1998 DODGE RAM 1500 relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 1621 of 2627

The fuel heater element and fuel heater relay
are not computer controlled.
The heater element operates on 12 volts, 300 watts
at 0 degrees F.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL HEATER
The fuel heater is used to prevent diesel fuel from
waxing during cold weather operation.
NOTE: The fuel heater element, fuel heater relay
and fuel heater temperature sensor are not con-
trolled by the Engine Control Module (ECM).
A malfunctioning fuel heater can cause a wax
build-up in the fuel filter/water separator. Wax
build-up in the filter/separator can cause engine
starting problems and prevent the engine from rev-
ving up. It can also cause blue or white fog-like
exhaust. If the heater is not operating in cold tem-
peratures, the engine may not operate due to fuel
waxing.
The fuel heater assembly is located on the side of
fuel filter housing.
The heater assembly is equipped with a built-in
fuel temperature sensor (thermostat) that senses fuel
temperature. When fuel temperature drops below 45
degrees 8 degrees F, the sensor allows current to
flow to built-in heater element to warm fuel. When
fuel temperature rises above 75 degrees 8 degrees
F, the sensor stops current flow to heater element
(circuit is open).
Voltage to operate fuel heater element is supplied
from ignition switch, through fuel heater relay (also
refer to Fuel Heater Relay), to fuel temperature sen-
sor and on to fuel heater element.
The heater element operates on 12 volts, 300 watts
at 0 degrees F. As temperature increases, power
requirements decrease.
A minimum of 7 volts is required to operate the
fuel heater. The resistance value of the heater ele-
ment is less than 1 ohm (cold) and up to 1000 ohms
warm.
TESTING
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from thermostat
(Fig. 3).
Ambient temperature must be below the circuit
close temperature. If necessary, induce this ambient
temperature by placing ice packs on thermostat to
produce an effective ambient temperature below cir-
cuit close temperature.
Measure resistance across two pins. Operating
range is 0.3 Ð 0.45 Ohms.
(2) If resistance is out of range, remove thermostat
and check resistance across terminal connections of
heater. The heater can be checked at room tempera-
ture. Operating range is 0.3 - 0.45 Ohms.(3) Replace heater if resistance is not within oper-
ating range.
(4) If heater is within operating range, replace
heater thermostat.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
The fuel heater/element/sensor assembly is located
inside of the fuel filter housing. Refer to Fuel Filter/
Water Separator Removal/Installation for procedures.
FUEL HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel heater relay is located in Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) (Fig. 5). Refer to label on inside of
PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
Battery voltage to operate the fuel heater element
is supplied from the ignition switch through the fuel
heater relay.The fuel heater element and fuel
heater relay are not computer controlled.
REMOVAL
The fuel heater relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 6). Refer to label under
PDC cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
Fig. 5 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER LOCATION
1 - CLIP
2 - BATTERY
3 - TRAY
4 - NEGATIVE CABLE
5 - POSITIVE CABLE
6 - CLIP
7 - FENDER INNER SHIELD
8 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
14 - 52 FUEL DELIVERY - DIESELDR
FUEL HEATER (Continued)
Page 1622 of 2627

(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel heater relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 6). Refer to label under
PDC cover for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION
A Robert Bosch high-pressure fuel injection pump
is used. The pump is attached to the back of the tim-
ing gear cover at the left / rear side of the engine.
OPERATION
The fuel injection pump supplies high pressure to
the fuel rail independent of engine speed. This high
pressure is then accumulated in the fuel rail. High
pressure fuel is constantly supplied to the injectors
by the fuel rail. The Engine Control Module (ECM)
controls the fueling and timing of the engine by actu-
ating the injectors.
Fuel enters the system from the electric fuel trans-
fer (lift) pump, which is attached to the fuel filter
assembly. Fuel is forced through the fuel filter ele-
ment and then enters the Fuel Pump/Gear Pump,
which is attached to the rear of the fuel injection
pump. The Fuel Pump/Gear Pump is a low-pressure
pump and produce pressures ranging from 551.5 kpa
(80 psi) to 1241 kpa (180) psi. Fuel then enters the
fuel injection pump. Low pressure fuel is then sup-
plied to the FCA (Fuel Control Actuator).
The FCA is an electronically controlled solenoid
valve. The ECM controls the amount of fuel that
enters the high-pressure pumping chambers by open-
ing and closing the FCA based on a demanded fuel
pressure. The FPS (Fuel Pressure Sensor) on the fuel
rail provides the actual fuel pressure. When the
actuator is opened, the maximum amount of fuel is
being supplied to the fuel injection pump. Any fuel
that does not enter the injection pump is directed to
the cascade overflow valve. The cascade overflow
valve regulates how much excess fuel is used for
lubrication of the pump and how much is returned to
the tank through the drain manifold.
Fuel entering the injection pump is pressurized to
between 300-1600 bar (4351-23206 psi) by three
radial pumping chambers. The pressurized fuel is
then supplied to the fuel rail.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL INJECTION
PUMP TIMING
With the Bosch injection pump, there are no
mechanical adjustments needed or necessary to
accomplish fuel injection timing. All timing and fuel
adjustments are electrically made by the engine
mounted Engine Control Module (ECM).
Fig. 6 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER LOCATION
1 - CLIP
2 - BATTERY
3 - TRAY
4 - NEGATIVE CABLE
5 - POSITIVE CABLE
6 - CLIP
7 - FENDER INNER SHIELD
8 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DRFUEL DELIVERY - DIESEL 14 - 53
FUEL HEATER RELAY (Continued)
Page 1637 of 2627

FUEL INJECTION - DIESEL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................68
OPERATION...........................68
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................71
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................71
OPERATION...........................71
REMOVAL.............................72
INSTALLATION.........................72
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................72
OPERATION...........................72
REMOVAL.............................73
INSTALLATION.........................73
FUEL CONTROL ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................74
OPERATION...........................74
REMOVAL.............................74
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................74
OPERATION...........................74
REMOVAL.............................75
INSTALLATION.........................77
FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
DESCRIPTION.........................78
OPERATION...........................78
REMOVAL.............................78
INSTALLATION.........................78INLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR/
PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................79
OPERATION...........................79
REMOVAL.............................79
INSTALLATION.........................79
INTAKE AIR HEATER
DESCRIPTION.........................80
OPERATION...........................80
REMOVAL.............................80
INSTALLATION.........................80
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................82
OPERATION...........................82
REMOVAL.............................82
INSTALLATION.........................82
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR/MAP
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................82
OPERATION...........................82
REMOVAL.............................82
INSTALLATION.........................82
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................83
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL.............................83
INSTALLATION.........................84
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................85
OPERATION...........................85
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Engine Mounted Sensor:The APPS assembly is
located at the top-left-front of the engine. A plastic
cover is used to cover the assembly. The actual sen-
sor is located behind its mounting bracket.
Battery Tray Mounted Sensor:The Accelerator
Pedal Position Sensor (APPS) assembly is located
under the vehicle battery tray. A cable connects the
assembly to the accelerator pedal. A plastic cover
with a movable door is used to cover the assembly.
OPERATION
Engine Mounted Sensor:The Accelerator Pedal
Position Sensor (APPS) is a linear potentiometer. Itprovides the Engine Control Module (ECM) with a
DC voltage signal proportional to the angle, or posi-
tion of the accelerator pedal.
Battery Tray Mounted Sensor:The APPS pro-
vides the ECM with two DC voltage signals which
change as the position of the accelerator changes.
One of the DC voltage signals will be half the voltage
of the other signal.
REMOVAL
Engine Mounted Sensor :
The APPS is serviced (replaced) as one assembly
including the lever, brackets and sensor. The APPS is
calibrated to its mounting bracket. The APPS assem-
bly is located at left-front of engine below plastic
cable/lever/linkage cover (Fig. 1).
14 - 68 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELDR
Page 1649 of 2627

INTAKE AIR HEATER
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold air heater element assembly
is located in the top of the intake manifold.
OPERATION
The air heater elements are used to heat incoming
air to the intake manifold. This is done to help
engine starting and improve driveability with cool or
cold outside temperatures.
Electrical supply for the 2 air heater elements is
controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM)
through the 2 air heater relays. Refer to Intake Man-
ifold Air Heater Relays for more information.
Two heavy-duty cables connect the 2 air heater ele-
ments to the 2 air heater relays. Each of these cables
will supply approximately 95 amps at 12 volts to an
individual heating element within the heater block
assembly.
Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual for electrical operation and complete descrip-
tion of the intake heaters, including pre-heat and
post-heat cycles.
REMOVAL
If servicing either of the heater elements, the
entire block/element assembly must be replaced.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries. Cover and isolate ends of both cables.
(2) Remove both the intake manifold air intake
tube (above injection pump), and its rubber connector
hose (Fig. 26).
(3) Lift 2 rubber covers (Fig. 27) to gain access to 2
positive (+) cable nuts. Remove these 2 nuts (Fig. 28)
and remove 2 cables from studs.
(4) Disconnect ground strap (Fig. 27) at heater ele-
ment stud.
(5) Remove wiring harness clips.
(6) Remove engine oil dipstick tube bracket from
air inlet connection and fuel filter housing.
(7) Remove 4 housing mounting bolts (Fig. 27) and
remove heater element assembly.
INSTALLATION
If servicing either of the heater elements, the
entire block/element assembly must be replaced.
(1) Using 2 new gaskets, position element assem-
bly and air housing to intake manifold.
(2) Install ground cable to air housing.
(3) Install 4 housing bolts and tighten to 24 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect 2 positive (+) heater cables at cable
mounting studs.Do not allow either of the cable
eyelets to contact any other metal source other
than the cable nuts/studs.
Fig. 24 INLET/PRESSURE SENSOR REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION
1 - INLET/PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
3 - SENSOR MOUNTING SCREWS (2)
4 - TOP OF AIR FILTER COVER
Fig. 25 SENSOR O-RING
1 - IAT/PRESSURE SENSOR
2 - O-RING
14 - 80 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELDR
INLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR/PRESSURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1651 of 2627

INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 2 intake manifold air heater relays are located
in the engine compartment. They are attached to a
common bracket. This bracket is attached to the
right battery tray (Fig. 29).
OPERATION
The Engine Control Module (ECM) operates the 2
heating elements through the 2 intake manifold air
heater relays.
Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures for an
electrical operation and complete description of the
intake heaters, including pre-heat and post-heat
cycles.
REMOVAL
The 2 intake manifold air heater relays are located
in the engine compartment. They are attached to a
common bracket. This bracket is attached to the
right battery tray (Fig. 29).
The mounting bracket and both relays are replaced
as an assembly.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Disconnect four relay trigger wires at both
relays. Note position of wiring before removing.
(3) Lift four rubber shields from all 4 cables.(4) Remove four nuts at cable connectors. Note
position of wiring before removing.
(5) Remove relay mounting bracket bolts and
remove relay assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install relay assembly to battery tray. Tighten
mounting bolts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect eight electrical connectors to relays.
(3) Connect battery cables to both batteries.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR/MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The combination, dual function Intake Manifold
Air Temperature Sensor/MAP Sensor is installed into
the top of the intake manifold.
OPERATION
The combination, dual function Intake Manifold
Air Temperature Sensor/MAP Sensor is installed into
the top of the intake manifold with the sensor ele-
ment extending into the air stream.
The IAT portion of the sensor provides an input
voltage to the Engine Control Module (ECM) indicat-
ing intake manifold air temperature. The MAP por-
tion of the sensor provides an input voltage to the
ECM indicating turbocharger boost pressure.
REMOVAL
The combination, dual function Intake Manifold
Air Temperature Sensor/MAP (IAT/MAP) sensor is
installed into the top of the intake manifold (Fig. 30).
(1) Clean area around sensor.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAT/MAP
sensor.
(3) Remove two T-15 Torx headed screws.
(4) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
(5) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 31).
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
(2) Lubricate sensor o-ring with clean engine oil.
(3) Clean sensor mounting area at intake mani-
fold.
(4) Position sensor into intake manifold.
(5) Install and tighten 2 sensor mounting screws
to 1 N´m (9 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
Fig. 29 INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR HEATER RELAYS
1 - BATTERY
2 - CABLES TO INTAKE HEATERS
3 - RELAY TRIGGER WIRES
4 - INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAYS (2)
14 - 82 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELDR
Page 1858 of 2627
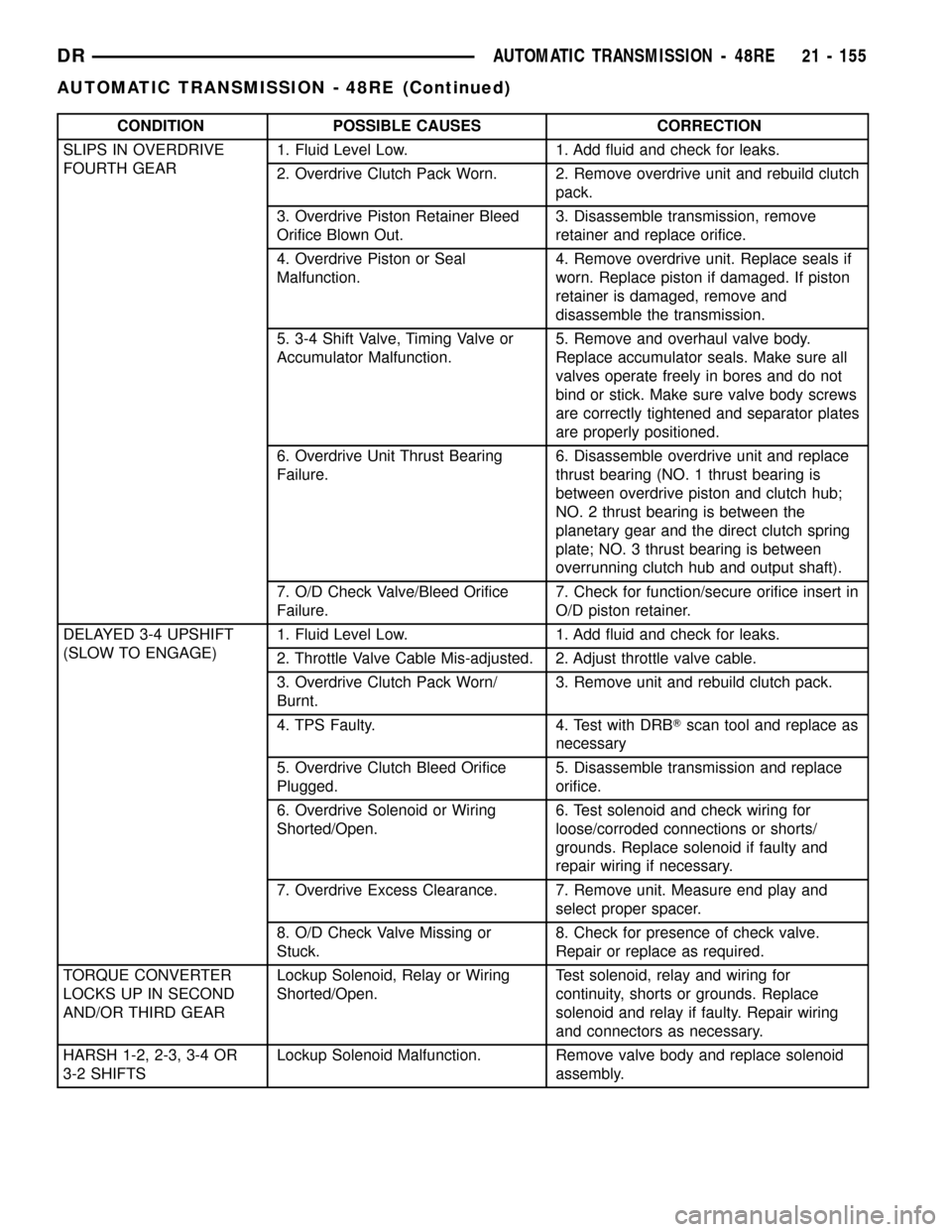
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SLIPS IN OVERDRIVE
FOURTH GEAR1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Overdrive Clutch Pack Worn. 2. Remove overdrive unit and rebuild clutch
pack.
3. Overdrive Piston Retainer Bleed
Orifice Blown Out.3. Disassemble transmission, remove
retainer and replace orifice.
4. Overdrive Piston or Seal
Malfunction.4. Remove overdrive unit. Replace seals if
worn. Replace piston if damaged. If piston
retainer is damaged, remove and
disassemble the transmission.
5. 3-4 Shift Valve, Timing Valve or
Accumulator Malfunction.5. Remove and overhaul valve body.
Replace accumulator seals. Make sure all
valves operate freely in bores and do not
bind or stick. Make sure valve body screws
are correctly tightened and separator plates
are properly positioned.
6. Overdrive Unit Thrust Bearing
Failure.6. Disassemble overdrive unit and replace
thrust bearing (NO. 1 thrust bearing is
between overdrive piston and clutch hub;
NO. 2 thrust bearing is between the
planetary gear and the direct clutch spring
plate; NO. 3 thrust bearing is between
overrunning clutch hub and output shaft).
7. O/D Check Valve/Bleed Orifice
Failure.7. Check for function/secure orifice insert in
O/D piston retainer.
DELAYED 3-4 UPSHIFT
(SLOW TO ENGAGE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks.
2. Throttle Valve Cable Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust throttle valve cable.
3. Overdrive Clutch Pack Worn/
Burnt.3. Remove unit and rebuild clutch pack.
4. TPS Faulty. 4. Test with DRBTscan tool and replace as
necessary
5. Overdrive Clutch Bleed Orifice
Plugged.5. Disassemble transmission and replace
orifice.
6. Overdrive Solenoid or Wiring
Shorted/Open.6. Test solenoid and check wiring for
loose/corroded connections or shorts/
grounds. Replace solenoid if faulty and
repair wiring if necessary.
7. Overdrive Excess Clearance. 7. Remove unit. Measure end play and
select proper spacer.
8. O/D Check Valve Missing or
Stuck.8. Check for presence of check valve.
Repair or replace as required.
TORQUE CONVERTER
LOCKS UP IN SECOND
AND/OR THIRD GEARLockup Solenoid, Relay or Wiring
Shorted/Open.Test solenoid, relay and wiring for
continuity, shorts or grounds. Replace
solenoid and relay if faulty. Repair wiring
and connectors as necessary.
HARSH 1-2, 2-3, 3-4 OR
3-2 SHIFTSLockup Solenoid Malfunction. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly.
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 155
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE (Continued)
Page 1901 of 2627

GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output
pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
77).
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmis-
sion line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid
valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in
the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower
side of the transfer plate (Fig. 77).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absenceof sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higher
than normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
Fig. 77 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 198 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48REDR
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1966 of 2627
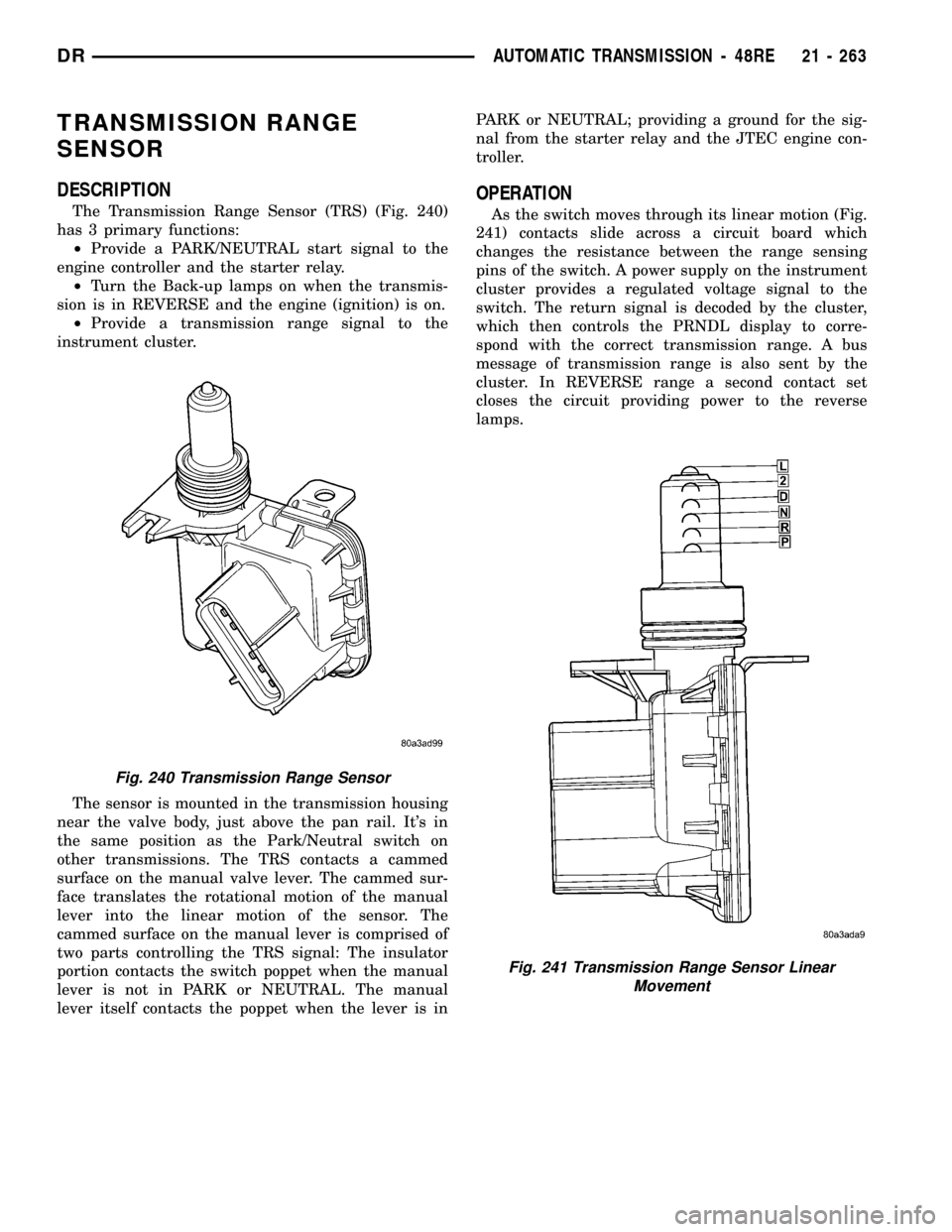
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 240)
has 3 primary functions:
²Provide a PARK/NEUTRAL start signal to the
engine controller and the starter relay.
²Turn the Back-up lamps on when the transmis-
sion is in REVERSE and the engine (ignition) is on.
²Provide a transmission range signal to the
instrument cluster.
The sensor is mounted in the transmission housing
near the valve body, just above the pan rail. It's in
the same position as the Park/Neutral switch on
other transmissions. The TRS contacts a cammed
surface on the manual valve lever. The cammed sur-
face translates the rotational motion of the manual
lever into the linear motion of the sensor. The
cammed surface on the manual lever is comprised of
two parts controlling the TRS signal: The insulator
portion contacts the switch poppet when the manual
lever is not in PARK or NEUTRAL. The manual
lever itself contacts the poppet when the lever is inPARK or NEUTRAL; providing a ground for the sig-
nal from the starter relay and the JTEC engine con-
troller.
OPERATION
As the switch moves through its linear motion (Fig.
241) contacts slide across a circuit board which
changes the resistance between the range sensing
pins of the switch. A power supply on the instrument
cluster provides a regulated voltage signal to the
switch. The return signal is decoded by the cluster,
which then controls the PRNDL display to corre-
spond with the correct transmission range. A bus
message of transmission range is also sent by the
cluster. In REVERSE range a second contact set
closes the circuit providing power to the reverse
lamps.
Fig. 240 Transmission Range Sensor
Fig. 241 Transmission Range Sensor Linear
Movement
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 263