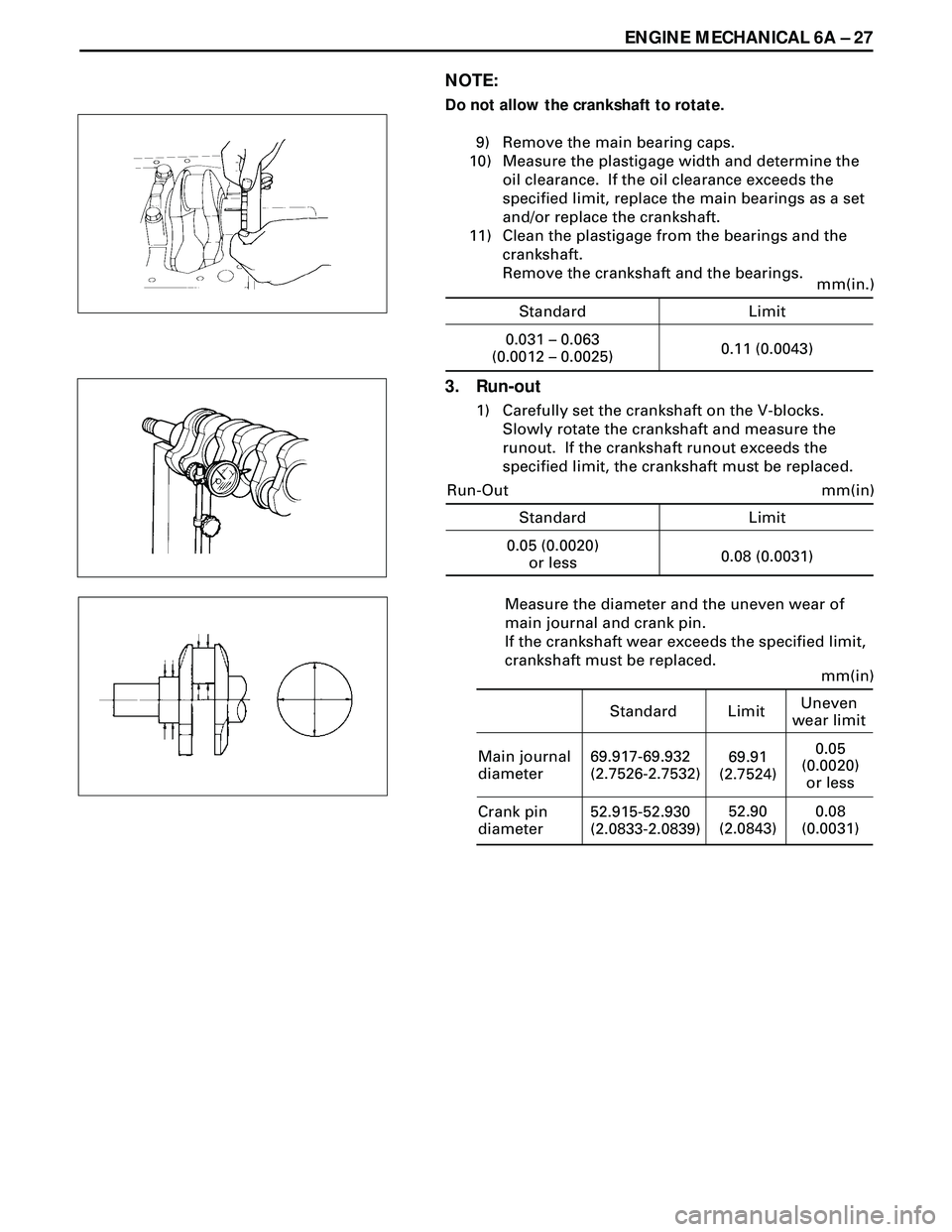
9) Remove the main bearing caps.
10) Measure the plastigage width and determine the
oil clearance. If the oil clearance exceeds the
specified limit, replace the main bearings as a set
and/or replace the crankshaft.
11) Clean the plastigage from the bearings and the
crankshaft.
Remove the crankshaft and the bearings.
3. Run-out
1) Carefully set the crankshaft on the V-blocks.
Slowly rotate the crankshaft and measure the
runout. If the crankshaft runout exceeds the
specified limit, the crankshaft must be replaced.
Measure the diameter and the uneven wear of
main journal and crank pin.
If the crankshaft wear exceeds the specified limit,
crankshaft must be replaced.
Standard Limit
mm(in.)
0.031 – 0.063
(0.0012 – 0.0025)0.11 (0.0043)
Standard Limit
mm(in)
0.05 (0.0020)
or less0.08 (0.0031) Run-Out
Standard Limitmm(in)
Main journal
diameter69.91
(2.7524)
69.917-69.932
(2.7526-2.7532)
Crank pin
diameter52.90
(2.0843) 52.915-52.930
(2.0833-2.0839)
Uneven
wear limit
0.05
(0.0020)
or less
0.08
(0.0031)
Page 1589 of 3573
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A Ð 39
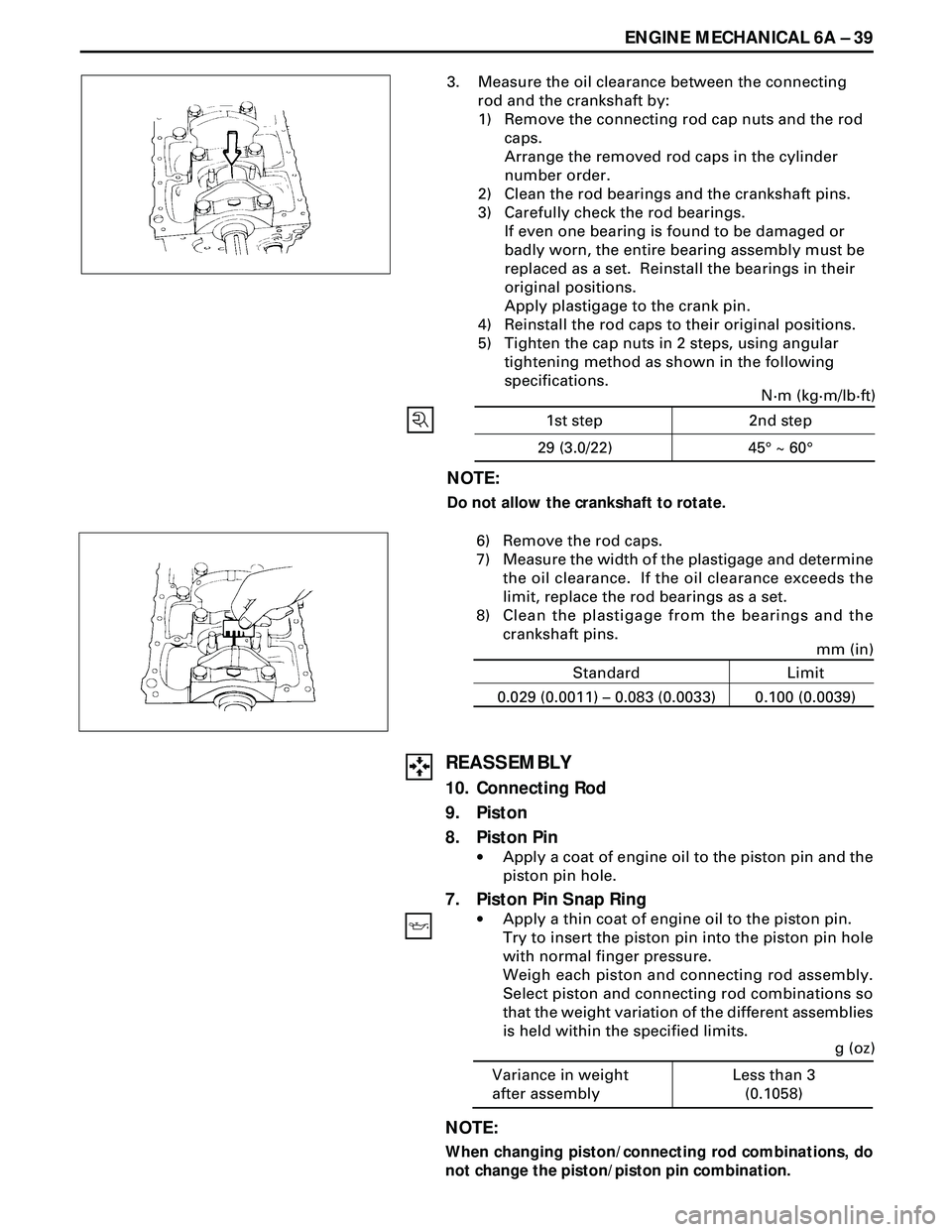
3. Measure the oil clearance between the connecting
rod and the crankshaft by:
1) Remove the connecting rod cap nuts and the rod
caps.
Arrange the removed rod caps in the cylinder
number order.
2) Clean the rod bearings and the crankshaft pins.
3) Carefully check the rod bearings.
If even one bearing is found to be damaged or
badly worn, the entire bearing assembly must be
replaced as a set. Reinstall the bearings in their
original positions.
Apply plastigage to the crank pin.
4) Reinstall the rod caps to their original positions.
5) Tighten the cap nuts in 2 steps, using angular
tightening method as shown in the following
specifications.
NOTE:
Do not allow the crankshaft to rotate.
N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
45¡ ~ 60¡ 1st step 2nd step
29 (3.0/22)
6) Remove the rod caps.
7) Measure the width of the plastigage and determine
the oil clearance. If the oil clearance exceeds the
limit, replace the rod bearings as a set.
8) Clean the plastigage from the bearings and the
crankshaft pins.
REASSEMBLY
10. Connecting Rod
9. Piston
8. Piston Pin
·Apply a coat of engine oil to the piston pin and the
piston pin hole.
7. Piston Pin Snap Ring
·Apply a thin coat of engine oil to the piston pin.
Try to insert the piston pin into the piston pin hole
with normal finger pressure.
Weigh each piston and connecting rod assembly.
Select piston and connecting rod combinations so
that the weight variation of the different assemblies
is held within the specified limits.
Variance in weight
after assemblyLess than 3
(0.1058)g (oz)
Standard Limit
0.029 (0.0011) – 0.083 (0.0033) 0.100 (0.0039)
mm (in)
NOTE:
When changing piston/connecting rod combinations, do
not change the piston/piston pin combination.
Page 1634 of 3573
6A2 Ð 32 4JG2-NA/4JG2-TURBO ENGINE
5. Vacuum Hose
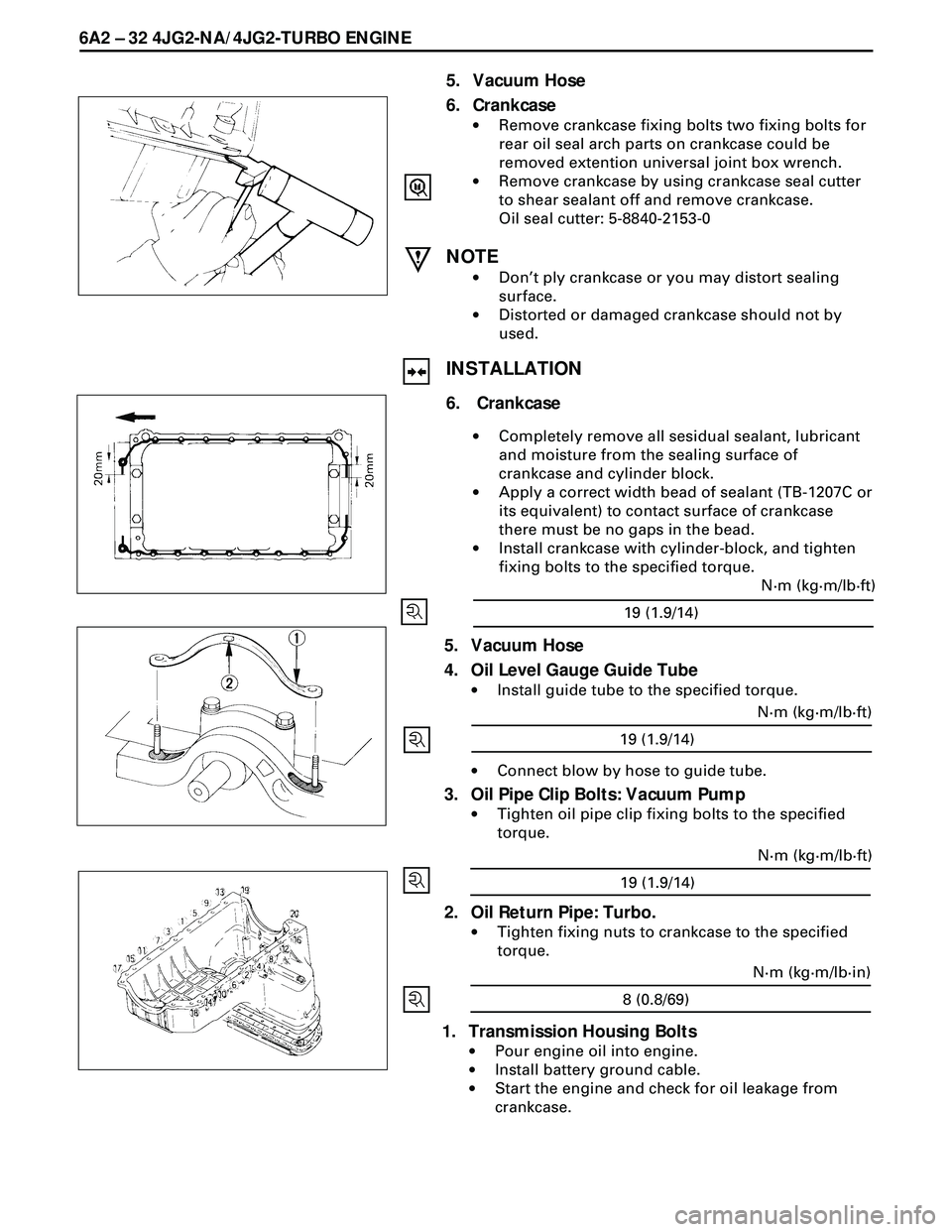
6. Crankcase
·Remove crankcase fixing bolts two fixing bolts for
rear oil seal arch parts on crankcase could be
removed extention universal joint box wrench.
·Remove crankcase by using crankcase seal cutter
to shear sealant off and remove crankcase.
Oil seal cutter: 5-8840-2153-0
NOTE
·DonÕt ply crankcase or you may distort sealing
surface.
·Distorted or damaged crankcase should not by
used.
INSTALLATION
6. Crankcase
·Completely remove all sesidual sealant, lubricant
and moisture from the sealing surface of
crankcase and cylinder block.
·Apply a correct width bead of sealant (TB-1207C or
its equivalent) to contact surface of crankcase
there must be no gaps in the bead.
·Install crankcase with cylinder-block, and tighten
fixing bolts to the specified torque.
5. Vacuum Hose
4. Oil Level Gauge Guide Tube
·Install guide tube to the specified torque.
·Connect blow by hose to guide tube.
3. Oil Pipe Clip Bolts: Vacuum Pump
·Tighten oil pipe clip fixing bolts to the specified
torque.
2. Oil Return Pipe: Turbo.
·Tighten fixing nuts to crankcase to the specified
torque.
1. Transmission Housing Bolts
·Pour engine oil into engine.
·Install battery ground cable.
·Start the engine and check for oil leakage from
crankcase.
19 (1.9/14)N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
19 (1.9/14)N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
19 (1.9/14)N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
8 (0.8/69)N·m (kg·m/lb·in)
Page 1739 of 3573
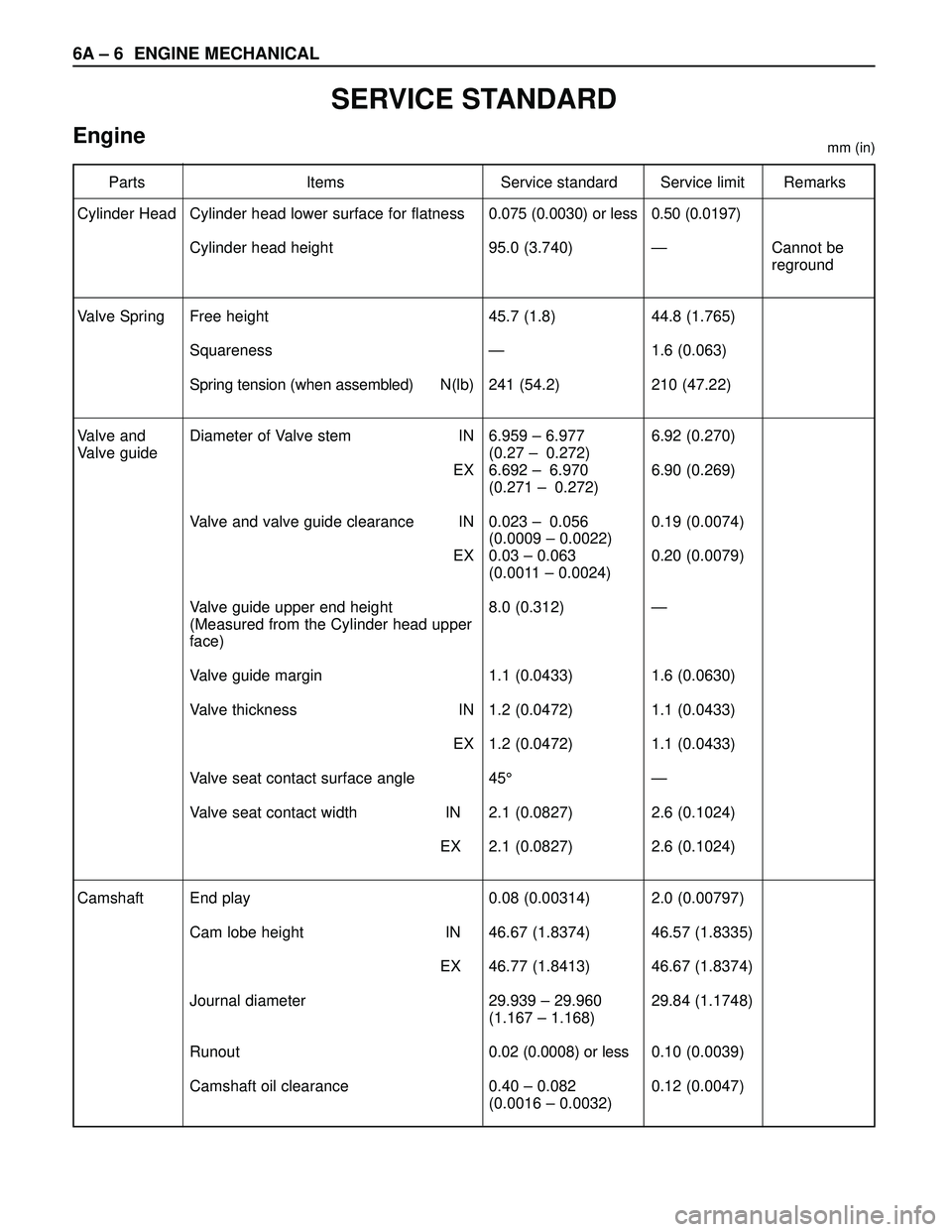
6A – 6 ENGINE MECHANICAL
SERVICE STANDARD
Enginemm (in)
Parts Items Service standard Service limit Remarks
Cylinder Head
Valve Spring
Valve and
Valve guide
Camshaft0.075 (0.0030) or less
95.0 (3.740)
45.7 (1.8)
—
241 (54.2)
6.959 – 6.977
(0.27 –0.272)
6.692 –6.970
(0.271 –0.272)
0.023 –0.056
(0.0009 – 0.0022)
0.03 – 0.063
(0.0011 – 0.0024)
8.0 (0.312)
1.1 (0.0433)
1.2 (0.0472)
1.2 (0.0472)
45°
2.1 (0.0827)
2.1 (0.0827)
0.08 (0.00314)
46.67 (1.8374)
46.77 (1.8413)
29.939 – 29.960
(1.167 – 1.168)
0.02 (0.0008) or less
0.40 – 0.082
(0.0016 – 0.0032)0.50 (0.0197)
—
44.8 (1.765)
1.6 (0.063)
210 (47.22)
6.92 (0.270)
6.90 (0.269)
0.19 (0.0074)
0.20 (0.0079)
—
1.6 (0.0630)
1.1 (0.0433)
1.1 (0.0433)
—
2.6 (0.1024)
2.6 (0.1024)
2.0 (0.00797)
46.57 (1.8335)
46.67 (1.8374)
29.84 (1.1748)
0.10 (0.0039)
0.12 (0.0047)Cannot be
reground Cylinder head lower surface for flatness
Cylinder head height
Free height
Squareness
Spring tension (when assembled) N(lb)
Diameter of Valve stem IN
EX
Valve and valve guide clearance IN
EX
Valve guide upper end height
(Measured from the Cylinder head upper
face)
Valve guide margin
Valve thickness IN
EX
Valve seat contact surface angle
Valve seat contact width IN
EX
End play
Cam lobe height IN
EX
Journal diameter
Runout
Camshaft oil clearance
Page 1783 of 3573
6A – 50 ENGINE MECHANICAL
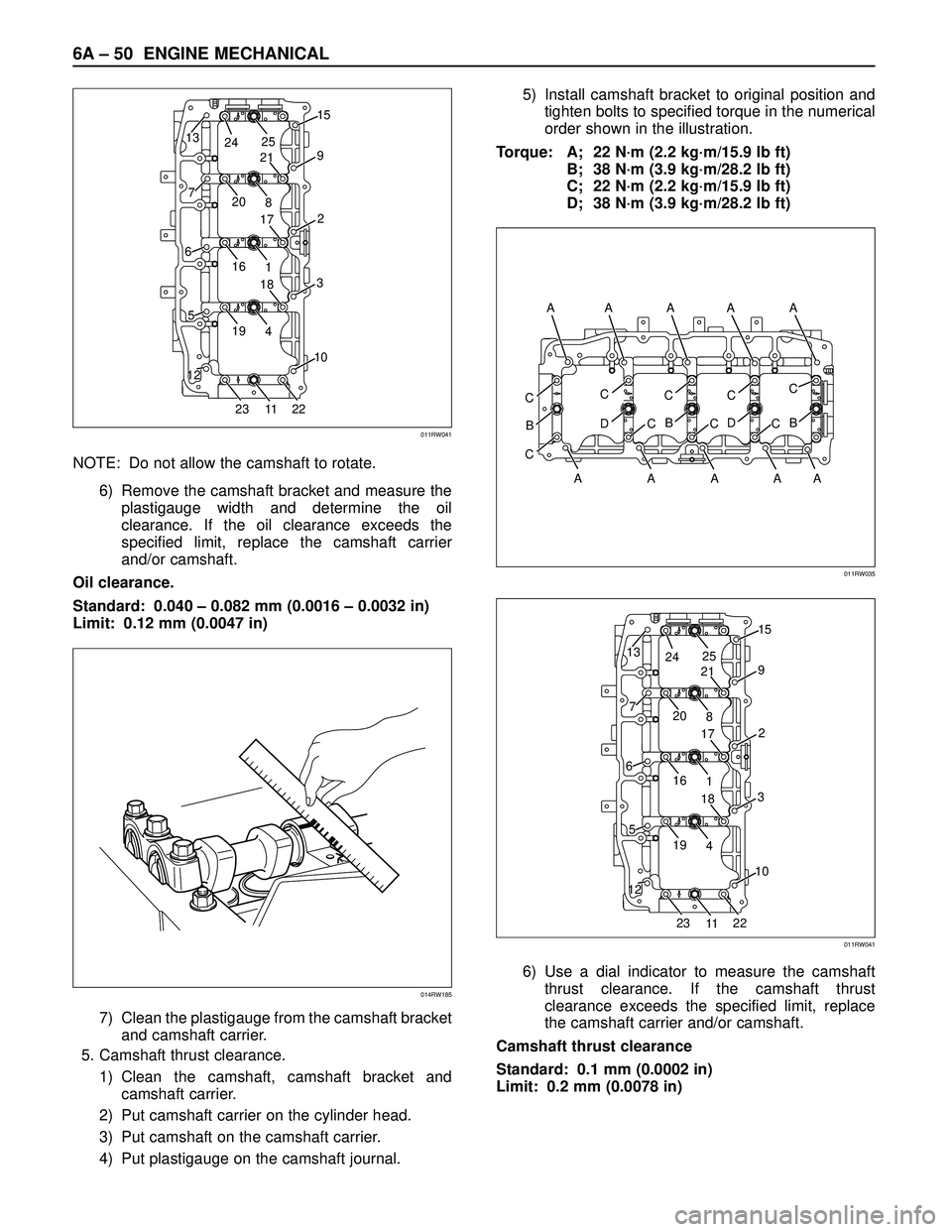
NOTE: Do not allow the camshaft to rotate.
6) Remove the camshaft bracket and measure the
plastigauge width and determine the oil
clearance. If the oil clearance exceeds the
specified limit, replace the camshaft carrier
and/or camshaft.
Oil clearance.
Standard: 0.040 – 0.082 mm (0.0016 – 0.0032 in)
Limit: 0.12 mm (0.0047 in)
7) Clean the plastigauge from the camshaft bracket
and camshaft carrier.
5. Camshaft thrust clearance.
1) Clean the camshaft, camshaft bracket and
camshaft carrier.
2) Put camshaft carrier on the cylinder head.
3) Put camshaft on the camshaft carrier.
4) Put plastigauge on the camshaft journal.5) Install camshaft bracket to original position and
tighten bolts to specified torque in the numerical
order shown in the illustration.
Torque: A; 22 N·m (2.2 kg·m/15.9 lb ft)
B; 38 N·m (3.9 kg·m/28.2 lb ft)
C; 22 N·m (2.2 kg·m/15.9 lb ft)
D; 38 N·m (3.9 kg·m/28.2 lb ft)
6) Use a dial indicator to measure the camshaft
thrust clearance. If the camshaft thrust
clearance exceeds the specified limit, replace
the camshaft carrier and/or camshaft.
Camshaft thrust clearance
Standard: 0.1 mm (0.0002 in)
Limit: 0.2 mm (0.0078 in)
13
7
6
5
1215
2
3
10
9
20
8
19
2322
4
161
11 25
24
21
17
18
011RW041
014RW185
CC
D
B
CC
B
CC
D
CC
B
C
A AA A A A
AAAA
011RW035
13
7
6
5
1215
2
3
10
9
20
8
19
2322
4
161
11 25
24
21
17
18
011RW041
Page 1797 of 3573
6A – 64 ENGINE MECHANICAL
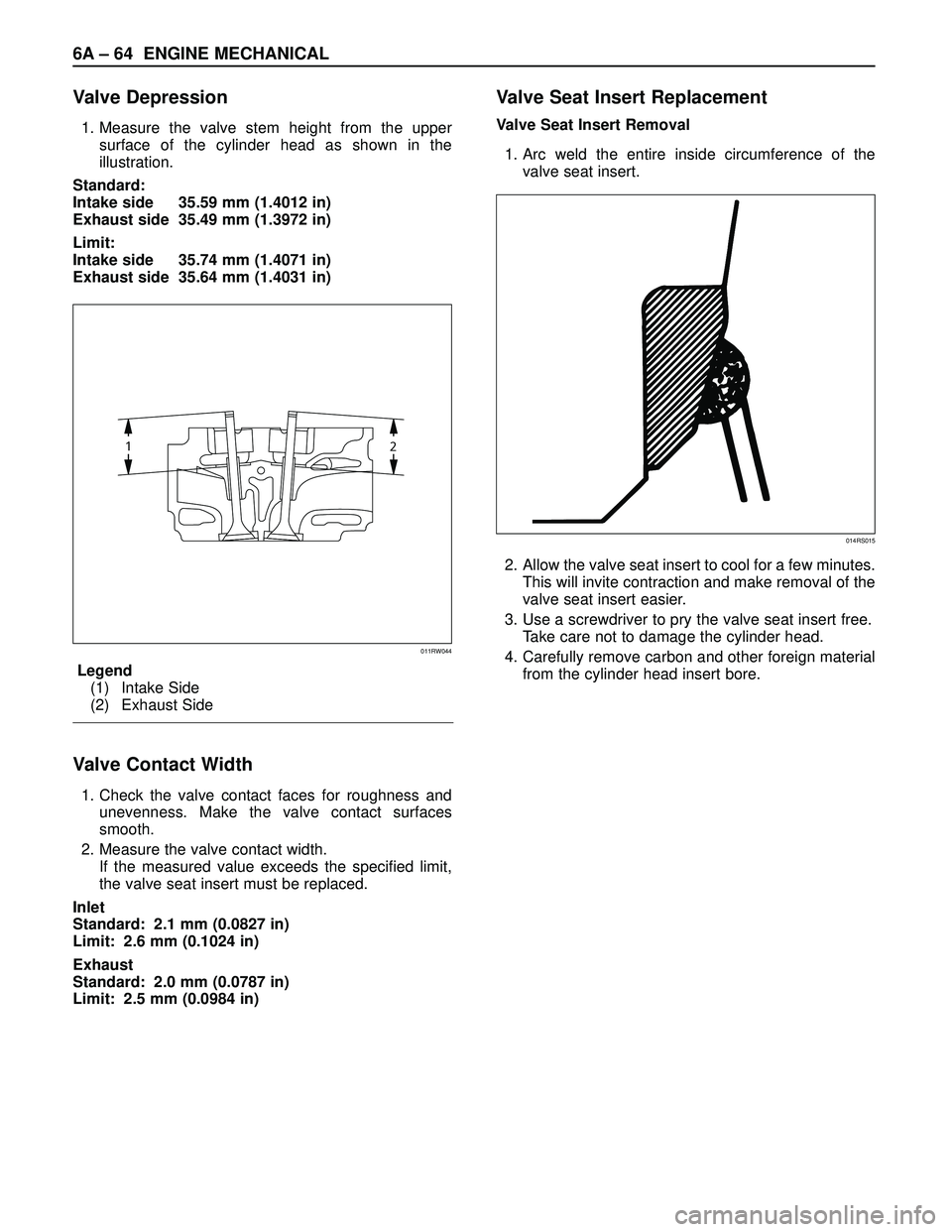
Valve Depression
1. Measure the valve stem height from the upper
surface of the cylinder head as shown in the
illustration.
Standard:
Intake side 35.59 mm (1.4012 in)
Exhaust side 35.49 mm (1.3972 in)
Limit:
Intake side 35.74 mm (1.4071 in)
Exhaust side 35.64 mm (1.4031 in)
Legend
(1) Intake Side
(2) Exhaust Side
Valve Contact Width
1. Check the valve contact faces for roughness and
unevenness. Make the valve contact surfaces
smooth.
2. Measure the valve contact width.
If the measured value exceeds the specified limit,
the valve seat insert must be replaced.
Inlet
Standard: 2.1 mm (0.0827 in)
Limit: 2.6 mm (0.1024 in)
Exhaust
Standard: 2.0 mm (0.0787 in)
Limit: 2.5 mm (0.0984 in)
Valve Seat Insert Replacement
Valve Seat Insert Removal
1. Arc weld the entire inside circumference of the
valve seat insert.
2. Allow the valve seat insert to cool for a few minutes.
This will invite contraction and make removal of the
valve seat insert easier.
3. Use a screwdriver to pry the valve seat insert free.
Take care not to damage the cylinder head.
4. Carefully remove carbon and other foreign material
from the cylinder head insert bore.
����
011RW044
014RS015
Page 1798 of 3573
ENGINE MECHANICAL 6A – 65
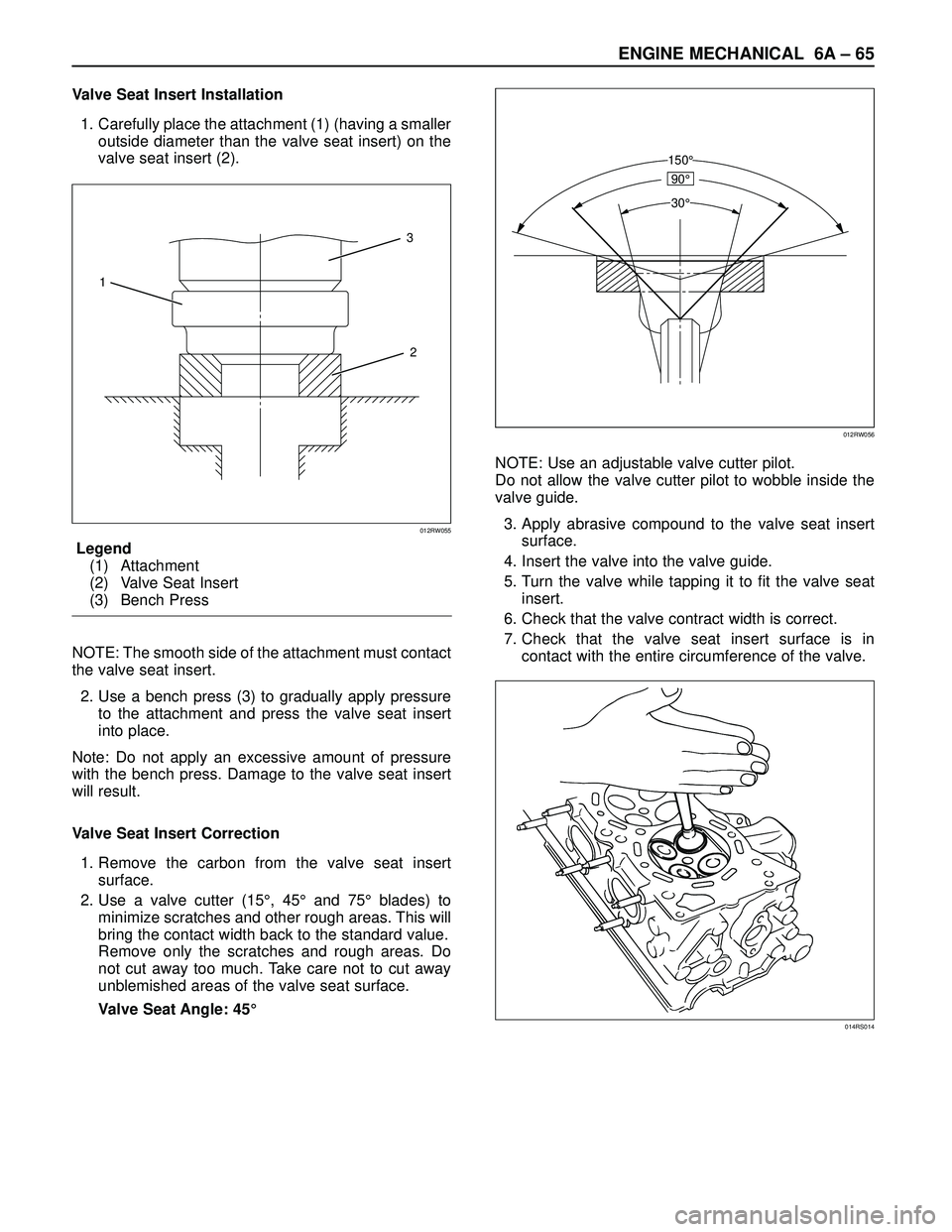
Valve Seat Insert Installation
1. Carefully place the attachment (1) (having a smaller
outside diameter than the valve seat insert) on the
valve seat insert (2).
Legend
(1) Attachment
(2) Valve Seat Insert
(3) Bench Press
NOTE: The smooth side of the attachment must contact
the valve seat insert.
2. Use a bench press (3) to gradually apply pressure
to the attachment and press the valve seat insert
into place.
Note: Do not apply an excessive amount of pressure
with the bench press. Damage to the valve seat insert
will result.
Valve Seat Insert Correction
1. Remove the carbon from the valve seat insert
surface.
2. Use a valve cutter (15°, 45°and 75°blades) to
minimize scratches and other rough areas. This will
bring the contact width back to the standard value.
Remove only the scratches and rough areas. Do
not cut away too much. Take care not to cut away
unblemished areas of the valve seat surface.
Valve Seat Angle: 45°NOTE: Use an adjustable valve cutter pilot.
Do not allow the valve cutter pilot to wobble inside the
valve guide.
3. Apply abrasive compound to the valve seat insert
surface.
4. Insert the valve into the valve guide.
5. Turn the valve while tapping it to fit the valve seat
insert.
6. Check that the valve contract width is correct.
7. Check that the valve seat insert surface is in
contact with the entire circumference of the valve.
3
2 1
012RW055
150°
90°
30°
012RW056
014RS014