Page 651 of 1681
SpecialTools
{
\
\
17-2
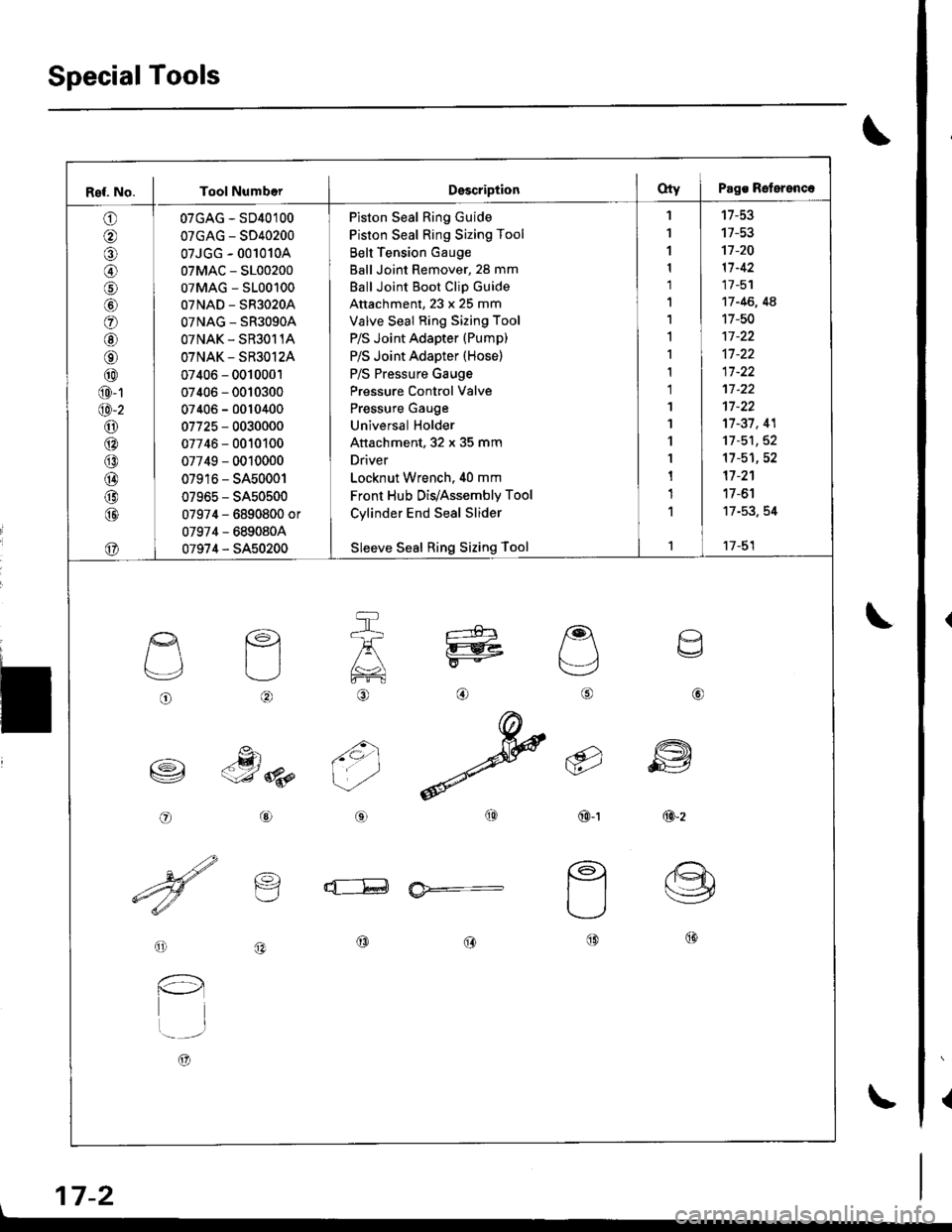
Ref. No. I Tool NumberDsscriptionOty I Pags Reterenc.
o
@
@
o
@
@
@
@
@
@-1
@-2
o6:^
@
@
@
@
@
07GAG - SD40100
07GAG - SD40200
07JGG - 001010A
07MAC - S100200
07MAG - S100100
07NAD - SR3020A
OTNAG _ SR3OgOA
OTNAK - SR3O11A
OTNAK - SR3O12A
07406 - 0010001
07406 - 0010300
07406 - 0010400
07725 - 0030000
07746 - 0010100
07749 - 0010000
07916 - SA50001
07965 - SA50500
07974 - 6890800 or
07974 - 6890804
07974 - SA50200
Piston Seal Ring Guide
Piston Seal Ring Sizing Tool
Belt Tension Gauge
Ball Joint Remover, 28 mm
Ball Joint Boot Clip Guide
Attachment, 23 x 25 mm
Valve Seal Ring Sizing Tool
P/S Joint Adapter (Pump)
P/S Joint Adapter (Hose)
P/S Pressure Gauge
Pressure Control Valve
Pressure Gauge
Universal Holder
Attachment, 32 x 35 mm
Driver
Locknut Wrench. 40 mm
Front Hub Dis/Assembly Tool
Cylinder End Seal Slider
Sleeve Seal Ring Sizing Tool
'I
1
1
1
1'|
1,l
I
1
1
1'I
'l
1
1
1
1
1
't7-53
17-53't]-20
11-42
17 -51
17 -46, 4A
17-50
17-37, 41
11-51,52't1-51,52
17 -2'�1
17 -6'l
17-53. 54
17-51
o
L'4,
o
€)
-g)c-J 8p
@
@
6i
(9')\E/'
@-t
a
6
ffi
@-z
d--E ia*=-
o
l-l
t..-_-.r
A)
@@@
\
Page 653 of 1681
System Description
Fluid Flow Diagram
The system is a compact rotary-valve-type power steering, connected to the steering gearbox. The fluid pressure is pro-
vided by a vane-type pump which is driven by the engine crank pulley. The amount of fluid and pressure is regulated by
the flow control valve built into the pump. The fluid pressure from the pump is delivered to the valve body unit around the
pinion of the steering gearbox. The valve inside the valve body unit controls the hydraulic pressure and changes the direc-
tion of the tlow. The fluid then flows to the power cylinder, where rack thrust is generated. Fluid returning from the power
cylinder flows back to the reservoir, where the fluid is "filtered" and supplied to the pump again
li
I
VALVE BODY UNIT
GEARBOXFLOW CONTROL VALVEPOWER CYLINDER
17-4
Page 657 of 1681

System DescriPtion
Steering Gearbox
it
The rack,and-pinion type steering gearbox has a Valve body unit incorporated with the pinion to control the steering fluid
pressure. steering fluid from the pump is regulated by a rotary valve in the valve body unit and is sent through the cylin-
derpipetothepowercy|inder,wherehydrauIicpressureisapp|ied.Thesteeringf|Uidintheothersideofthepowercy|in-
der returns through the cylinder pipe and valve body unit to the reservoir'
Valve Body Unit
Inside the valve body unit is the valve, which is coaxial with the pinion shaft, and controls the steering fluid pressure The
valve housing ls connected wirh the fluid pipe from the pump. return pipe to the reservoir, and the two cylinder pipes
from the respective power cylinder.
The pinion shaft is double - structured with the input shaft connected to the pinion gear, both of which are interconnected
with the torsion bar.
The pin inserted in the valve and the pinion shaft groove engage; this allows the pinion shaft to rotate together with the
Because of this construction. the difference in angle in the circumferential direction between the input shaft and the valve
becomes larger according ro the torsional strength ol the pinion or steering resistance. However. maximum torsion
between the shafts is regulated by the engaged splines of the shafts at the pin engagement section to hold the torsion bar
within the set value.
This allows the steering system to function as an ordinary rack-and-pinion type steering if the steering iluid is not pressur-
ized because of a faulty PumP.
VALVE
INPUT SHAFT
INPUT SHAFT
VALVE XOUSING
of
'I
lEng.ge with th€ Pinionshaft groove)
TORSION BARDift6rance in angle b6twe€n theinput ih.ft.nd pinion shalt
la-l
B
VALVE BODY UN]T
SECNON B.B
17-8
Page 658 of 1681

INPUT SHAFT
High assist at lower speedsl
When steering resistance is high, such as when driving at low speed, or when turning the wheel with the car stopped, the
diiference in angle created between the input shaft and the valve opens the tluid passage on one side, and closes the fluidpassage on the other side, at each pair of orifices. The fluid pressure lncreases in the side of the power cylinder fed by thelarger fluid passage. This increased pressure pushes on the rack piston, allowing the steering wheel to be turned with light
effon. On the other side of the power cylinder, the return passage opens allowing the steering fluid to return through theinput shaft to the reservoir. The fluid passages to the power cylinder automatically change in size, increasing as the steer-ing resistance increases. In other words, the passages become larger and power assist increases when the steering effort
would normally be high, (for example, when parking or making low speed turns), and the passages become smaller andpower assist decreases when the steering effort would normally be low, (for example, when driving at high speeds or
straight ahead).
FLUIO PASSAGE TOPOWER CYLINDER
Ce) r.r;
VK
Pressure Control
Low assist at higher speedsl
When steering resistance is low, such as when driving at high speeds, or when driving straight ahead. the lnput shaft is
near or in the neutral position, so there is liftle or no flow to any of the power cylinder orifices. Most of the feed pressure
from the pump is bypassed to the reservoir. Because of this, the pressure stays the same in both sides of the power cvlin-
der, resulting in low or no assist.
RETURN PASSAGE{To RESERVOIR)
POWER CYLINDERlHigh fluid pressurelI
ALVE FTom PUMP
RESERVOIR
SECTION A-A
17-9
Page 660 of 1681

From page 17-10
Normal
Check lorce required to turn thewhool (see page 17-'18).Start the engine and measu16the force required to turn thewheel to the right and left.Difference of the force requiredto twn the wheel to the right andto the left should be 5 N (0.5 kgf,1 lbl) or below.
Deformed
I
iFaulty cylinder lines
Not bent
Adjustment OK
Faulty valve body unit
Abnormal --> Faulty gearbox
Ch€ck th6 pans other than the gearbox-related parts lorDrooer rolaton.
. . lmproper rotation ofthe steering column-related pan{s}----------------- . tau[y $eenng lornt. Faulty rack endtio-rod ond balljoints. Intgrferonce in the steering system
Normal -----> lmproperly adjusted rack guide
Check lor bent rack shaft.
Check pump fluid pressure (seepage 17-22).Turn the steoring wheel fully tothe right and l€ft while idlingwilh the pressure control valveIully open, and measure the Iluidpressure. lt should be 6,400 -
7,400 kPa (65 - 75 kgflcmr, 924 -
1,067 psi).
Normal
Ch€ck the gearbox.Remove the gearbox and mea-sure the pinion torque.The lorque should be;. 0.7 - '1.2 N.m (7 - 12 kgf.cm, 6 -
10 lbf.in) wjth the steering rackin the straight driving position.
Abnormal
Adjust the rack guide {see page17-211, and recheck the pinion
torque.
17-11
Page 661 of 1681

Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting (cont'dl
Assist (excessively light steering) athigh speod.
Shock or vibration when wheel isturned to full lock.
Steering wheel will not return
smoothly.
a-, aa GrI r- tz
ll the problom is not correcled byadiusting the rack guide, adjustthe front wh66l alignment (see
s6ction 18).
Ch6ck th6 rack guide propgr ad-justment (see pago 17-21).
Check the rack guido lor proper
adjustment (see page 17-21).
Rack guid€ is adjusted properly.
lf the problem is not corrected byadjusting the rack guide, replscothe gearbox.Check the belt for slippage andadjust as nec€ssary {s6e page 17-20).
A and B cylinder lines are nor-mal, chgck wheol alignment (se€
section 18).
Whe6l alignment is abnormal,adjust as needod.
It should be 0.7 - 1.2 N.m {7 - 12kgl.cm.6 - 10 lbf.in) or belowwith the steering rack in thestraight ahoad driving position.
wh€el alignment is normal.R€mov€ the gearbox from thofram6 snd measure the pinion
torque on the gearbox.
lf the measurements are out ofsp€cifications. adjust the rackgurd9.
It the problom is not corrected byadiusting the rack guido. r€placethe goarbox.
{
I
Page 663 of 1681
I
Troubleshooting
17-14
Noise and Vibration
NOTEr Pump noise in first 2 - 3 minutes after starting in cold weather is normal.
Humming
Rattle or chattering
Humming due to pulsation oI lluid is normal, particularly when the wheel isturned with the vehicle stoooed.
Outlet hose (High-pressure hose)touching the frame.
Right cylinder end seal squeak.
Pump noise, though not loud, from tho valv6 body unit can be heard when turn-ing the steering wheel to full lock in either direction. This is normal. Do not hold
the steering wh6el at tull lock tor more that live seconds wh€n inspecting.
Loose steering shaft connector,tie-rod, or ball ioint.
Check and tighten, or replacepans as necessary,
Column shaft wobbling.Reolace the column assemblv.
Check ihe rack guide tor proper
adjustment (see page 17-21).Adiust, if nec€ssary.
Rattling sound and feeling when turning the steering wheel right and left with the
engine OFF is normal.
Page 665 of 1681

Troubleshooting
Fluid Leaks
Check the gearbox assembly for oil leaks carefully, Oil can leak out of various points, depending on location of the
faulty oil seals/seal rings. Check the following before removing the gearbox from the frame.
Stoo.ing GearboxReplace the valv€ oil seal fromthe valvo houging.Leaking from the oil seal on thetop of the valve housing.
Roplace the valve oil seal fromthe pinion shaft.Leaking trom cylinder 6nd intol€ft ti6-rod boot,
B€place tho cylindgr ond seal onthe gear housing side.
Replaco th€ cylindor end seal onths cylinder end side.Leaking from cylinder end intoright tie-rod boot.
Leaking from the thaft upper endsection or pin ongagement sgc-tion ofth6 Dinion shaftRoDlace tho valve bodv unit.I
I
Tighten connector. lf it€ still leak-ing. replace th€ lin€, cylinder orvalve housing.
Leaking lrom cylind6r line A or Bconn6ction {Et flare nut).
Leaking caused by a damagedcylinder line A or B.Replace cylinder line A or B.
Tightgn tho connector. ll its stillleaking, r€place the hos€, joint
fitting or valv€ housing.
Leaking from outlet line andreturn line joint fitting on thevalv6 body unit (at flare nut).
17-16